Fusion and Correspondence
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
pyramid of binocular vision
The ______ is an artificial concept based on three independent, but not exclusive, components – sensory, integrative, and motor. Is a good guideline for approaching binocular vision issues.
sensory
portion of the pyramid of binocular vision that includes the anatomic, physiologic, and psychologic activities involved in the collection and transmission of visual information to the cortex. Serves as the foundation of binocular vision.
integrative
portion of the pyramid of binocular vision that includes activities involved in the fusion of the two cortical images to form a single binocular percept of visual. Serves as a bridge between sensory and motor processing. Should be manipulated with caution because the consequence of its elimination is not easily reversed.
motor
portion of the of the pyramid of binocular vision that includes activities necessary to properly align the eyes at various distances and directions of gaze. Represent the apex of the pyramid and is the last to be treated. Anomalies of this process often have a significant effect on visual comfort and performance
Ametropia
a refractive condition where the far point of the eye is not at infinity. Can cause sensory anomaly in binocular vision. Ie) myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism
Amblyopia
reduced visual acuity that is not correctable with best refraction. A sensory anomaly of binocular vision.
Eccentric fixation
occurs when an amblyope does not use central foveal area for fixation under monocular conditions. A sensory anomaly of binocular vision.
Ptosis, keratoconus, media opacities, retinal disease, visual pathway disease
5 diseases that can cause BV anomalies due to defective sensory processing.
Suppression
a lack or inability of perception of normally visible objects in all or part of the field of vision in one eye. Occurs due to cortical inhibition. An integrative anomaly of binocular vision.
Anomalous retinal correspondence
occurs when the fovea of two eyes are not aligned for a common visual direction. An integrative anomaly of binocular vision.
Horror fusionalis
the inability to obtain fusion or superimposition of haploscopically presented targets. An integrative anomaly of binocular vision.
Aniseikonia
difference in image size between the right and left eye. An integrative anomaly of binocular vision.
Vergence dysfunction
the most commonly diagnosed binocular anomalies. Ie) esophoria, exophoria, convergence insufficiency, etc. A motor anomaly of binocular vision.
Strabismus
crossing of the eyes arising congenitally or due to trauma, surgery, tumor, etc. A motor anomaly of binocular vision.
Nystagmus
rhythmic oscillation of the eyes, beyond normal fixational or end gaze movements. A motor anomaly of binocular vision.
Binocular fusion
the process by which two images, one from each eye, give rise to a single unified percept of an object. Separating the two eyes prevents this. Ie) patching one eye
Simultaneous perception
degree of fusion which is the ability to view two disparate (dissimilar) images simultaneously as a single superimposed image. Can be tested with a major amblyoscope. Is not true fusion. Seeing only one image indicates suppression. Seeing flashes between the two images indicates diplopia or binocular confusion.
Flat fusion
degree of fusion which is the ability to view two similar images simultaneously as a single superimposed image. Involves binocular summation, binocular correspondence, and fusion without depth.
Stereopsis
degree of fusion that is of the highest level. Is the ability to perceive binocular depth perception via the stimulation of non-corresponding retinal points.
Motor fusion
the use of vergence eye movements to position the eyes so that the corresponding retinal points are super imposed. The ability to align the eyes in order to maintain sensory fusion. Is the exclusive function of the extrafoveal retinal periphery stimulated by retinal disparity outside of panum's area. Cannot exist without sensory fusion.
Sensory fusion
the neurophysiological and psychological process by which the visual cortex combines superimposed views from each eye into a single percept. The ability to appreciate two similar images, and to interpret them as one. Can exist without motor fusion, but images must be similar in size, brightness, and sharpness.
motor
Anomalous correspondence occurs as a result of inadequate ____ fusion
motor AND sensory
Suppression occurs as a result of inadequate ______ fusion
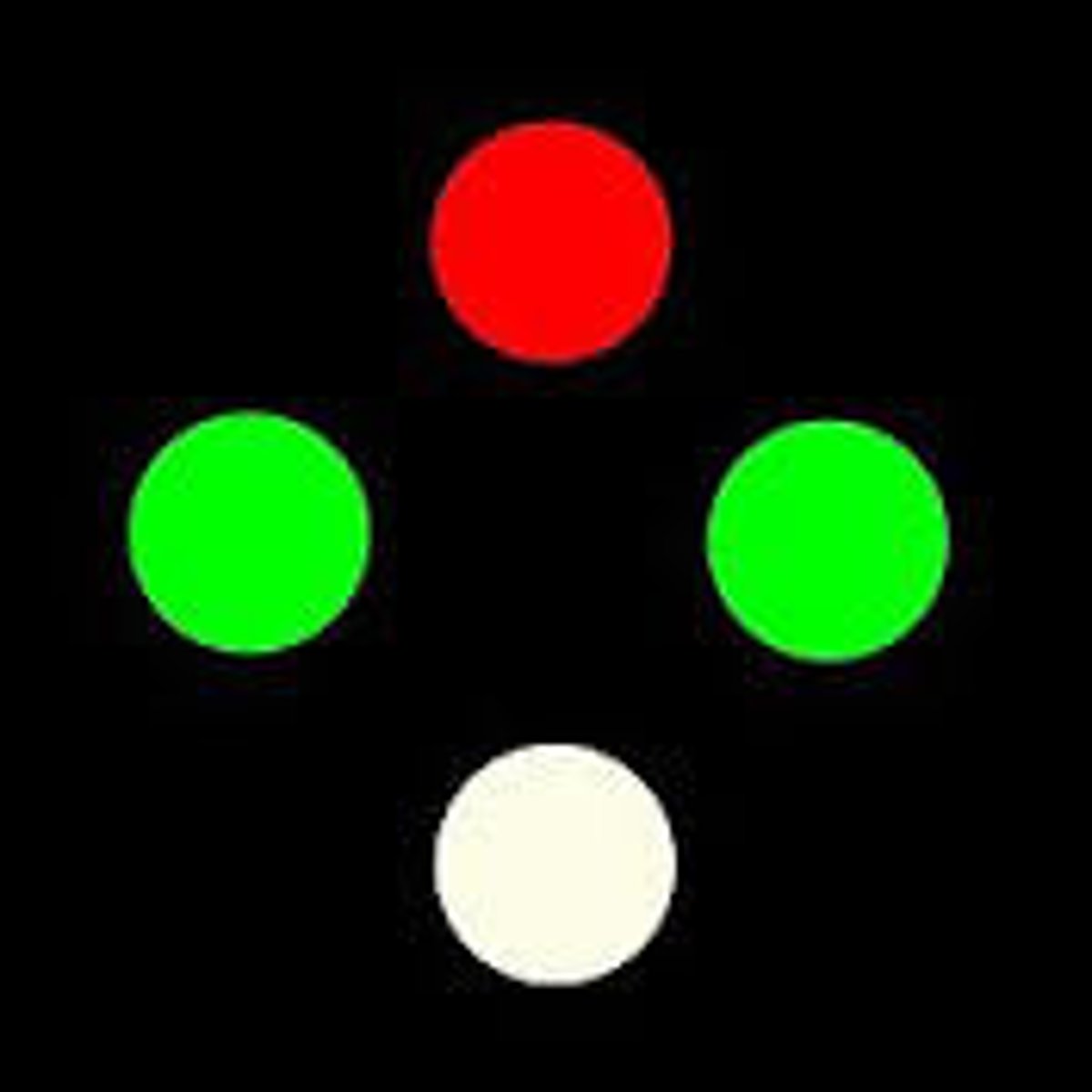
Worth 4 dot
test which utilizes red green glasses to assess fusion. A patient that sees all four circles has fusion. A patient that sees only green is suppressing the eye with the red filter and vice versa.
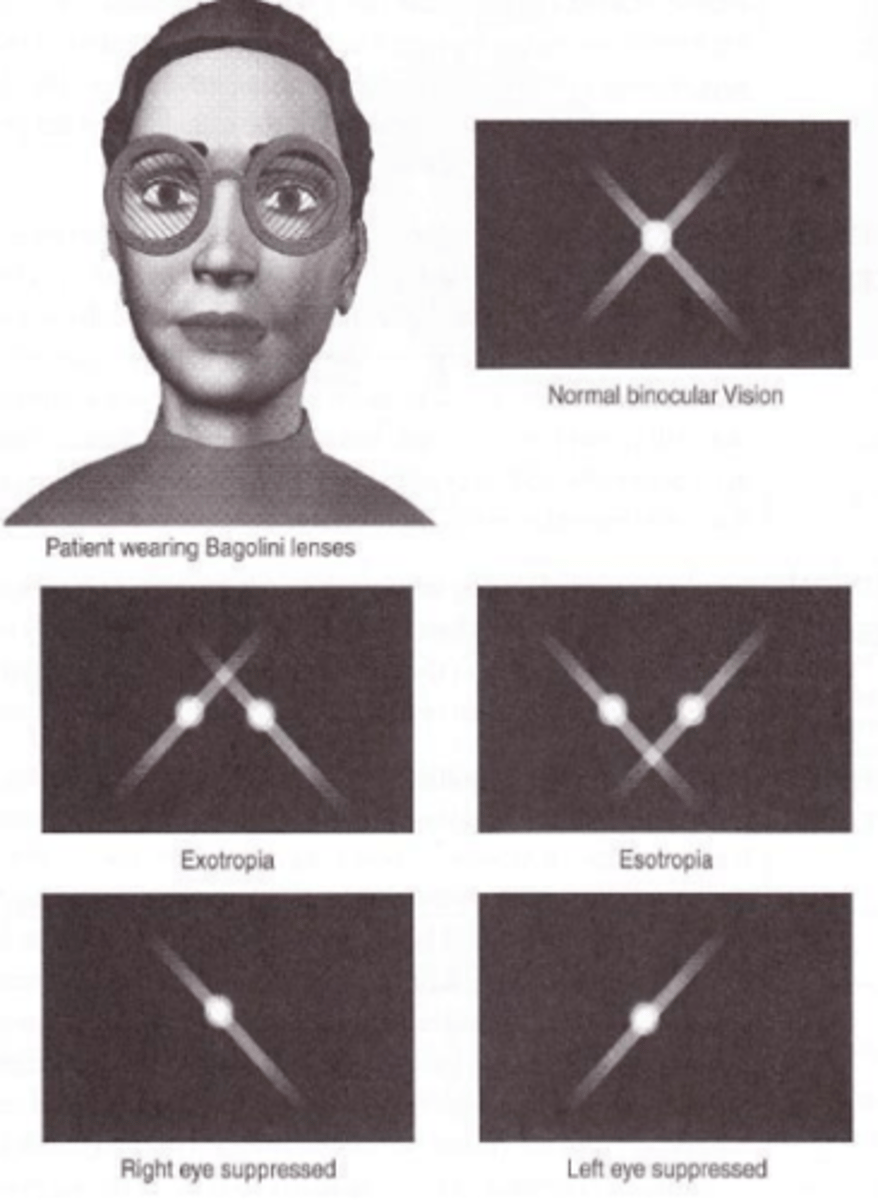
Bagollini striated lens test
test which utilizes a striated plano lens over one eye oriented at 45 degrees and at 135 degrees in the other eye to assess fusion. A patient with fusion will see an X image. A patient with suppression will see only a single streak. A patient with strabismus will see two crosses, but they will not cross in the center.
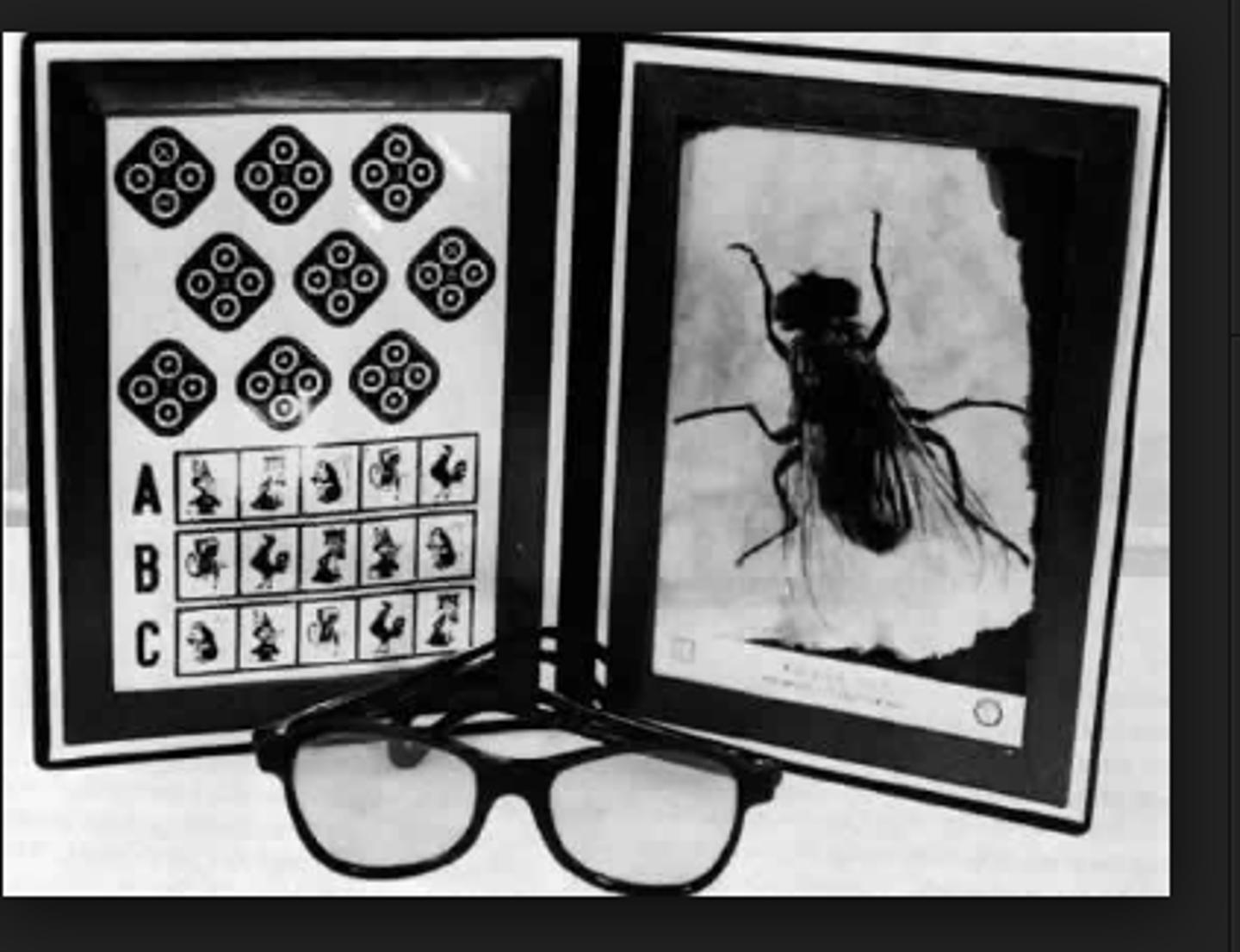
Stereopsis test
test that assess third degree fusion, local and global.

Alternation/suppression theory
theory of fusion stating that only one of the monocular images reaches consciousness at a time, alternating between right and left eye views. Based off of the ideal of binocular rivalry. Proven to be false under natural viewing conditions.
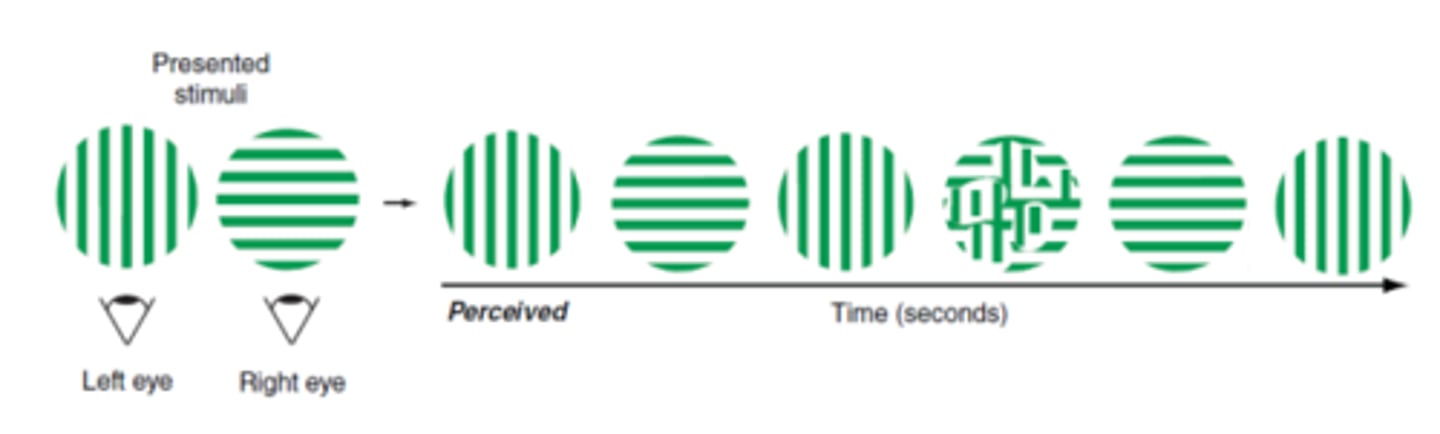
Fusion theory
theory of fusion stating that we can attend to similar images in both eyes at the same time. Proven to be true under natural viewing conditions.
binocular rivalry (dissimilar images), monocular depth cues
what are two minor exceptions to the fusion theory?
horopter
line of points in space whose images fall on corresponding retinal areas of the right and left eyes.
Panum's fusional space
the region in visual space, surrounding the horopter, over which fusion can occur. Proves that images that are not at exact corresponding retinal points can still be fused.
Panum's fusional area
The area on one retina such that any point in it will fuse with a single point on the other retina. Proves that images that are not at exact corresponding retinal points can still be fused.
Panum's limiting case
the minimum conditions for the perception of stereopsis. Includes 3 lines, one for one eye and two for the other. Used in research to determine Panum's fusional area.
50
Target becomes diplopic ____% of the time at the edge of Panum's area
horizontally
is Panum's area is 3-6x larger horizontally or vertically?
5-20, increase
Panum's area is _____ arcmin foveally and (increases or decreases) with eccentricity
Aniseikonia
condition where there is an image size difference between the right and left eye. This is better tolerated in the periphery due to a large Panum's fusional area. Small amounts of image size disparity in the central field of view will cause a loss of binocular vision. Therefore, central vision suppression is much more common in strabismus.
anomalous retinal correspondence
In the case of ______, Panum's fusional area may be abnormally large
Dichoptic (bi-ocular)
similar or dissimilar information presented independently to each eye. In normal binocular vision, the two eyes will contribute equally or one eye may be favored slightly.
FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
test that confirmed dichoptic/bi-ocular viewing may favor one eye over the other. Shows that the dominant eye activates a larger portion of the striate cortex. May differ at distance versus near.
Utrocular discrimination
the ability to identify the stimulated eye under binocular conditions. Very difficult to achieve because monocular information is lost to conscious perception. May be utilized internally by the visual system without our awareness.
Fusional vergence demand
the amount of fusional vergence required to keep the eyes aligned
Negative fusional vergence
the type of fusional vergence required to align the eyes straight from an esophoria position
Positive fusional vergence
the type of fusional vergence required to align the eyes from an exophoria position
strabismus
If a heterophoria is not compensated with fusional vergence, this will result in...
Fixation Disparity
a purposeful small error in vergence that prevents the image from the fixation target from falling on corresponding retinal points. If this occurs more than a few minutes of arc, this indicated binocular vision problems.
Nonius lines
fine lines (similar to vernier testing) used to measurement of fixation disparity.
wesson and sheedy
two disparometers used in measuring fixation disparity
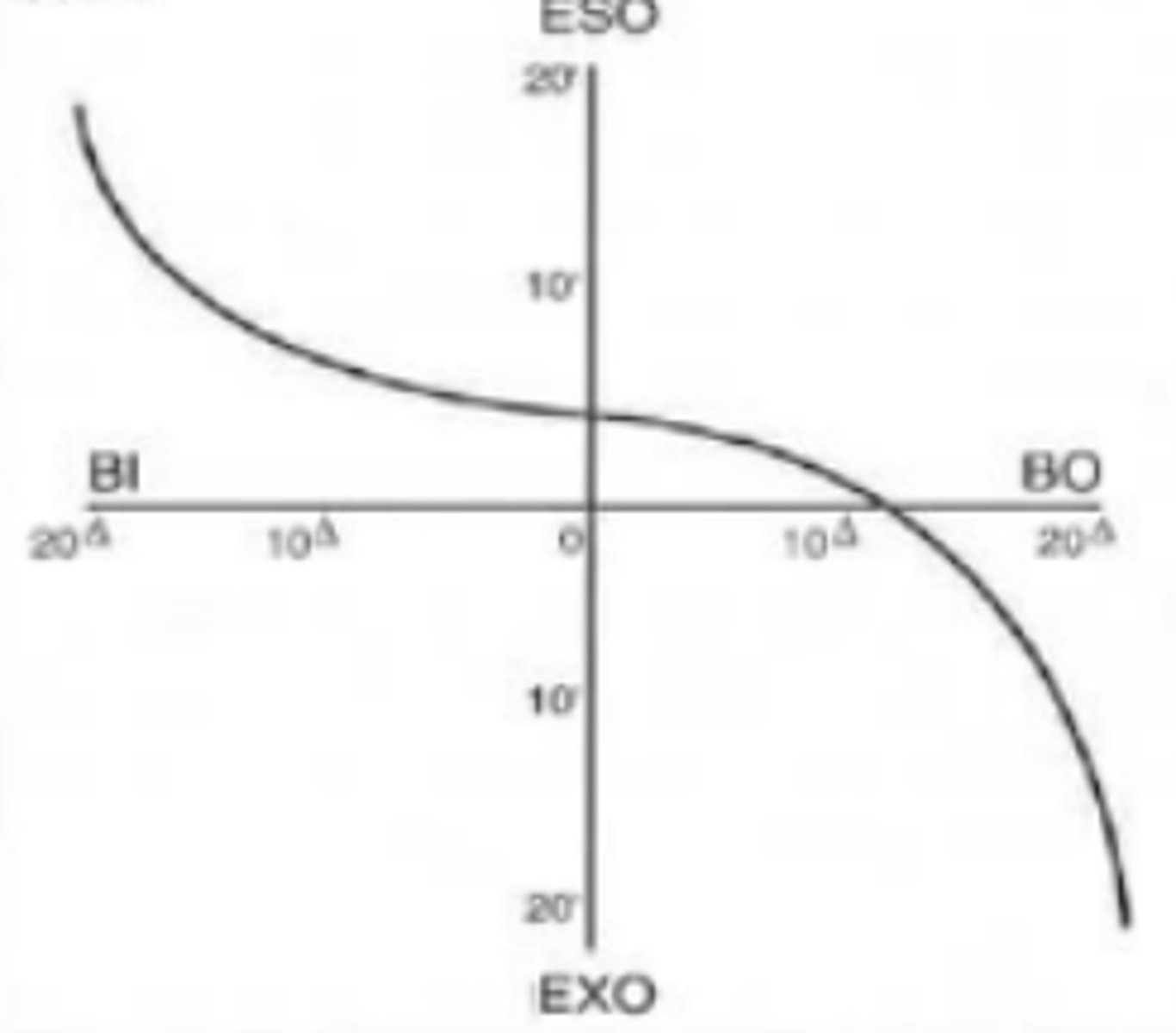
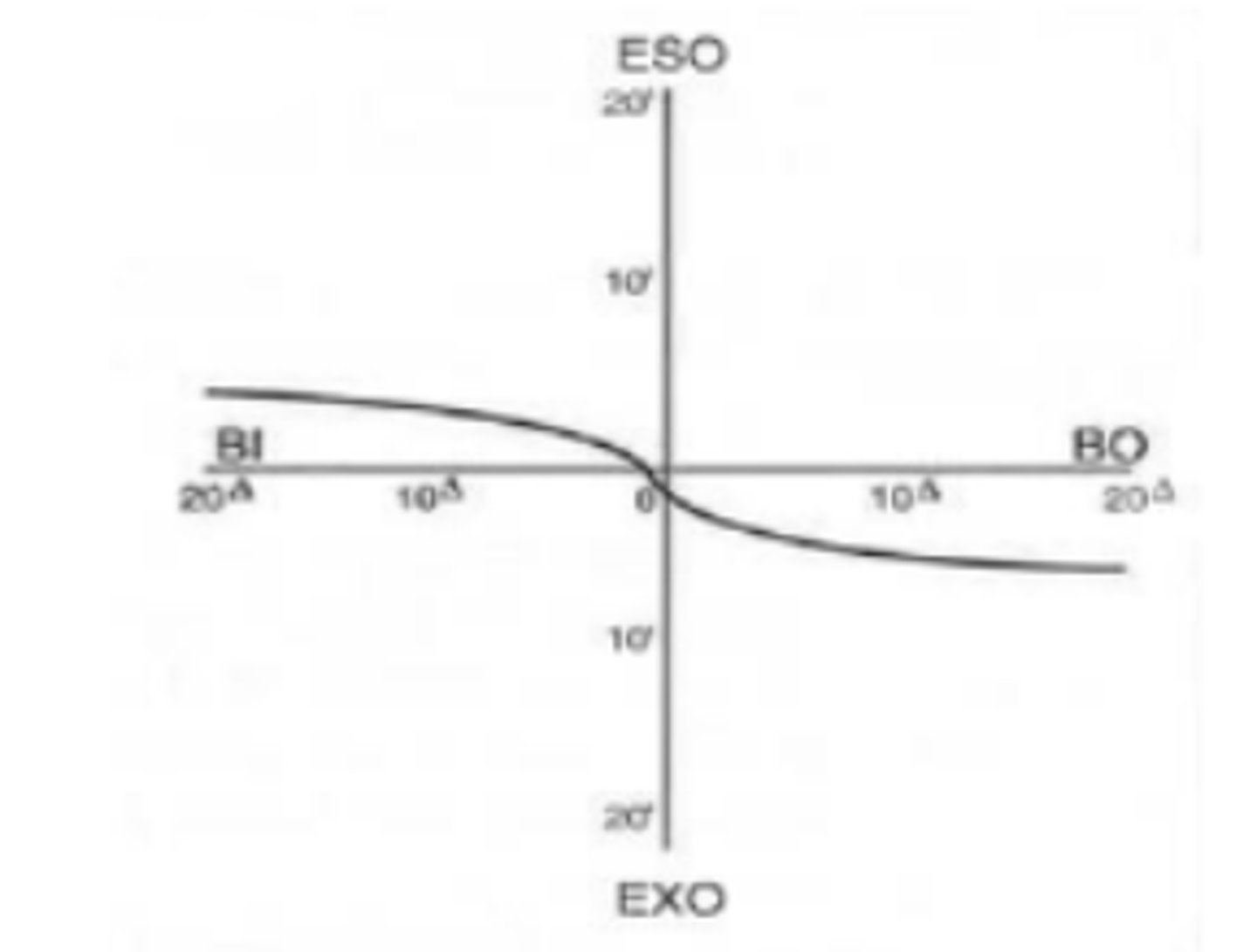
Forced vergence fixation disparity curve
curve used to predict how a patient will respond to prism and other stresses on the vergence system by measuring fixation when prism is induced. The steeper the curve, the more likely binocular vision problems will occur with induced stresses
Type I
forced vergence fixation disparity curve that is symmetric with a gradual change in fixation disparity except at extreme values. Relatively common (60-70%) in most patients. The steeper the center of the curve, the higher the chances of binocular vision problems.
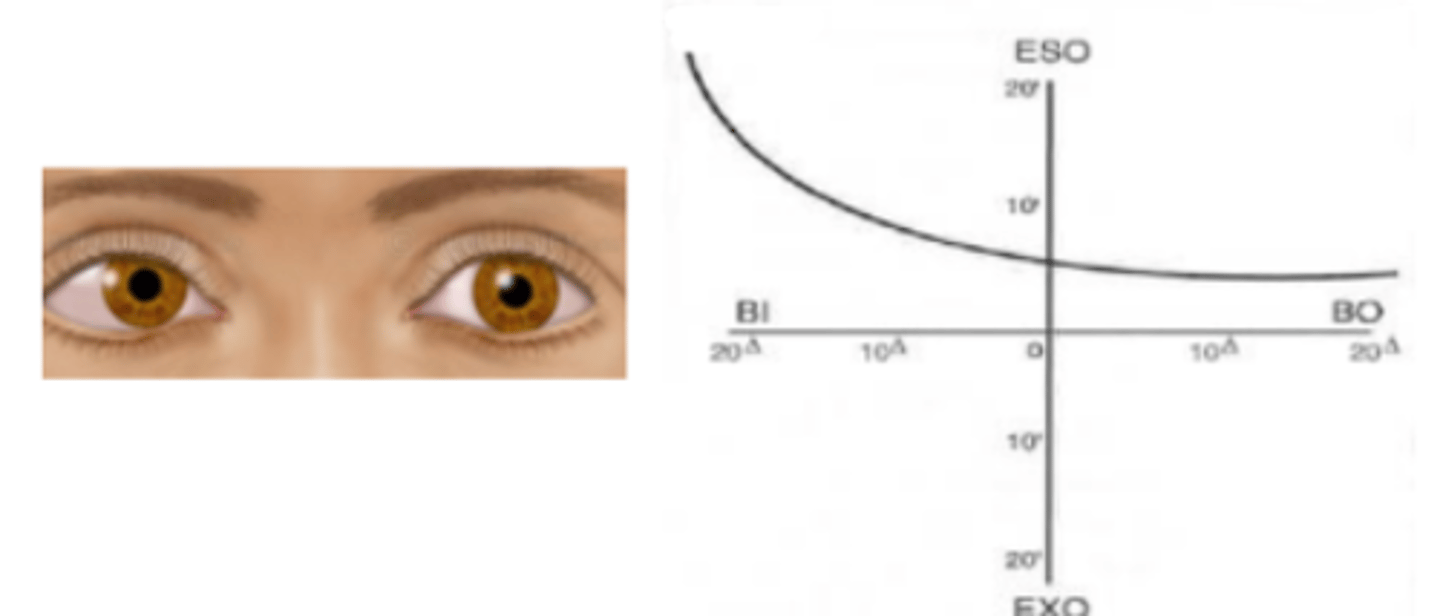
Type II
forced vergence fixation disparity curve that represents an intolerance of forced divergence (BI) as seen in patients having esophoria. Appears as a flat slope on the BO side and a steep slope on the BI side. Seen in about 25% of patients at distance and near.
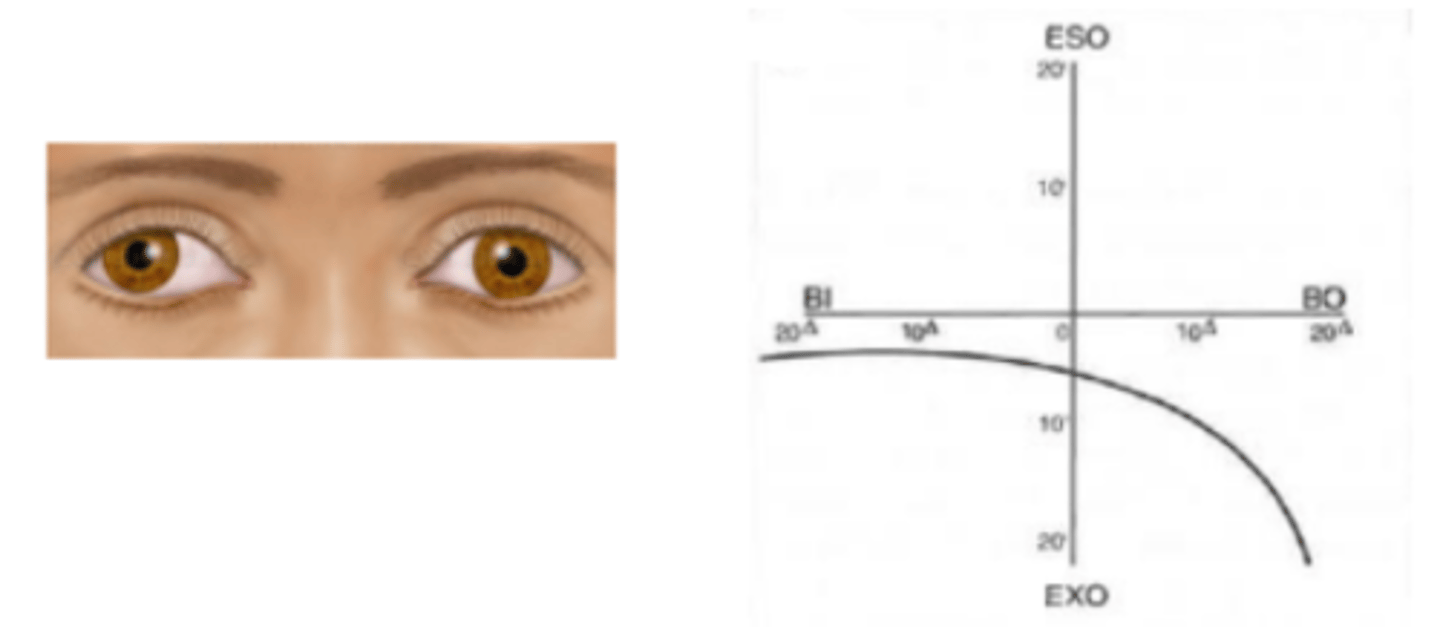
Type III
forced vergence fixation disparity curve that represents an intolerance of forced convergence (BO) as seen in patients having exophoria. Appears as a flat slope on the BI side and a steep slope on the BO side. Seen in about 10% of people at near and 0% at distance.
Type IV
forced vergence fixation disparity curve that is flat for both base out and in. Is associated with aniseikonia and sensory fusion problems. Seen in about 5% of patients at distance and near.
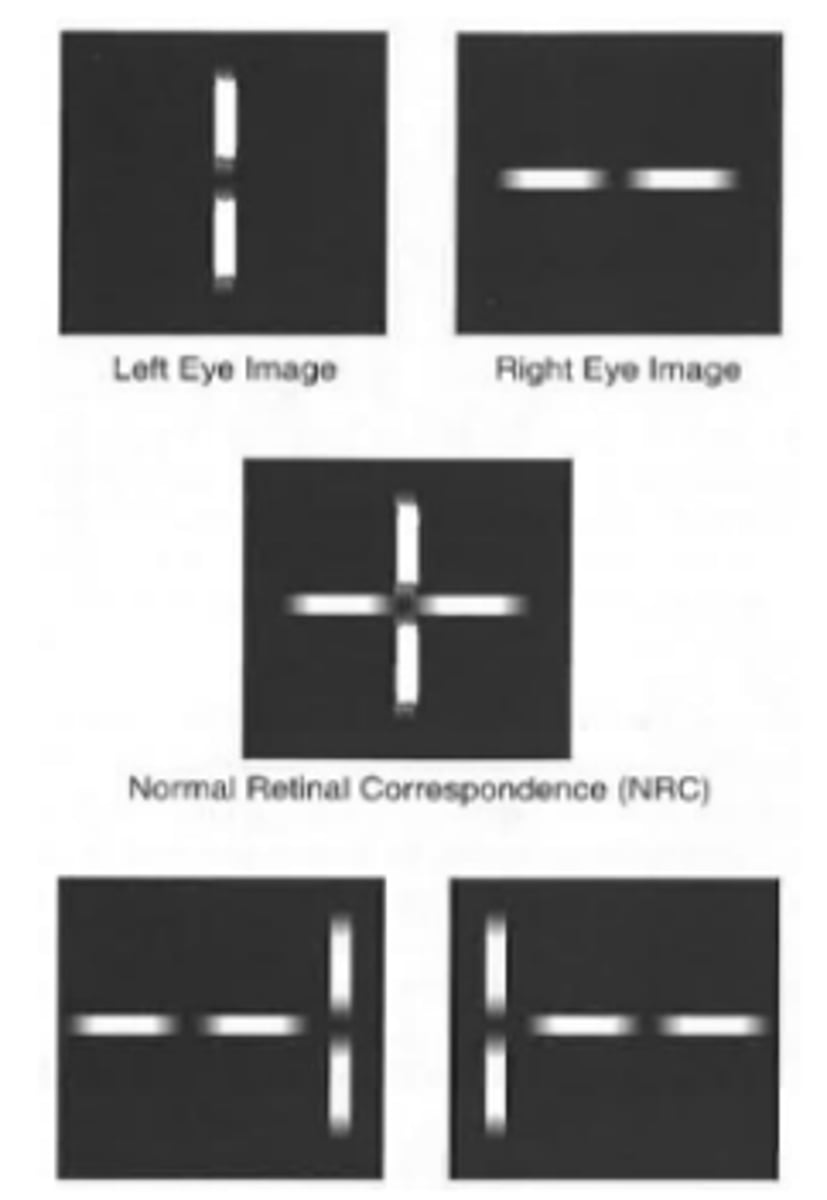
Normal retinal correspondence
binocular vision condition where both fovea have a common visual direction and the retinal elements nasal to one eye and temporal to the other also correspond.
Anomalous retinal correspondence
binocular vision condition where the fovea of one eye has a common visual direction with an extrafoveal area of the other eye. Two fovea no longer correspond with one another. Is a cortical phenomenon.
Harmonious ARC
a shift in corresponding retinal points that matches the angle of the strabismic deviation. Most common.
Unharmonious ARC
imprecise shifting of corresponding retinal points that does not match the angle of strabismic deviation.
Eccentric fixation
an off foveal point in the retina of a strabismic eye that is used for fixation under monocular and binocular conditions. Is an adaptation of the visual system to misalignment. Is a cortical phenomenon
Hering-Bielschowsky after image test
test that can be used to measure eccentric fixation. Achieved by the observation of two crossing lines seen by each eye.
eso
If a patient is holding a Maddox rod over their right eye and the red line is appearing to the right of the white light, this patient has an ____ eye position
exo
If a patient is holding a Maddox rod over their right eye and the red line is appear to the left of the white light, this patient has an ____ eye position
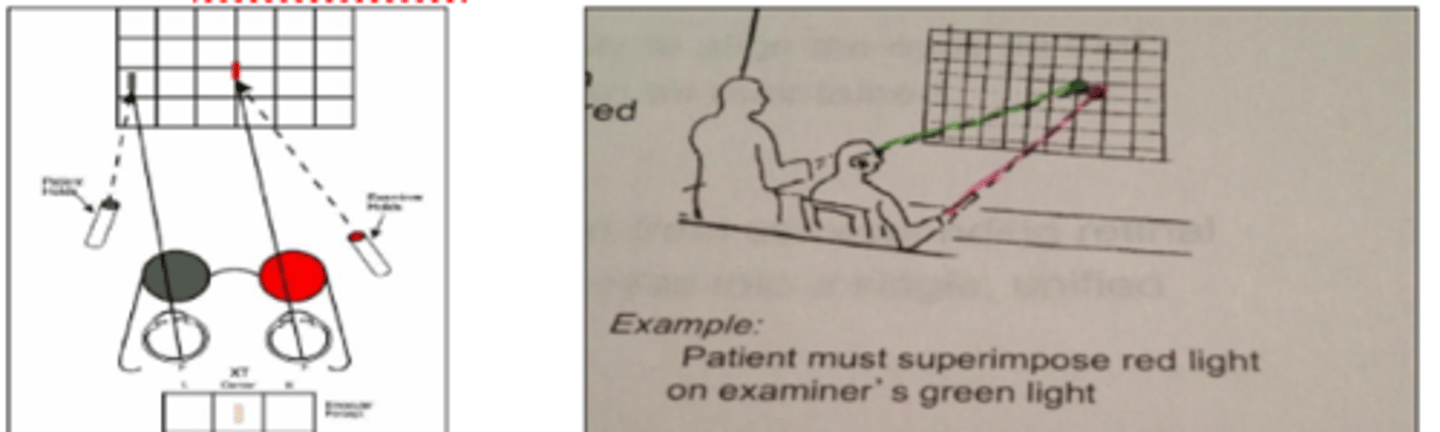
Hess-Lancaster test
test where the patient wears red green glasses and if they are able to superimpose the two images they are orthophoric.
Angle of anomaly
the difference between the subjective and objective strabismus angle measurement.
Sensory theory
theory of ARC stating that sensory adaptation compensates for a constant angle of strabismus.
Motor theory
theory of ARC stating that egocentric direction is altered by the pattern of innervation to the oculomotor muscles. Change in corresponding retinal points is registered with oculomotor system signaling.
Abnormal disparity vergence stimulus detection
theory of ARC stating that ARC is what causes strabismus due to a neurophysiological disturbance.
exophoria
does treatment of exophoria or esophoria tend to more successful?