Echo Techniques I Exam 4 FINAL
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
m-mode records _____, ______, and _____
distance, motion, echo strength
cursor should be placed ______ to the structure
perpendicular
___ is measured on the y-axis and ____ is measured on the x-axis
depth; time
for AoV, the cursor is placed on the ________
aortic cusps
for MV, the cursor is placed at the tip of the ________
mitral leaflets
for LV, the cursor is placed in front of the ____, past the ___________, including the CT
PM; mitral leaflet tips
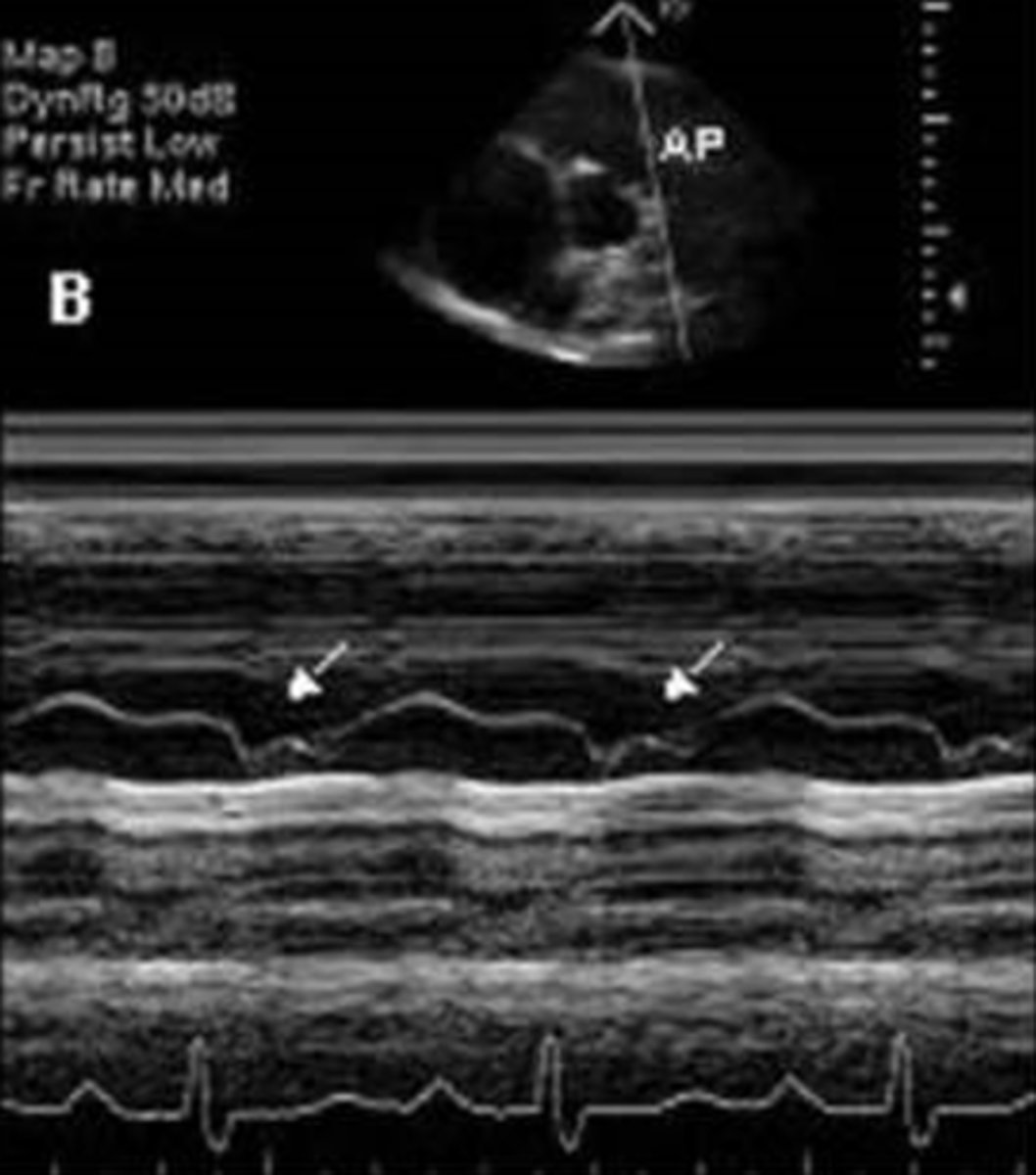
for PV, have the DEFAC as mitral and in case of PHTN, you will see what is known as "___________"
flying W
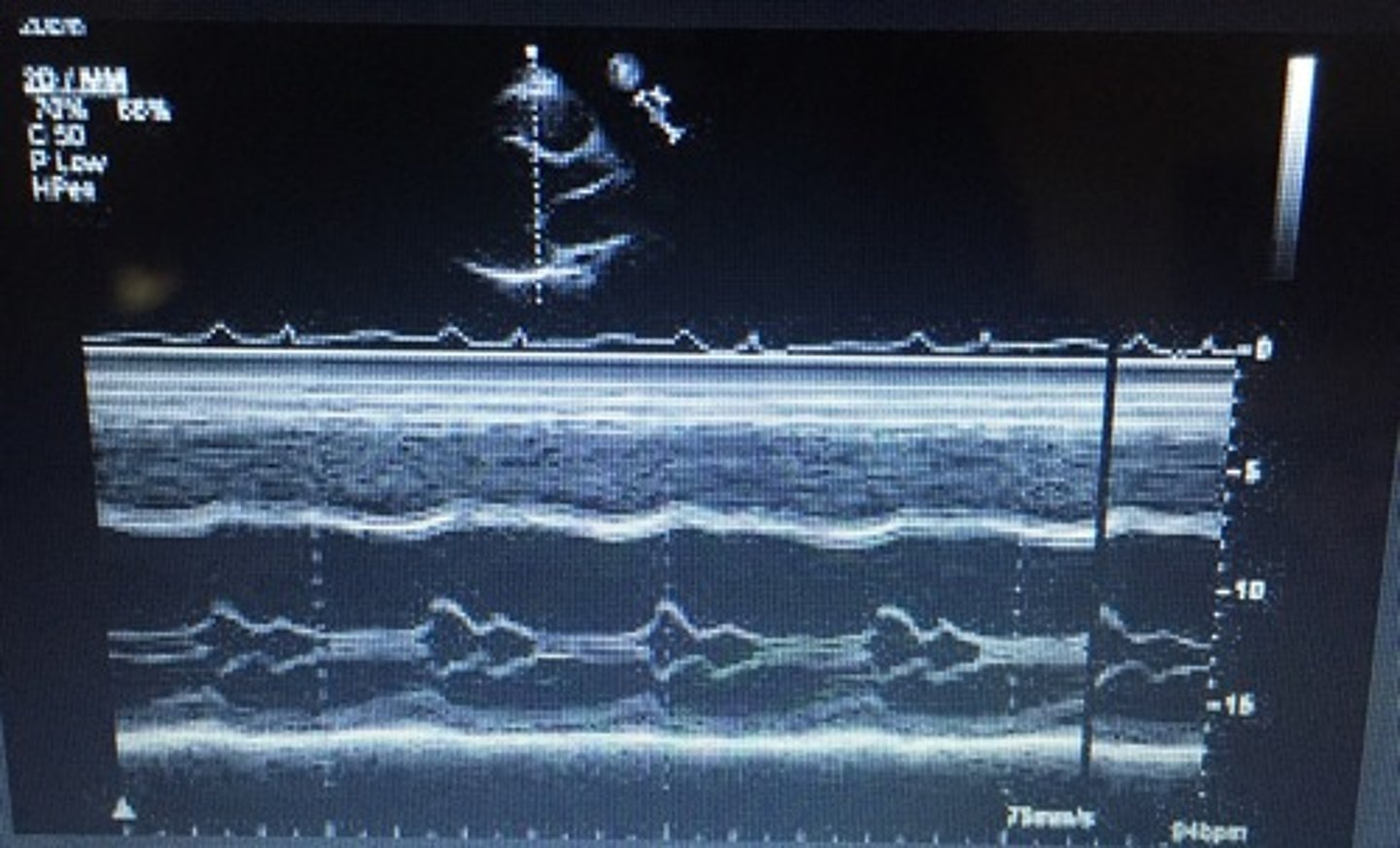
narrowing of the AoV orifice; band of bright echoes on 2-D and M-Mode
aortic stenosis (AS)
how is aortic stenosis acquired
senile calcification, rheumatic fever, congenital (bicuspid 1-2% of population and unicuspid extremely rare)
there is an _____ in LVEDP and LV ______ in cases of aortic stenosis
increase; hypertrophy
what mimics aortic stenosis
subvalvular stenosis and supravalvular stenosis
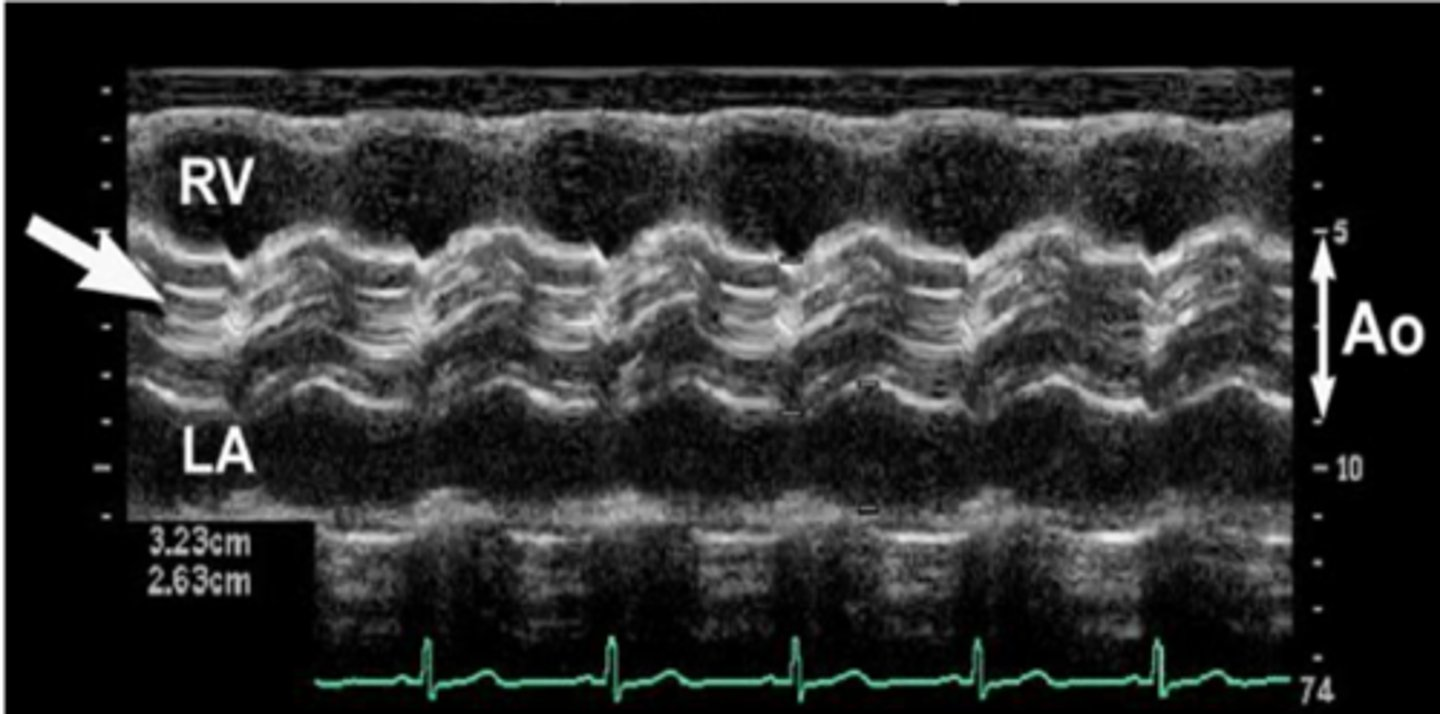
cusp missing from AoV; aortic valve closure line is ECCENTRIC (not centered) and thicker
bicuspid aortic valve
in cases of a bicuspid aortic valve the ____ and the ___ are the only cusps seen
RCC; LCC
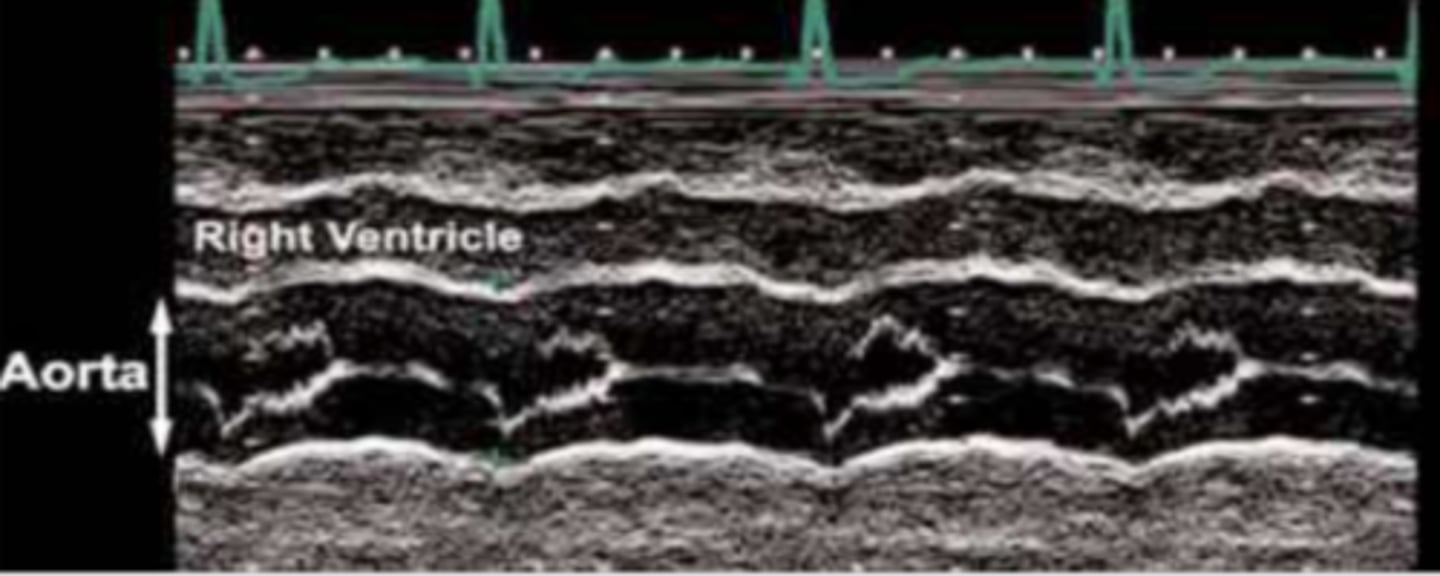
AoV closes early; noted with hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, like idiopathic hypertrophic sub-aortic stenosis; decreased pressure for LV to aorta
premature closure of AoV
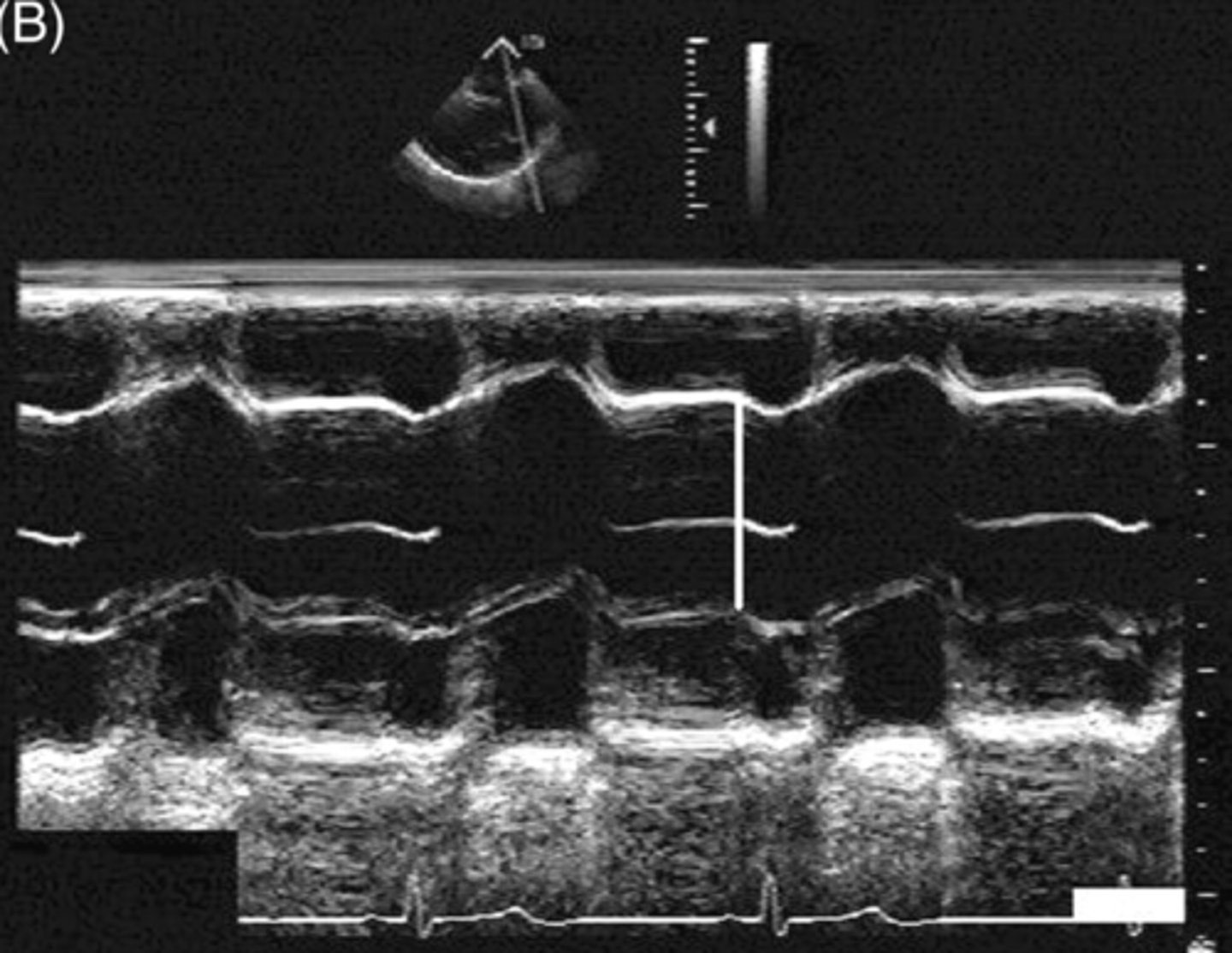
larger than 1:1 ratio between LA and AOR with larger AOR
dilated aortic root
dilated aortic root is caused by ________ and ________
Marfans syndrome; untreated HTN
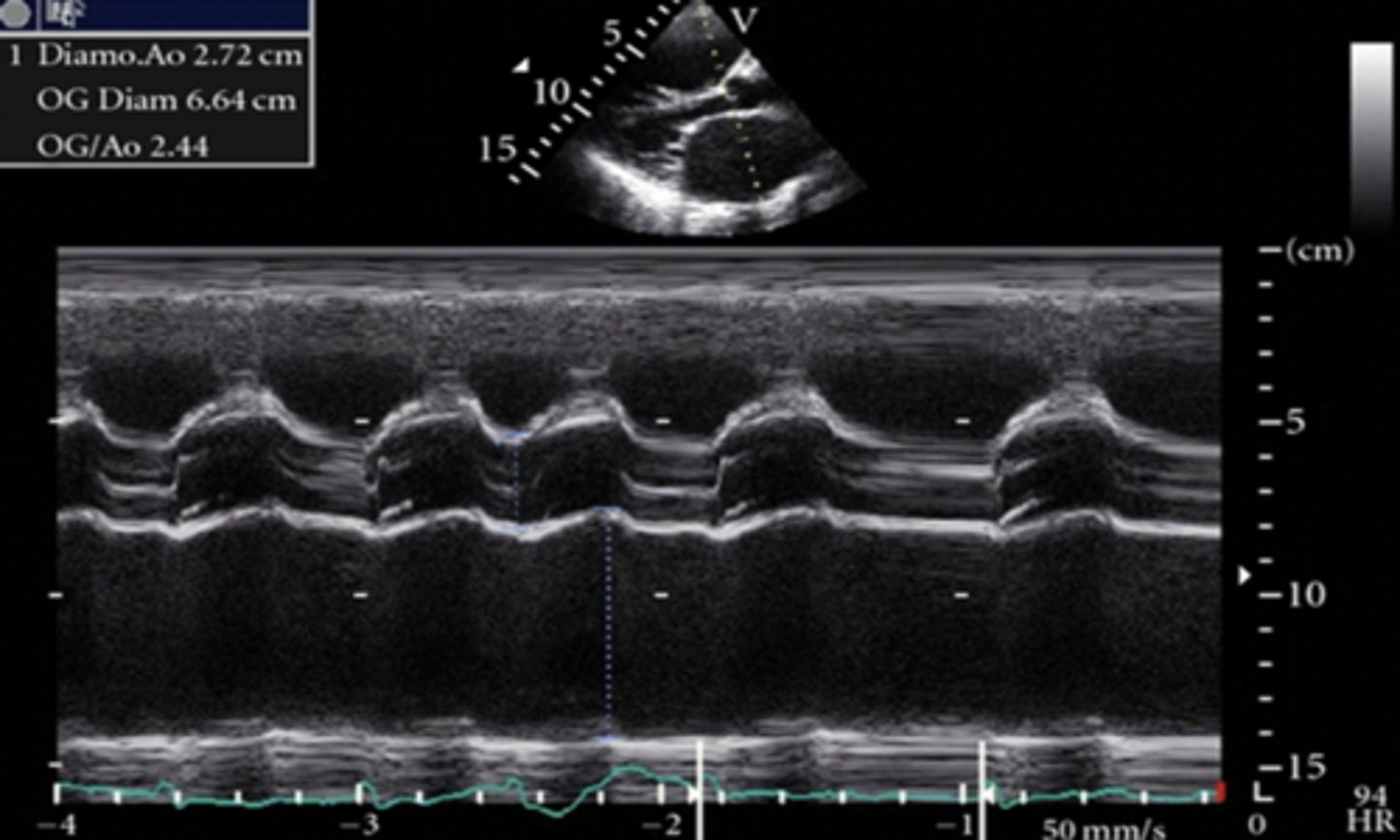
larger than 1:1 ratio between LA and AOR with larger LA
dilated left atrium
a dilated left atrium is caused by _________, _______, _______, ________, or ________________
mitral regurgitation, mitral stenosis, significant LVEDP, mitral valve prolapse, and chronic severe aortic insufficiency
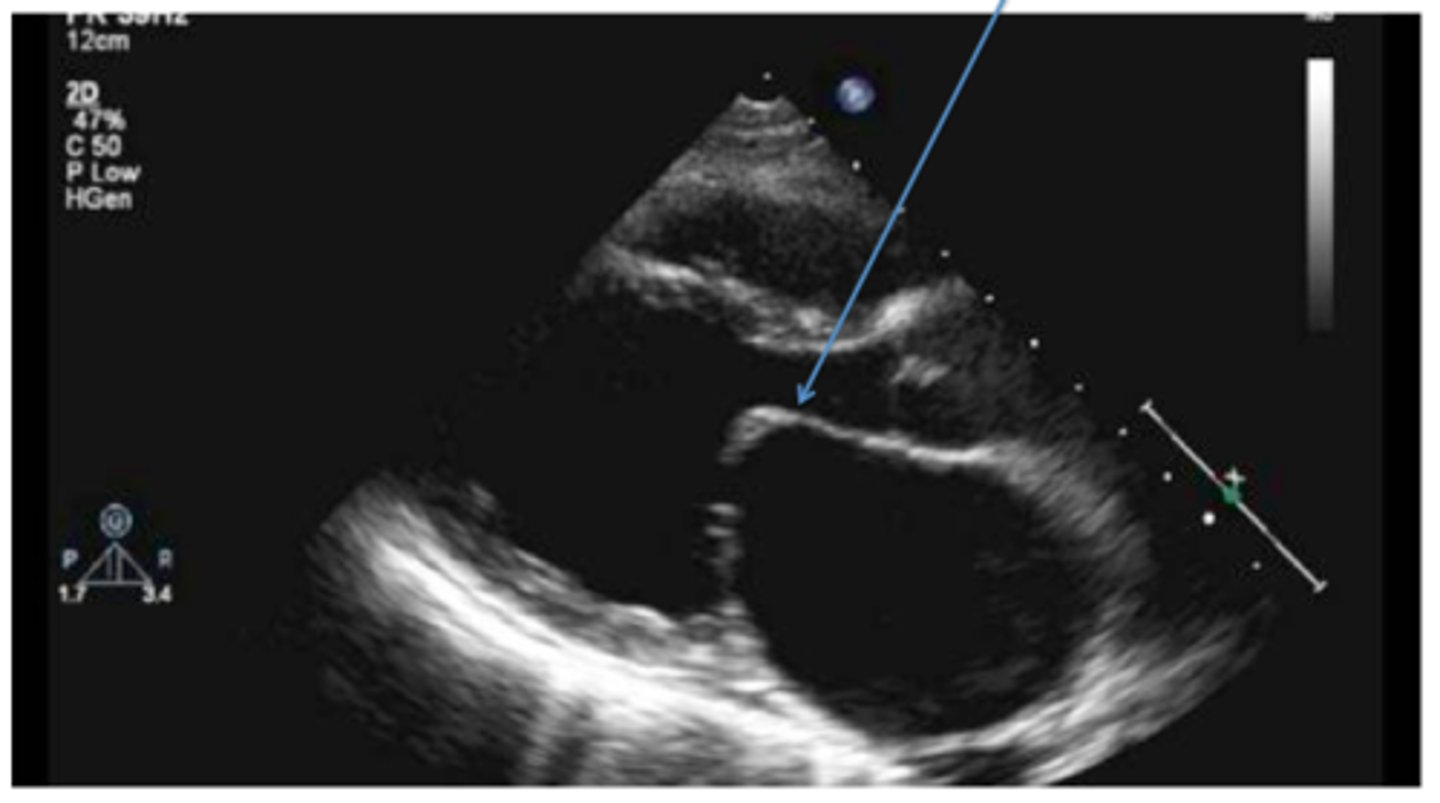
a benign cardiac tumor usually attached to the IAS
left atrium myxoma
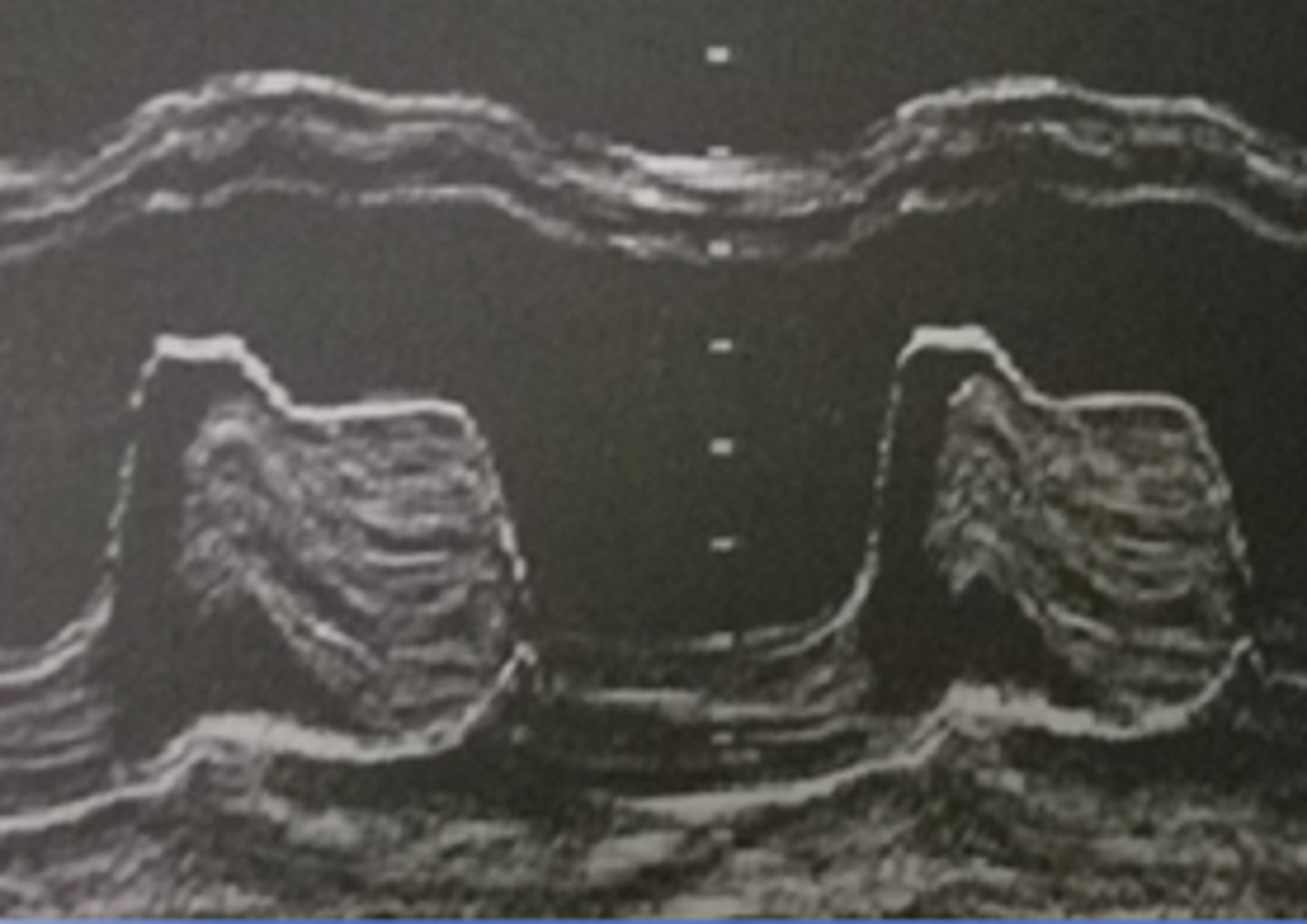
narrowing of the MV orifice with bright band of echoes in 2D and M-mode; thickening of AML and PML with anterior motion of PML; LA dilation and increased pressure; hockey puck appearance; decreased E-F slope and D-E excursion with diastolic doming
mitral valve stenosis
(D)EFAC
onset of diastole
D(E)FAC
early diastole
DE(F)AC
first peak
DEF(A)C
atrial systole
DEFA(C)
closure of MV
D-E excursion
rapid diastolic opening (1.8-2.8cm)
E-F slope
motion of AML during diastole (70-150mm/s)
EPSS
distance between E point and IVS (2-7mm)
what are some complications of mitral stenosis
mitral regurgitation, pulmonary hypertension, shortness of breath, and A-fib
what are some causes of mitral stenosis
rheumatic fever, congenital, and mitral annular calcification
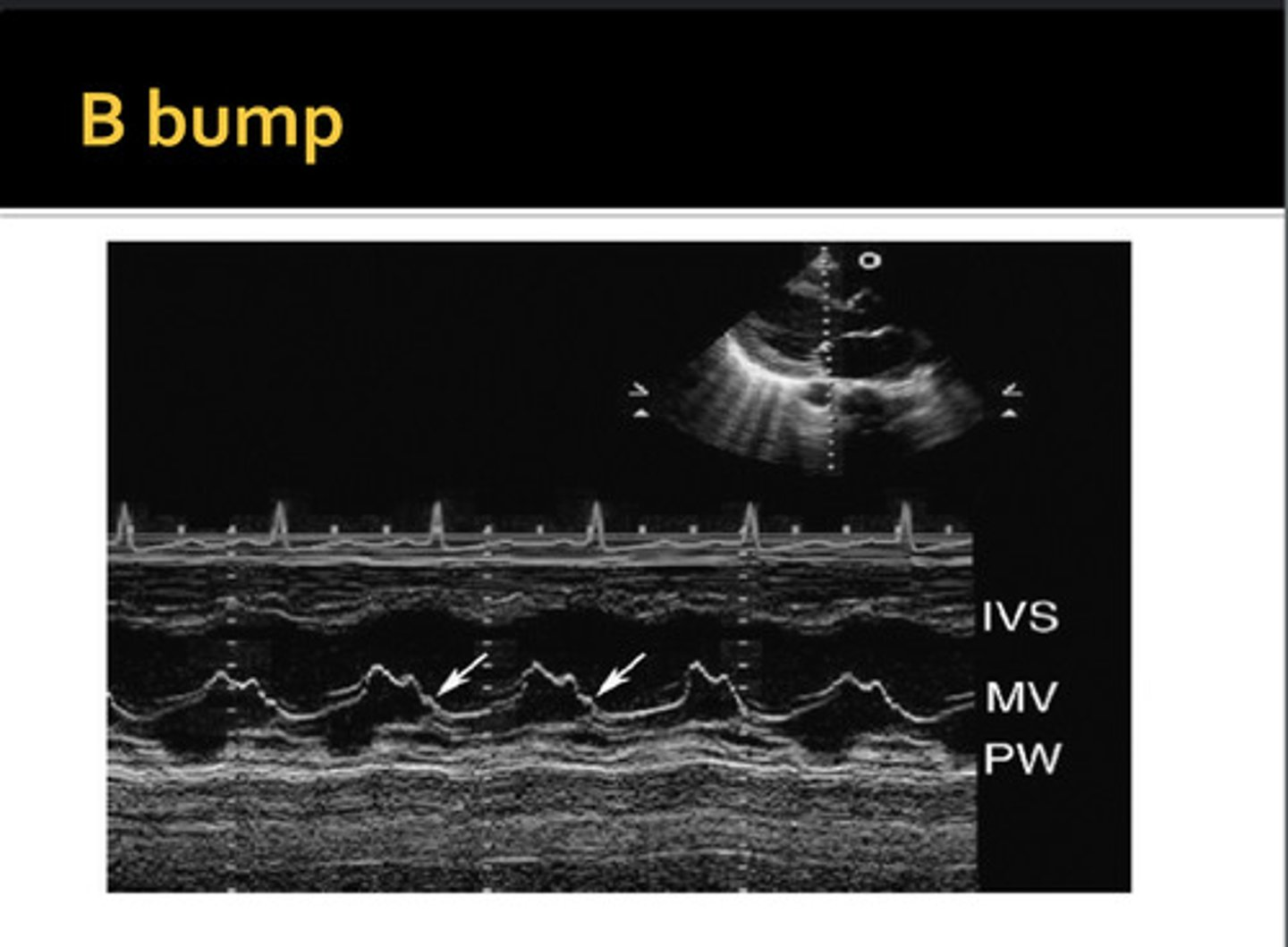
extra hump between A-C; commonly seen with dilated cardiomyopathy and LV dilation; increased LVDP and LA pressure; decreased EF% and EPSS is >10mm
B-Bump/B-Notch/ A-C Shoulder
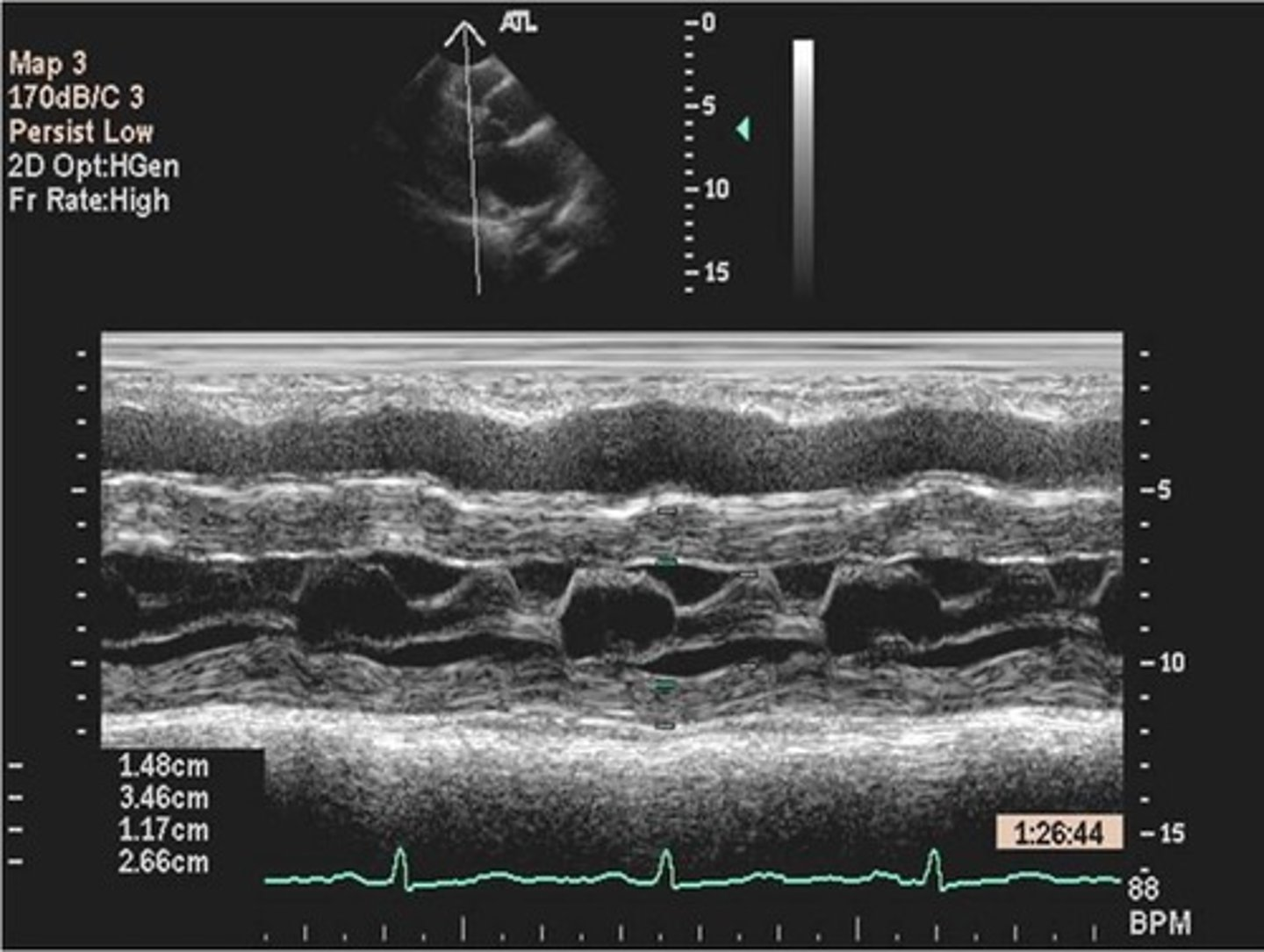
MV leaflets move anteriorly towards the LVOT in systole; seen in hypertrophic cardiomyopathies such as ASH, IHSS, HOCM, and subaortic outflow tract obstruction
systolic anterior motion (SAM)
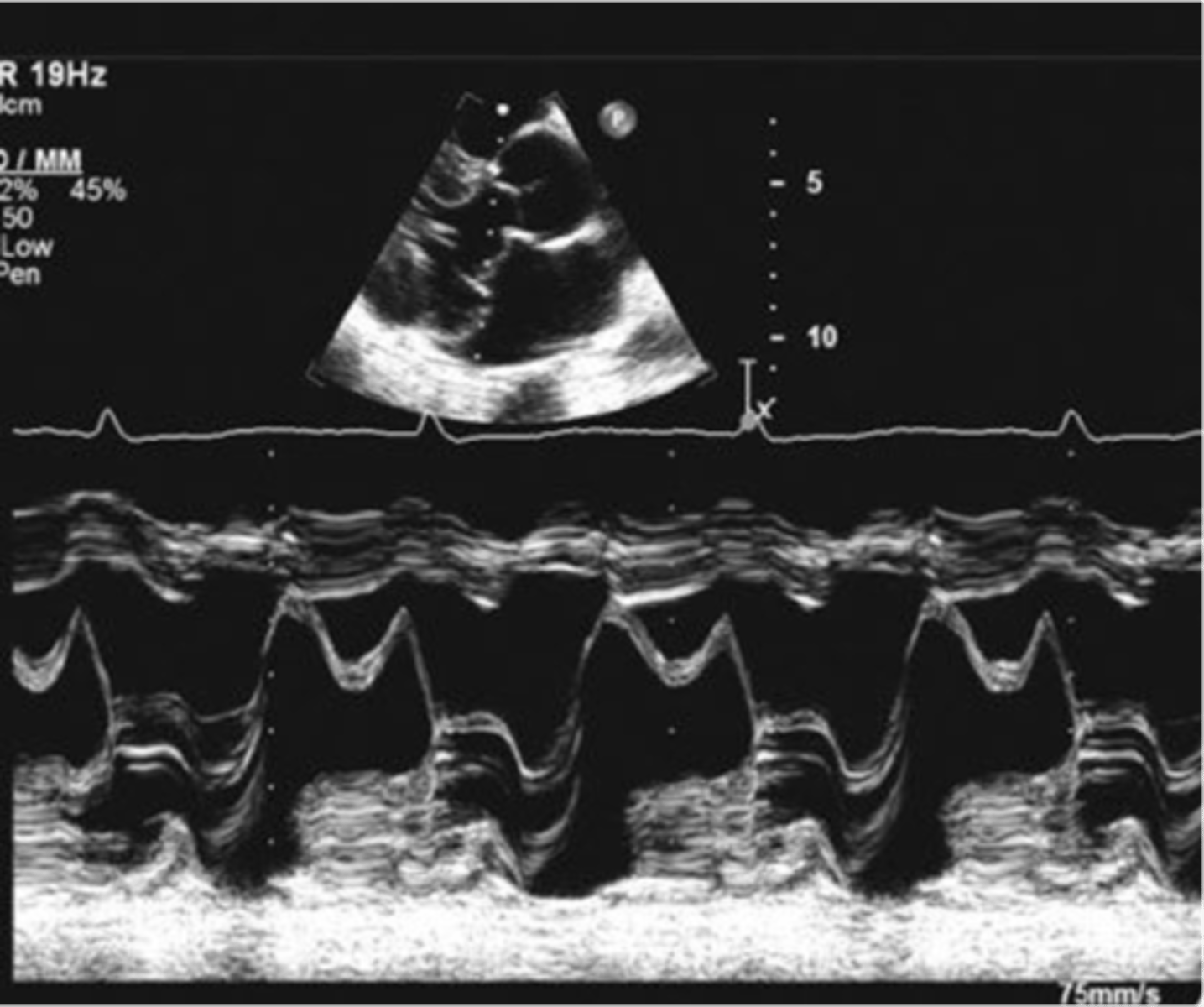
posterior motion of MV leaflets beyond the MV annular plane during systole; hammocking appearance
mitral valve prolapse
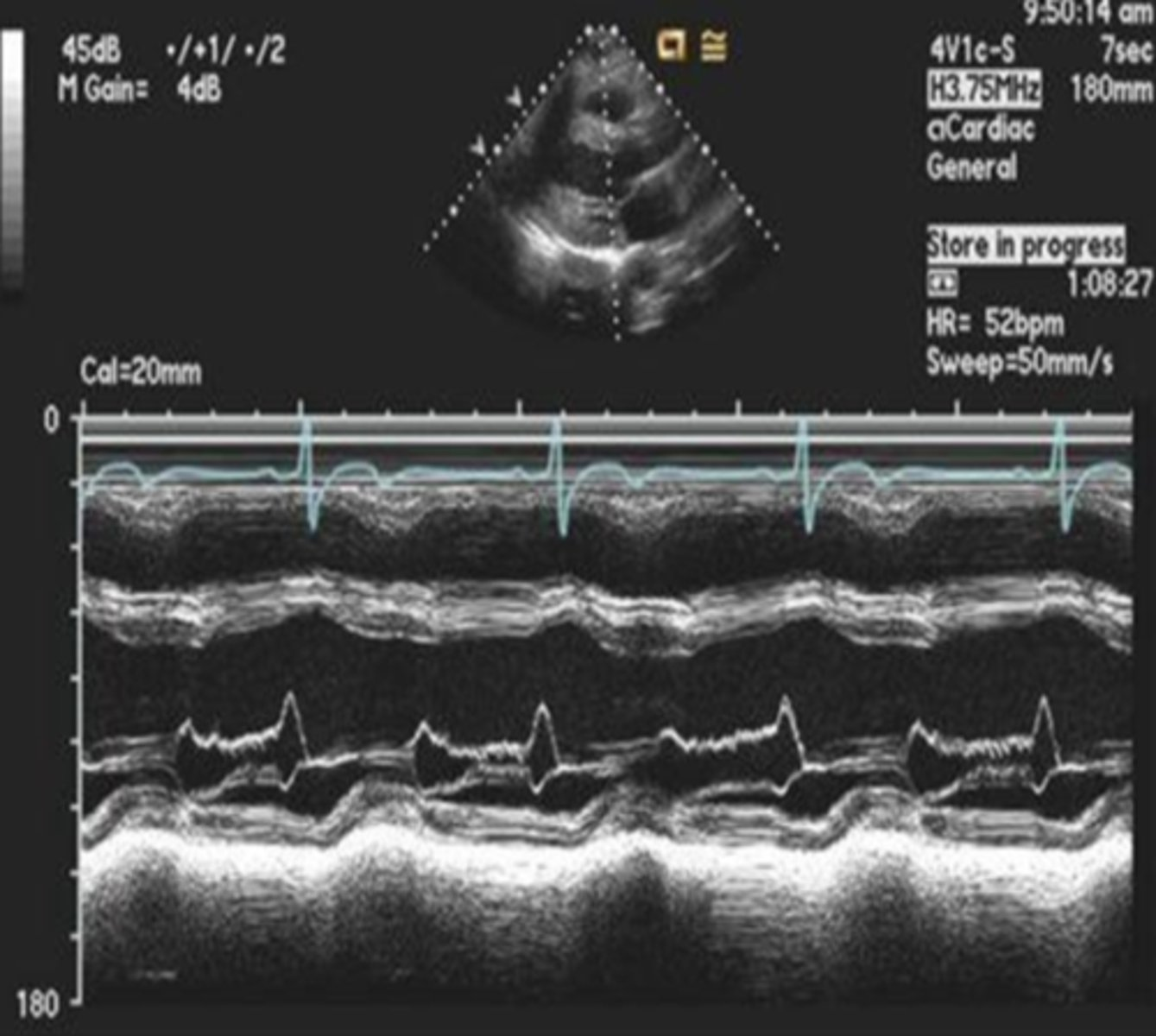
diastolic flutter of the AML with aortic regurgitation
MV flutter
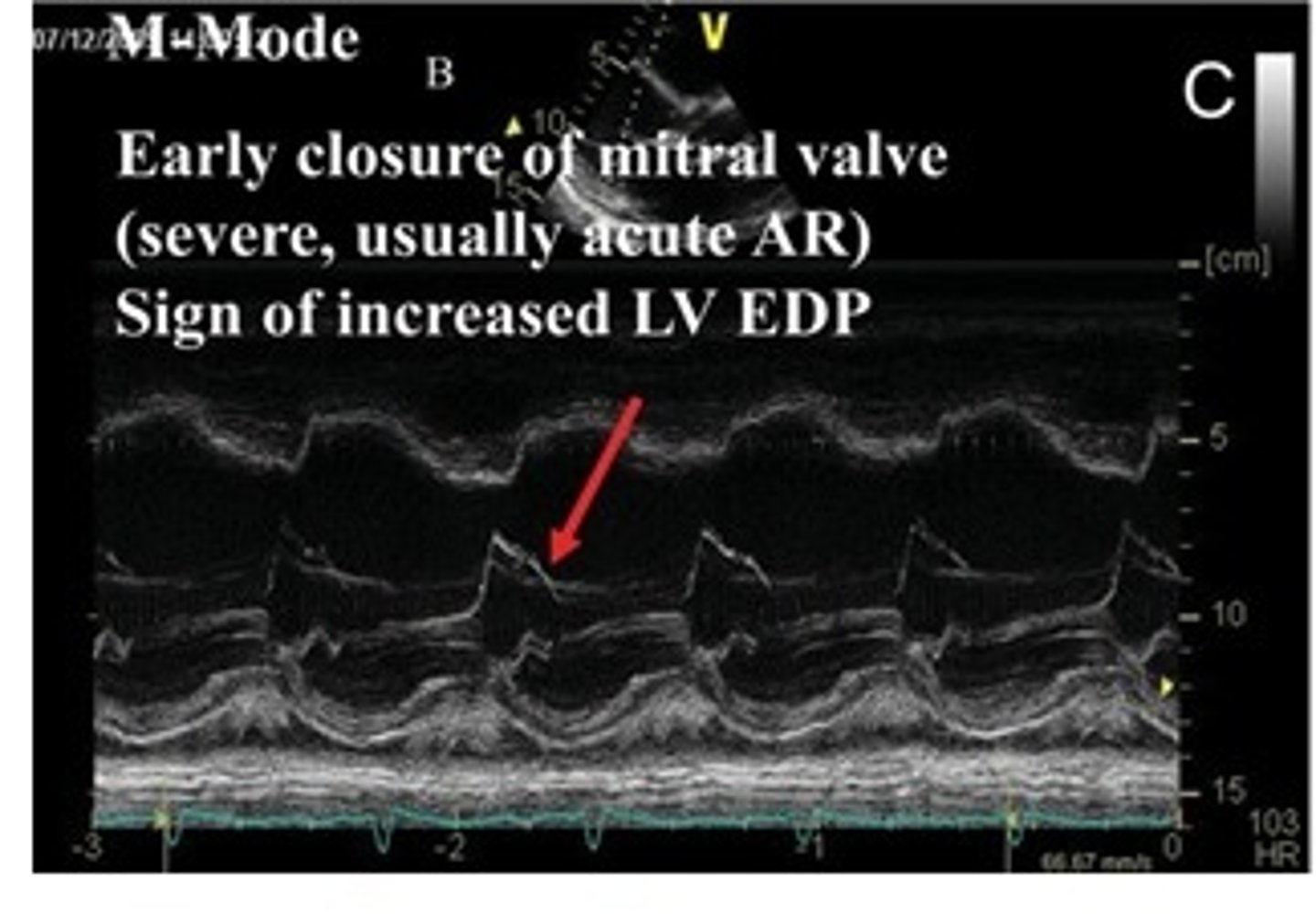
early closure of MV; severe cases will be AR(AI) and increased LVEDP
premature close of MV
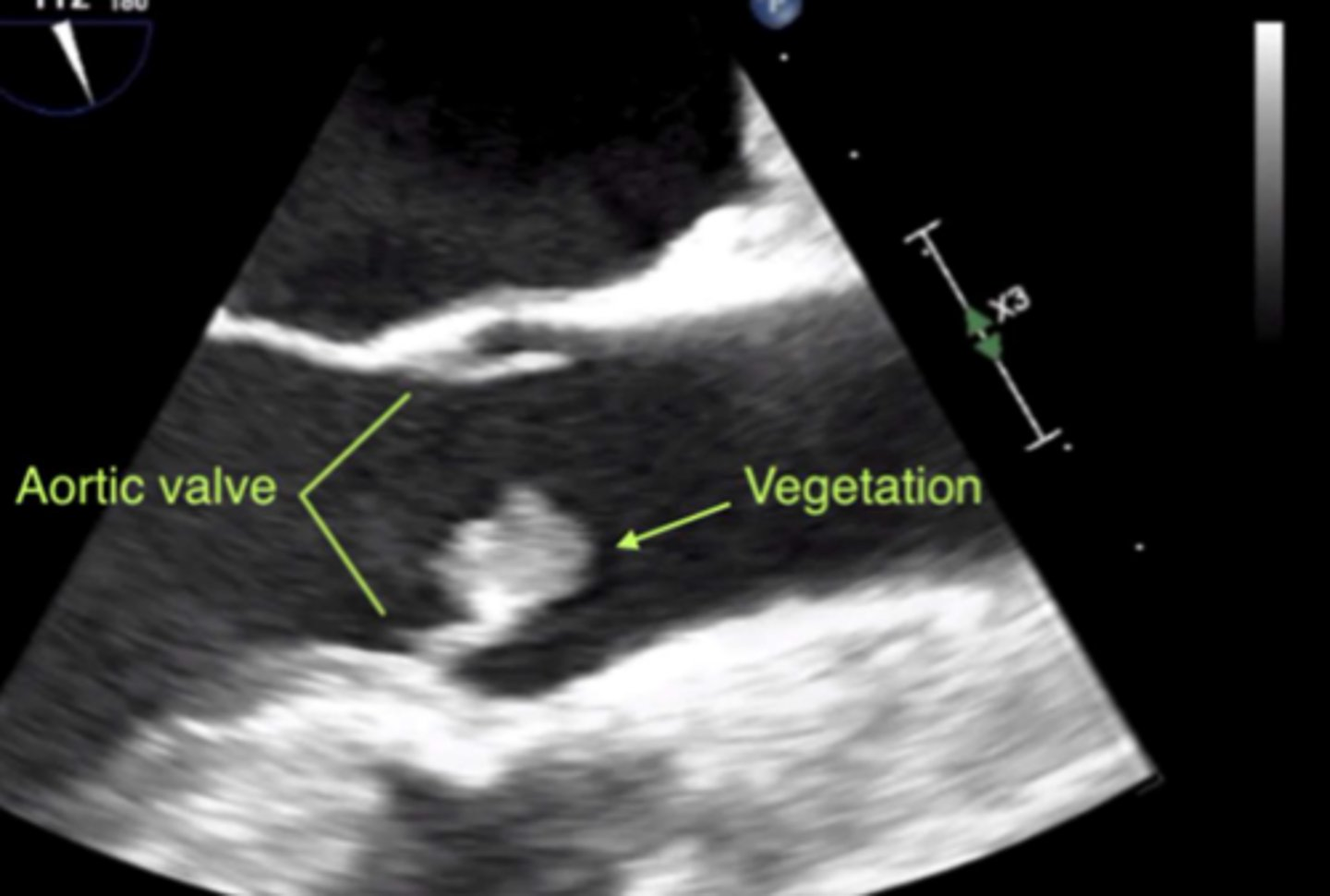
irregular shaped, echo-dense mass on cardiac valve, often associated with infective endocarditis
vegetation
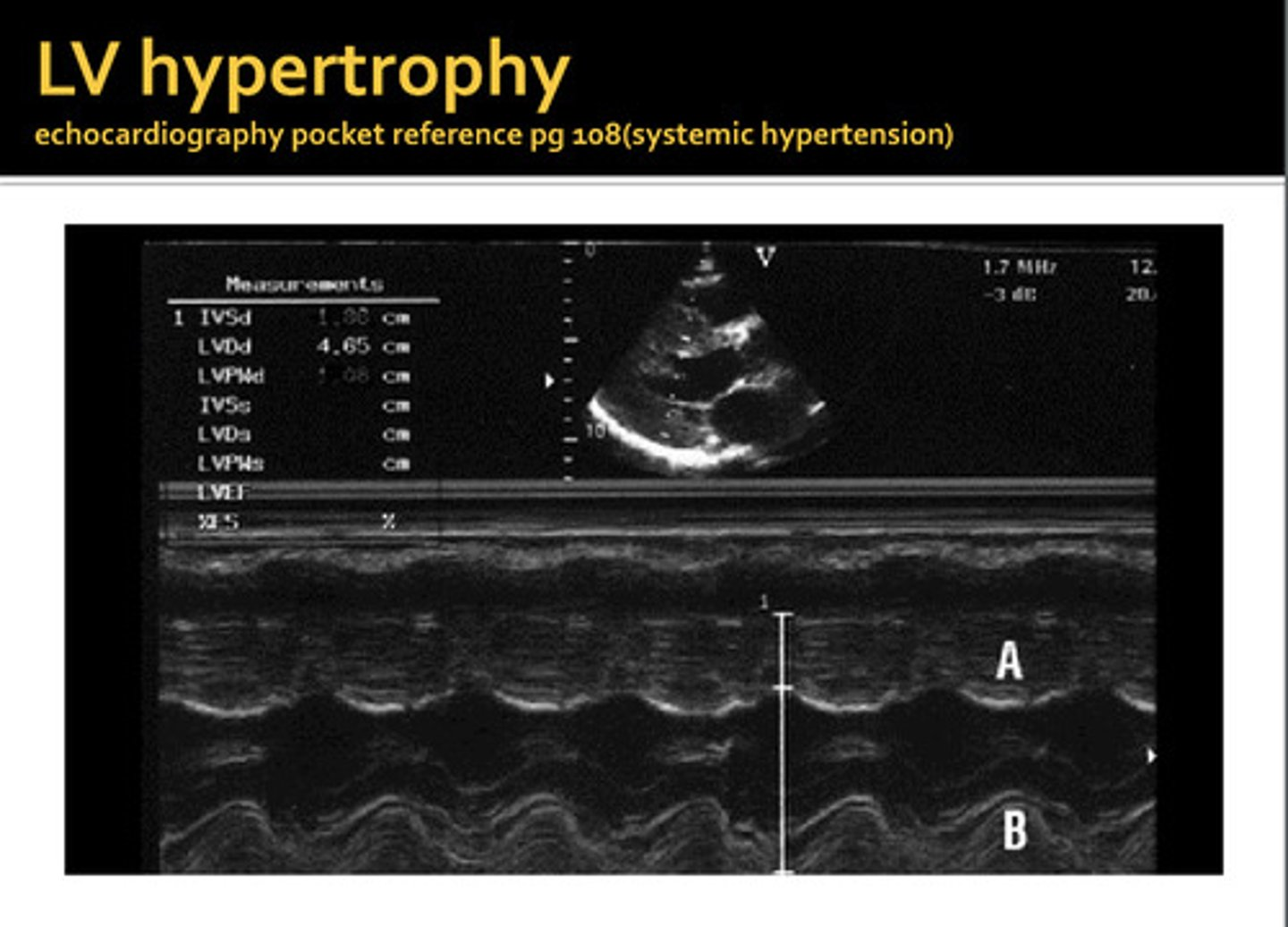
thickening of the septal and/or posterior wall, can be symmetrical or asymmetrical
LV hypertrophy
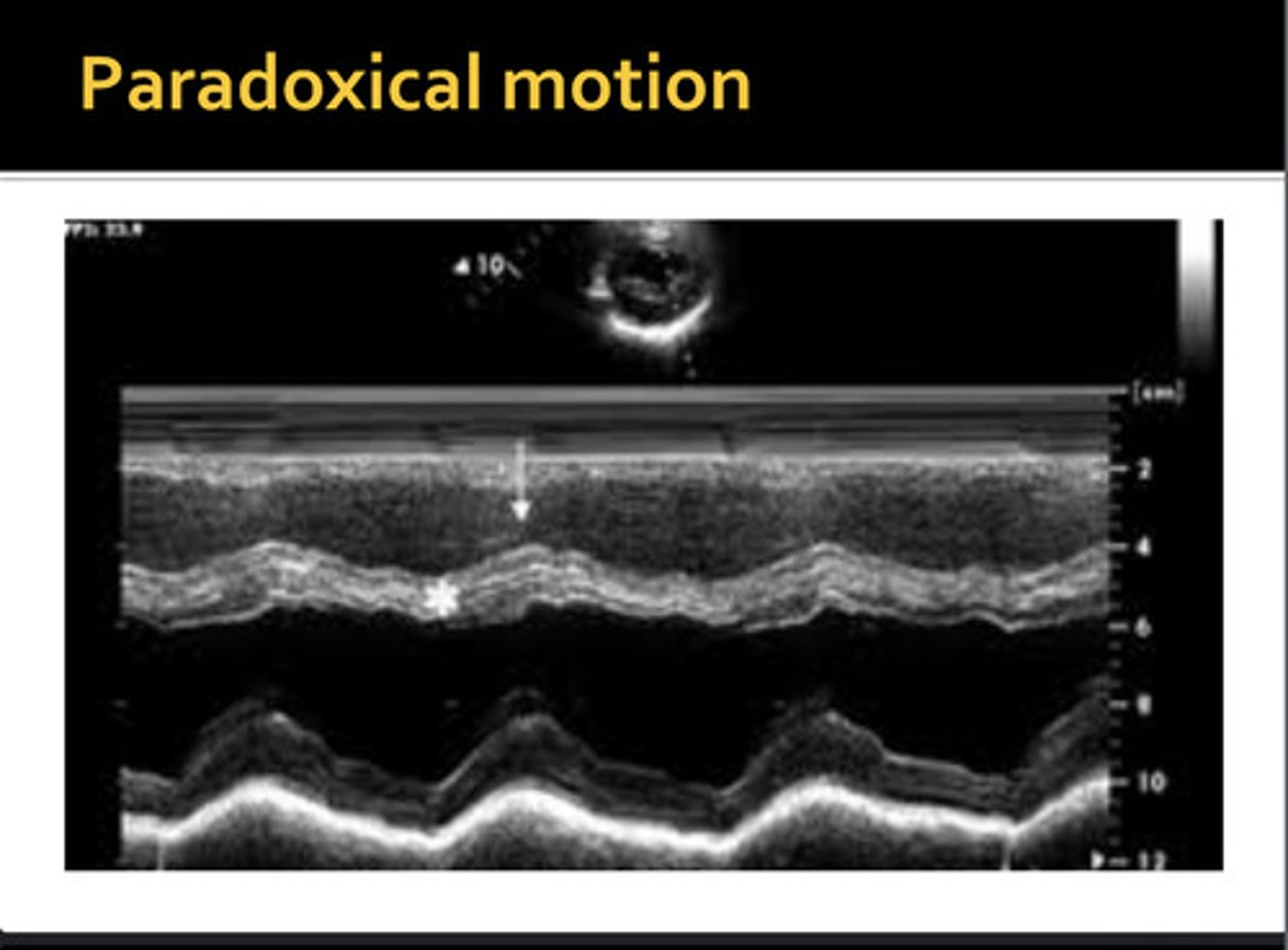
movement away from the opposite wall during systole; IVS moves away from free wall and posterior inferior away from pericardium
paradoxical wall motion
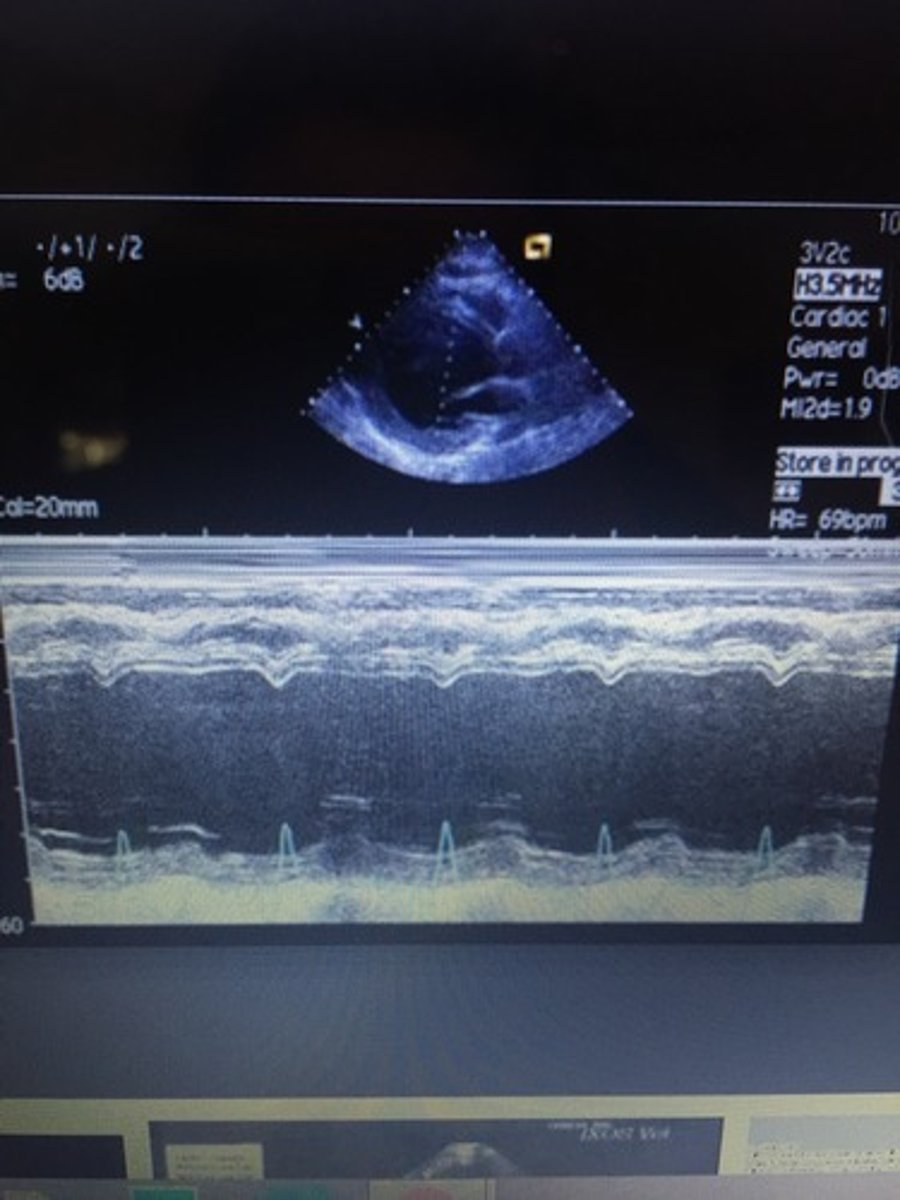
LV dilation with poorly contracting septal or posterior walls; EPSS >10mm/s and decreased EF%; leads to congestive heart failure
dilated cardiomyopathy
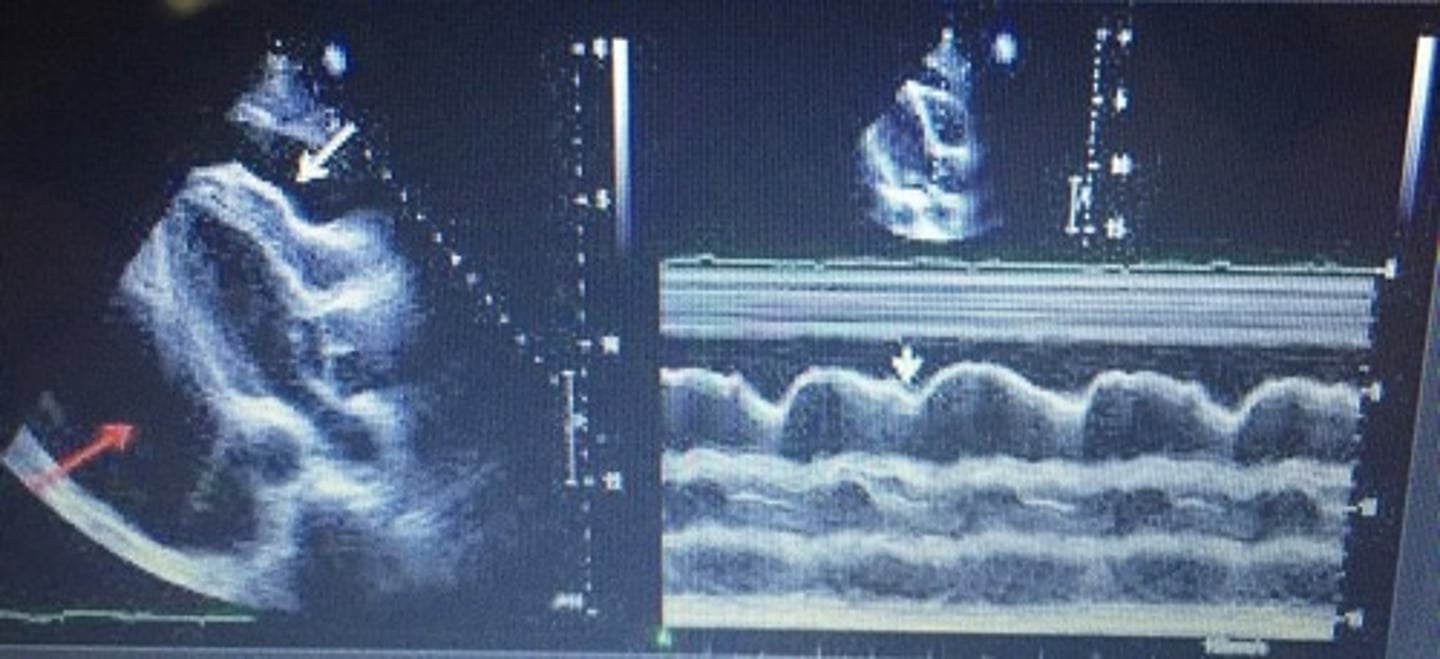
build-up of fluid in the pericardium (above DA)
pericardial effusion
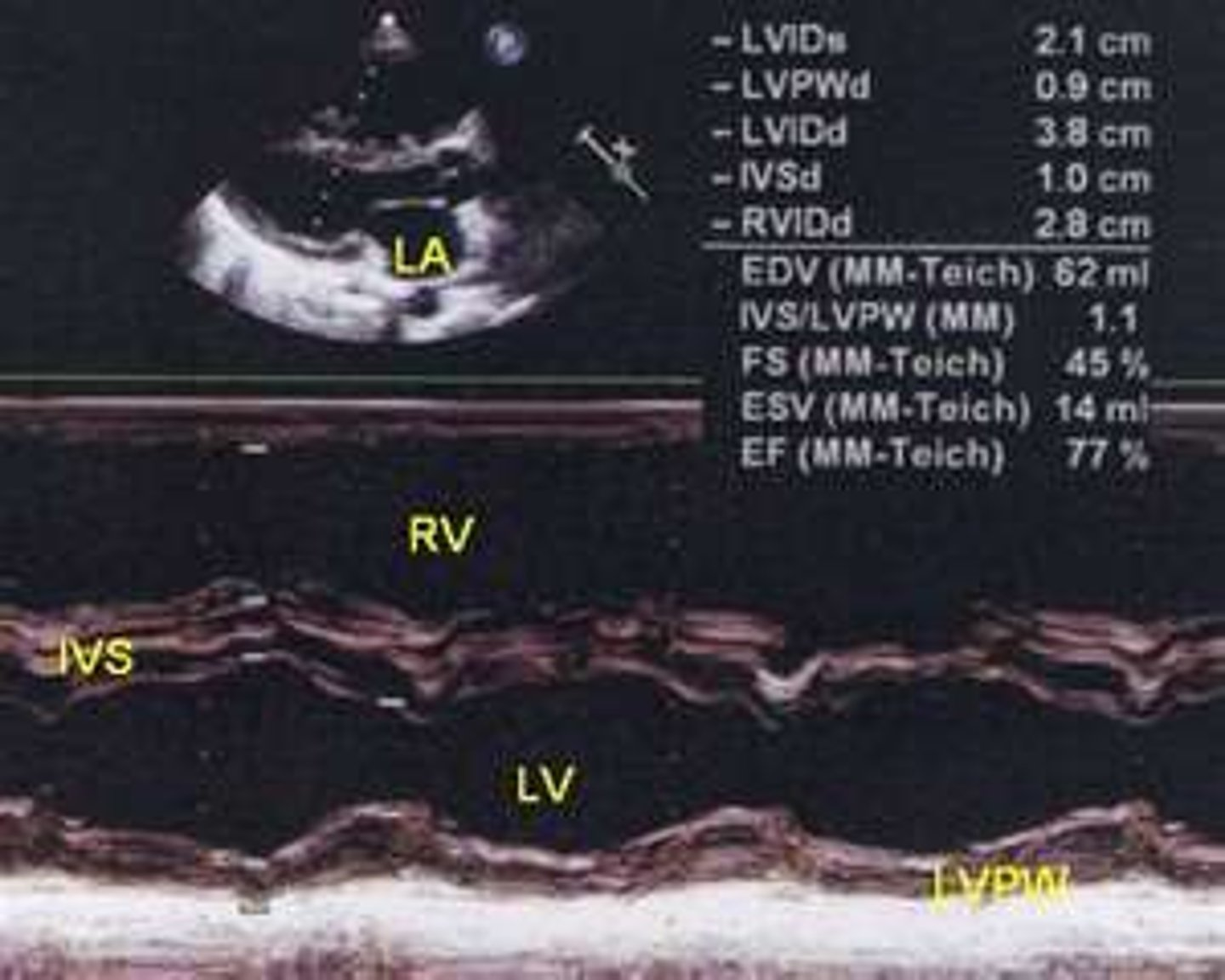
consistent with dyskinetic wall motion and appears as D-shaped septum in PAP view
right ventricular volume overload (RVVO)
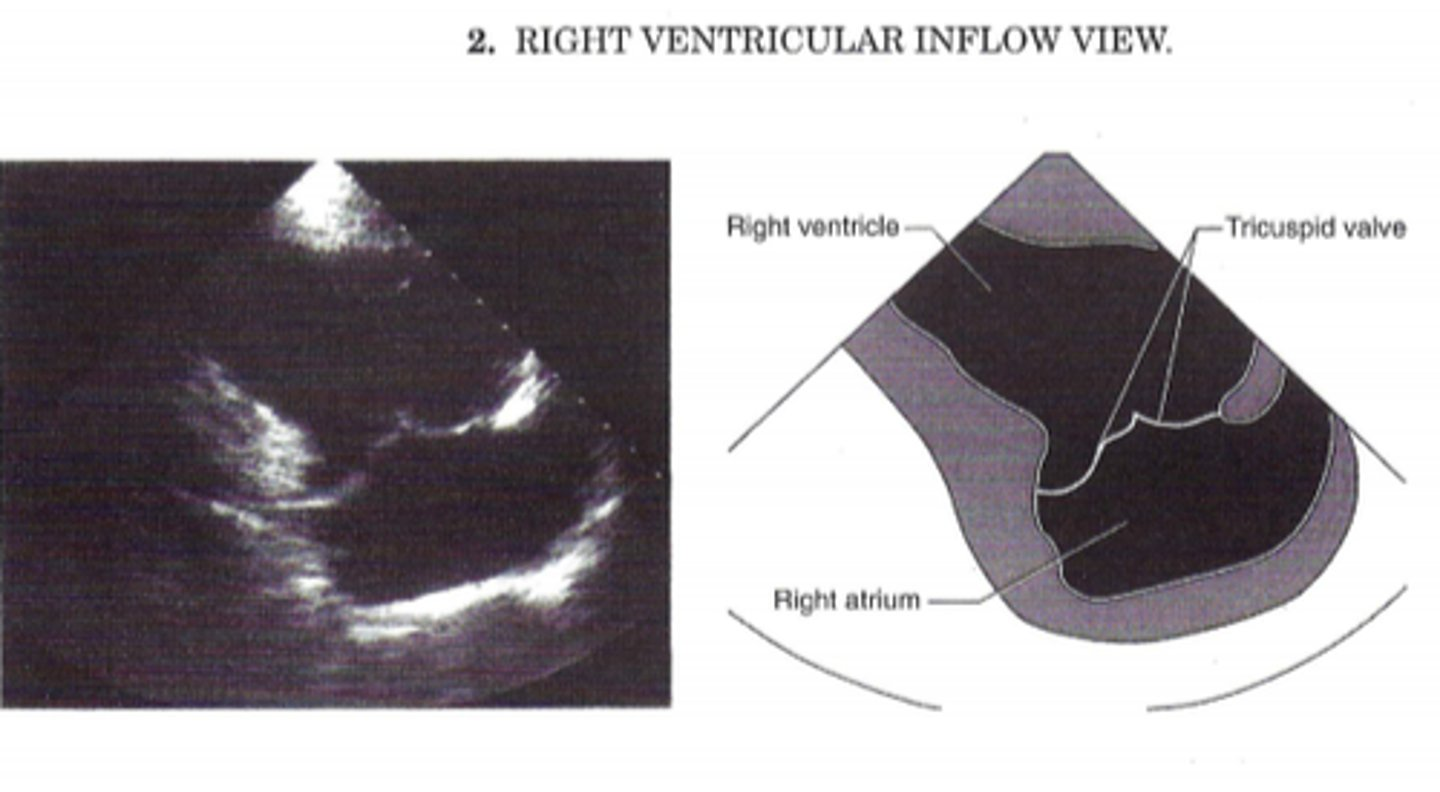
RVIT is used to visualize ____
TV
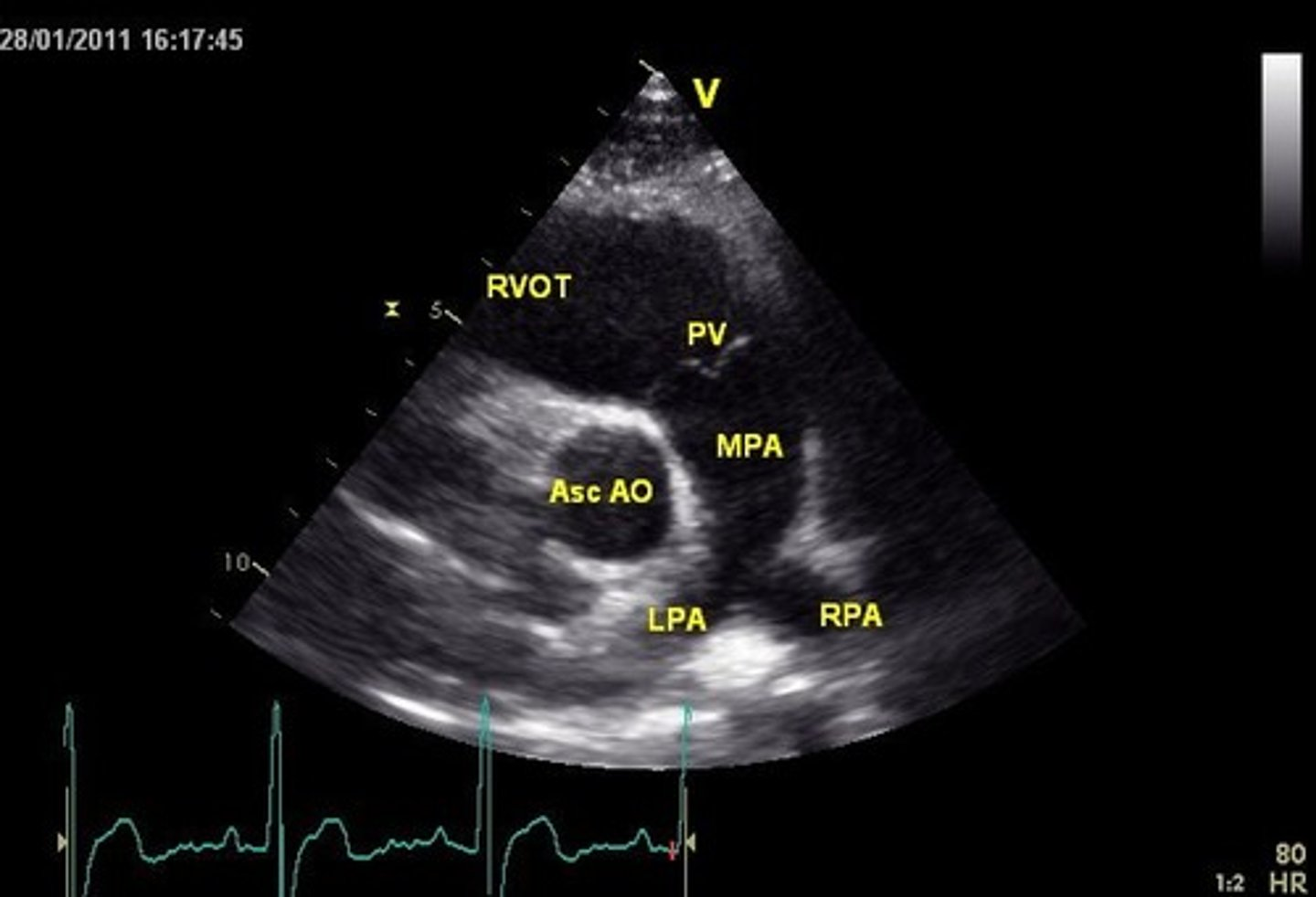
RVOT is used to visualize _______
PV
PSLA is used to visualize ____ and _____
MV and AoV
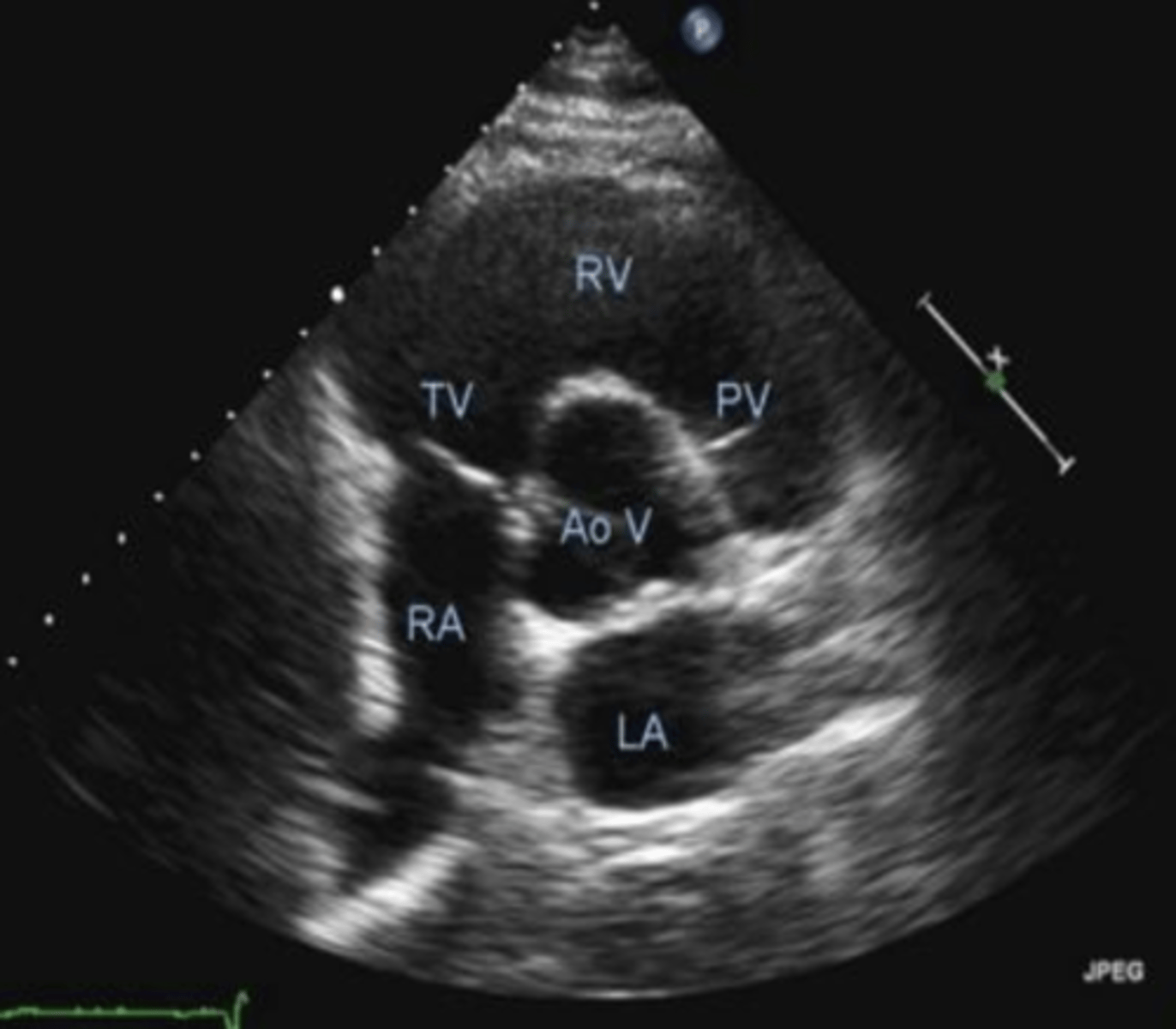
PSSA AoV is used to visualize _____, ____, and ___
TV, PV, AoV
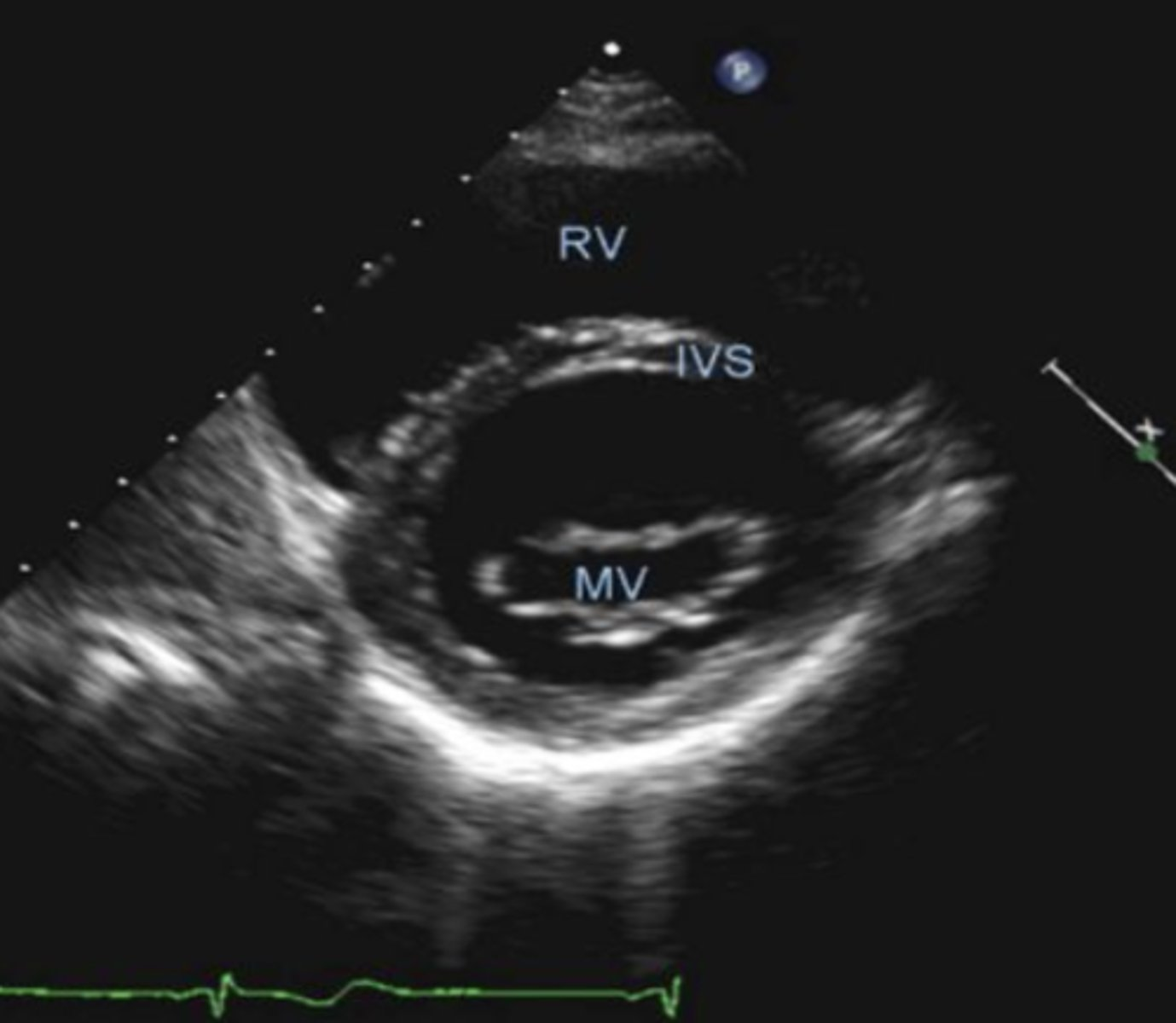
PSSA MV is used to visualize _____
MV
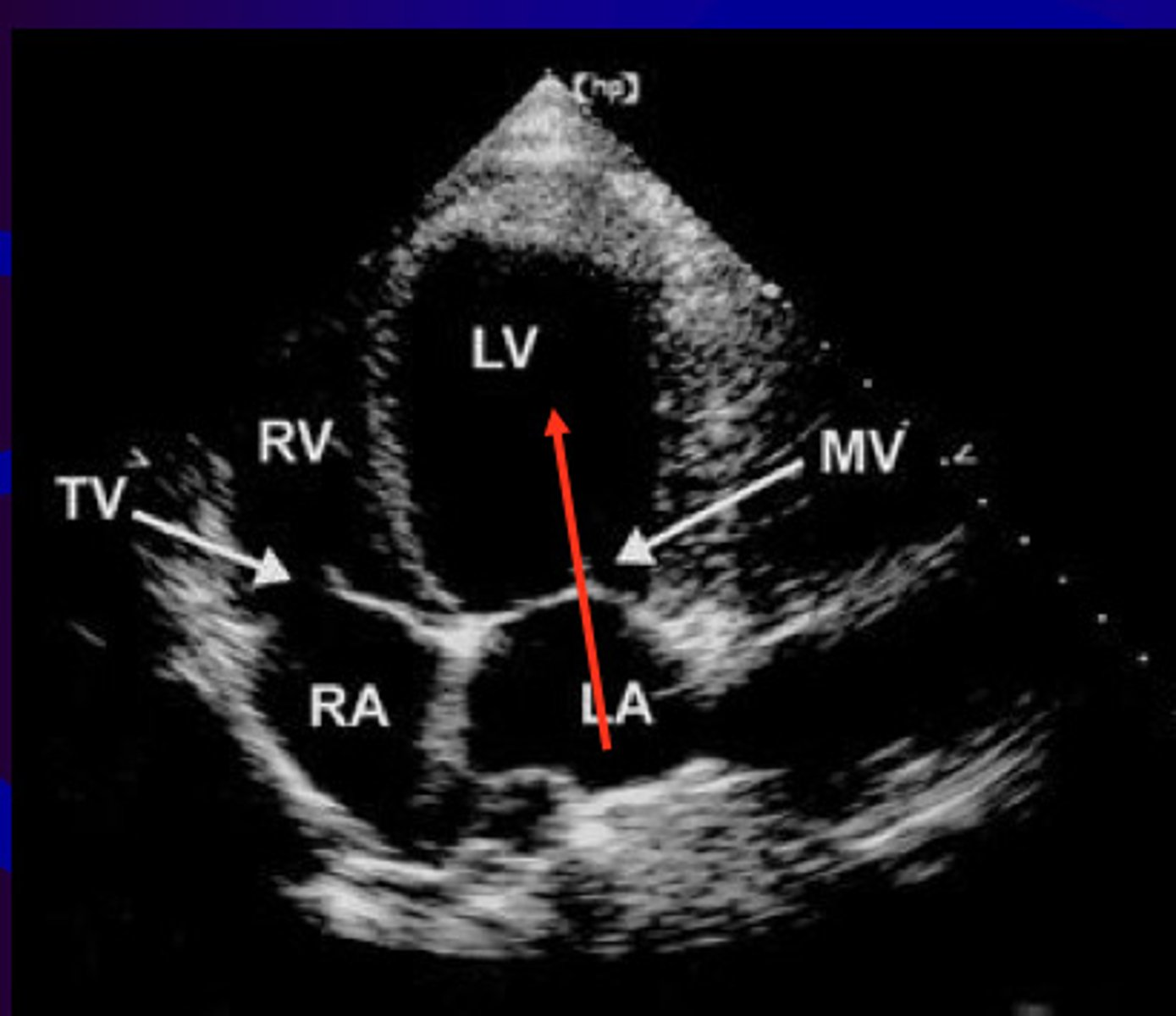
A4 is used to visualize _____ and ____
MV, TV
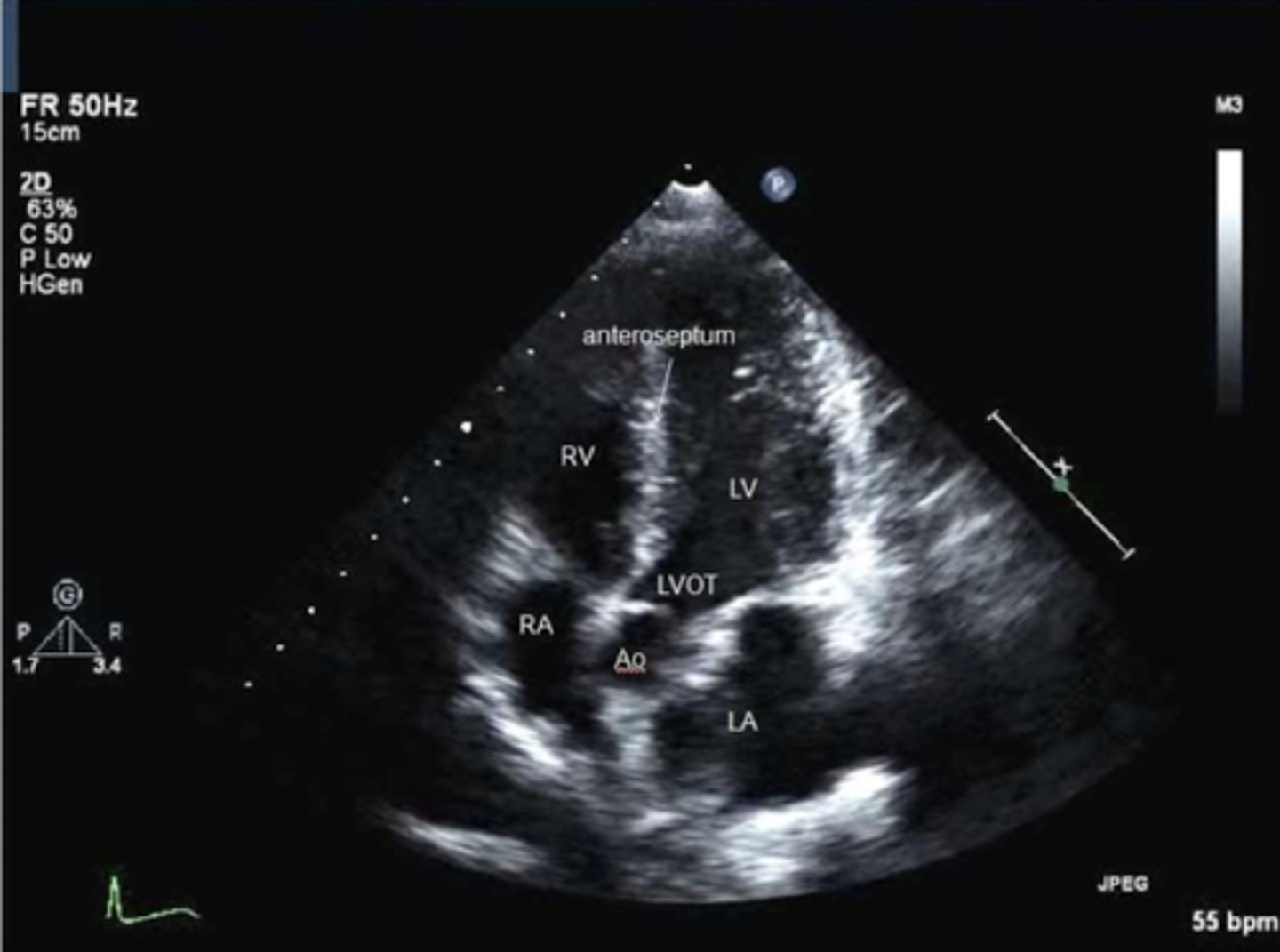
A5 is used to visualize ____, ____, and _____
TV, MV, and AoV
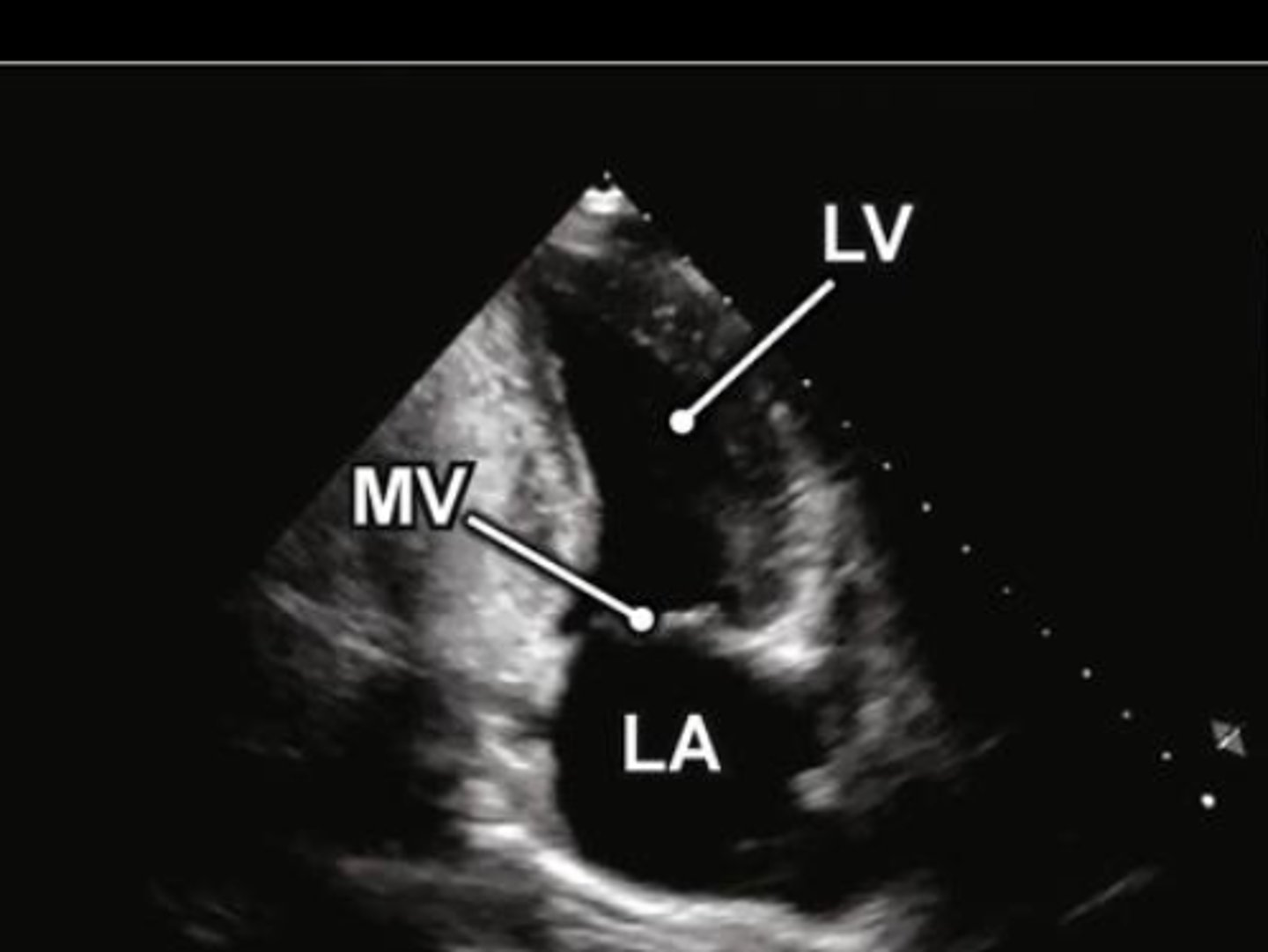
A2 is used to visualize _____
MV
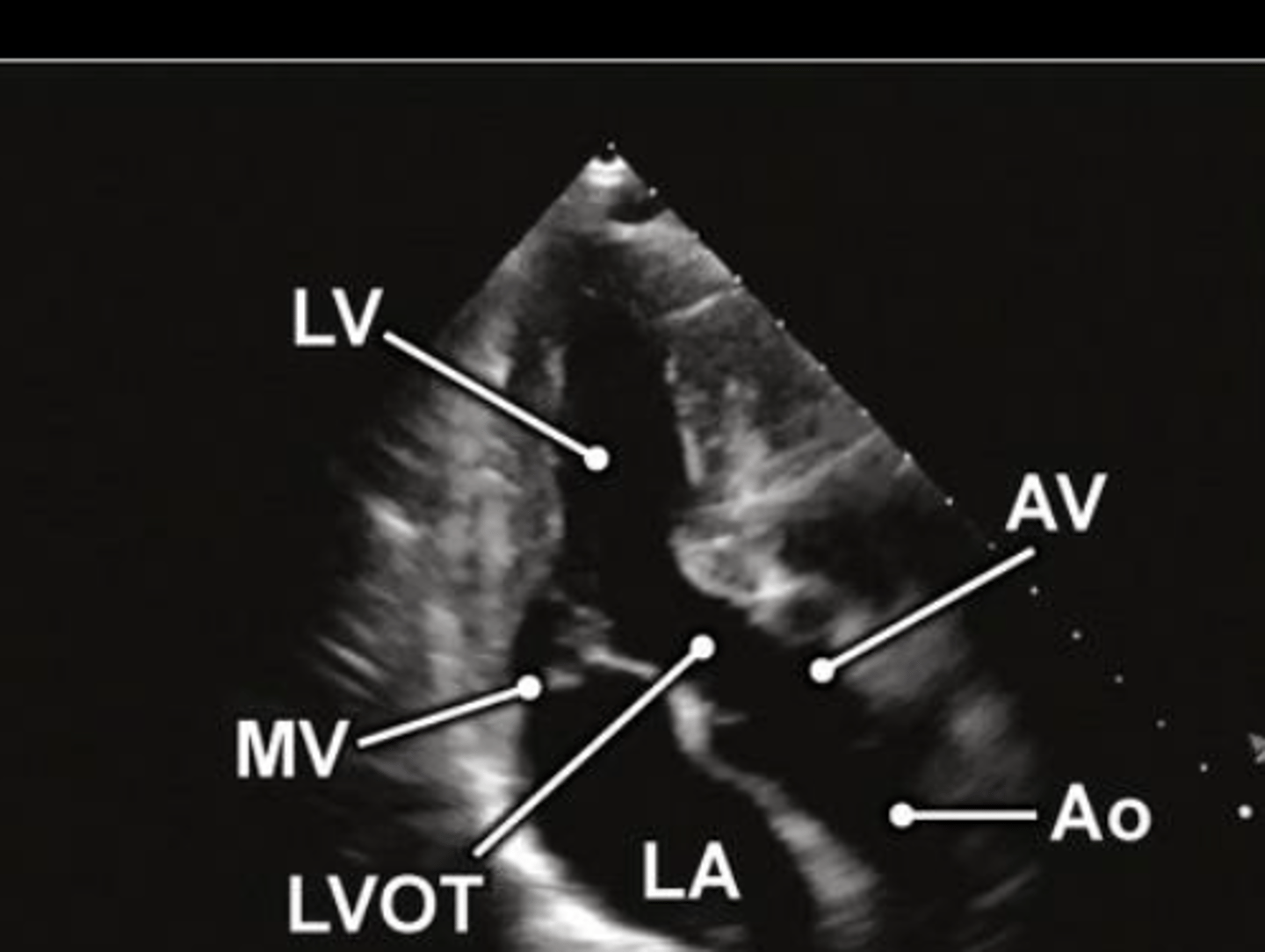
A3 is used to visualize ___ and ____
MV and AoV
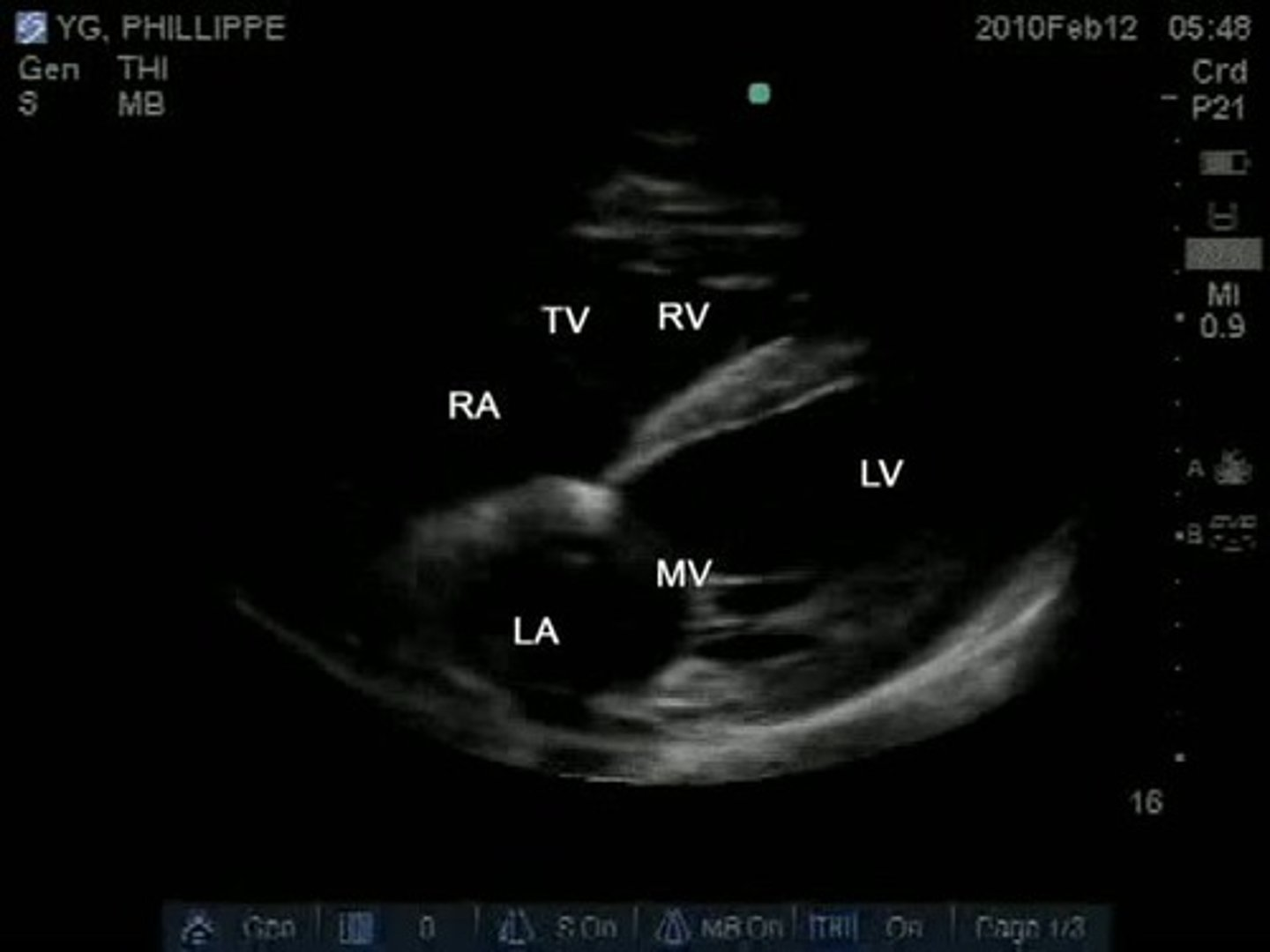
subcostal 4 is used to visualize _______, ___, ___, ____, and ___
four chambers, TV, MV, IVS, IAS
all chambers and vessels appear _______
anechoic