CH. 28 - Pregnancy and Childbirth
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Gestation
Pregnancy
Lasts an average of 266 days from conception to childbirth
Gestational calendar is measured from first day of the woman’s last menstrual period (LMP)
Birth is predicted 280 days (40 weeks) from the first day of the last menstrual period
The bigger the baby, the longer the gestation time
Term
The duration of pregnancy
Trimesters
three 3-month intervals in the term
Conceptus
all the products of conception
the embryo or fetus, the placenta, and associated membranes
Blastocyst
The developing individual is a hollow ball for the first 2 weeks
blastocyst is the individual before implanting into the endometrium
Embryo
From day 16 through week 8
blastocyst becomes and embryo once it implants into the endometrium
Fetus
from beginning of week 9 to birth
Fetus us attached to a disc-shaped placenta by the umbilical cord
placenta provides nutrition and waste disposal, secretes hormones that regulate pregnancy, mammary development, and fetal development
before placenta is formed and the baby is a fetus, the baby gets nutrients from uterine glands
Neonate
newborn to 6 weeks
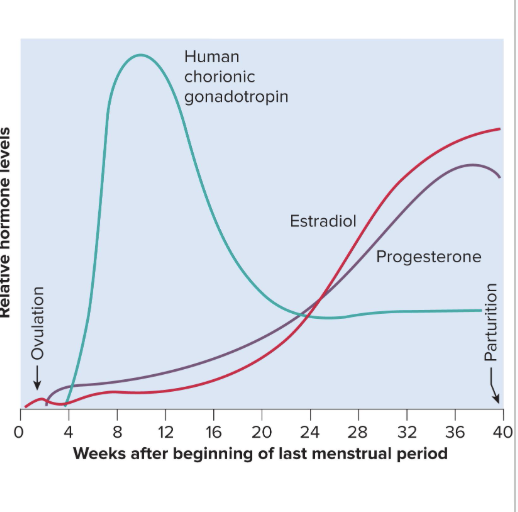
Hormones with strongest influence on pregnancy:
Estrogens
Progesterone
Human chorionic gonadotropin
Human chorionic somatomammotropin
Where are these hormones secreted from during pregancy?
All are primarily secreted by the placenta
Corpus luteum is important source for first several weeks
If corpus luteum ia removed before 7 weeks, pregnancy terminates
From week 7 to week 17, the corpus luteum degenerates and the placenta takes over
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG)
Secreted by the blastocyst and placenta
Detectable in urine 8 to 9 days after conception by home pregnancy test kits
Stimulates growth of corpus luteum and keeps it around longer than normal
HCG comes from the chorion of the embryo, travels to gonads, and causes them to release more progesterone and estrogen
Estrogens
estrogen skyrockets during pregnancy
Increases to 30 times the normal amount by the end of pregnancy
Corpus luteum is the source for first 12 weeks until placenta takes over
Helps maintain endometrium
Causes tissue growth in fetus and mother
Mother’s uterus and external genitalia enlarge
Mammary ducts grow, breast tissue nearly doubles in size
higher estrogen increases relaxin, which relaxes pubic symphysis and widens pelvis
Higher estrogen, higher libido
Progesterone
Secreted by placenta and corpus luteum
Suppresses FSH and LH, preventing follicular development during pregnancy so we aren’t growing multiple babies at different stages
Suppresses uterine contractions
This prevents premature childbirth and menstruation
Causes endometrium to get thicker
is important bc the endometrium is eaten by the blastocyst for nutrients in the beginning stages of pregnancy before placenta is formed
Stimulates development of alveoli in mammary glands
progesterone starts to drop at very end of third trimester, allowing for labor and delivery
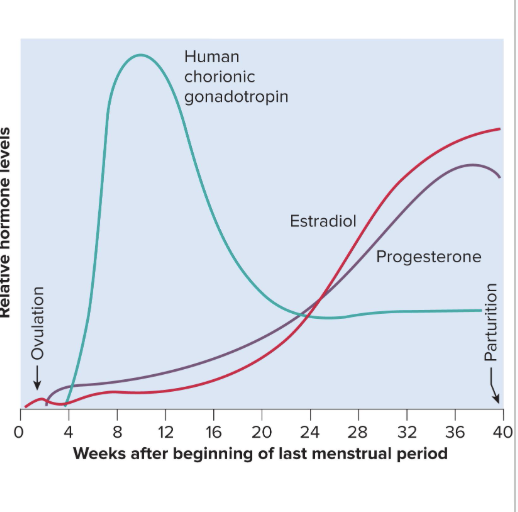
Human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (HCS)
Comes from the chorion and causes another gland to make secretions
is basically a low level human growth hormone
Placenta begins its secretion of HCS at about week 5
Amount secreted increases steadily until term
There is a high concentration of HCS but the function is poorly understood
causes babies tissues to differentiate
also cause mothers tissues to differentiate
also makes mother less sensitive to insulin bc they need more glucose in blood for baby
sometimes theres too much HCS, causing pregnancy induced diabetes
will go away when HCS level goes down (usually when giving birth)
What happens the pituitary gland during pregnancy?
Woman’s pituitary gland grows about 50% larger during pregnancy
Produces elevated levels of thyrotropin, prolactin, and ACTH
these stimulate thyroid, lactate production, and salt retention
What happens to the thyroid gland during pregnancy?
Thyroid gland becomes 50% larger due to HCG, thyrotropin, and human chorionic thyrotropin from placenta
Increases metabolic rate of mother and fetus
This elevation is going to cause mother to feel like she is overheating
What happens to the parathyroid glands during pregnancy?
Parathyroid glands enlarge and increase osteoclast activity
causes there to be more parathyroid hormone, leading osteoclasts to be unregulated
this causes more calcium and phosphate to be put into blood stream
ACTH
Causes there to be a lot of salt retention
Stimulates glucocorticoid secretion
This breaks down and mobilizes amino acids for fetal protein synthesis
Aldosterone
Aldosterone secretion rises
promotes fluid retention and increases mother’s blood volume
Relaxin
Relaxin is secreted by corpus luteum and placenta
It helps progesterone in stimulating multiplication of uterine lining cells
Promotes growth of blood vessels in the pregnant uterus
Loosens connective tissues
How much does the uterus weigh pregnant vs. not pregnant? How far does the uterus expand during pregnancy?
Uterus weighs about 900 g at the end of pregnancy
Weighs only 50 g when not pregnant
Uterus expands up to the diaphragm when pregnant, almost reaching the xiphoid process
Linea Nigra
some mothers will experience an up regulation of melanocytes, causing more pigment right through the midsagittal plane of abdomen
Position of the baby in utero and during birth:
during pregnancy, the baby is typically sitting head right side up
In the 7th month of gestation, the fetus normally turns into the head-down vertex position
Most babies are born head first
Head acting as a wedge that widens the mother’s cervix, vagina, and vulva during birth
breach - when baby tries to be born in a non head first way
Role of baby during birth:
Fetus is a passive player in its own birth
Expulsion achieved by contractions of mother’s uterine and abdominal muscles
Fetus may play a role chemically by releasing stress hormones to help enhance uterine contractions
Fetus sends chemical messages that signify when it is developed enough to be born
Braxton Hicks Contractions
Relatively weak contractions of the uterus over the course of gestation
Strengthen late in pregnancy
often causes false labor
During third trimester, there is still elevated progesterone, so it will down-regulate the uterine contractions so there isn't early delivery
Contractions transform suddenly into more powerful labor contractions, leading to active labor
Parturition
The process of giving birth
Marked by the onset of true labor contractions
Uterine Contractility
Contractility increases closer and closer to birth of child
As the uterus gets bigger and stretched, there will be more spontaneous contractions
they help to strengthen the smooth muscle of uterus
Progesterone and estradiol balance may be one factor in this pattern o
Progesterone inhibits uterine contractions, but its secretion levels off or declines after 6 months
Estradiol stimulates uterine contractions, and continues to rise through pregnancy
Oxytocin (OT)
As pregnancy nears full term, the posterior pituitary releases more oxytocin (OT), and the uterus produces more OT receptors
Oxytocin promotes labor in two ways
stimulates contraction of smooth muscle, affecting myometrium of uterus
Stimulates fetal membranes to produce prostaglandins, which help oxytocin in producing labor contractions
prostaglandins dilate the cervix
How does the conceptus help promote its own birth?
Conceptus (placenta and fetus) may produce chemical stimuli to promote its own birth
Fetal cortisol rises and may increase estrogen secretion by the placenta
Fetal pituitary produces oxytocin, which stimulates fetal membranes to produce prostaglandin and start uterine contractions
How does uterine stretching help initiate labor?
Stretching of smooth muscle increases contractility of smooth muscle
as the uterus stretches and contracts, more oxytocin is released, causing more contractions, causing more oxytocin
positive feedback loop
Labor Contractions (timing, where they are, where they are strongest/weakest, etc)
Labor contractions begin about 30 minutes apart and eventually occur every 1 to 3 minutes
Periodically relax to increase blood flow and oxygen delivery to placenta and fetus
Contractions are strongest in fundus and body of uterus
Contractions are weakest in the cervix
Contractions push the fetus downward
Woman feels need to “bear down”
Contraction of abdominal muscles aids in expelling the fetus (valsalva maneuver)
Positive Feedback Theory of Labor
Labor is induced by stretching of cervix from baby’s head
This triggers a reflex contraction of the uterine body
the contraction pushes the fetus downward
This stretches the cervix even more
Creates a self-amplifying cycle of stretch and contraction
What does cervical stretching cause?
Cervical stretching induces a neuroendocrine reflex that causes the posterior pituitary to release oxytocin
oxytocin is carried by the blood and stimulates uterine muscles to contract
Directly and through the action of prostaglandin
Cervical stretching → oxytocin secretion → uterine contraction → cervical stretching
What is given for induced labor?
Pitocin
artificial oxytocin
What causes the pain during labor contractions?
At first, pain of labor is mainly due to ischemia (cut off blood supply) of the myometrium
Muscles hurt when they are deprived of blood, and contractions restrict circulation
As fetus enters vagina, pain becomes stronger due to the stretching of the cervix, vagina, and perineum
sometimes with tearing
Pain is a product of two factors
Unusually large brain and head of the human infant
Narrow pelvic outlet
Episiotomy
an incision in the vulva to widen the vaginal orifice to prevent random tearing
not always done
3 Stages of Labor
Dilation
Expulsion
Placental stage
Primipara
Woman giving birth for the first time
stages of labor tend to be longer
Multipara
Woman who has previously given birth
stages of labor tend to be shorter
Grandmultipara
Woman who has previously given birth five times or more
Dilation Stage
the longest stage
lasting 8 to 24 hours
Cervical canal dilates to 10 cm
effacement (thinning) of cervix occurs
Fetal membranes rupture and amniotic fluid is lost
“water breaking”
Late dilation
dilation reaches 10 cm in 24 hours or less in primipara and in as little as a few minutes in multipara
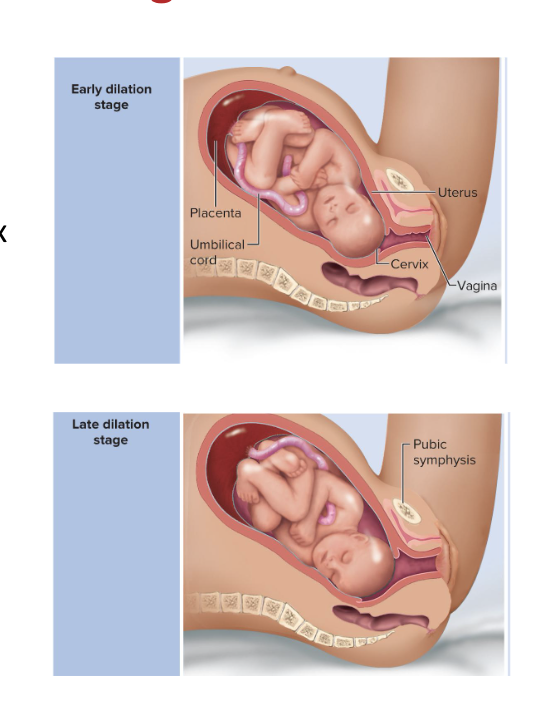
How to measure dilation:
each finger that fits into cervix is 1 cm
feel for lip of cervix to feel for 10 cm
cervix lip will be a little nub at the edge of uterus when fully dilated
Expulsion Stage
begins with the entry of the head into vagina and lasts until the baby is expelled
30-60 minutes in primipara; shorter in multipara
Crowning occurs — when baby’s head is visible
Delivery of the head is the most difficult part
After expulsion, doctor drains blood from umbilical vein into baby
Umbilical cord is clamped and cut
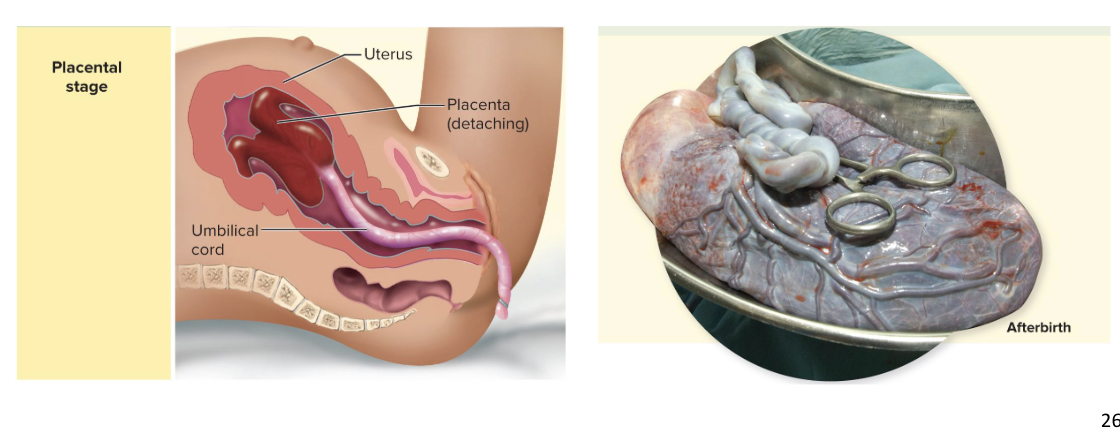
Placental Stage
uterine contractions cause placental separation and “delivery”
Membranes (called the afterbirth) are inspected to make sure everything has been expelled
Puerperium
The first 6 weeks postpartum (after birth)
Period where mother’s anatomy and physiology stabilize and reproductive organs return nearly to pregravid state (pre-pregnancy state)
Involution occurs
Involution
shrinkage of the uterus in the first 6 weeks postpartum
Loses 50% of its weight in the first week
Involution is achieved by autolysis (self-digestion) of uterine cells by their own enzymes
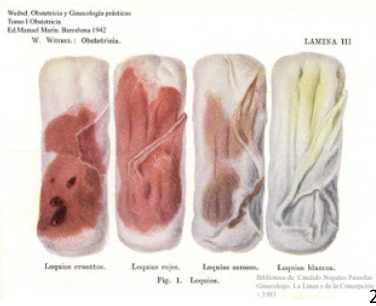
For about 10 days, the mother produces a vaginal discharge, called lochia
is bloody at first and then turns serous (clear)
What promotes involution of the uterus?
Breast-feeding promotes involution
Suppresses estrogen secretion which normally makes the uterus more flaccid
Stimulates oxytocin secretion which causes the myometrium to contract and firm up the uterus sooner
Lactation
the synthesis and ejection of milk from the mammary glands
Lasts as little as 1 week in women who do not breast-feed their infants
Can continue for many years as long as the breast is stimulated by a nursing infant or a mechanical device
Women traditionally nursed their infants until a median age of about 2.8 years, now its about 6 months
Development of the Mammary Glands
When not pregnant, mammary glands are small and not developed
High estrogen levels in pregnancy causes ducts of mammary glands to grow and branch
Growth hormone, insulin, glucocorticoids, and prolactin contribute to this development
Progesterone stimulates the budding and development of acini at the end of the ducts
Acini are organized into lobules within each breast lobe
one acini per lobe
each have their own duct that leads to the nipple
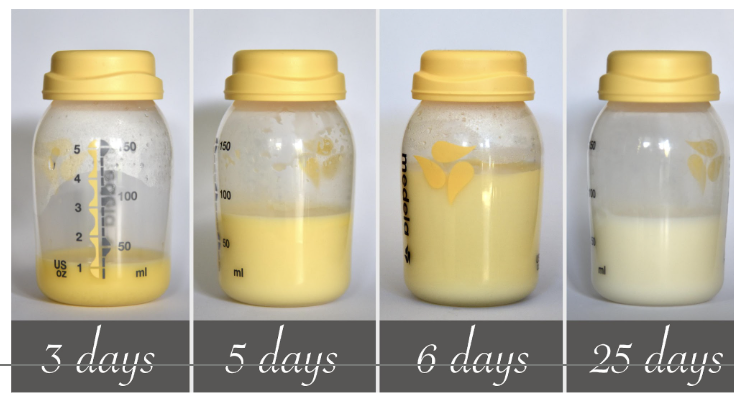
Colostrum
Similar to breast milk in protein and lactose, but contains a lot more fat
forms in late pregnancy
is the sole nutrition source for first 1 to 3 days after birth
Thick consistency and a cloudy yellow color
Contains IgA to protect baby from gastroenteritis
converting to colostrum to regular breast milk is a gradual process
the more the child consumes, the more the mother produces
as more breast milk is produced, it becomes more diluted

Prolactin
Promotes milk synthesis
from anterior pituitary
Inhibited by dopamine when not pregnant
Synthesis of prolactin begins 5 weeks into pregnancy, by full term it is 10 to 20 times the normal level
Has little effect on mammary glands until after birth since steroids from placenta down regulate mammary glands
Milk synthesis also requires growth hormone, cortisol, insulin, and parathyroid hormone to mobilize necessary amino acids, fatty acids, glucose, and calcium
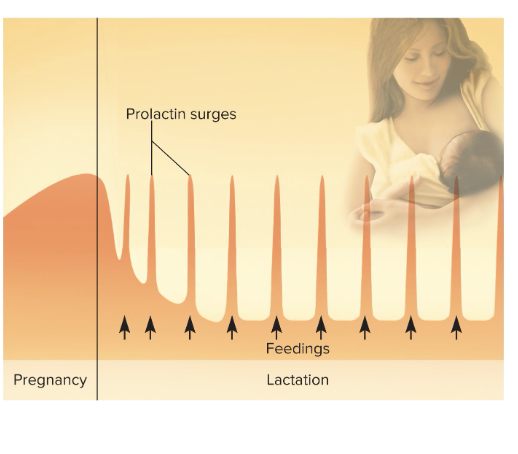
Prolactin after birth:
At birth, prolactin secretion drops to nonpregnancy levels
Every time infant nurses, prolactin levels spike
This stimulates synthesis of milk for the next feeding
more stimulation, the more spikes in prolactin, up-regulating milk synthesize
Without nursing, milk production stops in 1 week
Only 5% to 10% women become pregnant while breast-feeding
bc breastfeeding down regulates ovarian cycle and GnRH production
makes breast feeding a natural means of spacing births
Milk Ejection
Need manual stimulation of areola to eject milk
oxytocin gets released and causes smooth muscle contractions to help squeeze milk into duct
Milk ejection is controlled by a neuroendocrine reflex
Milk flows within 30 to 60 seconds after suckling begins
Breast Milk
Supplies antibodies and colonizes intestine with beneficial bacteria
Nursing woman can produce 1.5 L of milk per day
Breast milk changes composition
Changes over the first 2 weeks
Varies from one time of day to another
Varies over 20 minute feeding
At the end of a feeding there is less lactose and protein, but six times the fat
Meconium
green, bile-filled fecal material in newborn
Colostrum and milk have a laxative effect that clears intestine of meconium
this is why babies tend to have to defecate when breastfeeding
Why is cows milk not a good substitute for breast milk?
Has 1/3 less lactose but 3x as much protein
Harder to digest and more nitrogenous waste (causing diaper rash)
Contraception
any procedure or device intended to prevent pregnancy
Behavioral Methods of Contraception
Abstinence
Rhythm method (periodic abstinence)
timing intercourse to avoid intercourse during ovulation
Withdrawal (coitus interruptus)
Barrier and Spermicidal Methods of Contraception
Male and female condom
diaphragm / sponge
putting something in vaginal canal to block the external os
Spermicides: foams, creams, jellies
Hormonal Methods
Most hormonal methods prevent ovulation
“The pill”
“Morning after pills”
RU-486
The Pill
an estrogen and progestin (form of progesterone) patch, injection, or vaginal ring
Ovarian follicles do not mature bc FSH, LH are inhibited by the estrogen and progesterone
Morning After Pills
emergency contraceptive pills
These pills have a high dose of estrogen and progestin, or progestin alone
Inhibit ovulation, movement of sperm and egg, and implantation
Induce menstruation if implantation has not occurred
RU-486
AKA “abortion pill”
progesterone antagonist
goal is to remove embryo from uterus
Induces chemical abortion up to 2 months into pregnancy.
Two doses over two days
Can be reversed with high dose of progesterone after first dose of RU-486.
If second dose of RU-486 has been administered, reversal is not possible
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
Device that is left in place in the uterus for an extended period of time
Irritates uterine lining and interferes with implantation
Surgical Sterilization
Clamping or cutting the genital ducts (uterine tubes or ductus deferens)