Resistors in Series or in Parallel - (Physics 3)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
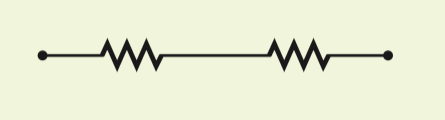
Series
Describes two or more components of a circuit that provide a single path for current
When many resistors are connected in series,
The current in each resistor is the same
Equivalent resistance
Total resistance of the circuit
Usage of equivalent resistance
To find the current
Resistors in series equation
R_eq = R1 + R2 + R3…
R_eq
The sum of the individual resistances that have been connected in series
The equivalent resistance of a series combination of resistors…
Is always greater than any individual resistance
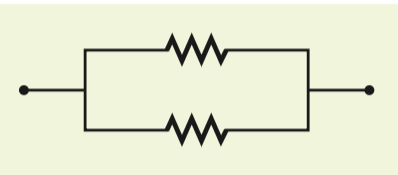
Parallel
Describes two or more components of a circuit that provide separate conducting paths for currents
(because the components are connected across common points or junctions)
Resistors in parallel equation
1/R_eq = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 …
The equivalent resistance for a parallel arrangement of resistors must always be…
Less than the smallest resistance in the group of resistors
Schematic diagram series
Schematic diagram parallel
Current series
I = i1 = i2 = i3… (same for each resistor)
Current parallel
I = i1 + i2 + i3… (sum of currents)
Potential difference series
△V = △V1 + △V2 + △V3… (sum of potential differences)
Potential difference parallel
△V = △V1 = △V2 = △V3 (same for each resistor)
Equivalent resistance series
R_eq = R1 + R2 + R3… (sum of individual resistances)
Equivalent resistance parallel
1/R_eq = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 (reciprocal sum of resistances)