WWI and the Conflict in Palestine
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:40 PM on 3/8/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
1
New cards
How did the end of the Ottoman Empire change the Middle East?
When the Ottoman Empire was on the verge of political collapse by the end of the 19th century, European powers like Britain, Russia, and France were interested to take over the Middle East. Heading into WWI, Britain expressed interest in positioning themselves to take control of the Middle East. They believed it was important for strategic and economic reasons. In 1870, Brittain gained control over the Suez canal, which is located on the trade route to South and East Asia, and they desired to protect and maintain their control over the canal.
2
New cards
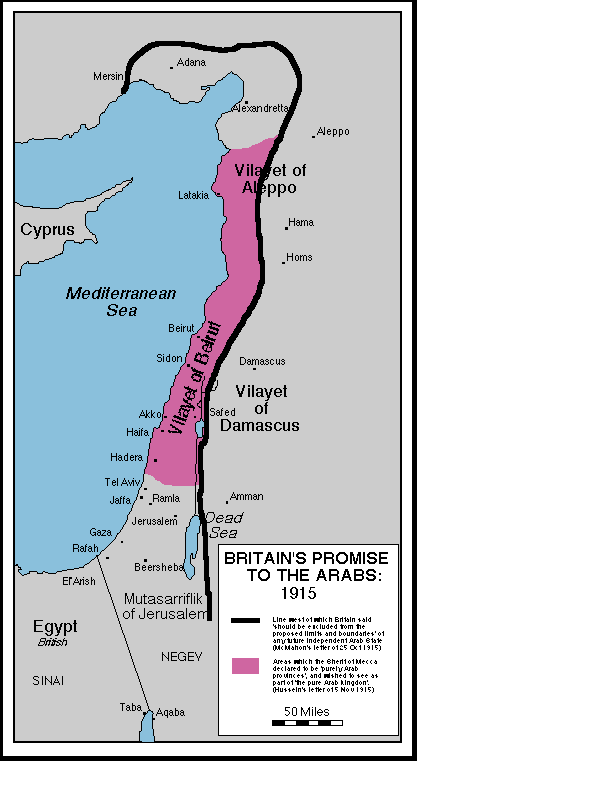
What was the Hussein-McMahon Correspondence?
Before WWI, Hussein informed the British of his opposition to the Ottoman Sultan, and sought British support to establish an independent Arab Kingdom. The Sultan proposed Arab support against the Ottomans if Britain would grant independence of all the Arab provinces of the Ottoman Empire. The British were interested in encouraging an Arab revolt against the Ottomans, and desired their support. McMahon and Hussein exchanged eight letters and Britain ambiguously recognized support of Arab independence in return for Arab support agains the Turks. Hussein argued that ALL the Arab territories should be included, however McMahon instead identified areas to be reserved for British control. The final boundaries were left unresolved, and in June of 1916, Hussein declared independence of the Arabs from the Turks. After the war, a dispute arose regarding whether Palestine was promised to the Arabs as part of the correspondence. Hussein claims that although Palestine was never explicitly mentioned, it was implied, while in the Churchill-White Paper, the British clarified that it was not part of the deal.
3
New cards
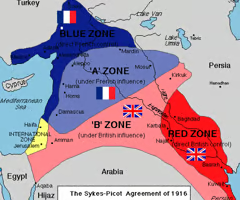
What was the Sykes-Picot Agreement?
In May of 1916, a secret agreement to divide the Ottoman territory was signed between Britain and France. The agreement supports an independent state in areas A & B, while Palestine was intended to become an international region
4
New cards
What is the Balfour Declaration?
On November 2, 1917, Lord Balfour (Britain's foreign minister) wrote a letter on behalf of the British government to Lord Rothschild, where he states, "His Majesty's Government views with favour the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people, and will use their best endeavours to facilitate the achievement of this object." The British support for a Jewish homeland in Palestine was the first time in history any major empire favoured the idea of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. The League of Nations accepted the declaration in 1922.

5
New cards
What did David Ben Gurion have to say about the Balfour Declaration?
Ben Gurion states the Britain had made a significant gesture to the Jews by recognizing the Jews existent as a nation and a right to country. Ben Gurion states that now the must build the national home with body, soul, strength, and capital.
6
New cards
What did Dawoud El-Alami have to say about the Balfour declaration?
The British were unsure how the war would end, and made promises to different groups to keep them on their side. The Balfour declaration includes a condition that the rights of locals should not be harmed, however he believes that the British promise was unfair.
7
New cards
What occurred at the 1919 Paris Peace conference?
At the end of WWI, the Allies met at Versailles to draw up a peace treaty ending WWI. They redrew the map of Europes, as many pre-war empires no longer existed, and also decided that the Arab lands will be divided by the League of Nations and a mandate system would be established. Britain would assume rule over Iraq, Palestine, and France would assume rule over Syria and Lebanon. Within 10 years these lands would be self-governed, but allied intervention was implemented in order to ensure that they remain stable and reliant on Allied powers.
8
New cards
How did Faisal respond to the Paris Peace conference?
Faisal realized that during the Paris Peace Conference, it was clear that the plan for an independent Arab state would not come to be In July 1919, Faisal, the son of Hussein, called for an independent Greater Syria, incorporating Syria, Lebanon, and Palestine.
9
New cards
What was the Faisal-Weizmann Agreement?
Faisal originally rejected the establishment of a Jewish commonwealth in Palestine. Despite Arab rejection, Chaim Weizmann was convicted that if Fasal educated himself regarding the Zionist movement, he would accept their movement. Chaim tried to reach an understanding to accommodate both Arab and Jewish national aspirations in Palestine. Faisal then stated that the Arabs are sympathetic with the Zionist movement, as both parties are looking for a reformed and revived Middle East. He said that the Arab movement and the Jewish movement complete one another, as they are both nationalists movements not imperial. There is room in Syria for both the Jews and Arabs, and neither can be successful without the other. Faisal looks forward to a future where they both help each other, so they can have a place in the community of civilized peoples. In March of 1920 however, the French rejected Faisal's proclamation as a king, and by July, Fasial fled from Damascus. Once Faisal left Syria, Faisal relinquished from Weizmann, and became a vocal opponent of Zionism.
10
New cards
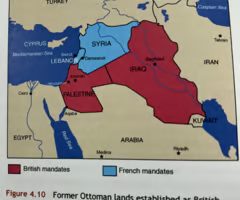
What was the San Remo Conference?
In April 1920, the Allies met in San Remo, Italy, where the territories of the Ottoman Empire were formally turned over to Britain and France. The San Remo conference led to the introduction to the Mandate system, where Britain received two areas of land, being Iraq and Palestine, while France received Syria and Lebanon. It was internationally-backed agreement that recognized Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan and Israel. Also, at San Remo the allied powers recognized the legitimacy of the Jewish people's aspiration to constitute themselves as an organized national community in their ancient homeland. The policy in the Balfour Declaration became a legally binding international treaty between the major powers.
11
New cards
What happened during the 1920 Arab Riots?
The Arabs felt betrayed by the British due to their Mandate system. This system clearly did not reflect the Hussein-McMahon Agreement. The Arabs fully rejected the mandate system and the recognition of the Jewish claims to the land. This led to violence erupting among Arab leaders, where they made false accusations that the Jews were planning to destroy all Muslim Holy sites. Jerusalems mayor called on Muslims to "spill Jewish blood" and a newspaper declared "If we don't use force against the Zionists we will never be rid of them. The crowd chants "we will drink the blood of the Jews" Arabs entered the Jewish quarter in Jerusalem, where they attacked Jews and ransacked their homes. Riots lasted 4 days, where 300 Jews were evacuated and seven were killed. Hundreds were also wounded.
12
New cards
What is the Haganah?
The Haganah was formed out of response to the Arab riots as there were beliefs among the Jews that the British were unable to protect the Jews. The original role of was to defend Jewish neighbourhoods and farms from Arab attacks, and the groups would serve under the direction of the Yishuv (Jewish political leadership committee.)
13
New cards
How did a distinct Palestinian movement arise?
Jews were gaining full support from the British, so the Palestinian committee created its own national movement. It states that the territory of Palestine, is a distinct political entity; Jewish political and moral rights in Palestine are totally rejected; The unity of Palestinian Arabs is more important than loyalty to religion, geography, or clan; The British administration is called to stop sale of land to Jews; Future Jewish immigration should not be permitted; The British administration is called to recognize the Arab as the legitimate representative of the populatio..
14
New cards
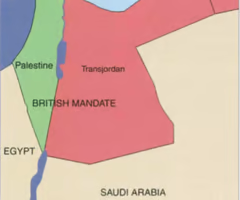
What was the 1922 Churchill-White Paper?
In an attempt to calm the rising tension, British colonial secretary Winston Churchill tried to clarify to both the Arabs and Jews that the terms of the Balfour declaration will only apply to the territory west of the Jordan River (reassuring Arabs that it wasn't Britains intent that the whole of Palestine should constitute a Jewish national home.) The British also stated that the promised Jewish national identity of the Balfour declaration has already been achieved, as Jews already have their own school, language, and electric companies, making it necessary to declare a Jewish state; where Jews will be permanent residents. However Jewish immigration should not be permitted to exceed whatever the economic capacity of the country at the time to absorb new arrivals.
15
New cards
How is the Churchill-White paper seen as a compromise?
For the Arabs, Palestine does not become a Jewish state, and they get the territory east of the Jordan river as exclusively theirs. The Jews get to continue moving to Palestine, with permanent resident status and establishing an institutional identity. The Brits benefit because the more that Jews move to Palestine, the more the economy is built up and the more the Brits will make.
16
New cards
What was the British reaction to the Churchill White paper?
The paper ensures that Britain will be successful economically. It sends a clear message to Arabs that the Jews have no national rights on the east side of the Jordan River, that the Arab fears of a Jewish state are unfounded and therefore rioting is not necessary, and that the British allowed continued immigration making both the Jews and Britain happy, while making it clear that there will be no Jewish state.
17
New cards
Why do the Arabs and Jews not like the Churchill White Paper?
The Arabs want all the land, without the Jews, and they dont want more Jewish immigration. The Jews don't like it as although they'd be allowed to move to the part of Palestine that they want to, they don't achieve the goal of Jewish statehood. The Churchill White paper was successfully endorsed by the the British House of Commons. The Jews unhappily accepted the plan, while the Arabs rejected it.