Topic 2 Molecular Biology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
• 2.1 Molecules and Metabolism • 2.2 Water • 2.3 Carbohydrates and Lipids • 2.4 Proteins • 2.5 Enzymes • 2.8 Cell Respiration • 2.9 Photosynthesis
Last updated 7:06 AM on 8/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
metabolism- anabolism
synthesising energy + small molecules → large molecules
hydrolysis and condensation reactions
hydrolysis and condensation reactions
2
New cards
metabolism- catabolism
breaking large molecules → energy + small molecules
produces energy
produces energy
3
New cards
carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO)
made of saccharides in the form of glucose
made of saccharides in the form of glucose
4
New cards
lipids/fatty acids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen (CHO)
insoluble in water, made of triglycerides (image; bonded with ester bonds; produced with condensation reaction)
saturation: saturated = all hydrogens, monounsaturated = missing one hydrogen, polyunsaturated = more than one hydrogen missing (trans is missing on different side)
insoluble in water, made of triglycerides (image; bonded with ester bonds; produced with condensation reaction)
saturation: saturated = all hydrogens, monounsaturated = missing one hydrogen, polyunsaturated = more than one hydrogen missing (trans is missing on different side)
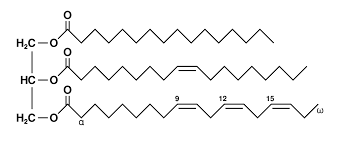
5
New cards
proteins
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur? (CHONS)
made up of 20 different amino acids (amine, carboxyl, R chain)
amino acids bonded together by ribosomes to form polypeptides (which are sequenced off DNA)
fibrous proteins are long like robes, structural eg spider silk; globular proteins are blobs, hormonal eg insulin
heat helps them activate unless there is too much in which case they denature.
made up of 20 different amino acids (amine, carboxyl, R chain)
amino acids bonded together by ribosomes to form polypeptides (which are sequenced off DNA)
fibrous proteins are long like robes, structural eg spider silk; globular proteins are blobs, hormonal eg insulin
heat helps them activate unless there is too much in which case they denature.
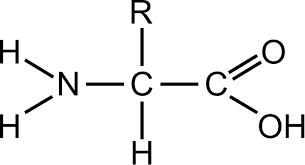
6
New cards
nucleic acids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus (CHONP)
7
New cards
alpha d glucose
in carbs
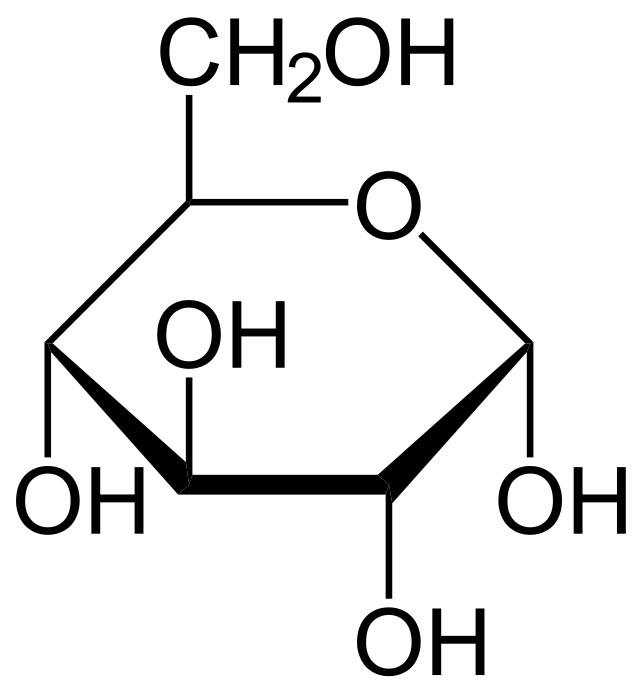
8
New cards
beta d glucose
every second one is flipped to create sheets
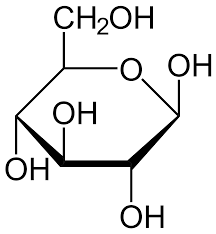
9
New cards
ribose
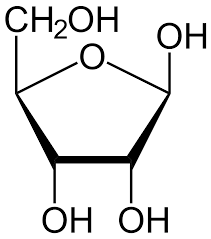
10
New cards
saturated fatty acid
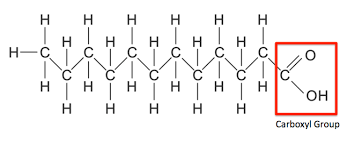
11
New cards
saccharides
sugar units in carbohydrates. saccharide > disaccharide > polysaccharide. polysaccharides are made of alpha d glucose and are in chains in carbs.
12
New cards
disaccharides
condensation to form, hydrolysis to break
13
New cards
starch
stores glucose in plants, made of either unbranched amylose or branched amylopectin (branches based off on which carbon the glycosidic links are)
14
New cards
properties of water
adhesion, cohesion, polar, solvent, high specific heat capacity, latent heat of vaporisation
substances can either be hydrophilic or hydrophobic
substances can either be hydrophilic or hydrophobic
15
New cards
hydrogen bonds
between two different hydrogens. each bond itself is weak, but there are so many bonds that together they are strong.
16
New cards
anaerobic cell respiration
in animals: glucose → lactic acid/lactate + ATP (minimal)
oxygen debt- must bring more oxygen into the body to break down the lactate
in yeast/plants: glucose → carbon dioxide + ethanol
similar to fermenting alcohol
oxygen debt- must bring more oxygen into the body to break down the lactate
in yeast/plants: glucose → carbon dioxide + ethanol
similar to fermenting alcohol
17
New cards
aerobic cell respiration
glucose + oxygen → water + carbon dioxide + ATP (lots)
longer than anaerobic but gives more yield
longer than anaerobic but gives more yield
18
New cards
ATP
adenosine triphosphate; respiration happens to produce this. the energy currency of the cell.
19
New cards
photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
opposite of respiration. the water comes from transpiration through roots, oxygen comes from atmosphere diffusion.
endergonic reaction = relies energy input in form of light
limiting factors: temperature, light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration
opposite of respiration. the water comes from transpiration through roots, oxygen comes from atmosphere diffusion.
endergonic reaction = relies energy input in form of light
limiting factors: temperature, light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration
20
New cards
absorbance/action spectra
measure wavelength of light in relation to plant productivity
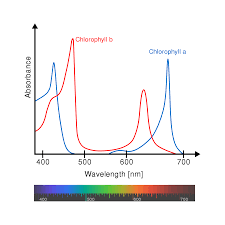
21
New cards
chlorophyll
green pigment in plants that helps to absorb light as green is in the middle of the colour spectrum and reflects back the least of the colours.
22
New cards
carotenoids
help to fill in the absorption blanks where the cholorophyll can’t (cause its green)