Plants and Humans- Exam 2
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Photosynthesis
How plants use sunlight to make their own food.
Carbon dioxide + water
Reactants in the photosynthesis process.
Glucose + oxygen
Products of the photosynthesis process.
Chlorophyll A
The main pigment for photosynthesis that uses light energy, carbon dioxide, and water to create glucose and oxygen.
Chlorophyll B
Primarily absorbs blue and red-orange light.
Carotenoids
Absorb blue and green light.
Chloroplasts
Double membraned organelles where photosynthesis occurs.
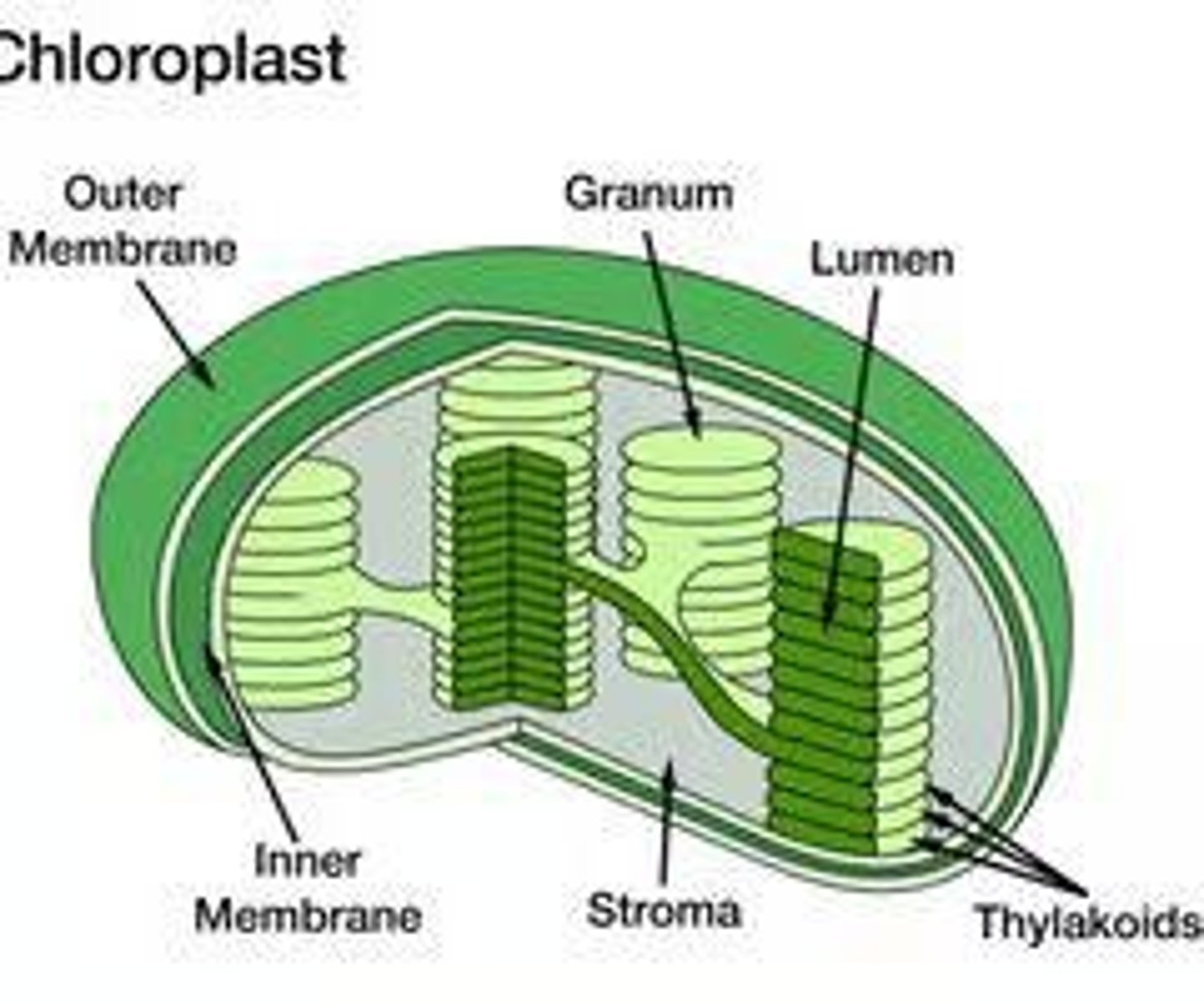
Granum
Stack of thylakoids found in chloroplasts.
Thylakoids
Quarter shaped disks found in chloroplasts.
Stroma
Fluid found inside the chloroplast.
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O --> light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2.
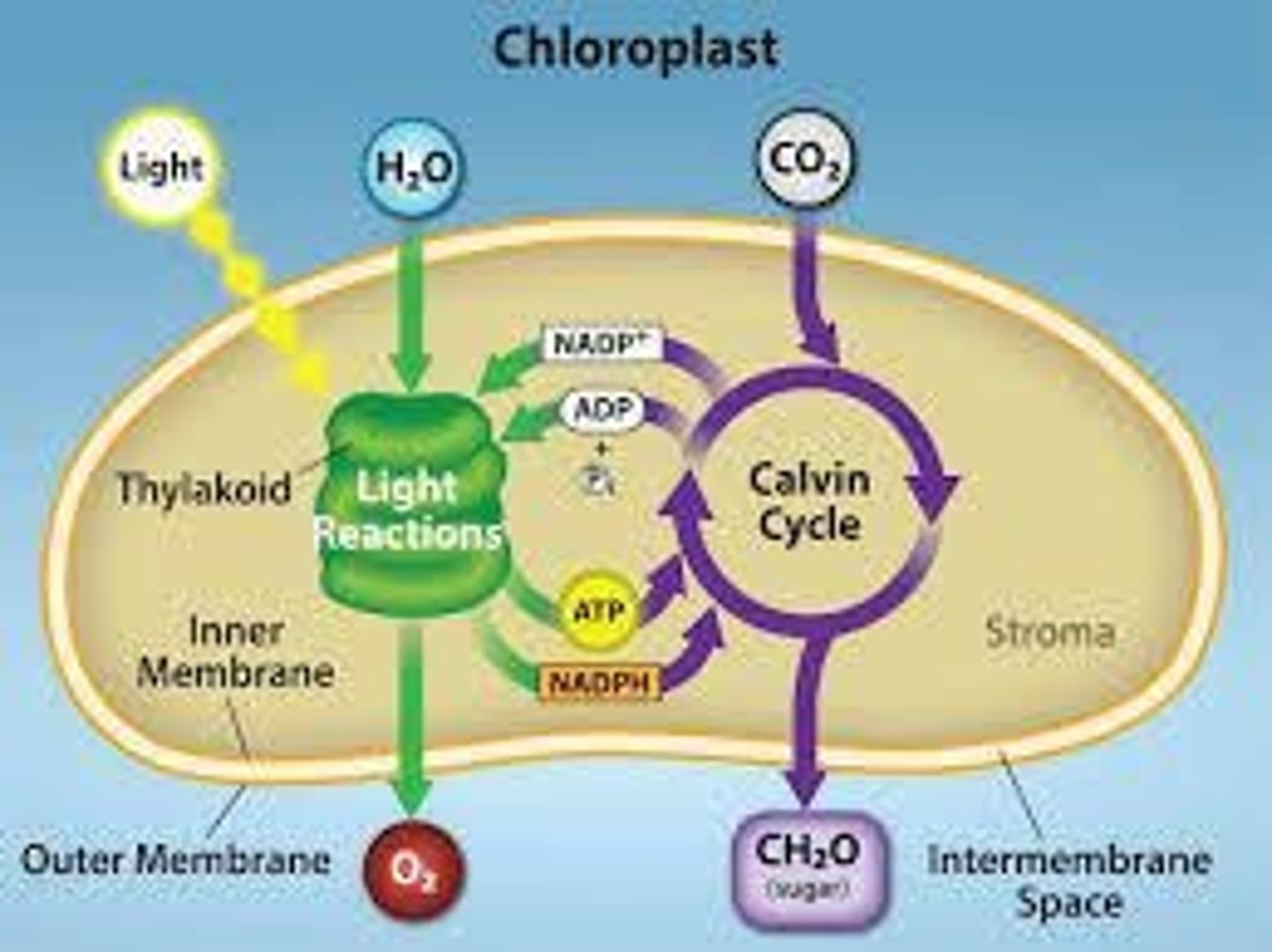
Light Dependent Reaction
Converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH, using water and releasing oxygen as a byproduct.
Calvin Cycle/Light Independent Reaction
A series of chemical reactions that convert carbon dioxide and hydrogen-carrier compounds into glucose, using energy from ATP and NADPH produced during the light-dependent reactions.
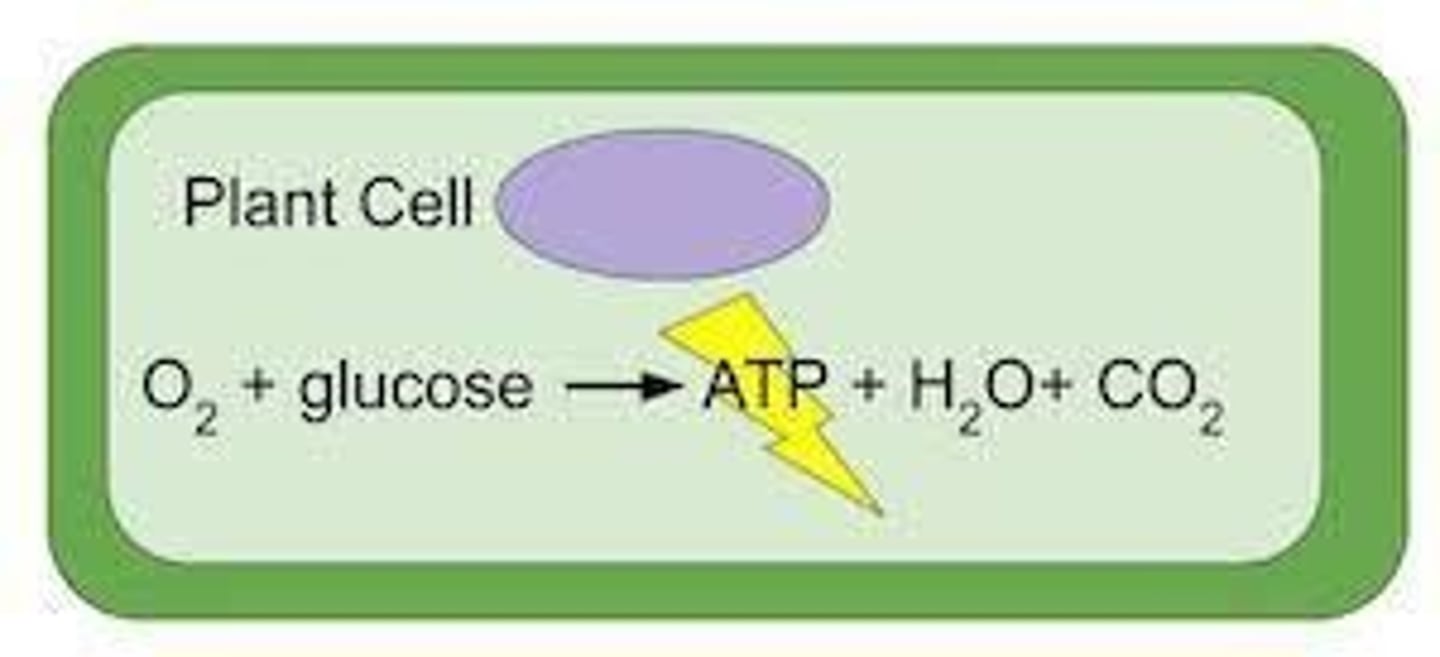
Cellular Respiration
The process that releases energy by breaking down food molecules in the presence of oxygen to create ATP.
Ethylene
Responsible for fruit ripening.
Auxin
Responsible for cell elongation and apical dominance.
Abscisic acid
Protects plants from drought stress/stress responses.
Gibberellin
Regulates seed germination and enzymes in a plant are produced after the embryo secretes this hormone.
Cytokinin
Responsible for activating cell division.
Seed Germination
The process by which a seed develops into a new plant, starting with water uptake (imbibition) and activating metabolic enzymes, leading to root and shoot growth.
Morphogenic response
Change in development or quality in plant.
All-or-None response
Responds completely or not at all to a stimulus.
Tropic Response
Directional plant growth movements in response to environmental stimuli like light, gravity, or touch.
Dosage-Dependent Response
The response depends on the dose.
Phototropism
Growth in response to light.
Gravitropism (Geotropism)
Growth in response to gravity.
Etiolation
Differences in development when seedlings are grown in the dark.
Nastic Response
Plant responses to environmental stimuli where the direction of the movement is not determined by the direction of the stimulus.
Statoliths
Starch grains inside the statocyte
Statocytes
Groups of sensory cells that help determine the direction of gravity
Climacteric fruits
Fruits that ripen AFTER they have been harvested (bananas, tomatoes, apples)
Non-climacteric fruits
Fruits that are best ripened fully BEFORE being harvested
Sexual Reproduction
Genetically diverse reproduction; flowering plants reproduce sexually through a process called pollination
Asexual/Vegetative Propagation
NOT genetically diverse; parent plant sends out a runner along the ground which helps form new plants
Mitosis
Occurs in asexual reproduction (creating clones of DNA)
Interphase
The first stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows and copies its DNA
Cell Nuclear Division
The division of DNA in the nucleus
Cytokinesis
Division of the cytoplasm
Diploids
Cells with two complete sets of chromosomes
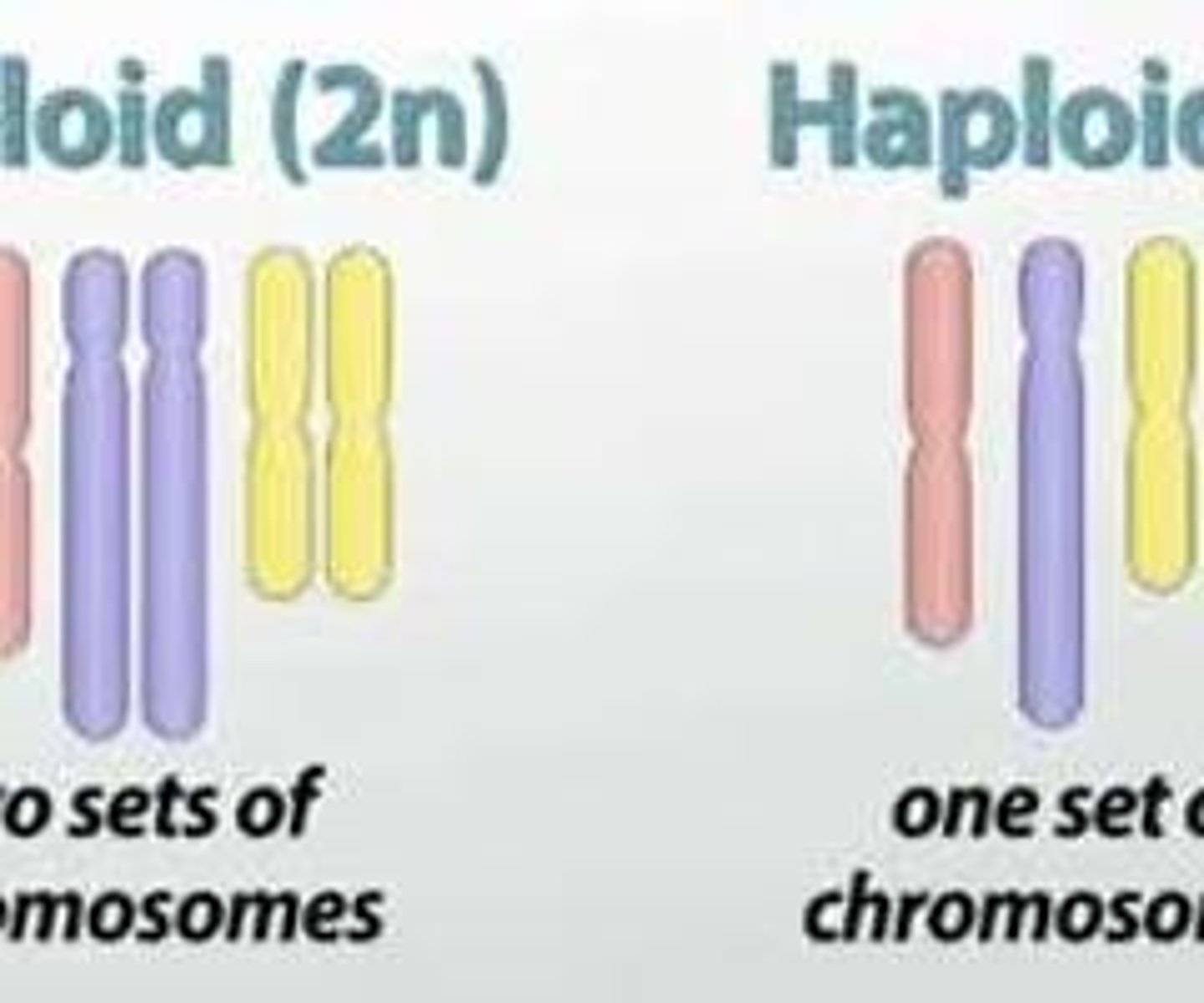
Haploid
Cells with one set of chromosomes
Sister chromatid
One half of a duplicated chromosome
Chromatin
Made up of DNA and proteins
Meiosis
A process that occurs in reproductive cells and is associated with sexual reproduction
Alternation of generations
Alternating life cycles of haploid (N) and diploid (2N)
Gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing generation
Sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing generation
Double fertilization
A process leading to seed formation in Angiosperms, where one haploid sperm unites with a haploid egg to form a diploid zygote, and a second sperm unites with the two haploid central cell nuclei to produce triploid endosperm.
Prophase I
Homologous chromosomes pair up with each other; crossing over occurs
Metaphase I
Homologous chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes are separated
Telophase I
Amount of DNA is halved
Prophase II
Nuclear envelope breaks down; spindles form; DNA forms visible x-shaped structures
Anaphase II
The DNA is separated
Telophase II
Chromosomes arrive at opposite poles; nuclei form, and the chromosome begins decondensing
Cytokinesis after Meiosis II
Ends up with 4 daughter cells with half the DNA we started with
Population
Individuals of the same species living in the same place at the same time
Population Genetics
the study of the frequency of alleles in a population
Gene pool
ALL of the alleles for an individual in the population. Factors that can change the gene pool include gene drift, artificial selection, natural selection
Gene drift
Random change in alleles, purely a random event, more likely in small populations
Artificial selection
selective breeding of plants and animals to promote the occurrence of desirable traits in offspring
Natural Selection
survival of the fittest
Variation
all members of the population CANNOT have the same alleles
Overproduction
more offspring is produced that can actually survive
Competition principle
limited resources in the environment
Survival to Reproduce
individuals are better adapted to the environment are more likely to reproduce and pass on that trait
Species
A group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
Speciation
The process of a new species development
Allopatric Speciation
Involves geographic separation. A mode of speciation where a population becomes geographically isolated, leading to the formation of new species due to the lack of gene flow between the separated groups
Sympatric Speciation
Involves the species remaining in the same place. The evolution of a new species from a surviving ancestral species, where both continue to inhabit the same geographic region without any physical barriers to gene flow.
Divergent Evolution
when two or more species sharing a common ancestor become more different over time. Ex: elephants and mammoths
Convergent Evolution
the independent evolution of similar features in different lineages. Ex: sharks and dolphins
Adaptive Radiation
evolution from a common ancestor of many species adapted to diverse environments. Ex: Darwin's finches
Taxonomy
the science of naming and classifying organisms
Order of taxonomy
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
Domain
3; bacteria, archaea and eukarya
Kingdom
6, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia
Phylogenetic tree
A branching diagram that represents evolutionary relationships
Cladogram
Diagram that shows the development of characteristics
Cytokinesis
Splitting of the diploid gamete into two haploid daughter cells
Mitosis vs. meiosis
Mitosis is involved in growth and development of vegetative parts, producing two identical diploid cells, while meiosis is crucial for sexual reproduction, producing four haploid gametes with half the genetic material
Result of mitosis
Two genetically identical diploid cells
Result of meiosis
Four genetically unique haploid cells