Handout 2: General addition & multiplication rule, [B|A]
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
When do we use the general addition rule?
If events A and B are disjoint, we use simple addition
If events A and B are not disjoint, we use the general addition rule to not double count!
What is the general addition rule?
P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A and B)
What is conditional probability?
This presumes that an event has occurred
ex. if you have lung cancer, assume you were a smoker
How do you find the probability of event B given event A?
P[B|A] = P[A and B] / P[A]
always divide by the probability of the event given! (B, GIVEN A)
ex. finding the probability of being in 1st class and surviving (not disjoint)
![<p>P[B|A] = P[A and B] / P[A]</p><ul><li><p>always divide by the probability of the event given! (B, GIVEN A)</p></li><li><p>ex. finding the probability of being in 1st class and surviving (not disjoint)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/844effd6-7792-4e0e-8abb-37c0b9abaa0a.png)
When would you use the general multiplication rule?
When events A and B are independent, we can use the multiplication rule
BUT the general multiplication rule is used when events A and B are dependent
What is the general multiplication rule?
P[A and B] = P[A] x P[B | A]
P[B and A] = P[B] x P[A | B]
![<p>P[A and B] = P[A] x P[B | A]</p><p>P[B and A] = P[B] x P[A | B]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/339fb8b2-f6c7-4150-9952-b390b6b93b5a.png)
What is interdependence?
If events A does not help you find the probability of B, they are independent
Disjoint events are dependent (knowing something about 1 reveals info about the other)
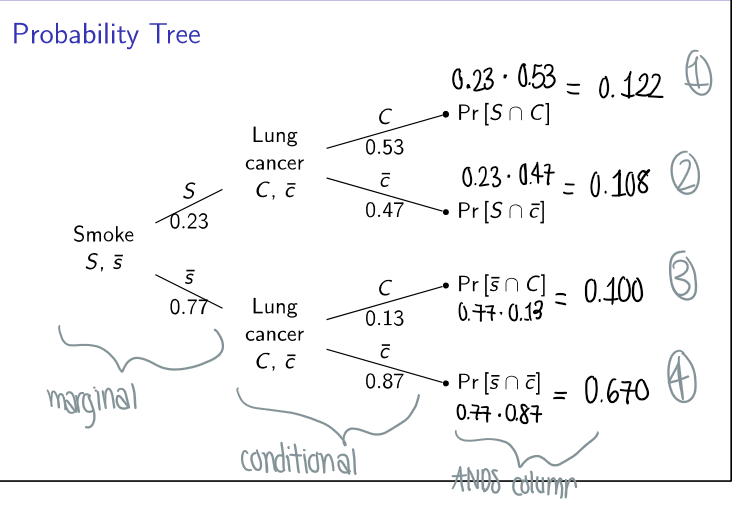
What is a possibility tree?
A different representation of a contingency table