PROJECT MANAGEMENT - MIDTERMS
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Project Management
The application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements
It is a structured approach to planning, executing, monitoring, and closing temporary efforts to deliver a unique product or service
Project Manager (PM)
Oversees scope, budget, timeline, risks, communication
System Analyst
Gathers requirements, analyzes feasibility
Developers/Programmers
Build and test software components
UI/UX Designers
Ensure intuitive user interfaces
QA Testers
Conduct functional and non-functional testing
Network/Infra Engineers
Handle deployment, hardware, and cloud
Stakeholders
Internal or external parties with project interest
Project Management Institute (PMI)
Global non-profit that promotes best practices in project management
PMP (Project Management Professional)
CAPM (Certified Associate in Project Management)
Offers globally recognized certifications
Project Management Body of Knowledge
A framework of standards, not a methodology
Creep
Requirements increase mid-project
Poor Communication
Technical and business teams disconnect
Unrealistic Deadlines
Misalignment of time and complexity
Inadequate Risk Management
Ignoring security, compliance risks
Technology Volatility
Rapid changes in frameworks, tools
Creep
Poor Communication
Unrealistic Deadlines
Technology Volatility
Inadequate Risk Management
Challenges in IT Project Management
Project Management Institute (PMI)
has defined five project management process groups, or project management phases, which come together to form the project life cycle.
Initiation
Define objectives, feasibility, and stakeholders
Planning
Scope, budget, scheduling, risk management
Execution
Development, design, coding, configuration
Monitoring & Control
Track KPIs, quality, timeline
Closure
Deployment, documentation, handover
Initiation
Planning
Execution
Monitoring & Control
Closure
Common Phases (PMBOK and real-world IT practices)
Project Initiation
Aims to clarify a project’s vague brief and define its key success criteria
the client requirements are collected, project stakeholders are identified, and essential project elements such as the scope, timeline, and budget are determined.
OUTCOME: Defined parts of projects
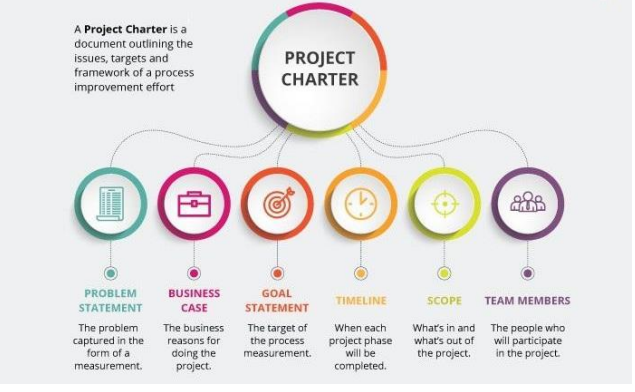
Project Charter
It is a formal document that authorizes a project and defines its objectives, scope, and key stakeholders
Business Case
It is a document that justifies a project by demonstrating its benefits or necessity.
Feasibility Study
This comprehensive evaluation determines a proposed project’s practicality and financial viability.
Stakeholder Register
It identifies all the stakeholders involved in the project, their interests, influence level, communication requirements, and expectations
Project Kickoff Meeting Agenda
It provides insights into the project overview, roles and responsibilities of the team, key milestones, timelines, and communication protocols.
Project Planning
Involves defining tasks and creating a project roadmap for guidance throughout the project
is where plans and schedules are developed to guide the project team in executing the project effectively.
OUTCOME: Roadmap
Roadmap
is created detailing how the project will be executed, monitored, and controlled.
Project Goals
Managers establish SMART (Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Time-bound) goals that align with the project’s outcome.
Project Scope Document
It defines all the elements of the project scope along with its objectives, schedules, tasks, and deliverables.
Stakeholder Management Plan
This document outlines how to engage with project stakeholders and includes a strategy for managing stakeholder conflicts and issues.
Resource Management Plan
It defines the resource requirements of the project. Moreover, it outlines how resources will be allocated, optimized, and managed throughout the lifecycle.
Budget Management Plan
This plan outlines the process of estimating, allocating, and monitoring the costs associated with a project.
Change Management Document
This document summarizes the formal process for handling change requests systematically without disrupting the overall project.
Risk Management Plan
It details how to identify, assess, categorize, and mitigate potential project risks.
Project Execution
Resources are onboarded and briefed, ground rules are established, and the team executes the planned work
The project manager and the team implement the project plan.
Maintaining and controlling the communication flow among the resource pool and project stakeholders
OUTCOME: Tasks
Tasks Assignment & Execution
Project managers allocate resources to suitable tasks based on their roles, skills, availability, and expertise. It also involves executing the tasks sequentially based on the project schedule and work breakdown structure (WBS).
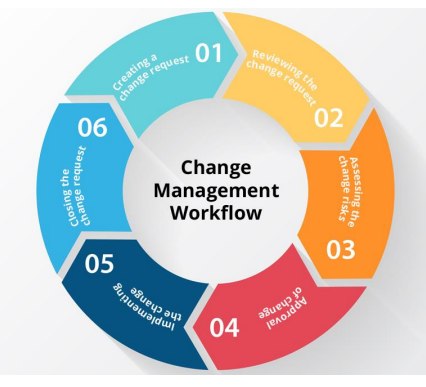
Managing Change Requests
Project managers accommodate change requests through a formal process that involves a Change Control Board
Mitigating Risks
The project team proactively monitors risks identified during the planning phase and implements appropriate mitigation and contingency plans to control them.
Team Collaboration
Project managers, team members, and stakeholders must collaborate effectively to ensure deliverables and milestones are completed on time and as per expectations.
Project Monitoring & Controlling
This phase entails collecting and analyzing data from timesheets and project management software to track and compare project progress, milestone/task completion, budget usage, and time allocation against the initial plan.
Runs in parallel with the execution phase.
Involved regularly monitoring KPIs such as project performance, deliverable quality, and cost
Allows project managers to intervene promptly, make adjustments, and maintain alignment with the project’s goals, budget, and timline
OUTCOME: Understanding if you’re meeting timeline, cost, quality, and success goals
Tracking Project Performance
It is done by measuring project progress against the plan using metrics like Scheduled Variance (SV), Cost Variance (CV), and Earned Value (EV).
Assuring Quality
Managers can conduct regular reviews and implement quality control measures to ensure project work meets pre-defined standards
Communicating Updates
By creating project management reports managers can share project statuses, workloads, variance, etc
Taking Corrective Actions
Managers can implement corrective measures to address deviations from the project plan (e.g., reallocating resources or adjusting timelines).
Conducting Regular Meetings
Project managers organize regular review meetings with clients and stakeholders to ensure deliverables align with their expectations.
Project Closure
It’s useful to hold a post-project review meeting to discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the project and how to improve in the future
Ensure the promised outcomes are achieved within the defined limits and are evaluated based on the project management triangle (scope, time, and cost).
OUTCOME: Finished Project
Completing Project Deliverables
This ensures all the project deliverables and objectives outlined in the project scope are completed and delivered.
Conducting Final Evaluation
It assesses the overall project performance against key criteria such as scope, time, and budget
Obtaining Stakeholder Acceptance
This presents the final deliverables to stakeholders and securing formal approvals.
Documenting Lessons Learned
This document comprises feedback, lists challenges faced during execution, and highlights improvement opportunities for future projects.
Close Contracts & Financials
This step ensures the deals with contractors/external vendors are closed and invoices are correctly settled.
Archive Project Documentation
It involves storing all key documents such as project plans, scope documents, and reports to be used as references for future projects.
Releasing Project Resources
This process releases the team members from their existing roles and transitions them to other projects.
Project Management Methodology
is a set of principles, tools and techniques that are used to plan, execute and manage projects.
help project managers lead team members and manage work while facilitating team collaboration.
Traditional Project Management
include the more traditional methods of project management where a sequential and upfront approach is adopted to execute project management strategies.
Waterfall Methodology
Employs a sequential process that is based on predetermined deadlines, specifications, and results.
the individual execution teams are not required to be in continual contact and are typically self-contained, until particular integrations are necessary.
is a linear and sequential approach to project management. It follows a strict methodology where each project phase, such as planning, design, development, and testing, must be completed before moving on to the next step.
This method is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and predictable outcomes.
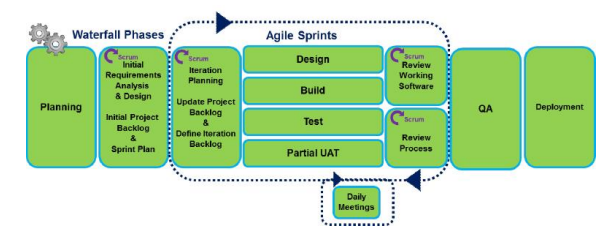
Agile Project Management
is a dynamic, iterative approach to project management that focuses on flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
embraces adaptability by breaking projects into smaller, manageable units called iterations or sprints
This enables teams to respond quickly to changes, refine their work based on ongoing feedback, and deliver value incrementally rather than waiting until the end of a long development cycle.

Agile
Scrum
Kanban
Commonly used agile methods of project management:
Agile methodology
is one of the most popular tools and techniques for project management.
It uses the ‘sprint approach’ where you can break a project in the form of sprints or cycles.
It is a method of project management that entails ongoing communication and iterative development.
is based on the idea that a project may be improved upon continually throughout its life cycle with changes being made swiftly and appropriately.

Scrum framework
helps teams focus on real priorities and the immediate requirements of the clients. This technique helps you leverage effective communication, teamwork, and speed of development in a project
a team is often led by a scrum master that is also called a Subject Matter Expert (SME), who is responsible for inculcating the values of the Agile methodology within the team.

Kanban methodology
is a visual way of controlling the flow of work through a process. It shows both the workflow (the process) and the actual work going through it.
aims to locate possible bottlenecks in your process and eliminate them, allowing work to move through it efficiently and cost-effectively at a high throughput
Hybrid project management
also known as blended project management—combines different aspects of Waterfall and Agile methodologies to craft a process that truly fits your team and projects.
Microsoft Planner
is a web-based, visual task management application designed to streamline project management within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem.
It offers a centralized hub for teams to organize, assign, track, and manage tasks, fostering collaboration and enhancing project visibility
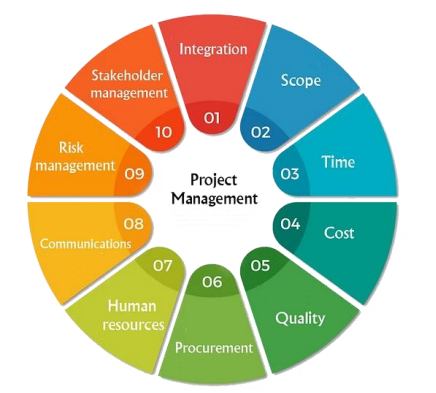
Integration Management
is the process, where the project manager, is handed the authority to monitor and coordinate the functions and activities taking place at various levels of the organization
is to ensure that the team works towards completing the given project by making sure that it meets the scope, budget, and time.
Project Integration Management
is all about sustaining stability in all areas of a project like; time, scope, cost, quality, human resources, communication, risk, procurement, and stakeholder, among others
involves overseeing the five project management phases that occur during the project lifecycle.
happens both within a project and across an organization
Project Charter
documents highlevel project information to inform stakeholders of deliverables, milestones and the roles and responsibilities of the project team.
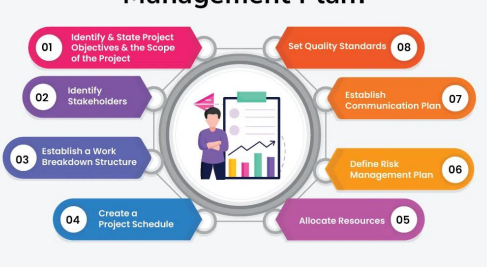
Project Management Plan
involves developing a more detailed project plan, which specifies the project scope statement, deliverables, timeline, milestones, and metrics to evaluate success.
is used to meet overall requirements and objectives.
project execution
which the project manager takes charge of the day-to-day work that must be done
This phase ensures that tasks are being carried out effectively according to the project plan and scope statement.
Project knowledge management
refers to the process of using existing information or obtaining additional knowledge to reach project goals.
This step ensures team members have all the information they need to produce the required deliverables.
Monitor and Control Project Work
The purpose of this step is to keep the project on track. If there are any deviations from the project plan, they need to be identified and corrected.
Preventive action
an action performed to reduce the negative impact of project risks
Corrective action
an action performed to bring the future project performance back in line with the project plan
Defect repair
an action to repair or replace a documented project defect
change control log
to document all change requests, including which ones were approved, the associated costs and resources, and how they impact the project timeline
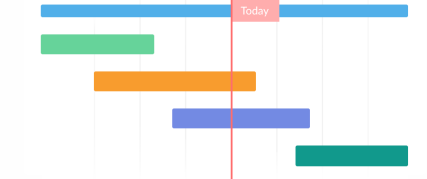
project management timeline
is a schedule for your entire project from inception to completion. It will break your entire project into smaller tasks and milestones, with a deadline assigned to each
project timeline
ensures that your project is transparent and well planned. It helps managers to anticipate bottlenecks and streamline workflows.
is more like a big-picture overview of your project, showing key milestones and deadlines in a visual format.
project schedule
is like a detailed todo list for your project, outlining all the tasks, when they need to be done, and who is responsible for them.
Tasks to be completed
Keep tasks specific and focused when segmenting them.
Start and end dates of tasks
Avoid getting too granular by including end times.
Duration of each task
Project timelines are intended to convey essential task details concisely.
Task dependencies
Dependencies are other tasks that must be completed before you can move on to the next piece of work.
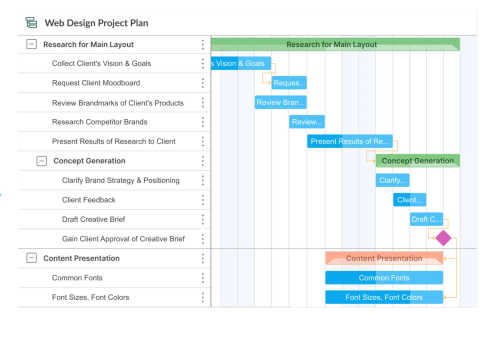
Gantt Chart
consists of several horizontal lines, each representing a specific task. These lines indicate the amount of work your team has completed and reveal how long it took to finish each task event.
Suitable when a project is in progress
Provides accurate due dates
suits small projects
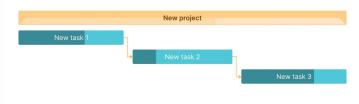
PERT Chart
Project (or Program) Evaluation and Review Technique
definition derives from this abbreviation: it is a PM tool that graphically represents a project’s tasks, terms, and dependencies between them
More suitable on a planning stage
Shows only task durations
Suits middle and large plans
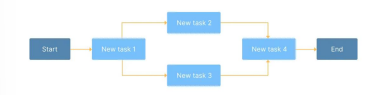
critical path method (CPM)
is a project management process that identifies key activities in a process and evaluates the time each task will take.
Project Scope Management
refers to the systematic process of defining, documenting, and controlling what is and what is not included in a project. It establishes the boundaries, deliverables, and work required to ensure successful completion.
Scope Planning
is the process of developing a written scope management plan that details how the project scope will be defined, validated, and controlled.
Process for Preparing Scope Statement
Guidelines for drafting a clear scope statement.
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Creation
Process of decomposing work into smaller components
Scope Verification
How deliverables will be accepted and validated.
Scope Control
Procedures for handling changes and monitoring adherence.
Roles and Responsibilities
Identifies accountable individuals.
Planning
define the project work and the scope baseline, and create a scope statement.
Controlling
monitor progress against the scope management plan, track scope changes, and manage scope creep.
Closing
audit final deliverables against the original scope management plan and project plan