Chapter 22: Genetic Testing and Treatment
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What services and types of information does a genetic counselor provide?
-Provide information on modes of inheritance, disease risks & symptoms, available tests & treatments
-Interpret direct-to-consumer genetic tests & assist other healthcare professionals w/ genetic information on their practices

How are the services that a genetic counselor provides different from those of a nurse or a physician?
While a genetic counselor provides genetic-based information for the client and works with the patient to deliberate and necessary tests and care, nurses or physicians focus more on a broader aspect of medical care in order to treat specific illnesses or diagnoses.
What are some reasons for prenatal genetic testing
Tests to see if embryo has genetic abnormalities, defects, or anomalies
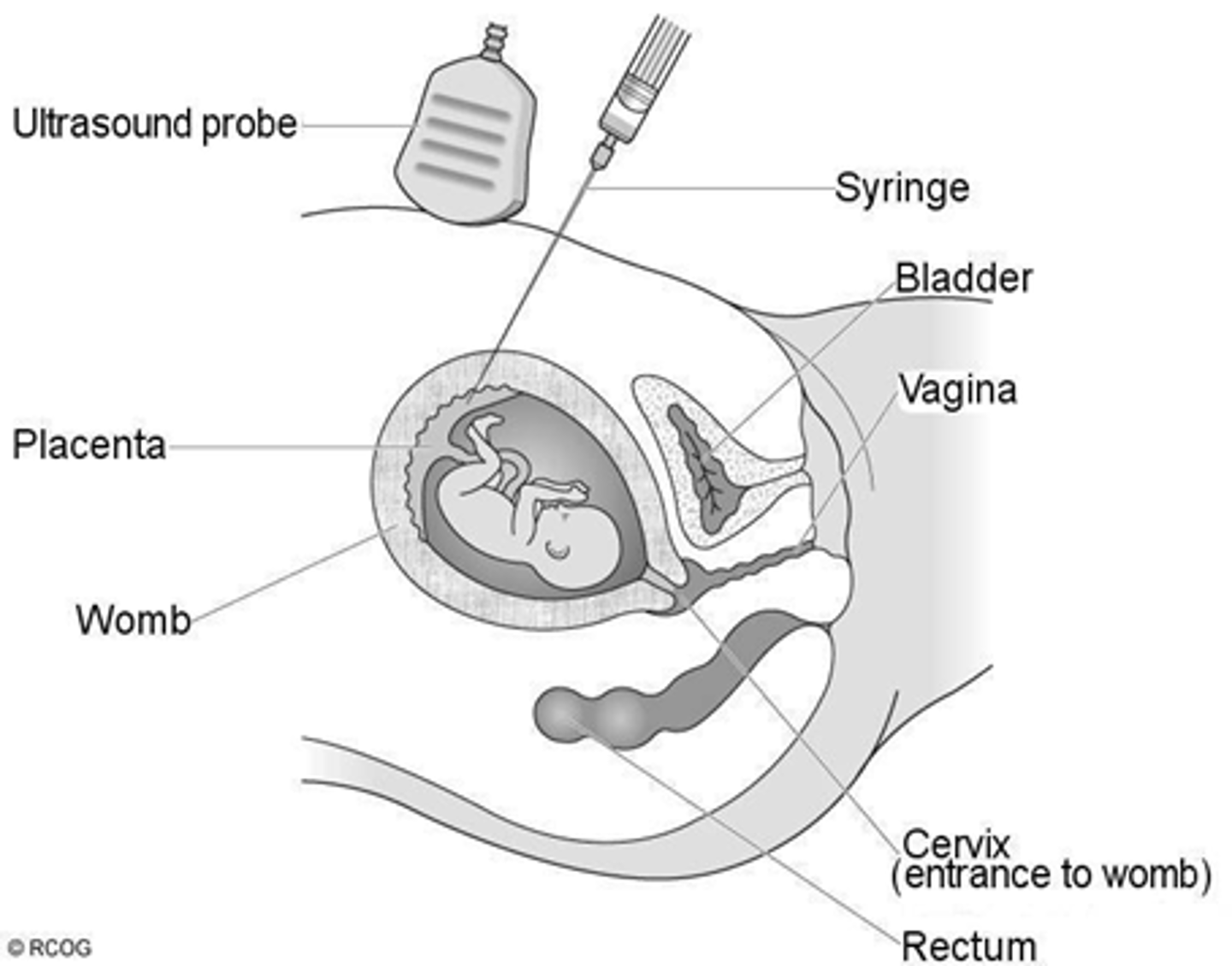
What are some reasons for newborn genetic testing
-Usually tests for inborn errors of metabolism
-Identifies unusual metabolites or chemical imbalances that indicate disease via chemistry
What is the first genetic test that was created for newborns
Guthrie test for PKA
What are some reasons for children genetic testing
detects very small deletion and duplications that are associated with:
Autism spectrum disorder
Developmental delay
What are some reasons for adult genetic testing
detect risk of developing cancer
family planning
What are some of the issues associated with direct-to-consumer testing for inborn athletic ability
Tests are too simplistic
Testing for a single gene is not enough, you need access to resources, training, and facilities with equipment
What are some of the issues associated with direct-to-consumer testing for nutrigenetics
Companies were "scamming" consumers with inaccurate information and making pitches to purchase costly supplements
What is a Pharmacogenetic test
detects a variant of a single gene that affects drug metabolism
What is Pharmacogenomic test
detects variants of multiple genes or gene expression patterns that affect drug metabolism
Advantages of using pharmacogenetics and pharmacogenomics to select the best drugs for patients
-Identify patients likely to have adverse reaction
-Select drug most likely to be effective
-Monitor response to drug treatment
-Predict course of illness (prognosis)
Treatments of genetic diseases
-Removing affected body part (amputation)
-Replacing affected body part or biochemical with material from a donor (transplantation)
-Delivering pure, human proteins derived from recombinant DNA technology
-Refolding correctly a misfolded protein Blocking gene expression (gene silencing)
-Using gene therapy to add wild type alleles without removing mutant alleles
-Using gene editing and genome editing to replace, delete, or add alleles
Ex-vivo therapy
applied to cells outside of body that are then returned via IV infusion or into spinal fluid

In-vivo therapy
applied directly to an interior body part through catheter inserted and snaked into appropriate organ
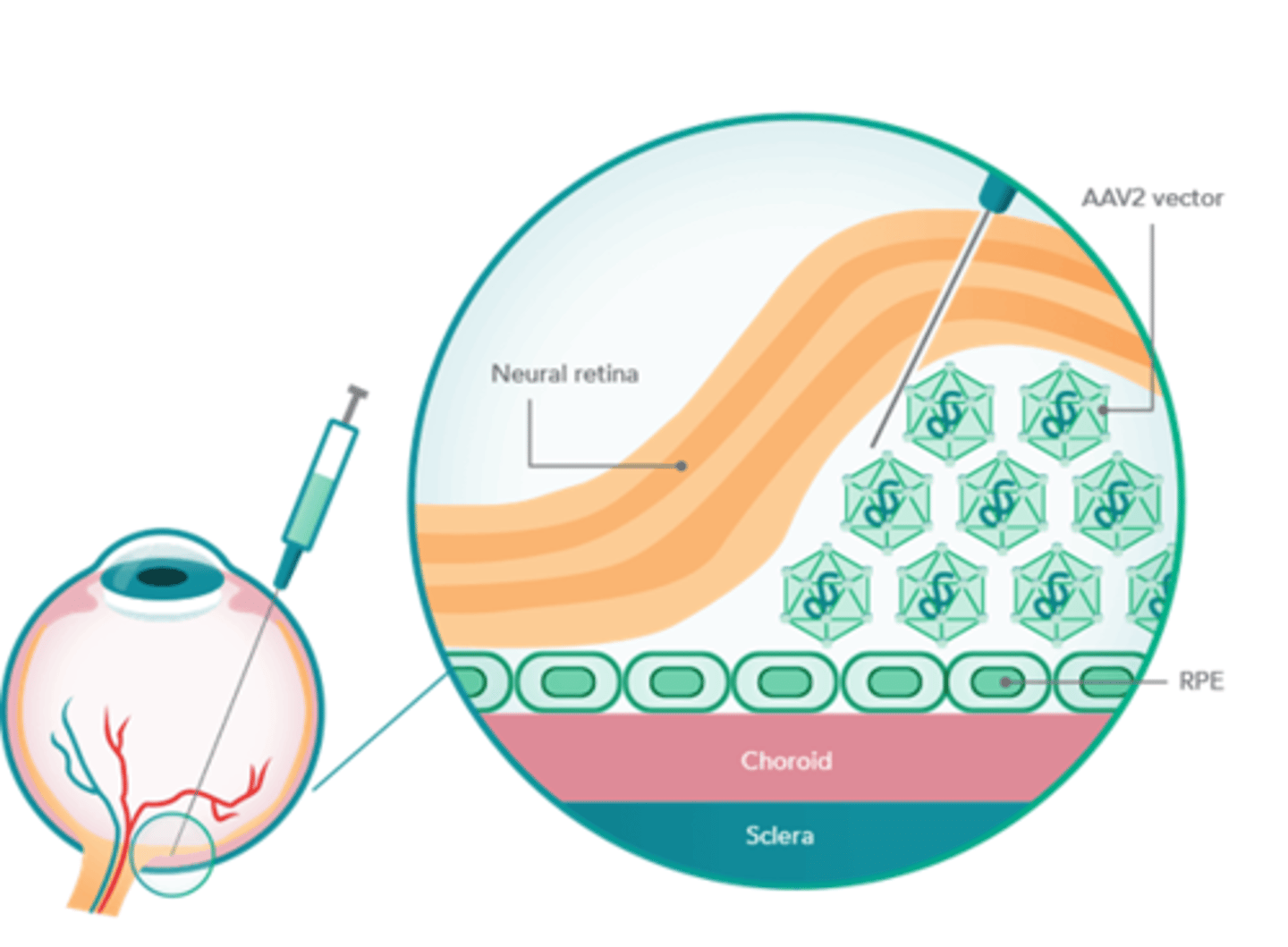
Is ex-vivo therapy or in-vivo therapy more invasive
in-vivo
Describe adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency
-Can cause severe combined immune deficiency (SCID)
Describe what happened with Ashanthi DeSilva and adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency
Leukocytes (WBCs) harvested and redesigned to harbor functional ADA genes > reinserted back to her (ex-vivo) gene therapy- doing well!
Describe ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency
Causes build upon ammonia > brain function is affected
Describe what happened with Jesse Gelsinger and ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency
Treated using adenovirus vector into his liver > liver failure, high hemoglobin, and elevated ammonia > brain dead 🙁
Germline gene therapy
gamete or zygote alteration heritable changes; NOT done in humans; transgenic organisms (usually)
Somatic gene therapy
corrects only the cells that the disease affects; NOT heritable
Why is CRISPR-Cas 9 considered a possible replacement for gene therapy?
More precise type of gene therapy
-Delivers a gene to a specific part of genome, and can also replace, remove, or add a gene.
-Can act at multiple precise sites in the genome.
Gene therapy
adds correct DNA sequences may insert into a chromosome at random or remain outside (episome)
Gene editing
corrects DNA sequences by adding, deleting, or replacing DNA at mutation site