Week 3: scientific method and descriptive stats
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
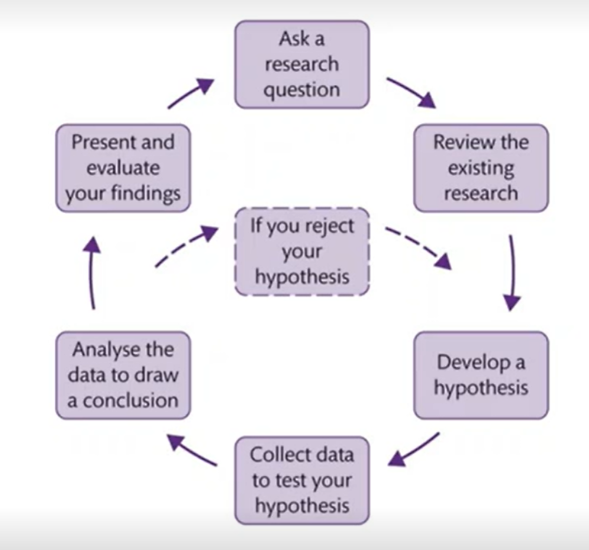
The scientific method
Descriptive statistics
Summarises the mid-point and spread of data
Inferential statistics
Identify significant differences/relationships in data
Measures of central tendency
Mode, median, mean
What kind of data should the mode be used for
nominal
What kind of data should the median be used for
ordinal
What kind of data should the mean be used for
interval and ratio
Measures of dispersion
Range, Interquartile range, Standard deviation, Variance
Experimental variance/ between groups variance
The difference between two groups (comes from manipulating variables)
Random variance/within groups variance
Spread of data within the group (random as we don’t know why participants have different scores)
What is a type 1 error
Don’t accept a null hypothesis so accept the alternative, but there is no existing effect at the population level (false positive)
What is a type 2 error
Accept null hypothesis when there actually is a significant difference at the population level
The probability of a type 1 error having occurred
What does statistical significance actually tell us
.05 (5%)
What is the alpha level typically used in psych research
No
If the observed p value is greater than the alpha value is the result significant?
Bimodal (2 modes) or multimodal (more than 2 modes)
What is it called when a data set has multiple peaks
Within group variance
The difference in scores across participants doing the same condition
The difference in scores between conditions
Between group variance
If there is a lot of between group variance and less within group, a result is more likely to be significant. The result may be caused by high within group variance there is no significant difference between conditions as it can be explained by random variance
How are significant results related to between group and within group variance