TTU CHEM 1307 Exam I
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Texas Tech University, Prof. Casadonte
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
H
1 Hydrogen
He
2 Helium
Li
3 Lithium
Be
4 Beryllium
B
5 Boron
C
6 Carbon
N
7 Nitrogen
O
8 Oxygen
F
9 Fluorine
Ne
10 Neon
Na
11 Sodium
Mg
12 Magnesium
Al
13 Aluminum
Si
14 Silicon
P
15 Phosphorous
S
16 Sulfur
Cl
17 Chlorine
Ar
18 Argon
K
19 Potassium
Ca
20 Calcium
Base Unit of Length
meter (m)
Base Unit of Mass
kilogram (kg)
Base Unit of Time
second (s)
Base Unit of Temperature
kelvin (K)
Base Unit of Moles
mole (mol)
Base Unit of Electric Current
ampere (A)
Base Unit of Luminous Intensity
candela (cd)
Deci-
10^-1
Centi-
10^-2
Milli-
10^-3
Micro-
10^-6
Nano-
10^-9
Pico-
10^-12
Femto-
10^-15
Atto-
10^-18
Deca-
10
Hecto
10²
Kilo-
10³
Mega-
10^6
Giga-
10^9
Tera-
10^12
What is the derived unit of energy?
joule (J)
What is the derived unit of force?
Newton (N)
What is the derived unit of power?
watt (W)
What is the derived unit of pressure?
pascal (Pa)
What is the derived unit of electric charge?
coulomb (C)
What is the derived unit of electric potential?
vol (V)
Force=______
ma
Acceleration=______
m/s²
Pressure=______
N/m²
Velocity=______
m/s
What is the pressure exerted by a column of dry air at sea level and 273K called?
14.7lbs/in²=101.325 kPa=______
1 atmosphere (atm)
Density=______
mass/volume
What is the freezing/boiling point of water in °F?
32/212
What is the freezing/boiling point of water in °C?
0/100
What is the freezing/boiling point of water in K?
273.15/373.15
What is the conversion from °C to °F?
F=9/5(C)=32
What term is defined by how close a measurement is to the correct value?
Accuracy
What term is defined by a measurement of how closely at least 2 measurements agree with each other or reproducibility?
Precision
Is volume a fundamental unit?
No
How many inches are in a foot?
12in
How many feet are in a yard?
3ft
How many centimeters are in a meter?
100
How many feet are in a mile?
5280ft
What is the speed of sound?
1000ft/sec
What law is defined by: matter can neither be created nor destroyed, although it can change forms into energy
Conservation of Matter
What law is defined by: in a chemical compound, the proportions by mass of the elements that compose it are fixed, regardless of how it was formed
Definite (Constant) Proportions
What law is defined by: two different compounds each containing the same elements will have mass ratios that are whole number multiples
Multiple Proportions
What law is defined by: the ratio of the volumes of any pair of gases in a gas phase chemical reaction (at the same temp and pressure) is the ratio of simple integers
Combining Volumes
What law is defined by: equal volumes of different gases at the same temp and pressure contain equal numbers of particles
Avogadro’s Hypothesis
What type of mixture has one or more visible boundaries between components?
Heterogeneous
What type of mixture has no visible boundaries between components (components are mixed as individual atoms or ions)?
Homogeneous

What kind of substance is represented by the image?
Pure substance
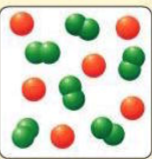
What kind of substance is represented by the image?
Heterogeneous

What kind of substance is represented by the image?
Homogeneous

What kind of substance is represented by the image?
Pure Compound
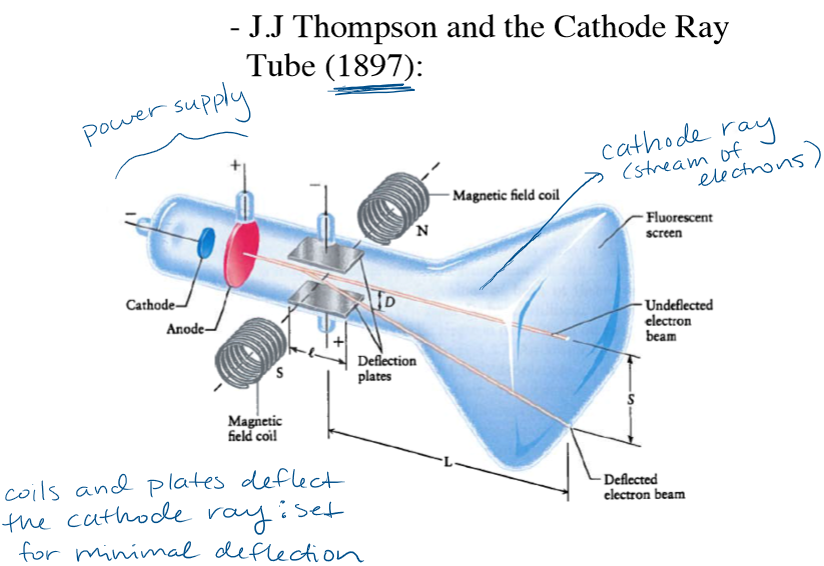
What did the Cathode Ray experiment determine?
Charge to mass ratio of electron
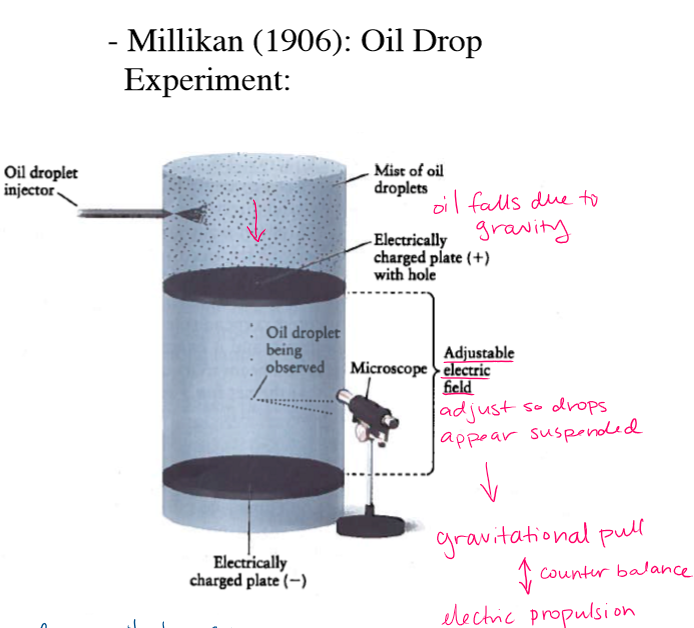
What is the Oil Drop experiment determine?
Charge and mass of electron
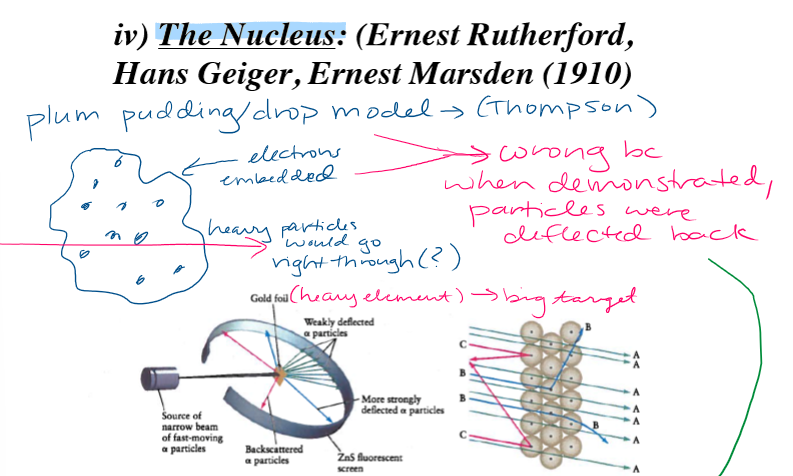
What did the Plum Pudding experiment determine?
Atom is mostly space and nucleus is dense
Atomic radius=______
100pm
Nucleus=______
0.005pm
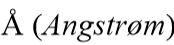
1A=100pm=______
0.1nm
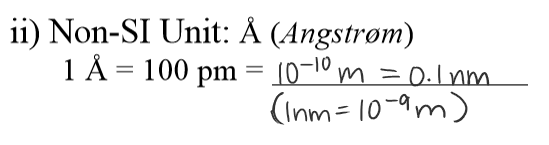
What is the number of protons in an atom of an element (neutral atom) called?
Atomic number
What is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom called?
Mass number
An atom with the same atomic number but different mass number caused by differing numbers of neutrons is called an _______
Isotope

What is the notation in the image called?
Isotope notation
What is 1/12 of the mass of one carbon-12 atom called?
Atomic Mass Unit (amu)
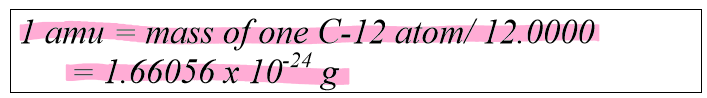
The atomic mass of an element is measured as the ______ ______ of the occurring isotopes
weighted average
1 mole=______
6.02214×10^23
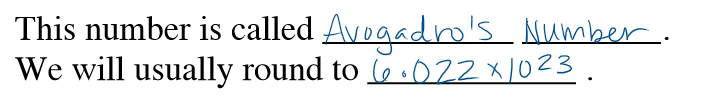
What is the mass of one mole of a substance called?
Molar mass
What are the starting materials in a chemical reaction called?
Reactants
What are the substances which are formed in a chemical reaction called?
Products
The amount of a reactant indicated by a balanced equation is called the ______
Stoichiometric amount
The reactant used up first in a chemical reaction is called the ______
Limiting Reactant
Non-limiting reactants are also known as ______
Excess Reactants
What is the amount of product from the balanced equation called (maximum possible yield)?
Theoretical yield
The ______ of a reaction is the quantity of product that can be obtained from the reaction
yield
What is the actual amount of product obtained in the reaction called?
Actual yield
What is the formula for Percent Yield?
(actual yield/theoretical yield)x100%
The smallest whole number ratio of moles in each substance is called the ______
Empirical formula