ID Lectures 56, 58-59: HIV | Quizlet
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Where did HIV originate?
cross species transmission from chimps in Central Africa
Where is HIV-1 commonly found?
in the US and around the world
Where is HIV-2 commonly found?
West Africa
HIV prevalence
Number of diagnosed and undiagnosed persons living with HIV
HIV Prevalence Rate
Number of persons living with HIV per 100,000 population
HIV Incidence
number of new HIV infections in a fixed time period
HIV incidence rate
number of new HIV infectios in a fixed time period per 100,000 population
The prevalence of HIV is higher in what populations?
Men who have sex with men
Transgender women
African Americans
Hispanics
Latinx populations
Does HIV effect everyone equally?
NO
Who is most at risk for contracting HIV?
MSM
Transgender women
IVDU
Describe the HIV life cycle.
1) Viral Entry via attachment to CD4 cell receptors and co receptors on the host cell
2) Reverse transcription
3) Integration into the host cell's DNA
4) Transcription Viral DNA to RNA
5) Translation (Replication)
6) Cleavage - long proteins are broken down into core proteins
7) Assembly - HIV RNA and viral proteins migrate to the host cell membrane
8) Budding and maturation - immature HIV virus buds from the host cell to go infect more host cells
What poses the highest risk of HIV transmission?
Blood
Semen
Vaginal fluids
Breast milk
Vaginal fluids
Sexual contact
Sharing dirty needles
What poses a lower risk of HIV transmission?
Vertical transmission
Needle sticks (HCW)
Does every exposure cause HIV transmission?
No!
What HIV virus is considered to be capable of causing infection?
Founder virus
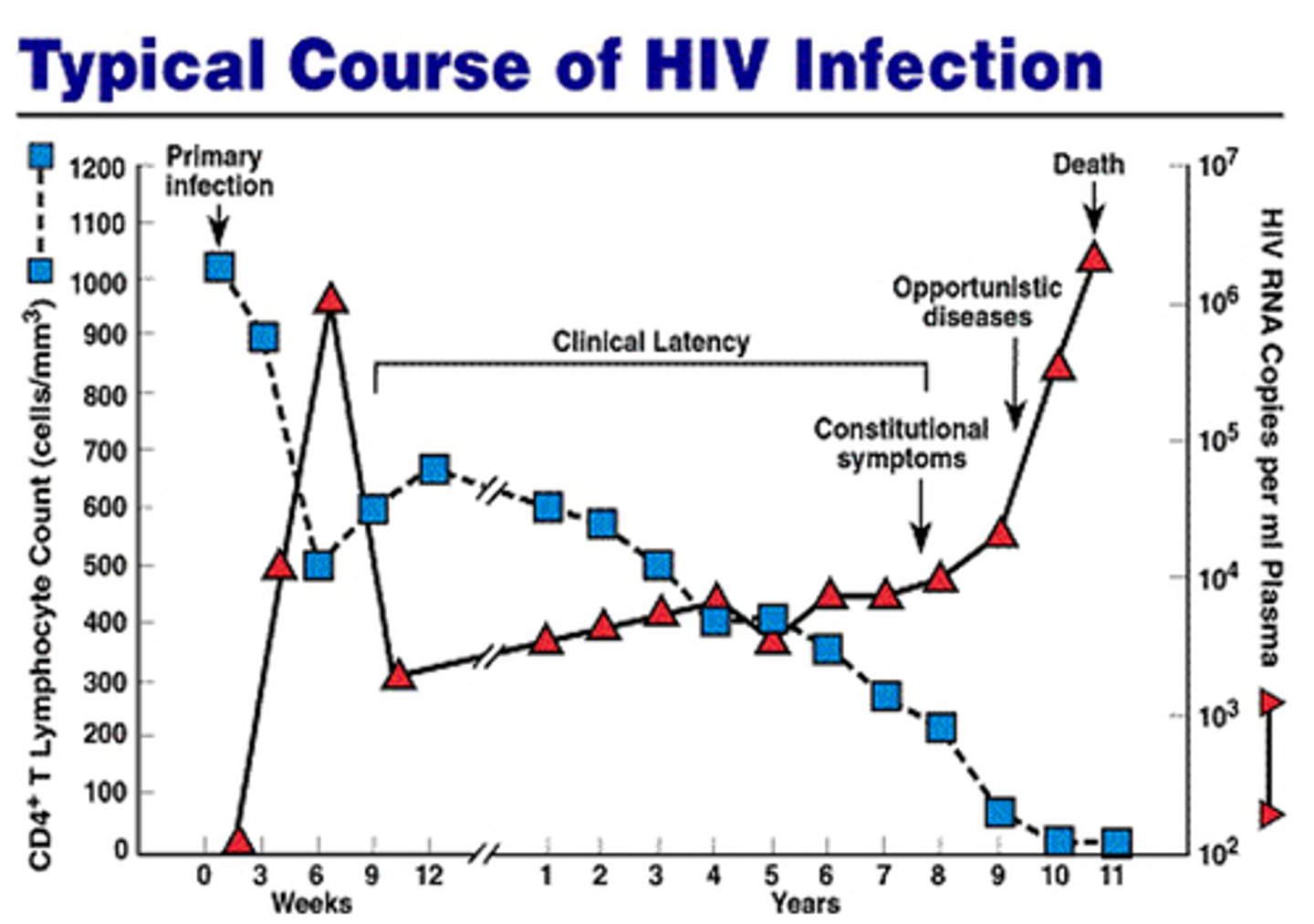
What happens to CD4 T cell counts during the early stage of HIV infection when left untreated?
Decreases until week 6 where it increases for a number weeks until it gradually decreases again
What are the CDC HIV screening recommendations?
routine annual screening for everyone aged 13-64
Every pregnancy
What are the USPSTF HIV screening recommendations?
All adults aged 15-65 years old
Repeated screening for those known to be at risk
Every pregnancy
What are the FIRST three things to be detected in HIV following exposure?
1. HIV RNA (~10 days)
2. p24Ag (~15 days)
3. EIA (~21 days)
What should be done if a patient comes to you after they screen themselves for HIV?
HIV Antigen/Antibody Immunoassay
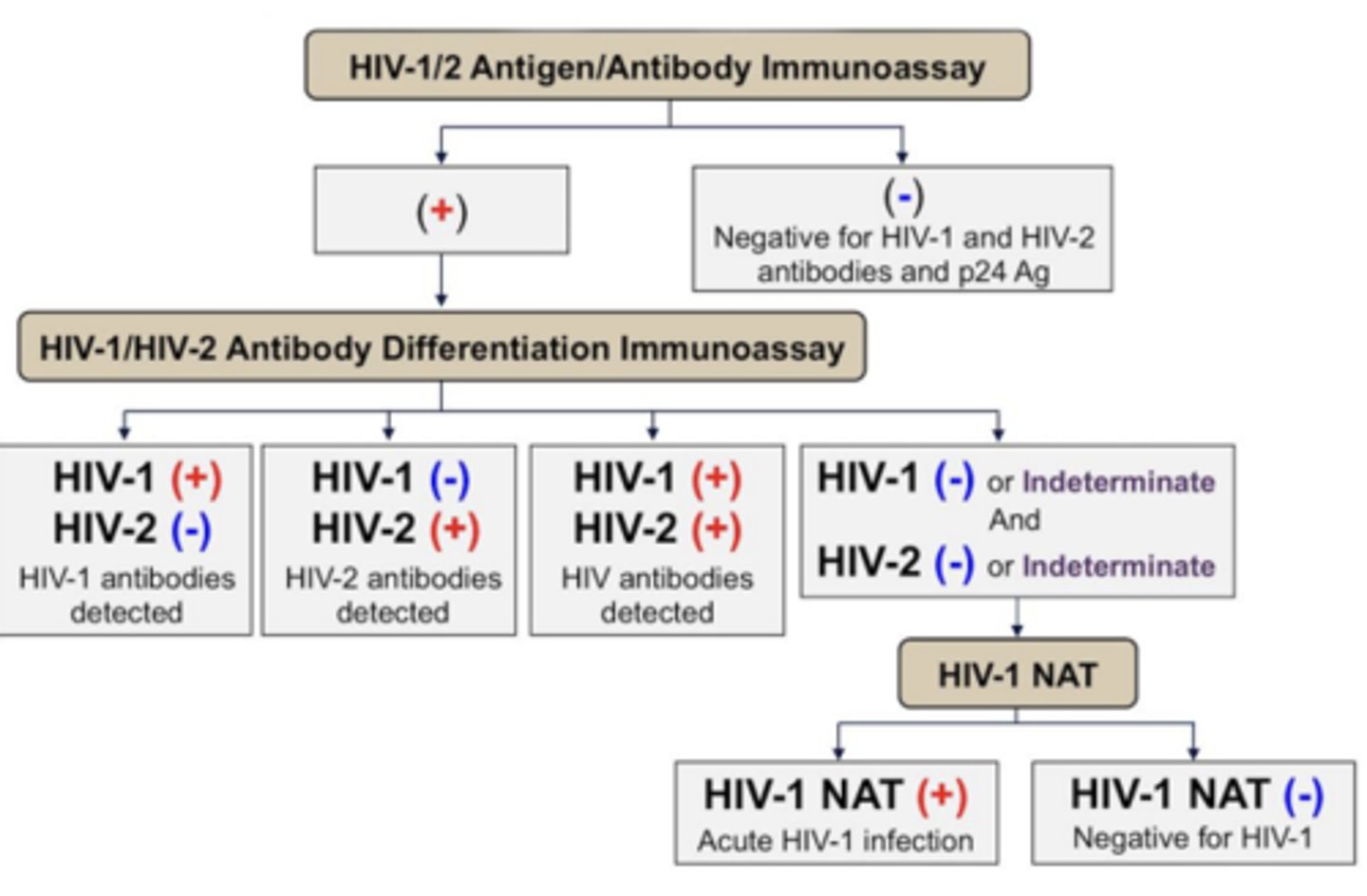
What should the next step be for a patient with a negative result on their HIV Antigen/Antibody Immunoassay?
Nothing, the negative test rules out the possibility of them having HIV
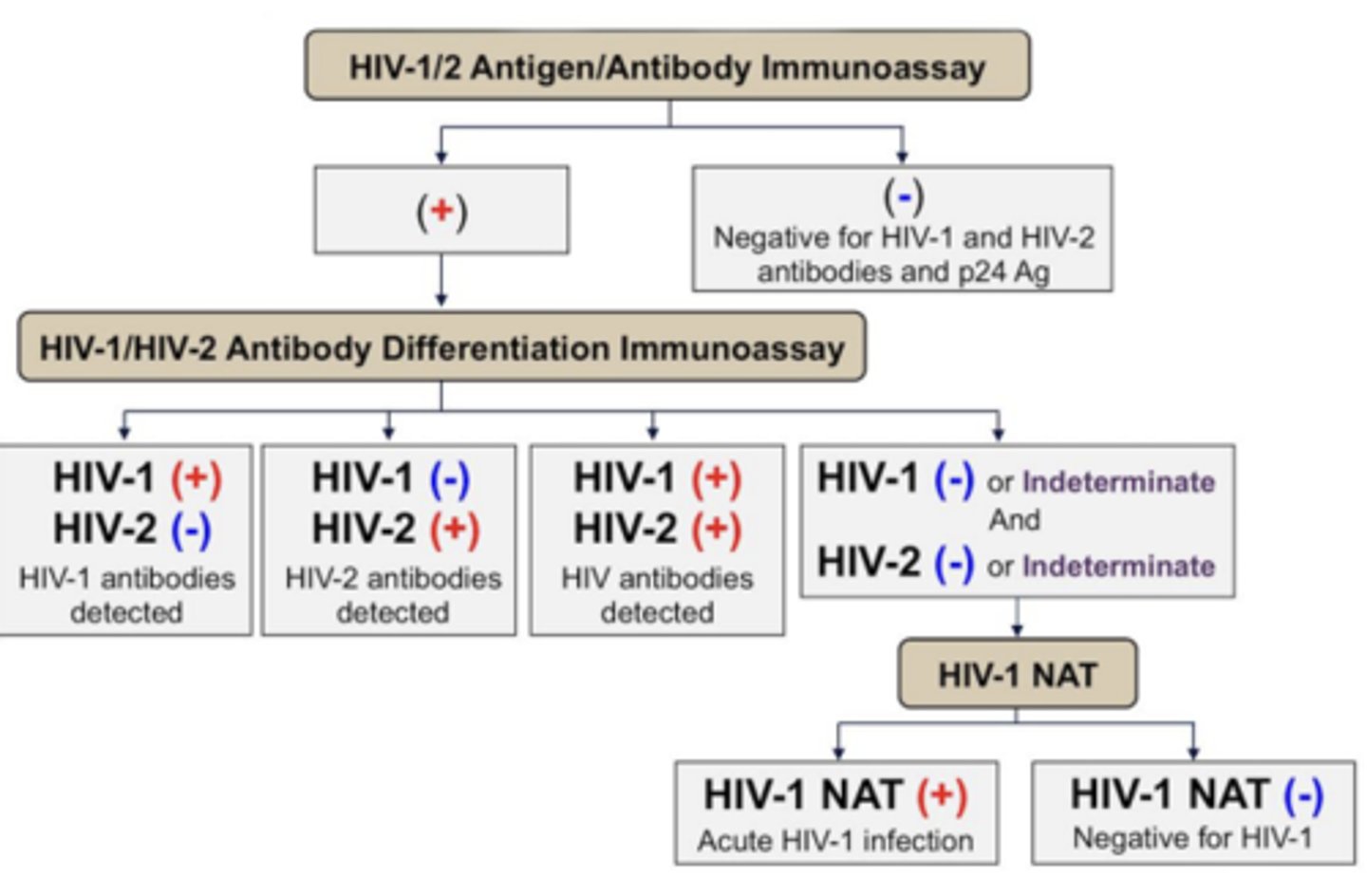
What should the next step be for a patient with a positive result on their HIV Antigen/Antibody Immunoassay?
Do a HIV Antibody Differentiation Immunoassay
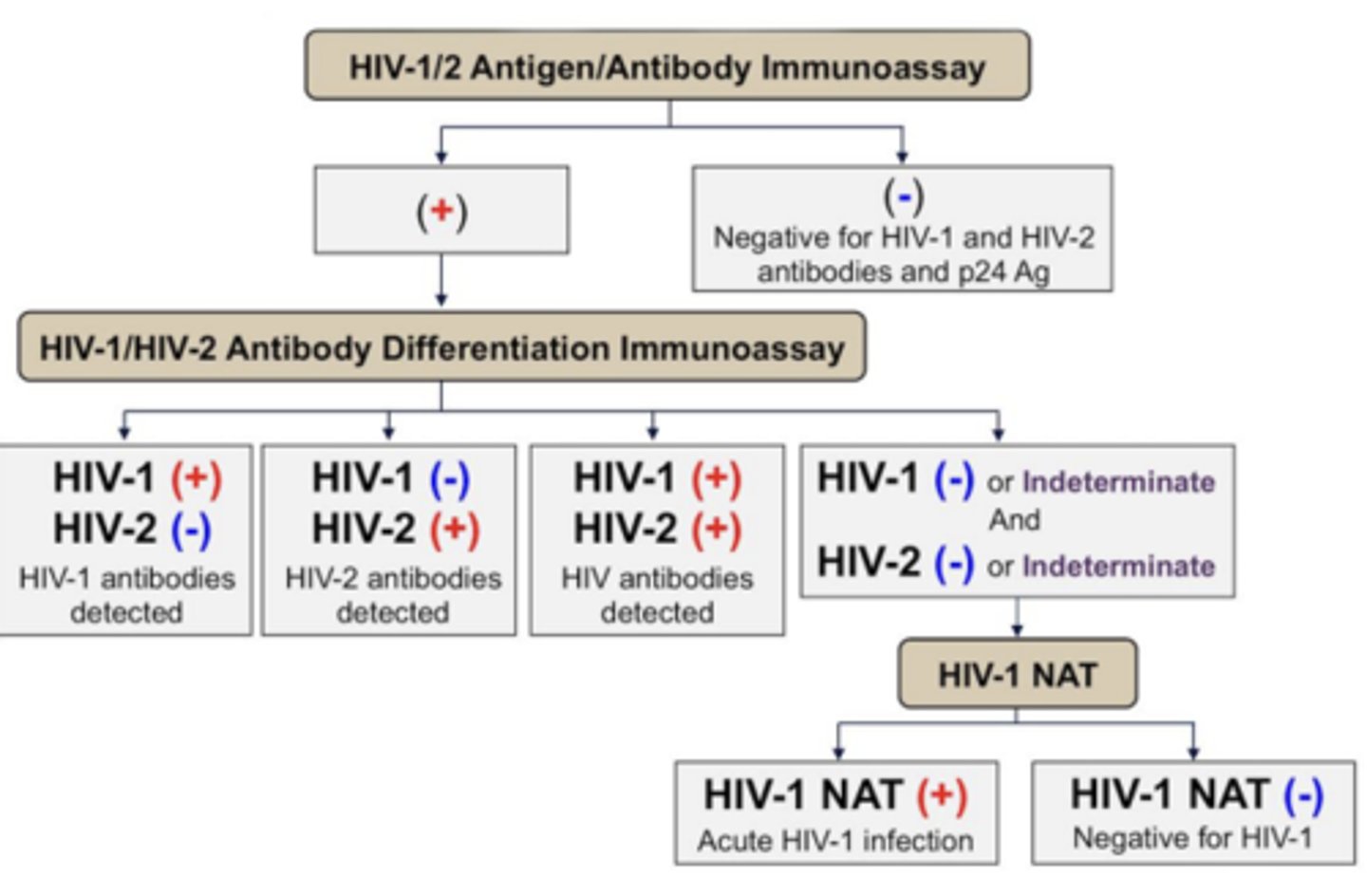
What should be the next step for a patient with a result of HIV-1 negative and HIV-2 negative differentiation immunoassay?
Perform HIV-1 NAT test which rules HIV-1 in or out
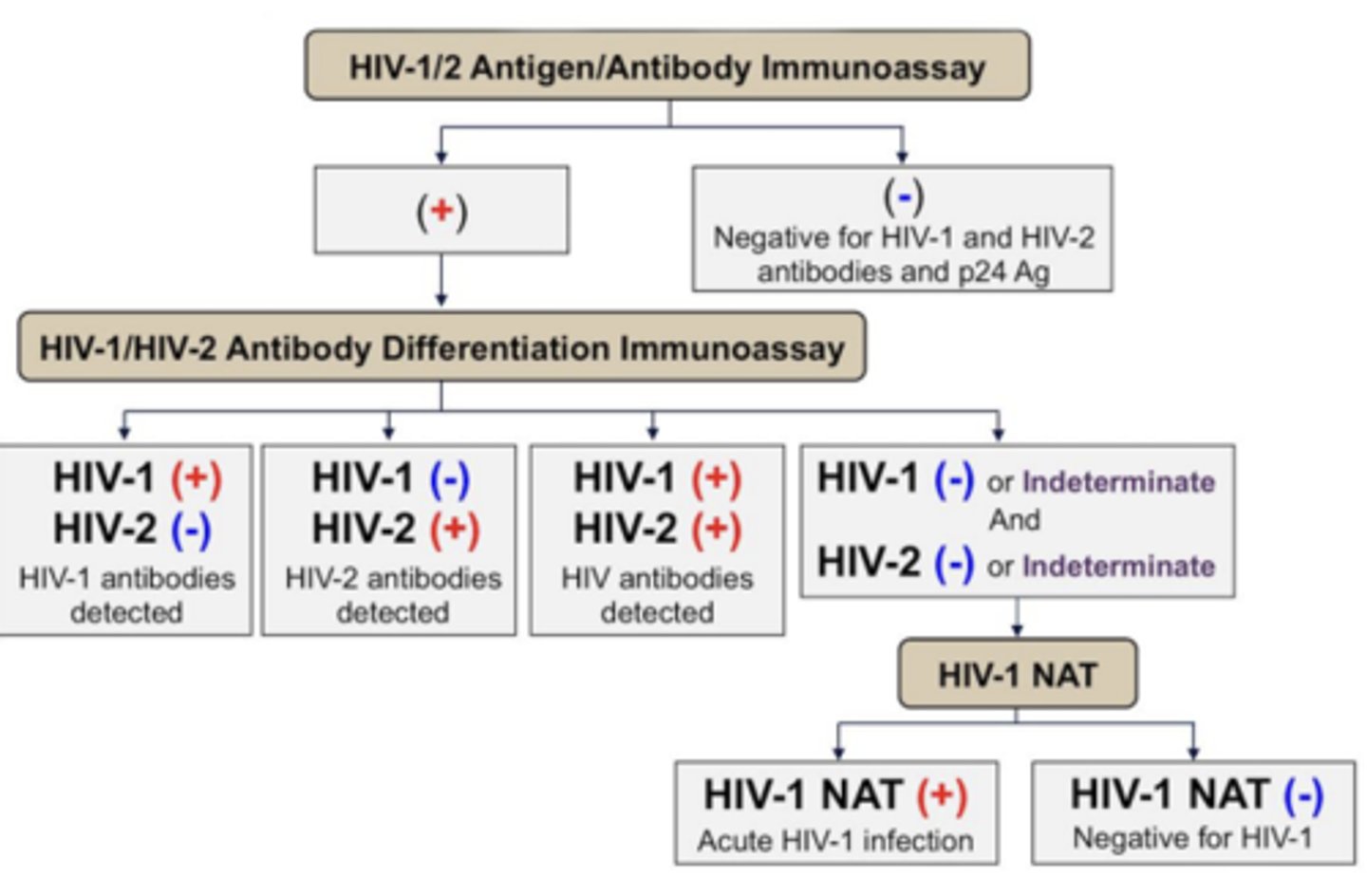
When is "Acute HIV"?
days 10-24 following infection
What components of health history are important to gather to determine if a person is at risk of HIV?
Diagnosis date
Vaccinations
Opportunistic infections
Blood work
Drug history
Sexual history
What laboratory values are critical to evaluate in people living with HIV?
CD4 Count
Viral load
Genotype
What is the purpose of genotype testing in HIV?
determines drug resistant mutations present in viral genes
What are the different stages of HIV?
Acute infection
Asymptomatic
Symptomatic
Advanced immunosuppression
What are the different stages of HIV infection?
Exposure event
Prime infection
Initial propagation
Local expansion
Regional lymphatic spread
Hematogenous spread
CD4 Count
predictor of disease progression and survival

What is the true marker of HIV drug action?
Viral load testing
Viral load testing
amount of virus in the blood
*goal is to be undetectable!*
At what CD4 level are patients at risk for developing opportunistic infections?
>500 = normal
201-499 = may have sx
<200 = advanced immunosuppression

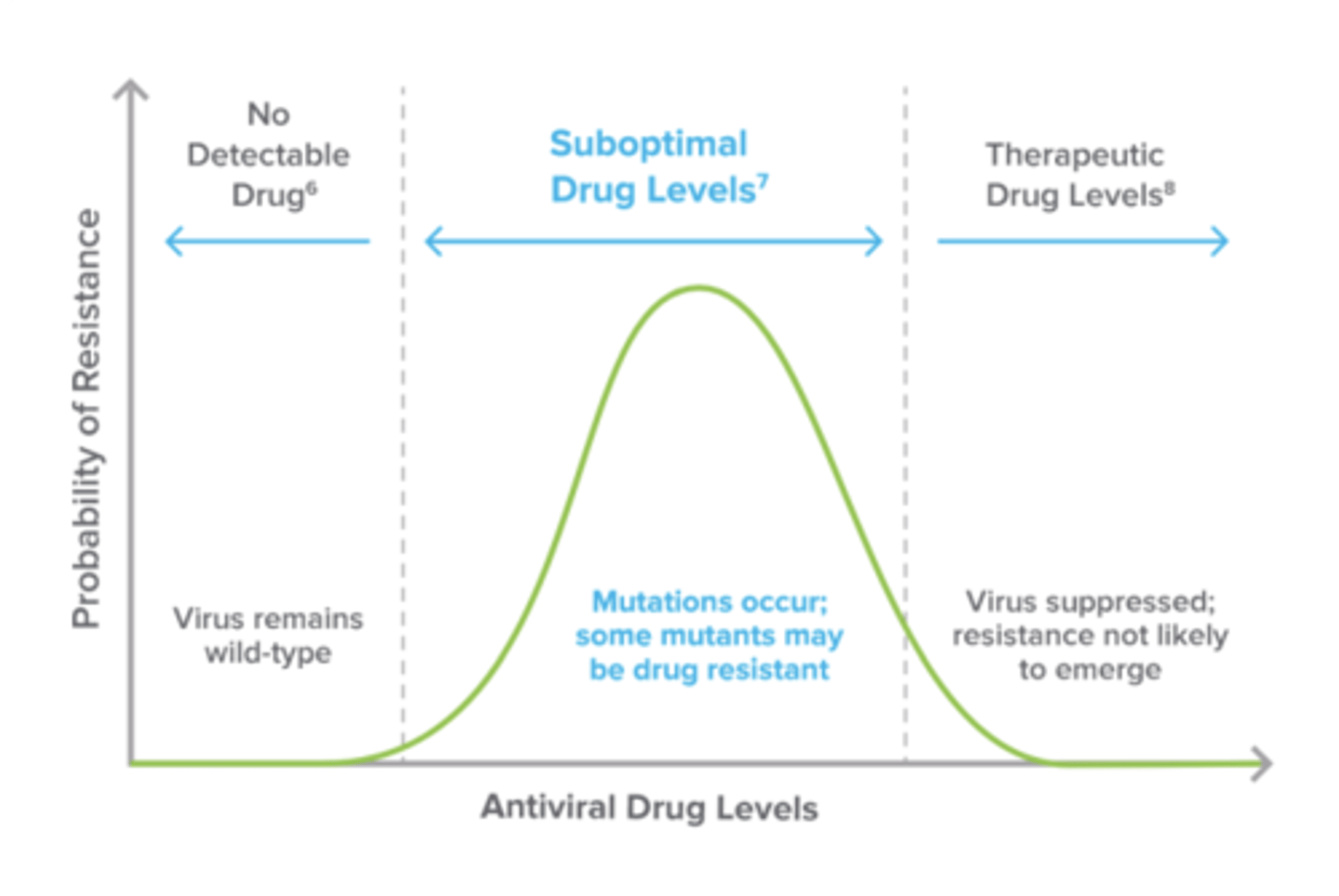
Why do we want to have patients achieve therapeutic HIV drug levels?
Mutations occur when there is some drug in the blood because the virus is not fully suppressed
What is the main goals of HIV treatment?
Maximally and durably suppress plasma HIV RNA levels
Restore and preserve immunologic function
Reduce HIV associated morbidity and prolong the duration and quality of survival
Prevent transmission
When should antiretroviral therapy (ART) be started?
on the day of HIV diagnosis regardless of CD4 counts
What are some reasons for a more rapid initiation of ART in patients?
Acute HIV
HCV/HBV
CVD/HIVAN
Pregnancy
Opportunistic infections
Lower CD4 counts or rapidly declining
Higher viral loads
What are some reasons to delay ART initiation if patients with HIV?
Psyche
Adherence
What is the backbone and anchor drugs of ART therapy?
2 nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
PLUS one of the below:
Integrase inhibitor
OR
An NNRTI
OR
Protease inhibitor with a PK booster
What is the recommended therapy for HIV treatment naive patients?
Dovato (Dolutegravir-Lamivudine)
Tivicay AND Truvada OR Descovy
Biktarvy (bictegravir-TAF-Emtricitabine)
What two steps of the HIV life cycle do we target?
Reverse transcription
Integration
Dual NRTIs
Descovy (tenofovir AF + emtricitabine)
Truvada (tenofovir DF + emtricitabine)
NNRTIs
Edurant (Rilpivirine)
Pifeltro (Doravirine)
Integrase inhibitors
Isentress (Raltegravir)
Tivicay (Dolutegravir)
Biktarvy
bictegravir/emtricitabine/TAF
Dual NRTI and Integrase inhibitor
Protease inhibitors
Prezista (Darunavir)
Reyataz (Atazanavir)
When should viral load be monitored after starting therapy?
At baseline
2-8 weeks after initiating tx
then every 4-8 weeks until load is suppressed
Then every 3-4 months for at least 2 years
After 2 years, every 6 months
When do we want HIV viral loads to be undetectable after starting treatment?
after about 3 months
When should CD4 count be monitored after starting therapy?
At baseline
At 3 months
Then every 3-6 months for 2 years
After 2 years it depends on CD4 count
Besides CD4 count and viral load, what other labratory tests are routinely monitored?
CBC and CMP
Which class of HIV treatment should patients avoid taking with polyvalent cations?
Integrase inhibitors
- separate by 2-6 hours
Which ART agents need an acidic environment for absorption?
Atazanavir
Rilpivirine
What needs to be avoided in patients taking Atazanavir or Rilpivirine?
PPIs
Which ART therapies can be taken with food?
Atazanavir
Darunavir
Etravirine
Rilpivirine (calorie requirement)
Elvitegravir
Which ART agent has a calorie requirement? What is it?
Rilpivirine - at least 300 calories
Which ART agent can be taken without food?
Efavirenz
Cabenuva
Cabotegravir + Rilpivirine injection
Which ART agents have significant CYP450 interactions?
Protease inhibitors
Which ART agents have to be given with a PK booster (Ritonavir or Cobicistat)?
Protease inhibitors
Capsid inhibitor
Lenacapavir (PO or SQ)
When is Lenacapavir used?
treatment of HIV-1 in combo with other drugs in heavily treatment-experienced adults with multidrug resistant HIV
aka last resort
NOT FDA approved - HIV prevention
What are the contraindications of Lenacapavir?
CYP3A inducers
Most ART agents act ________________.
intracellularly
What is the difference between TDF and TAF?
TDF is a prodrug that has to be converted into TFV
TAF requires no conversion and has less ADRs
All Protease inhibitors are CYP3A4 _______________.
substrates
What is the purpose of giving Ritonavir or Cobicistat with Protease inhibitors?
Better dosing profile
Less pill burden
Better serum concentrations
When should boosing be added to antiretroviral therapy?
WITH EVERY PROTEASE INHIBITOR REGIMEN
Common interactions with ART
Statins
Estrogen OCs
Corticosteroids
CNS agents
Methadone
Anticoagulatns/platelets
Anti-infectives
ED medications
Acid suppressing medications
What ART agents should be adjusted at a CrCl less than 50 mL/min?
Tenofovir DF
Lamivudine
Emtricitabine
Lovastatin and Simvastatin are contraindicated with what ART agents?
ATV/RTV
ATV/COBI
DRV/RTV
DRV/COBI
EVG/COBI/TDF/FTC
Which statins are SAFE to use with ART?
Pitavastatin
Atorvastatin (with RPV)
Which ART agent has the strongest association with bone diseases?
Tenofovir DF
What is a long term side effect of ART?
Weight gain
PrEP
pre-exposure prophylaxis that when taken long enough can block replication after HIV exposure
What are the approved PrEP medications?
Truvada
Descovy
Who should recieve PrEP?
MSM
Heterosexual men and women at risk
IVDU
Transgender persons
How long after taking PrEP, would someone be protected?
Rectal tissue - 7 days
Vaginal tissue and blood - 20 days
On demand PrEP (2-1-1)
2 tabs of Truvada 2-24 hours before sex, then followed by 1 dose 24 and 48 hours after
Post Exposure Prophylaxis in Pocket (PIP)
patients are provided with a 1 month supply of 3 drugs (typical ART treatment) so they can start whenever they are exposed