Brainstem
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What role does the reticular formation have?
Regulates consciousness and sleep wake cycles
What happens if there is a lesion in the reticular activating system (RAS)?
Stuporous state (slowed down and reduced ability to respond to stimuli)
What happens if there is a lesion to the reticular inhibitory system (RIS)?
Constant wakefulness
Does the reticular formation play a role in control of muscle tone?
Yes; the reticulospinal tracts can influence the alpha and gamma motor neurons. This influences tone in antigravity muscles
What are the 4 major functions of the reticular formation?
Regulation of consciousness (RAS & RIS)
Control of muscle tone
Control of pain
Regulation of circadian rhythm
Broadly, what does the midbrain do?
Relay system; transmits information for vision and hearing
What is the tegmentum?
Red nucleus and substantia nigra
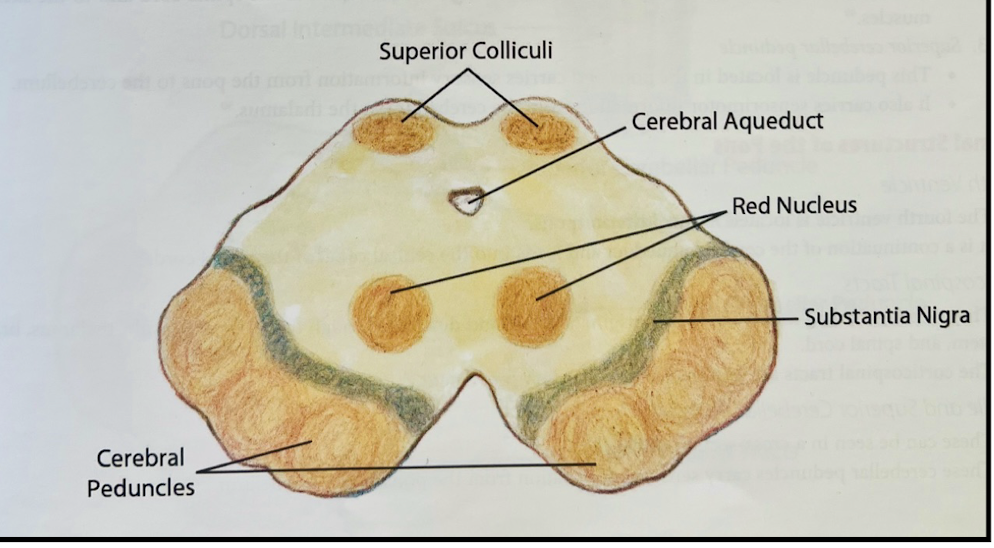
What is the tectum?
Superior and inferior colliculi
What cranial nerves come form the midbrain?
3 & 4
Where in the brainstem is the cerebral aqueduct located?
Midbrain
What are the structures that are in the midbrain (internally)?
Cerebral aqueduct
CN 3 & 4
Tectum (Superior colliculi [pair] and inferior colliculi [pair])
Tegmentum (red nucleus / substantia nigra)
What is the function of the substantia nigra?
Contributes to the control of movement (and reward)
Produces the NT dopamine
Responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement.
What is the function of the ventral tegmentum?
Regulates reward consumption, learning, memory, and addictive behaviors through mediate dopamine release
What is the funciton of the red nuclei?
Within tegmentum that is involved with coordination of sensorimotor information
What structures does the superior cerebellar artery (SCA) supply?
Cerebellum and midbrain
What structures does the AICA supply?
Cerebellum and pons
What structures does the PICA supply?
Cerebellum and medulla
What does the pons do?
Relay system
Mediates motor information on an unconscious level
Ex. making fine motor adjustments in the muscles to perform precise coordinated limb movement
What is the function of the cerebellar peduncles (middle, inferior, and superior)?
Carry sensory information from the pons to the cerebellum about the body’s position in space
What is the primary difference between the middle, inferior, and superior cerebellar peduncles?
The superior also carries information from the cerebellum to the thalamus
Where is the 4th ventricle located?
Posterior pons
What CNs are located in the pons?
CNs 5-8
The pons is mainly supplied by what arteries?
Pontine arteries.
Smaller part of blood supply also comes form the AICA and SCA
Where are ANS centers located in the brainstem? What does it control?
Medulla; BP, HR, respiration, reflex functions (vomiting, coughing, sneezing, swallowing)
What CNs are located in the medulla?
CNs 9-12
Would damage to CN nuclei cause ipsilateral or contralateral deficits?
Ipsilateral
Would spinal cord tract damage in the brain stem cause ipsilateral or contralateral deficits?
Contralateral
What is a persistent vegetative state (PVS)? What causes it?
Pt can open their eyes but do not have cognitive function and awareness
Typically results from cardiac or respiratory arrest (ischemia; 4-6 mins will cause PVS)
What structure is spared in PVS? What does this mean?
Brainstem typically spared; means cough, gag, and swallowing reflexes remain intact.
What is brain death?
All brain functions are lost
Can the heartbeat continue when brain death occurs? Why or why not?
It can continue because it is semi-autonomous from ANS regulation
Is there extensive damage to the RIS or RAS if brain death occurs?
RAS
Are cough, gag, and swallow reflexes still intact or are they lost when brain death occurs?
They are lost