A+P exam #1
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Anatomy vs Physiology
Anatomy: form, structure, relationship
Physiology: function, #, body dynamic/animated workings
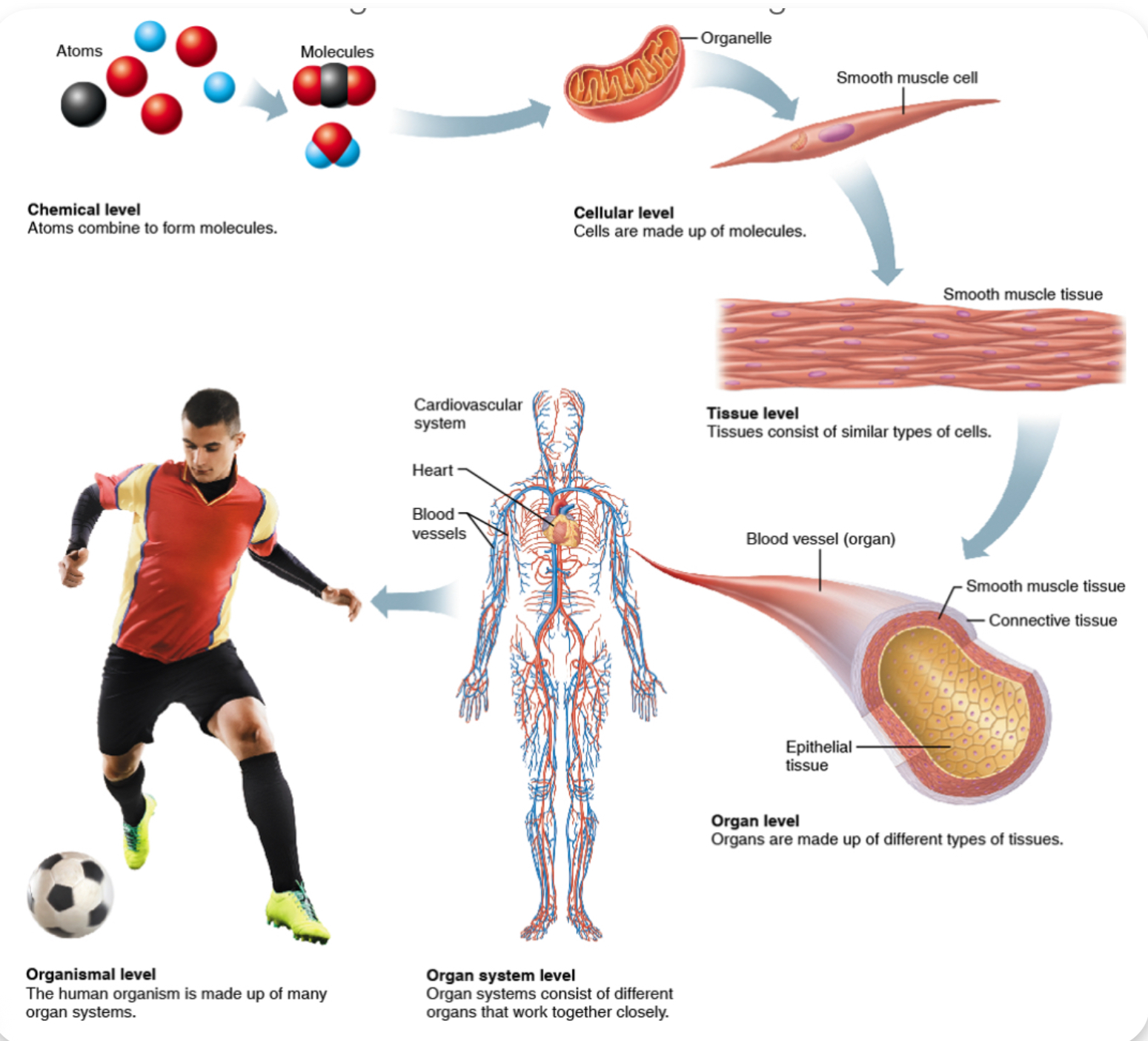
Levels of organization
Responsiveness/excitability
reflexes, ability to sense changes in environment and respond to, seen with all body cells just different with kind, helps with homeostasis
Multicellular organisms vs unicellular for digestion
multi- breaks down into simple molecules, goes to blood and body cells, cells work together, if group is indispensable injury/loss can disable/destroy the body
Uni- cells are digestion factory
Metabolism- what are the types (3)?
all chem reactions in body cells that are regulated by hormones from glands
catabolism- breaking substances into simple building blocks
anabolism- building blocks → more complex substances
cellular respiration- nutrients + O2 → ATP
Why is body temperature a survival need?
if too low reactions decrease and eventually stop and vise versa, muscular system releases the most heat
Why is atmospheric pressure a survival need?
force that air exerts on the body, need for proper breathing/gas exchange
high altitudes- decrease in AP and air is thin so gas exchange may be inadequate for cell respiration
What are the three plant derived nutrients that we need? What do they do for us?
carbs- many energy fuel for cells
vitamins/minerals- needed for chem reactions and O2 transport in cells, calcium (mineral) help make bones strong and is needed for blood clotting
What are the two animal derived nutrients that we need? What do they do for us?
proteins+ fats- help build cell structure
fats- reserve for energy-rich fuel
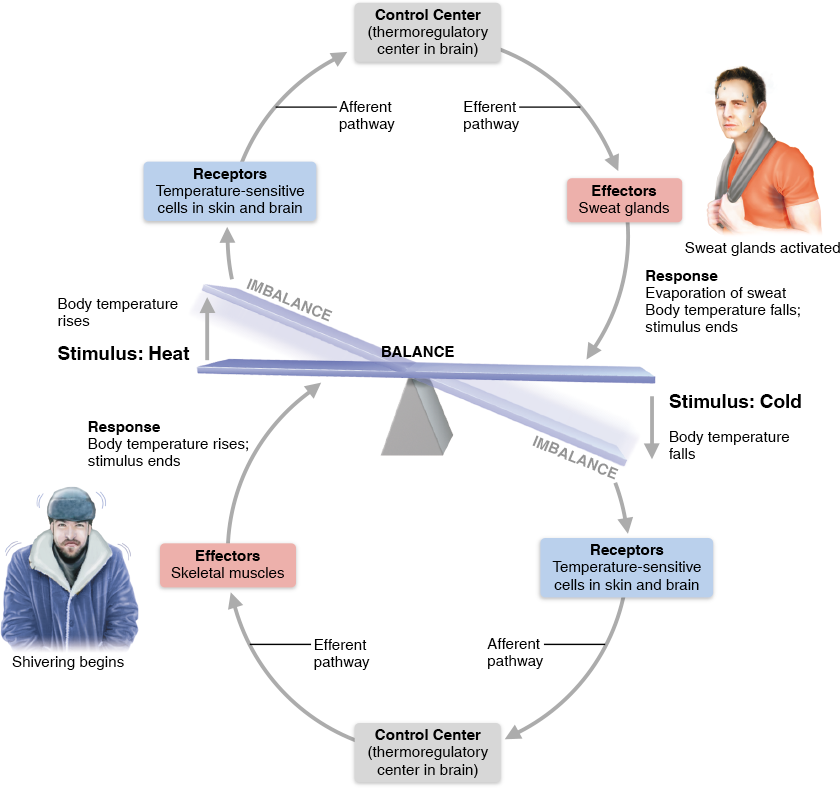
all homeostatic control mechanisms involve at least _ components working together to control the ____
3, variable
Control Center
determines set point (level for variable to be maintained), compares input to set to and determines response if needed
afferent pathway → approaches CC → exits to efferent pathway
Effector
carries out response for CC to stimulus, reduces so control process stops and vise versa
Negative feedback mechanism
most homeostatic control, output shuts off/reduces go effects of stimulus, of in opposite direction to get ideal value
ex. heart rate, bp, breathing, O2, CO2, mineral blood levels
Neural control mechanism example
the withdraw reflex
hormonal mechanism example
control of blood sugar- if high pancreas (CC) secretes insulin→ tells cells to absorb more glucose
if low stimulus for insulin release ends
Positive feedback loop
aka cascades, initial response increases go stimulus which leads in increase in response, continues and amplifies og stimulus, control of infrequent events w/o continuous adjustments w/ only local effects ex. labor contractions, blood clotting
What is homeostatic imbalance?
when neg feedback mechanisms are overwhelmed and destructive pos feedback takes over because when older systems are less efficient/internal environment becomes less and less stable → increase in risk of illness/aging changes/disease
Why use anatomical position (2)?
For reference, so radius and ulna are parallel, standing posterior with palms posterior and feet slightly apart
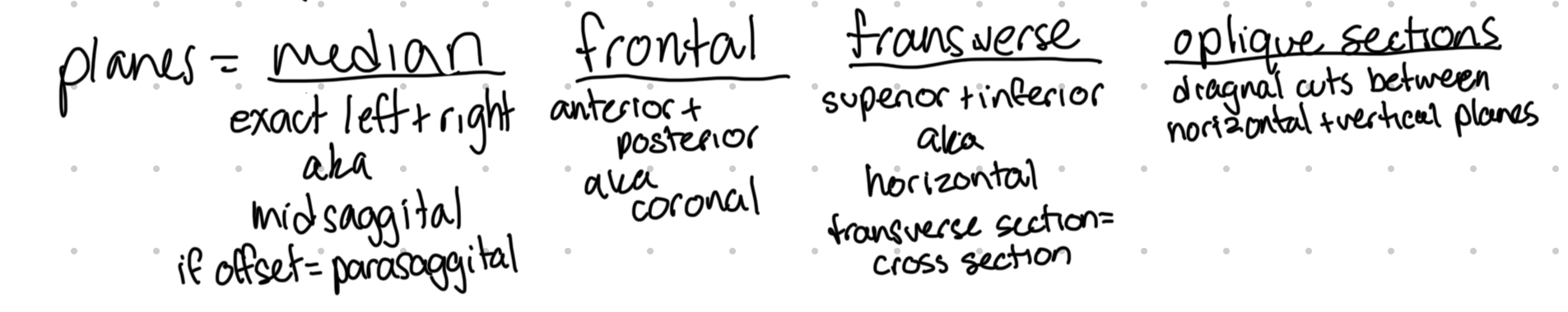
oblique sections
diagonal cuts between horizontal and vertical planes
What is a parasaggital cut?
offset median/midsaggital cut
mediastinum surrounds ______, ________, and other _______ organs
esophagus, trachea, thoracic
What two cavities are in the dorsal body cavity?
cranial cavity, vertebral cavity
What two cavities are in the ventral body cavity? What are their sub types?
Thoracic cavity- super mediastinum, pericardial, pleural
Abdomino- pelvic cavity- abdominal (organs of digestive), pelvic (reproductive, digestive, urinary, rectum)
What divides the ventral cavity into the thoracic cavity and abdominal- pelvic cavity?
Diaphragm
What separates living organisms from nonliving objects?
maintain boundaries, movement, responsiveness, digestion, metabolism, excretion, reproduction, growth
What are the two different kinda of closed serous membranes? How do you name serous membranes?
Visceral (covers organs), parietal (lines cavities)
type of covering+specific cavity
What are serous membranes? What is serous fluid?
thin, double layer membrane of organs/cavities in ventral body cavity
fluid- lubricates, secreted by most membranes
What are the three names of cavity that are used to name the type of serous membranes?
Peritoneum (adomino-pelvic), pericardial, pleura
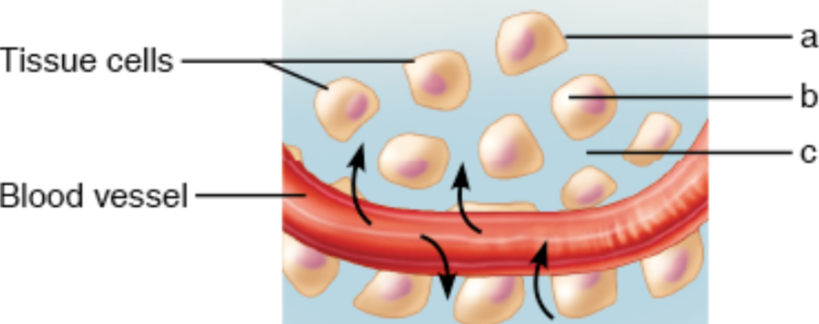
This is a picture of tissue cells and part of blood vessels. Cell nutrients and wastes are exchanged across important boundaries between fluid compartments. Name the boundary (a) and fluid in the compartments (b and c).
a- cell membrane
b- interstitial fluid
c- blood plasma
Why is the positive food back loop called that? What event stops it?
Changes proved in the same direction to amplify or stimulus, stops when problem is fixed (ex blood clotting)
Is thirst a part of a negative or positive feedback loop?
Negative because ur constantly trying to keep in check, balance beam
What are the three types of cuts
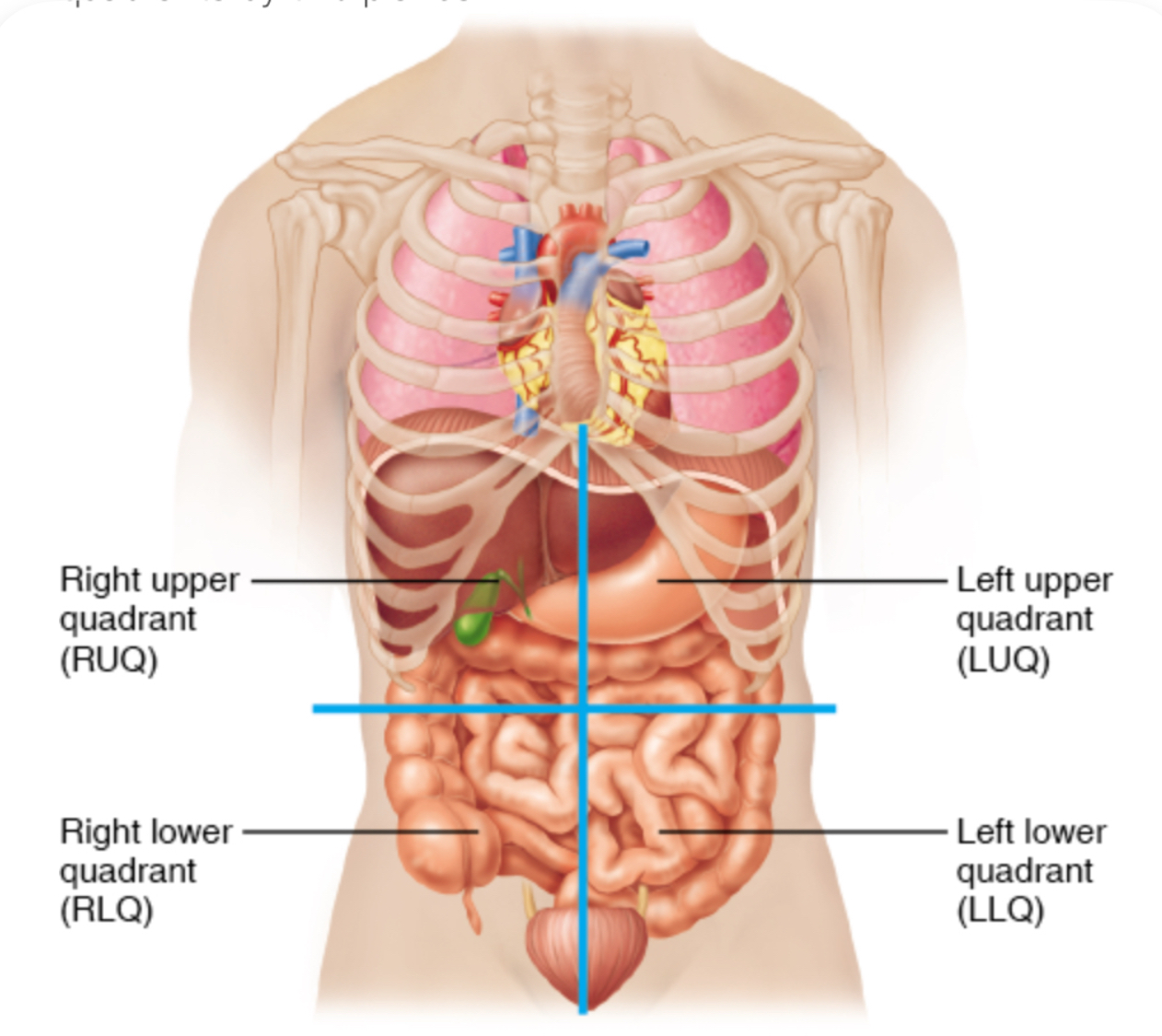
What organs are in each quadrant?
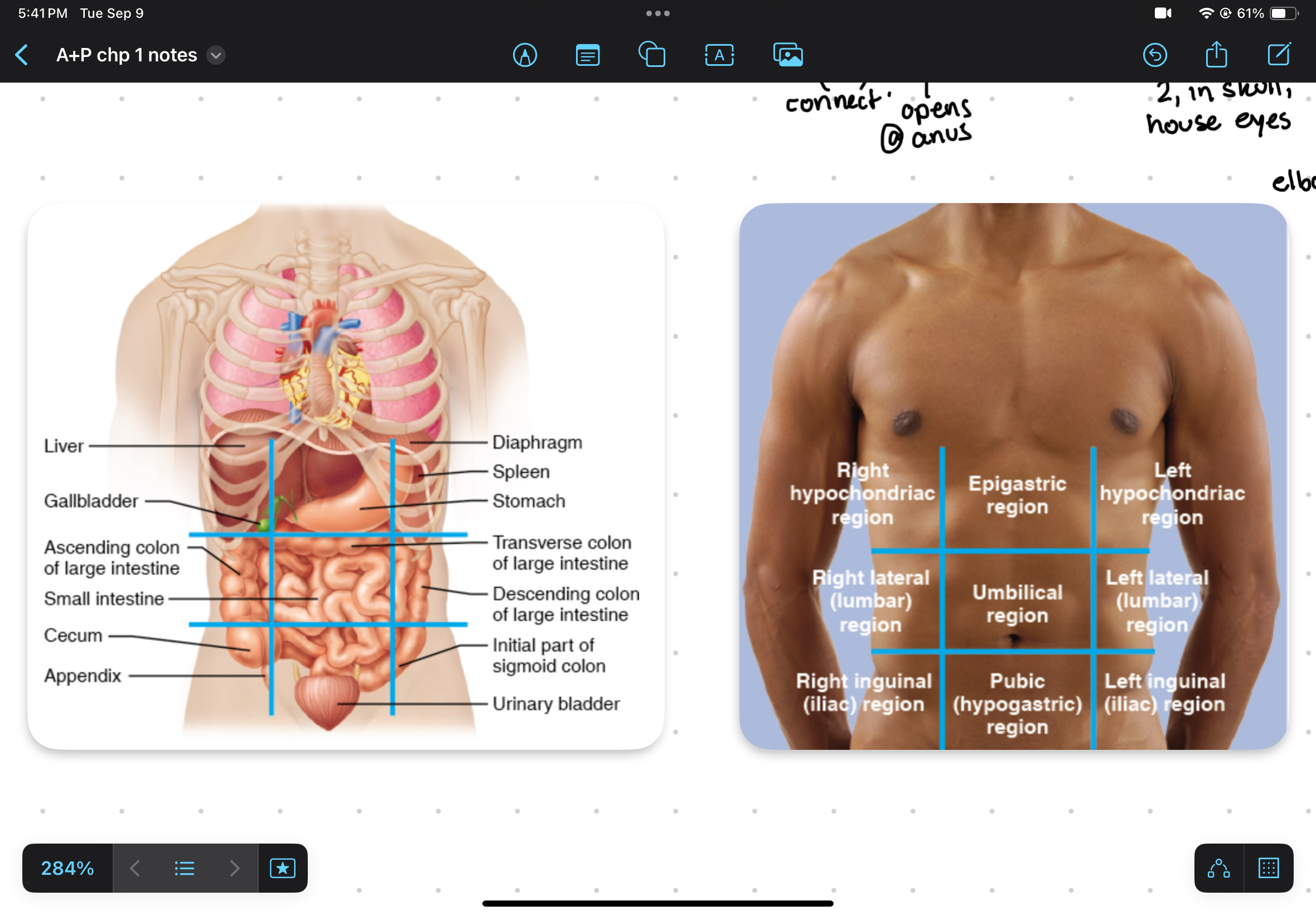
What’s the name of the 9 regions? What organs are in each?
What is the function of muscle tissue (2)? What are the 3 subsets?
Attaches to bone, movement by contracting (pulls bones/skin), cardiac, tightly packed well vascularized cells, skeletal (muscles to bone), smooth (in walls of hollow organs)
How does muscle tissue contract?
uses myofilaments (network of actin+myocin)
Skeletal muscle tissue- description, function, location
packed by CT in organs
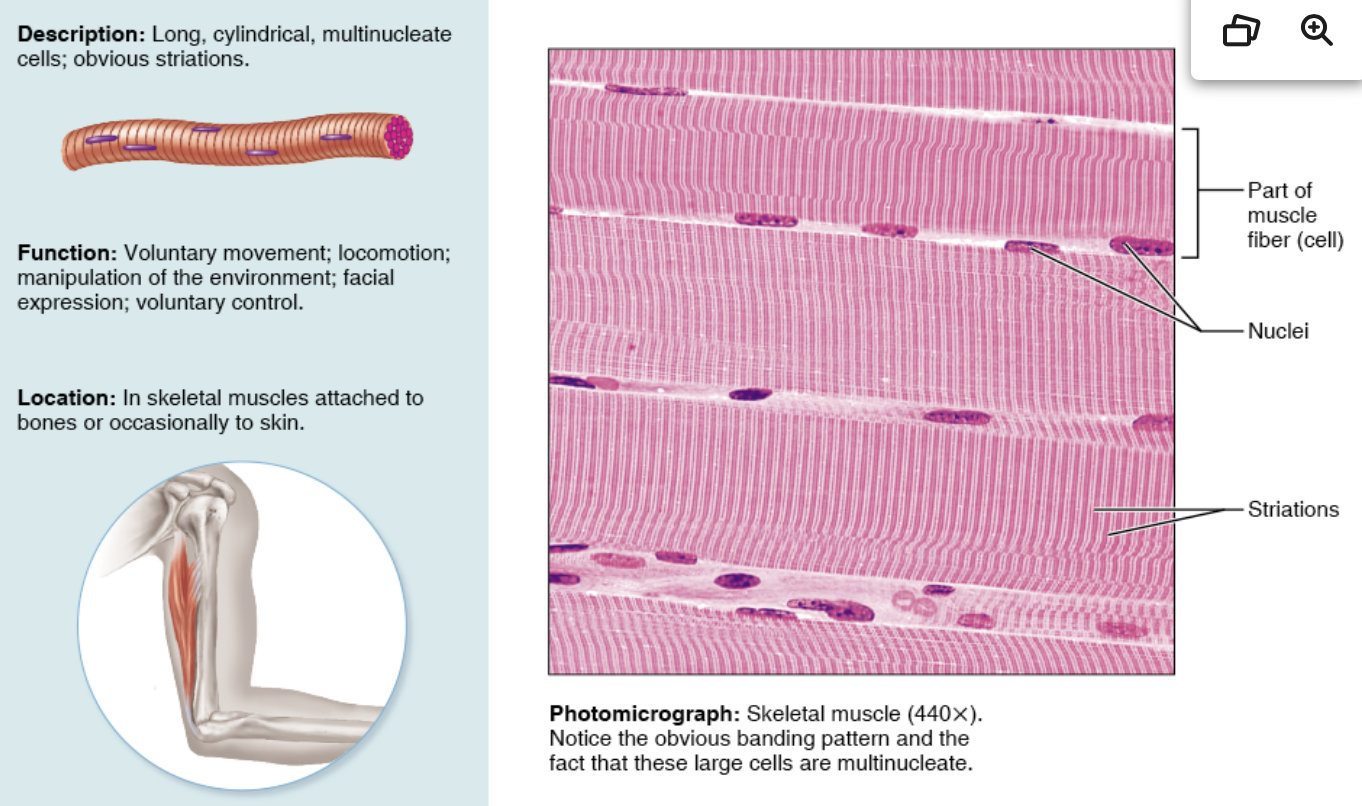
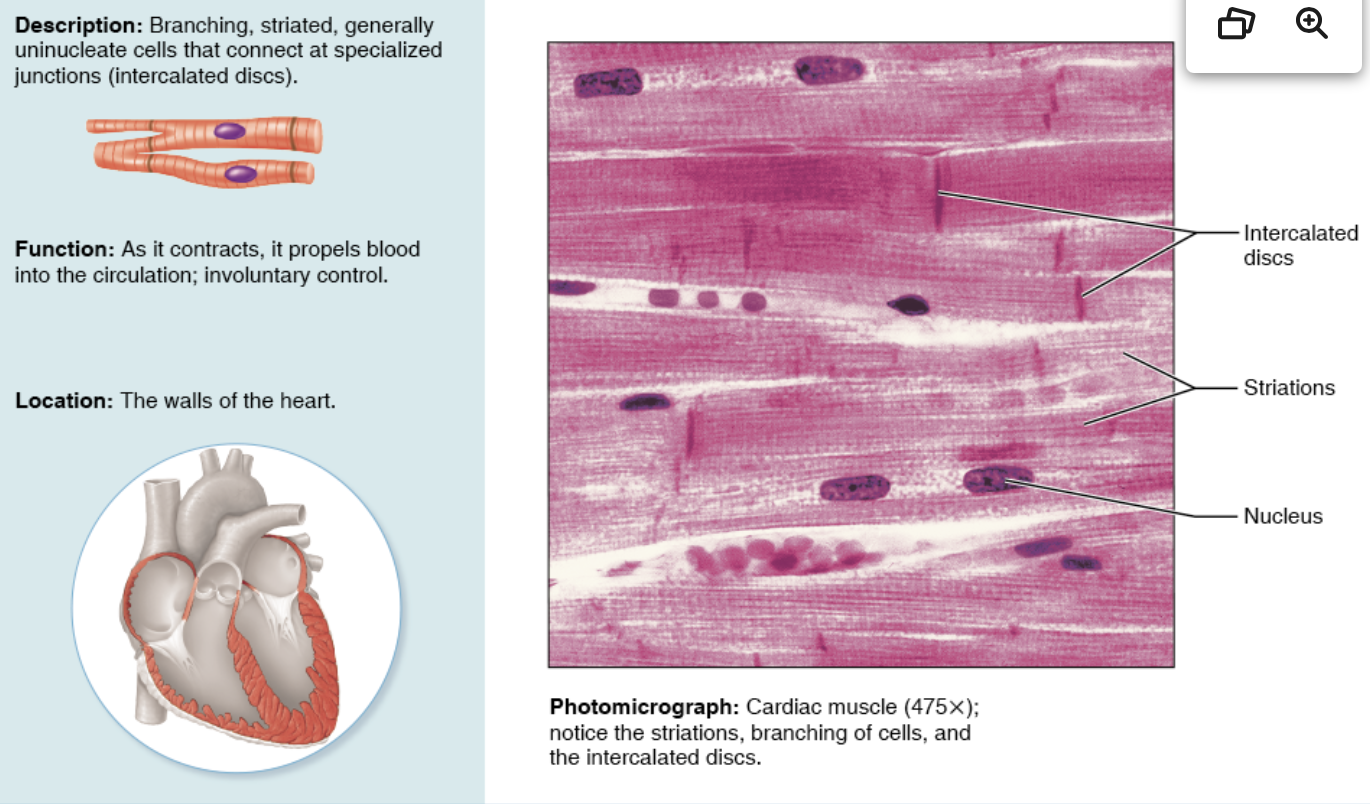
Cardiac muscle tissue- description, function, location
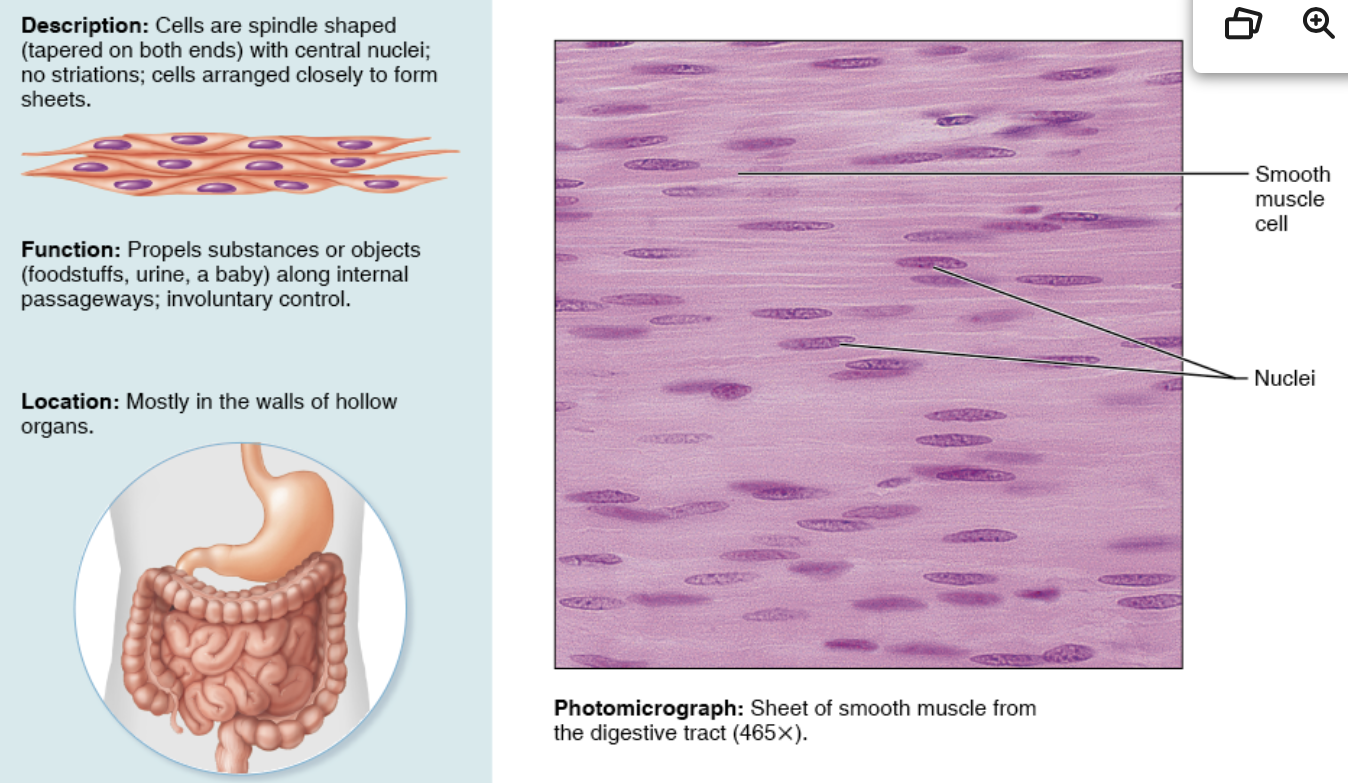
Smooth muscle tissue- description, function, location
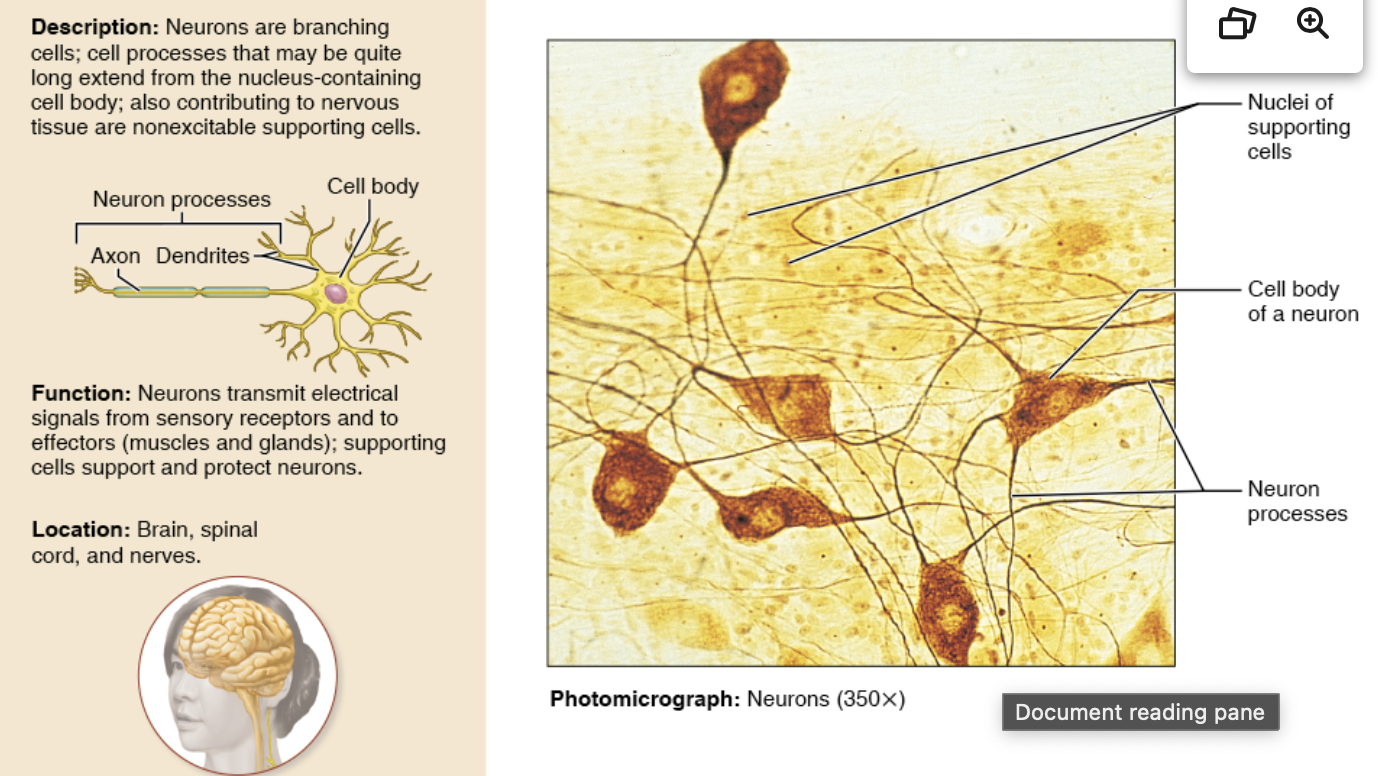
Nervous tissue- description, function, location
neurons- highly specialized to respond to stimuli using dendrites
supporting cells- are glial cells/neuroglia, nonconducting, support, insulate, protects
What are the functions of epithelial tissue (6)?
creates boundaries, protect, absorb, filtrate, secrete, excretes, sensory reception, lining of digestive tract/other hollow organs, glands, skin surface
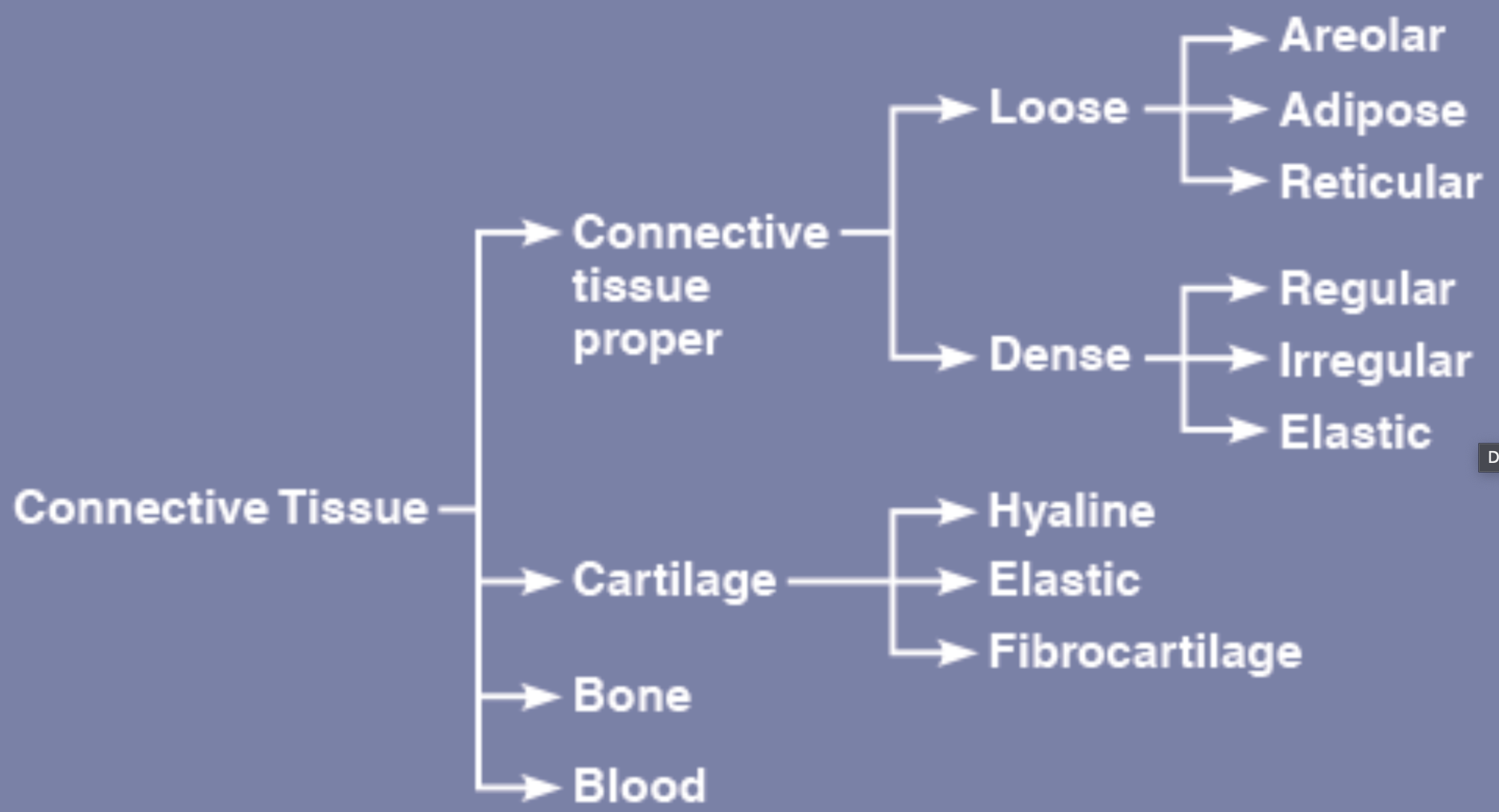
What are the functions of connective tissue? Where is it seen? What is it made of?
supports, insulates, stores, transports, protects, binds other tissues together
bones, tendons, fat and other soft padding tissue,
composed of cells, ground substance and fibers
2 main characteristics of CT
1) extracellular matrix= ground substance+fibers, nonliving, separates living tissue cells, helps w/ support/tension
2) common origin from mesenchyme an embryonic tissue
What are the three type of CT fibers? What protein is each made of? What does it contribute to the CT function?
1) collagen- made from collagen, gives strength
2) elastic- made from elastin, for stretch and recoil
3) reticular- made from diff types of collagen, surrounds and supports
What do the suffixes of CT cell types mean? What does each of them do?
-blast= immature cell- miotic, secretes ground substance/fibers and mature
-cyte= mature cell- maintain matrix health, can go back to blast to repair/regenerate
What are the 8 types of CT cells?
fibroblasts (CT proper), chondroblasts (cartilage), osteoblasts (bone), hematopoietic stem cell, adipocytes, WBC, mast cells, macrophages
Areolar loose CT
function- wraps/cusions organs, has macrophages, helps w/ inflammation, holds/conveys tissue fluid
location- under epi, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
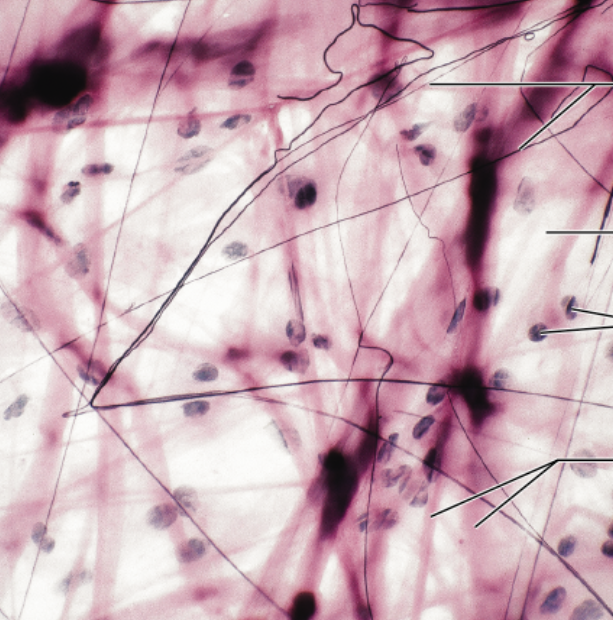
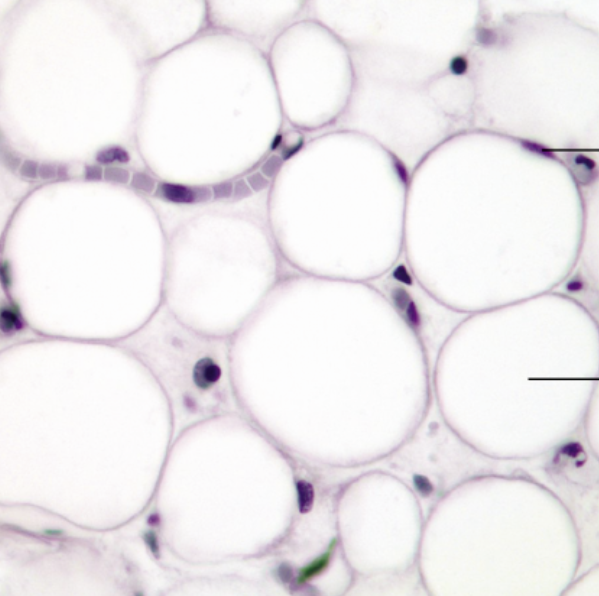
Adipose loose CT
function- reserve food fuel, insulates, supports/protects organs
location- in subcutaneous tissue, around kidneys/eyes, in ab and breasts
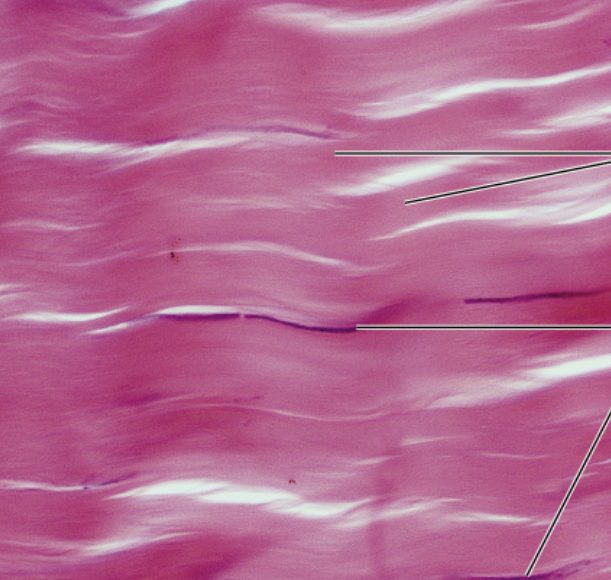
Regular dense CT
function- attaches muscle to bone/muscle or bone to bone, withstands stress from one direction
location- tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses
Elastic dense CT
function- recoil after stretching, maintains flow of blood through arteries
location- walls of large arteries, in ligaments in vertebral column, walls of bronchial tubes
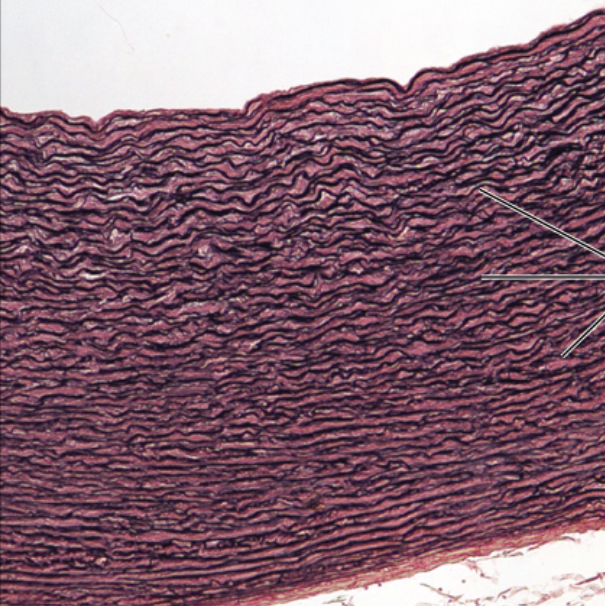

Hyaline cartilage CT
function- supports/reinforces, resilient cushion, resists compressive stress
location- embryonic skeleton, ends of long bones, costal cartilage, cartilage in nose/trachea/larynx
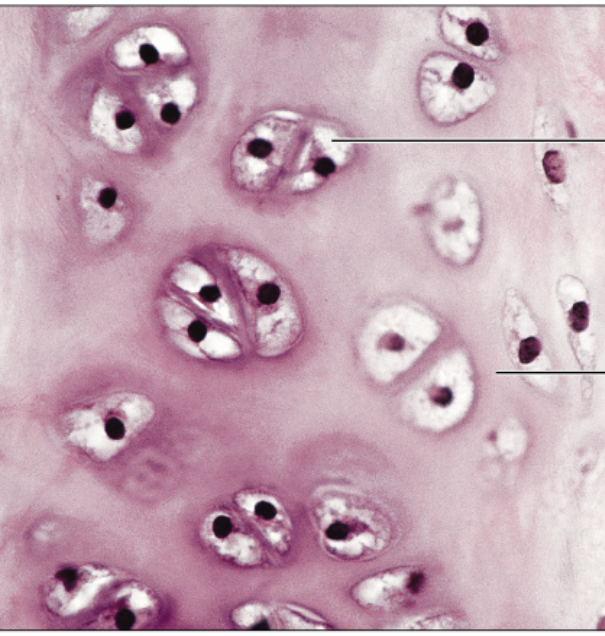
Elastic cartilage CT
function- maintains structure shape w/ flexibility
location- external ear, epiglottis
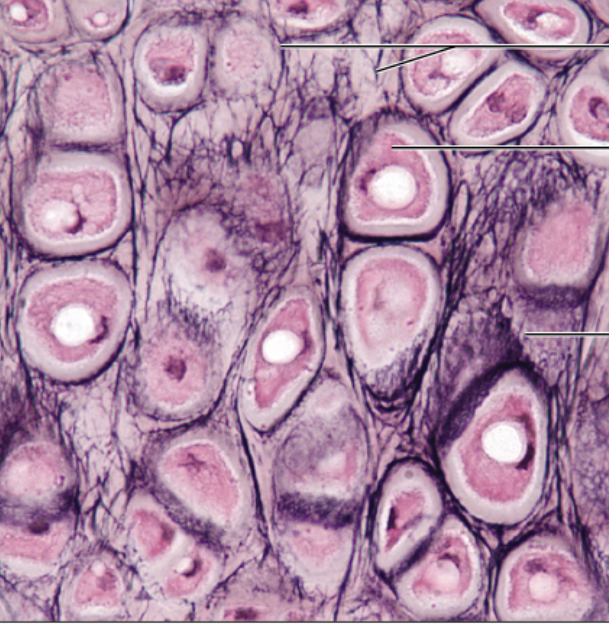
Fibrocartilage CT
function- tensile strength, absorbs compressive shock
location- intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint
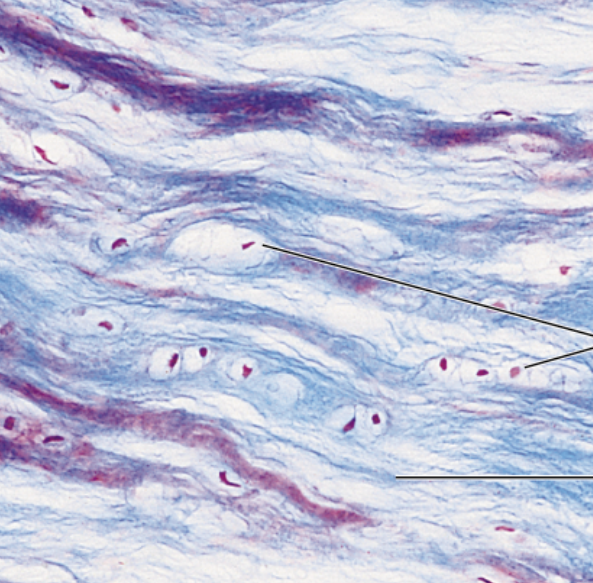
Macrophages
devour foreign material/dead tissue cells, in loose CT, bone marrow, lymphoid tissue, in CT/matrix
Mast cells
cluster on blood vessels, detect foreign microorganisms and initiate inflammatory response to cytoplasm
types of CT
What are the characteristics is epithelial tissue (7)?
Highly/tightly cellular in sheets, polar, avascular (needs nutrients to diffuse from CT), cell junctions, supported by connective tissue, innervated (has nerves), highly regenerative
Basal lamina
part of basement membrane between ET and CT, adjacent to basal surface, thin supporting sheet, noncellular, adhesive w/ glycoproteins/fine collagen fibers excretes by epi cells, selective filter, scaffolding for epi cells to repair wounds
Reticular lamina
part of basement membrane, deeper than basal lamina, extracellular material w/ collagen protein fibers from underlying CT
How are the epi cells sheets help together (2)
cell junctions- prevent substances from leaking through space
desmosomes- keep cells from pulling apart
Epithelial tissue is the only type with polarity (apical and basal surface). Why is this important?
For protection and to be best at different jobs
apical= open to world/internal organ, is smooth/slick or has microvilli
basal= attached to underlying CT
Microvilli
on some ET, finger like extensions of plasma membrane, increase surface area for absorption/secretion,
Motile cilia
on some ET, propel substances along free surface
Stratified epithelia are built for protection or to resist abrasion. What are simple epithelia better at?
absorption, secretion, filtration
What are the three types of epithelial cells?
Cuboidal , squamous, columnar
How do you name types of epithelial tissue?
amount of layers + shape of cells
simple= 1 layer
stratified= 1+ layers
Stratified squamous- function/location
protects underlying tissue in high abrasion area
nonkeratinized= moist linings of esophagus, mouth, vagina
keratinized= epidermis, dry epithelium
Simple columnar- function/location
absorption, secretion of mucus/enzymes/etc, ciliated type propels mucus/reproductive cells by ciliary action
nonciliated- stomach-rectum, gallbladder, excretory ducts of some glands
ciliated- small bronchi, uterine tubes, some parts of uterus
Simple cuboidal- function/location
secretion/absorption
kidney tubules, ducts/secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface
Simple squamos- function/location
allows materials to pass by diffusion/filtration where protection isn’t important, secretes lubricating substances in serosae
kidney glomeruli, air sacs, lining of heart/blood vessels/lymphatic vessels/serosae
What is the job of the endocrine glands? Are there ducts?
Release hormones in body that travel in blood, no ducts
Exocrine vs. endocrine glands
exo- to external skin/cavities, has ducts, in mucous, sweat, oil, salivary glands, liver, pancreas
endo- internal, no ducts, produces hormones, in digestive tract lining (mucosa), brain
What are the two types of exocrine glands?
Unicellular (goblet cells that produce mucin) and multicellular
How are multicellular exocrine glands classified?
according to the structure of their ducts and secretory regions
What are the two types of secretion for exocrine glands? How does it work? What glands go through these processes?
Merocrine= secrete via exocytosis (active process of vesicles to to surface and release), one cell can do multiple times, ex. salivary glands in mouth
Holocrine= cell ruptures to release secretion and a bit of cell fragments, makes new cells after, seen with only sebaceous glands on hair follicles
3 types of membranes
1) mucous membranes- lines open body cavities
2) serous membranes- line closed body cavities/organs
3) cutaneous membranes- skin