Pathology of the Aorta (Part 2)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
A Pseudoaneurysm (false) aneurysm is a
pulsatile mass (hematoma)
Pseudoaneurysm occur at
a puncture site, trauma, surgical anastomosis site, or infection
How does a Pseudoaneurysm differ from a true aneurysm
it doesn’t involve all three layers of the vessel
What is happening with the blood in a Pseudoaneurysm?
it is leaking into soft tissue through a hole in the innermost vessel lining
What is anastomosis?
a surgical procedure that creates a connection between two tubular structures, such as blood vessels, intestines, or airways
Blood circulation of a Pseudoaneurysm during systole
inward
Blood circulation of a Pseudoaneurysm during diastole
turbulent flow outward
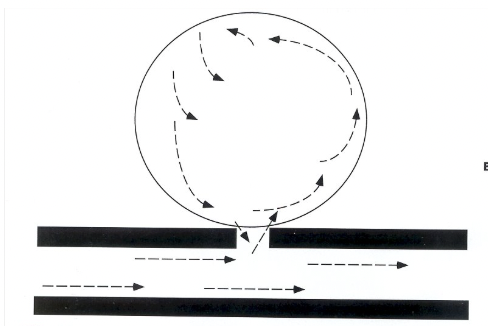
This image is showing
Flow of a Pseudoaneurysm
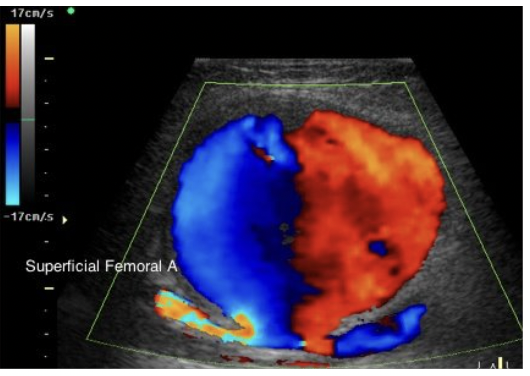
This image is showing
color flow of a Pseudoaneurysm
Pseudoaneurysm treatment:
compression of mass with transducer
20 min intervals X until gone or clotted off
monitor with color doppler to confirm communication is closed
may require surgical intervention
Idiopathic AAA
True AAA – lined by all 3 layers of aortic vessel
Develop infrarenal (> 85% of pts.)
Extend to bifurcation
no clear cause
Dissection is a
tear in vessel wall
Complications of idiopathic AAA
Rupture
Thrombosis
Dissection
Distal embolism
Infection
Obstruction
Invasion of adjacent structures
Branch artery occlusion or stenosis
Aneurysm may be described as
fusiform or saccular
fusiform aneurysm is the
most common type of aneurysm
fusiform aneurysm is a
atherosclerotic aneurysm
You will find a fusiform aneurysm
inf aorta near bif
gradual transition between normal and abormal
extends over length of aorta (Football shape)
extend into iliacs
When looking at a fusiform aneurysm on US you can find
atherosclerosis of vessel, decreased pulsations of walls, bright echoes = thickening & calcification
Saccular aneurysm is also knows as:
Bulbous
What is a saccular aneurysm
Sharp, sudden transition between normal & abnormal
Spherical & larger than fusiform
Connected to vascular lumen by a mouth
Follow path of AAA to:
R/O retroperitoneal mass or lymphadenopathy
Diminished pulsations due to clot formation
Saccular aneurysm is connected to the vascular lumen by
mouth
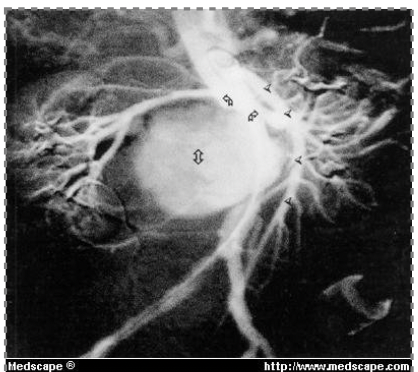
This image is showing a
saccular aneurysm
Large AAA may
compress or displace surrounding structure
mycotic aneurysms are
infected aneurysms (aorta)
How will a AAA compress or displace surrounding structures
CBD = obstruction
RA = HTN, ischemia
Ureter obstruction
Inflammatory Aortic Aneurysm / Mycotic Aneurysm is a
rare condition development of a mycotic (infected) AAA
Normal Iliac artery measures
< or equal to 2 cm (Needs to be measured in 2 planes)
IAA =
vessel diameter > 2cm or 1.5 X normal size
IAA measurement for surgical repair
> 3 cm
Protocol of IAA
Measure AP/length/ Width of IAA
Measure AP/Width of lumen
Assess clot or thrombus formation
Document Color and Pulse Doppler
Classic Symptoms of RUPTURED AAA
Excruciating abdominal pain
Shock
Expanding abdominal mass
Most common site of rupture: lateral wall inferior to RA
Extravasation (hemorrhage)
IAA rupture into
retrosigmoid colon, iliac vein or ureter
Need to document where the AAA is compared to renals because
it affects the kind of stent they put in
Clottication:
pain in arms and legs because there is not enough blood flow
Syphilis
STI that can cause inflammation in the aorta potentially causing an aneurysm
Cystic medial necrosis is a type of
marfans disease. The tunica medias collagen fibers in the aorta are breaking down increasing the risk of aneurysms
Grey Turner’s Syndrome
when aneurysm ruptures they will have bruising at flanks bc blood is pooling at abdomen