Physics: Magnetism and Electromagnetism - Unit 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
two poles of a magnet
North and South
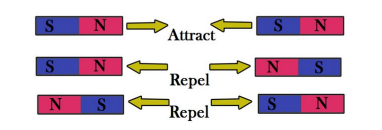
how do these different poles of the magnet interact
like poles repel
unlike poles attract

permanent magnet
a magnet that can produce it’s own magnetic field and will repel and attract other magnets when it is in contact with them
it is made from a magnetic material
it cannot be demagnetized
hard magnetic material
this are materials that get magnetised when an external magnetic field is applied and stay magnetised permanently when the external field is removed
soft magnetic material
this are materials that get magnetised when an external magnetic field is applied but they get demagnetised (lose their magnetic field) when the external field is removed
examples of magnetic materials
iron
cobalt
nickel
steel (iron+carbon)
magnetic field
this is a region surrounding a magnet where other magnets will experience a force
direction of the field lines in a magnetic field point
north to south
effect of the concentration of field lines
if the there is a high concentration of field lines, that means that the magnetic field is strong
if there is a weak concentration of field lines, that means that the magnetic field is weak
production of uniform magnetic field
to produce a uniform magnetic field, you place opposite poles of two magnets across each other, you create a uniform magnetic field where magnetic field lines are separated with a fixed distance between two magnets
how to use a plotting compass
place a compass (containing a needle magnet) on a piece of paper near the field
move the compass to different places on the paper
draw an arrow in each position in the same direction as the needle points
once you have gather enough data, you can join the arrows to make a complete field pattern
what must happen for a magnetic field to be created around a wire
when current flows through a wire, it induces a magnetic field
Fleming’s Left Hand rule


relationship between current, magnetic field and force
direction wise, they all act perpendicular to each other
how to increase the magnitude of the force acting on a current-carrying wire inside a magnetic field
increase the size of a current
increase the strength of magnetic field (use a stronger magnet)
motor effect
a current carrying wire is placed in a magnetic field and experiences a force that pushes the wire
the field from the current carrying wire interacts with the other magnetic field (the magnetic field it is placed in)
so a force is applied on the wire
the force pushed the wire, therefore the wire rotates
how do loudspeakers use current to work
coil is placed inside a magnet
an alternating current in this coil causes a magnetic field
when the field interacts with the magnet, a force is produced (motor effect)
this force pushes and pulls the wire/cone of the speaker, causing it to move in different directions
due to alternating current, the force causes the cone to vibrate
this causes pressure variations in the air (sound waves)
how do microphones convert sound into electrical signals
when sound is produced, the pressure variations in the waves cause the diaphragm to vibrate
coil of wire is connected to the diaphragm, so as the diaphragm moves, so does the coil of wire
the coil of wire is in a magnet so when it moves a voltage is induced in the coil
as there is a complete circuit, a current is also created
how are electric motors kept rotating
a commutator is used, this switches the current direction every half turn, which ensures that the coil keeps spinning
production of an electric current using a magnet and a conductor on a small-scale
moving a coil of wire into a magnet
moving a magnet into a coil of wire
once a voltage is induced, assuming there is a complete circuit, a current will also be induced
how is an electrical current produced on a large-scale
an electromagnet is rotated around a coil
factors affecting the size of an induced voltage
number of turns on the coil of wire
how strong the magnetic field is
how fast you move the magnet
how does a dynamo generate current
coil of wire rotates inside a magnetic field
a commutator is used to ensure it continues rotating in the same direction, therefore keeping the current flowing in the same direction
how is an electromagnetic induction used in alternators to generate alternating current
a coil of wire rotates in a magnetic field
the end of this coil is connected to slip rings which will cause the current to change direction while rotating
this means, alternating current is produced
shape of the magnetic field created around a straight wire when a current is running through
the shape of the magnetic field i circular from north to south
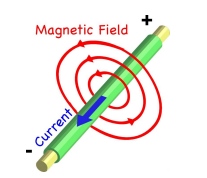

the right hand grip rule
this is used to determine the direction of a current or magnetic field around a wire


solenoid
a coil of wire which turns into an electromagnet when there is a current flowing through it
how can you make a magnetic field in a solenoid stronger
increase the current
use more turns of wire
use an iron core
transformer
this is a device which consists of a primary and secondary coil, which both surround an iron core
a transformer changes the size of an alternating voltage
in a transformer, how does an alternating current in one circuit cause an alternating current in the other
two coils of wire are placed by an iron core
one of the coils produces a changing magnetic field when an alternating current is passed though it
this field can be carried to the second coil through the iron core
the iron core can increase the strength of the field, causing the magnetic field to pass through the other coil
the magnetic field then causes a current in the next coil
what happens in a step-down transformer
in a step-down transformer, the secondary coil has fewer turns
advantage of a step down transformer: it means that the voltage can be reduced to a value safe enough to be used in houses
what happens in a step-down transformer
it can increase efficiency as it decreases the heat loss in transmission lines
this is because, for the same power, a higher voltage will lead to a lower current (P=VxI)
the lower the current, the less energy that is lost since P=I²R
how does a step-up transformer work
the primary coil has fewer turns than the secondary
an alternating current is connected to the primary coil
this produces a magnetic field
the iron core causes that magnetic field to pass through the secondary coil
the magnetic field induces a current in the secondary coil, but as it has more turns in the coil, the voltage will be higher
equation to determine the voltage/number of turns on primary and secondary coils
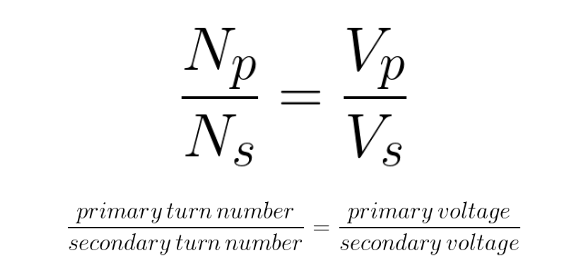
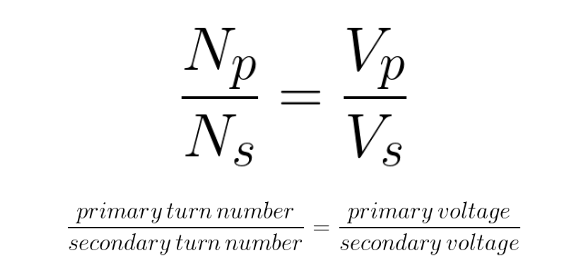
where are step-up and step-down transformers used in the national grid
step-up transformers are used at power stations
step-down transformers are used locally
equation for transformers with a 100% efficiency (using voltage and current)
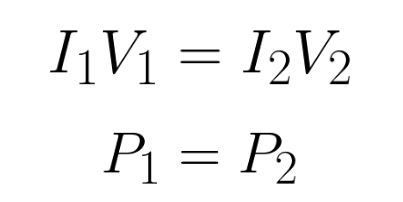
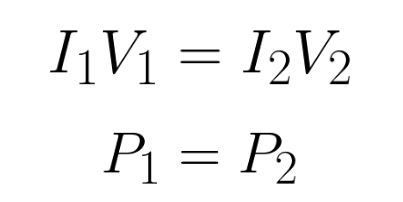
advantages of transmitting power in high voltage cables
high voltage cables lead to a lower current in the wires, reducing any energy lost to the environment via heating, and increasing the efficiency since P=1²R