lung cancer
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
symptoms of lung cancer
-most common symptoms: coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain and hemoptysis
-general symptom: fatigue, weight loss and night sweats
paraneoplastic syndrome
-hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (clubbing)
-hypercalcemia
more commonly seen in squamous cell
due to production of PTH-like hormone
-SIADH: most common syndrome in small cell carcinoma
-Cushing syndrome
-Eaton-Lambert syndrome
-does not preclude curative therapy
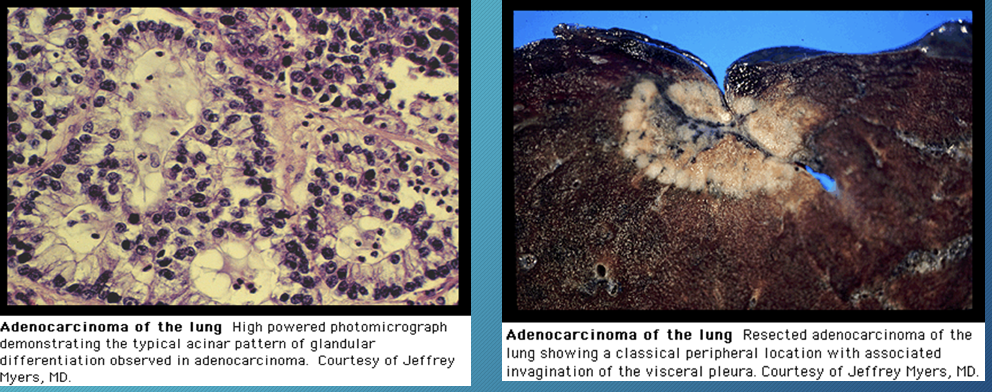
adenocarcinoma
most common form in nonsmokers
peripheral lesion
-bronchoalveolar cell carcinoma/ adenocarcinoma in situ: subtype of adenocarcinoma
solitary nodule, lobar consolidation or multiple nodules
slow growing with late metastases
lower likelihood of + PET scan
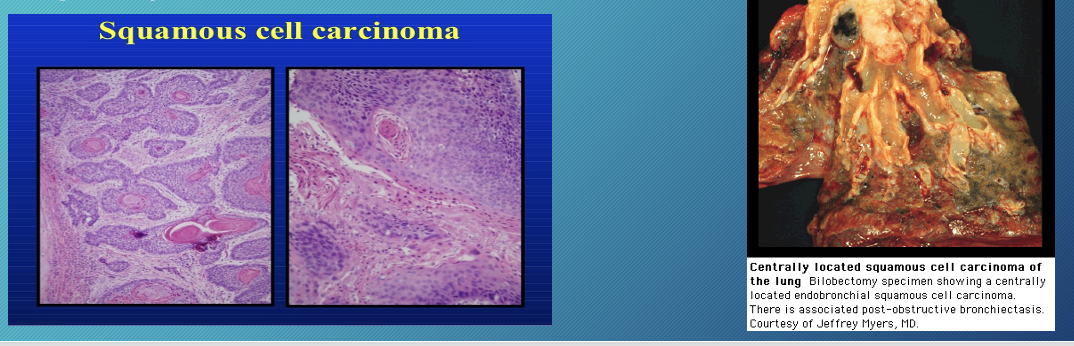
squamous cell carcinoma
2nd most common form of non-small cell carcinoma
found in smokers
associated with hypercalcemia and hypertrophic osteoarthropathy
less likely to metastasize than adenocarcinoma
centrally located and can cavitate
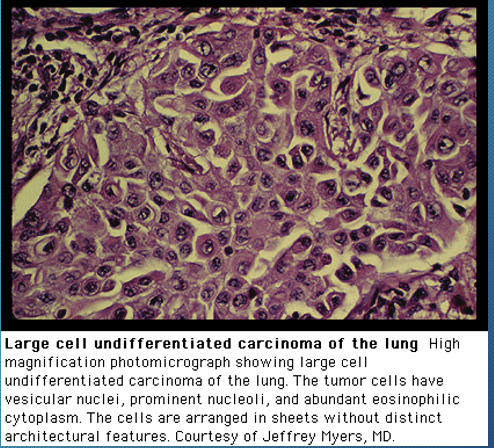
large cell carcinoma
-poorly differentiated non-cell carcinoma that are not classified by light microscopy
-prognosis closely resemble adenocarcinoma
-frequently shows necrosis
small cell carcinoma
10-15% of lung cancers
associated with smokers
central location, metastatic at time of presentation
***If you had to choose a paraneoplastic syndrome related to lung cancer, CHOOSE SMALL CELL (except hypercalcemia)
staging for lung cancer
-non-invasive staging: CT, PET
-invasive staging
non-surgical: EBUS/ bronchoscopy, toracentesi, needle biopsy
surgical: mediastinoscopy, anterior mediastiinotomy (Chamberlain procedure), VATS
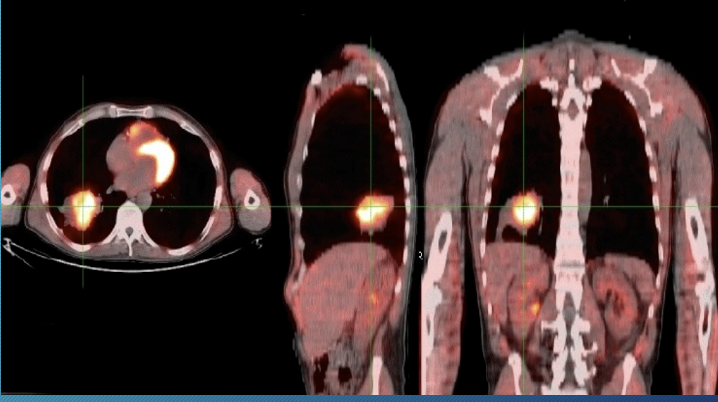
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
marker of active glucose metabolism and will accumulate in metabolically active tumor cells
90% sensitivity, 85% specificity
-false negative: small nodule < 8mm, carcinoid, BAC
-false positive: granulomatous infection/inflammation
video flexible bronchoscopy
excellent to evaluate endobronchial disease
-brushing and bronchial biopsies are high yield for visible lesion
-evaluate of obstruction for stent
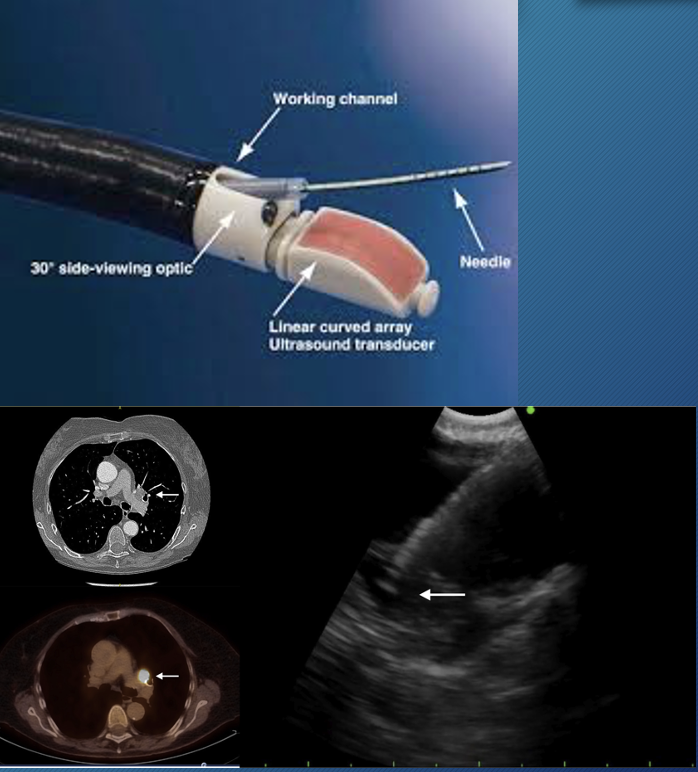
robotic-assisted bronchoscopy
allow physician to move a flexible bronchoscope with precision using a controller
allow physician to biopsy areas in lung that would have been impossible with standard bronchoscopy/needle biopsy
endobronchoscopic ultrasound (EBUS)
stage mediastinal and hilarious lymph nodes
diagnose lung cancer
perform on patients suspected of having N2, N3 lymph node involvement on CT scan or PET uptake
can also diagnose sarcoidosis, infection, lymphoma
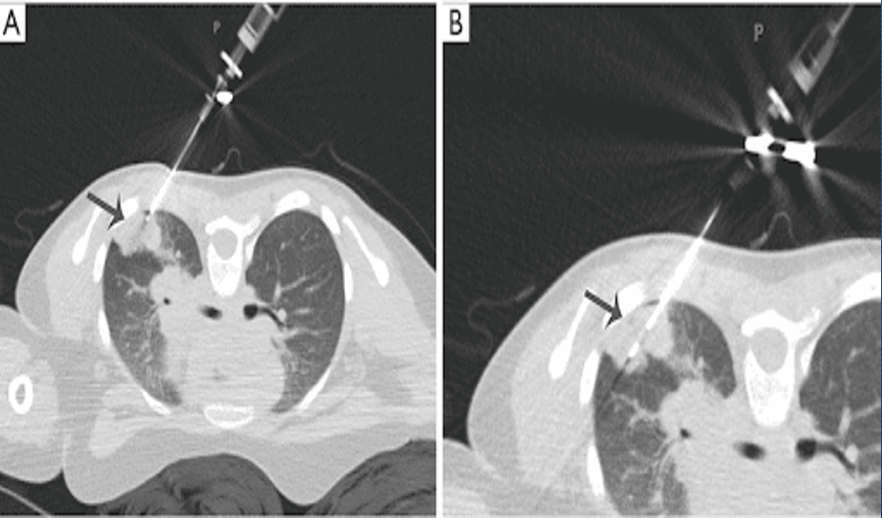
transthoracic needle biopsy
peripheral lesions away from diaphragm
25% chance of pneumothorax
benefit for patients who are poor operative candidates
negative needle biopsy may be a false negative
pleural fluid cytology
pleural effusion → thoracentesis: assist in staging of lung cancer
50% malignant pleural effusions are cytologically positive
negative cytology after 2 thoracentesis → consider VATS biopsy
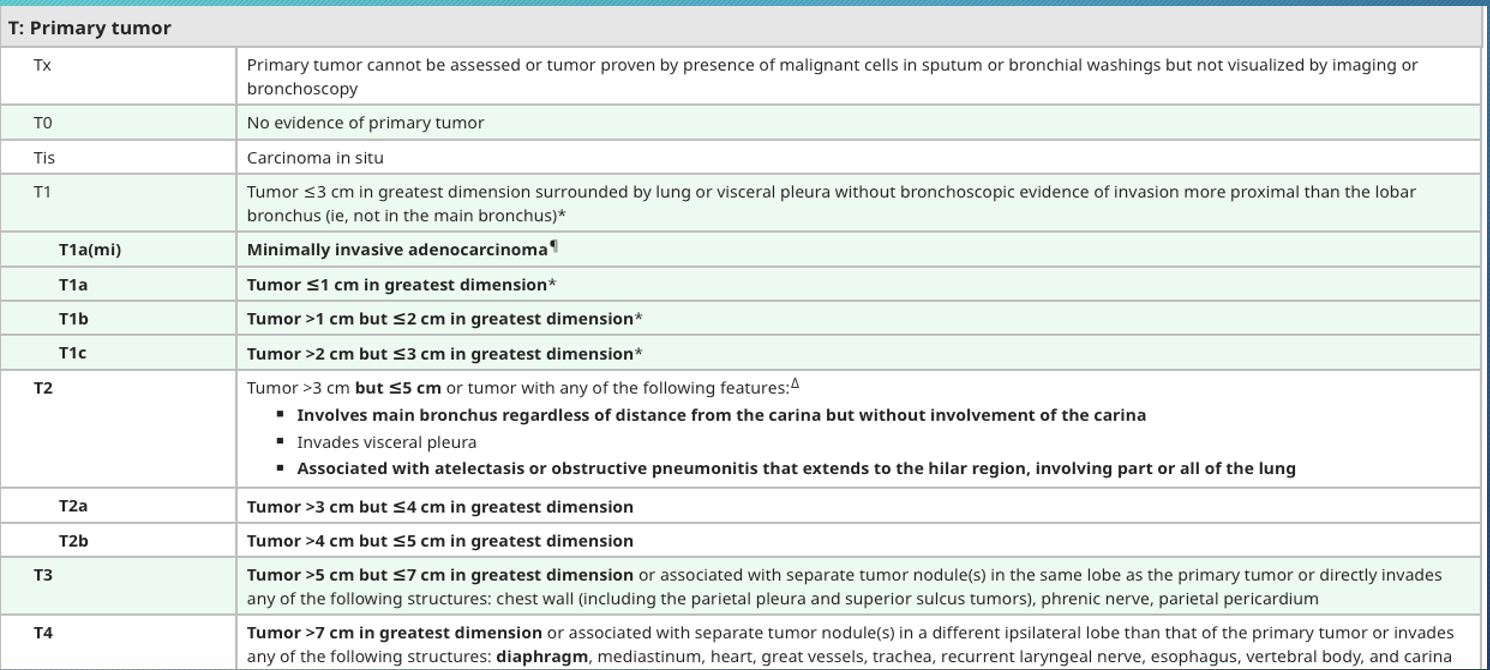
international lung cancer staging system
T: tumor size and level of invasion of adjacent structures
N: presence or absence of nodal spread and site of nodal spread
M: presence or absence of distant metastases
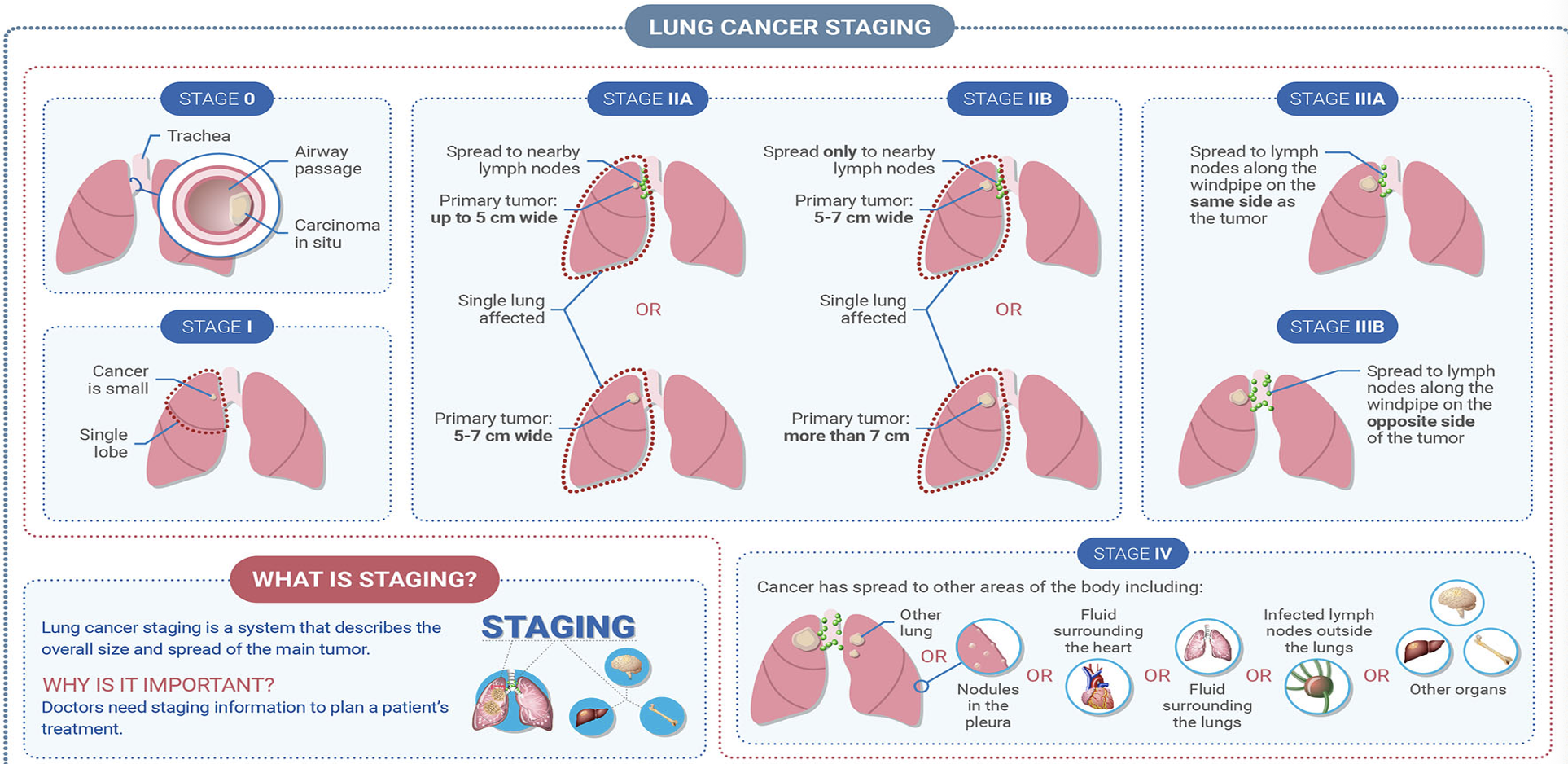
-Stage 0: carcinoma in situ
-Stage 1: small cancer at single lobe
-Stage 2a: spread to nearby lymph nodes, primary tumor up to 5 cm wide, single lung affected or primary tumor 5-7 cm wide
-Stage 2b: spread only to nearby lymph nodes, single lung affected or primary tumor more than 7 cm
-Stage 3a: spread to lymph nodes along the windpipe on same side as tumor
-Stage 3b: spread to lymph nodes along the windpipe on opposite side of tumor
-Stage 4: spread to other areas of body include other lung or nodule in pleura or fluid surrounding lungs or infected lymph nodes outside the lung or other organs
treatment of limited small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
chemotherapy with XRT
treatment of extensive small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
chemo & XRT
immunotherapy
Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment
-stage 1
surgery (radiation if inoperable 1A)
post op targeted therapy for 1B EGFR or ALK + or
neo adjuvant chemo immuno followed by surgery if EGFR or Alk negative
-stage 2
surgery with adjuvant chemotherapy or targeted therapy for EGFR or ALK +
neo adjuvant chemo immuno followed by surgery if EGFR/ Alk are negative
-stage 3
chemotherapy with radiation therapy
immuno for high PDL1
adjuvant immunotherapy or targeted therapy in EGFR or ALK +
neo adjuvant chemo immuno followed by surgery if EGFR-
-stage 4/recurrent: chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, supportive care
chemotherapy for non small cell lung cancer
2 or 3 drugs given together or 1 drug by itself
-carboplatin or cisplatin
-docetaxel (taxotere)
-gemcitabine (gemzar)
-nab-paclitaxel (abraxane)
-paclitaxel (taxol)
-peretrexed (Alimta)
-vinorelbine (navelbine)
targeted therapy
use drugs directed at specific cell signaling and regulatory pathways that are altered in neoplastic cells
block cancer cells from copying themselves and stop making additional copies
*actions of targeted drugs
-blocking or turn off chemical signals that tell cancer cells to grow or divide
-change proteins within cancer cells to signal it to die
-stop making new blood vessels to feed cancer cells
-trigger immune system to kill cancer cells
-carry toxins to cancer cells to kill them, but not normal cells
SCLC vs NSCLC
SCLC: fast growing, aggressive, respond to chemo and XRT
NSCLC: slow growing, surgery possible, less responsive to chemo/XRT
