Humoral Immunity, Immunoglobulins, Complement
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms related to humoral immunity, immunoglobulins, and the complement pathways, hypersensitivity types, and fever pathophysiology from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
B-Cell Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes that mature in the bone marrow and differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells or Memory B cells (clonal selection); central to humoral immunity.
Humoral
antibody
GAMED, 5 heavy chains
2 light chains, kappa and lambda
Memory B-Cells
Long-lived B cells formed during primary response; provide rapid protection upon re-exposure.
Clonal Selection
Process by which antigen selects specific B- or T-lymphocytes to proliferate; generates memory and plasma cells.
Plasma Cells
Differentiated B cells that secrete antibodies (immunoglobulins) in large quantities.
Immunoglobulin (Ig)
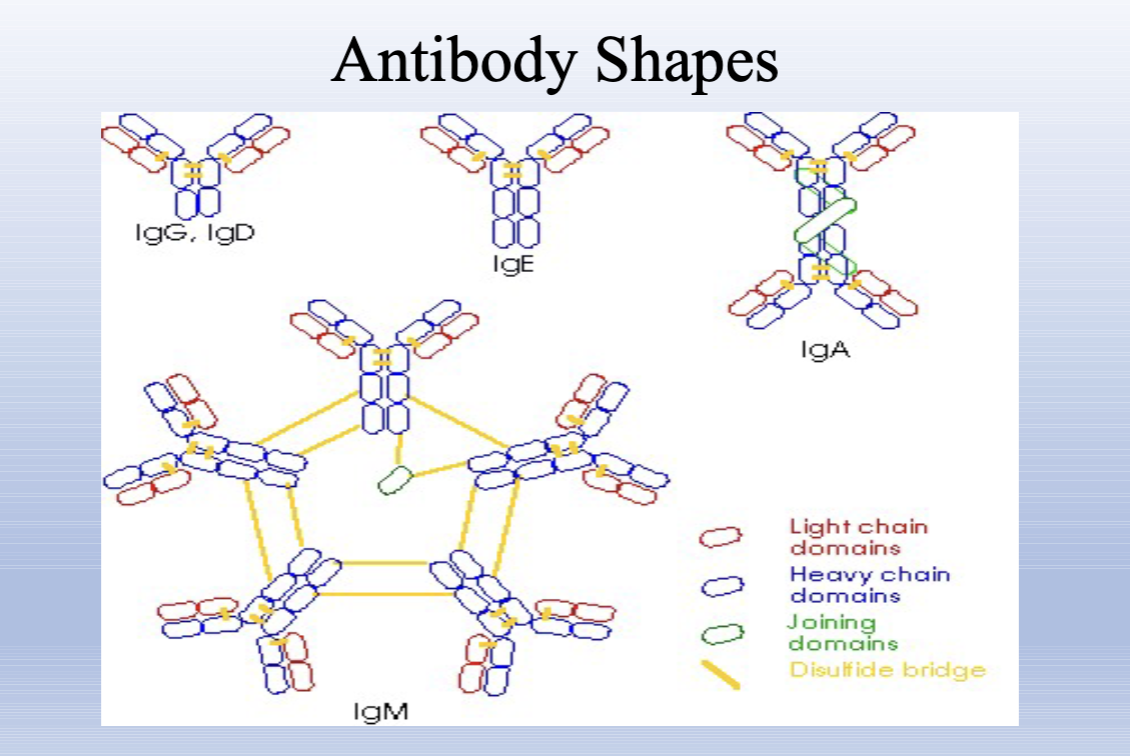
Antibodies; glycoproteins with heavy and light chains; five isotypes with distinct functions.
Heavy Chains
Long polypeptide chains forming the Fc portion; determine antibody class (G, A, M, E, D).
Light Chains
Kappa or lambda polypeptides that pair with heavy chains to form antigen-binding sites.
Primary v Secondary Antibody Response
When antigen encountered, Ab detectable in serum after long lag period (7-10 days)
small clone of B cells and plasma cells for the antigen is made and serum Ab concentration rise for several weeks
After rising several weeks (IgM, IgG) both decline to low levels, 1st Ab order are IgM,IgG,IgA
IgM levels decline earlier than IgG
Second encounter = rapid response (3-5 days) due to memory cells
Memory cells proliferate, amount of IgM similar to 1st response, IgG much more and last longer
Antibodies
Immunoglobulins made of glycoproteins that inactivate antigens and elicit an extracellular response
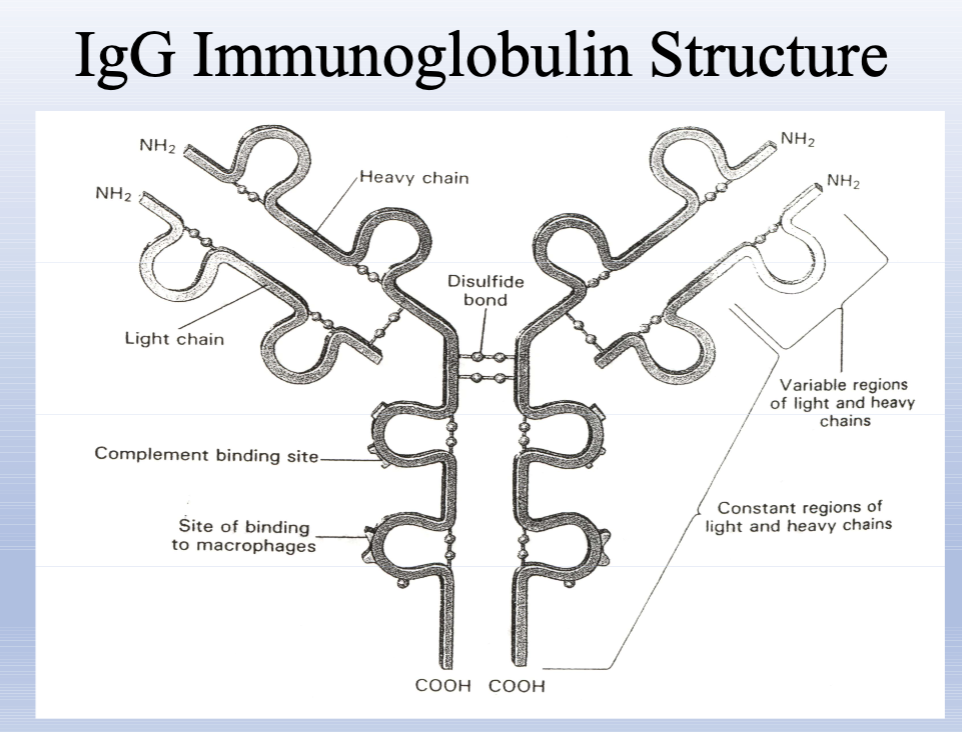
Y shaped molecule
Immunoglobulins
Composed to two long polypeptides, heavy chains, and two shorter light chains.
bound bu disulfide bonds
Stem of Y only heavy chains (Fc)
Diverging arm are light and heavy chains (Fab)
Fab Fragment
Antigen-binding region of the antibody containing variable regions of heavy and light chains.
Fc Fragment
Stem of the antibody; constant region of heavy chains; interacts with Fc receptors and complement.
IgG
Most abundant serum antibody (≈80%); crosses the placenta; activates complement (need 2); opsonizes; provides passive immunity via milk.
functions as an opsonin (coats antigen to make susceptible for phagocytosis by neuts)
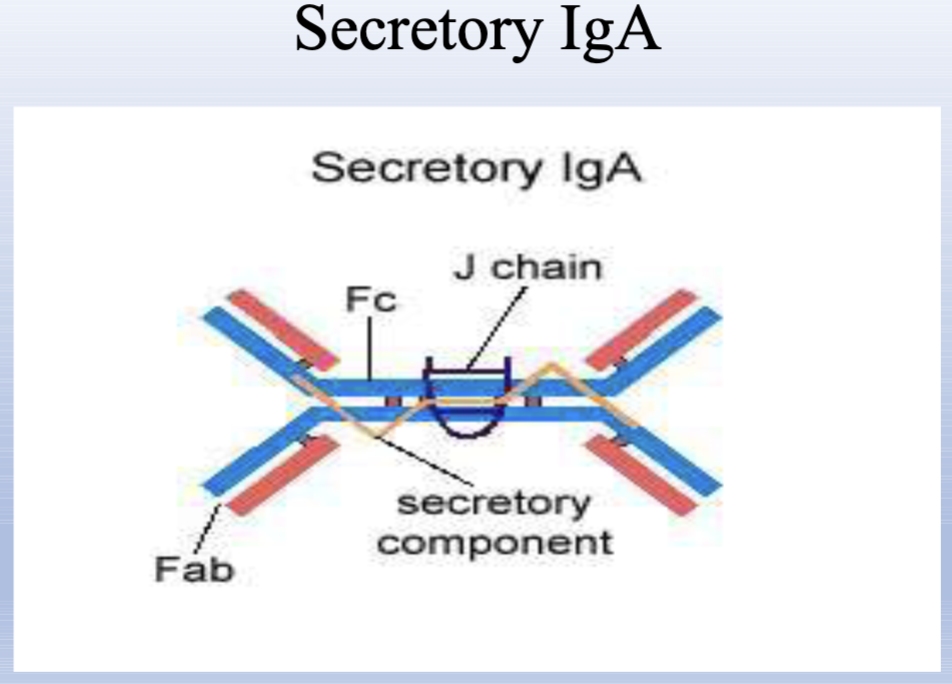
IgA
10-15% of immunoglobulins, Secretory antibody found in tears, saliva, gut secretions, nasal secretions, and milk; contains J chain and secretory component; protects mucosal surfaces.
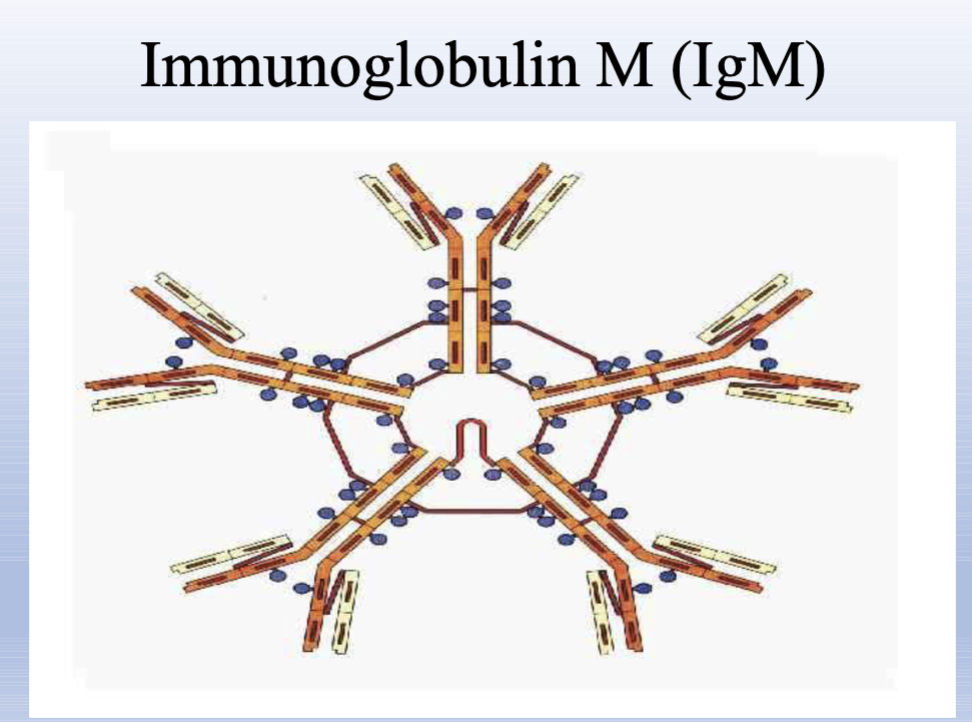
IgM
5-10% of immunoglobulins, Pentameric antibody with up to five binding sites; first to appear in primary response; activates complement.
IgE
Less than 1%, Antibody of allergy and antiparasite defense; binds to mast cells/basophils causing degranulation and release of mediators.
elicits hypersensitivity reactions and helps eosinophils kill parasites
IgD
Less than 1%, B-cell surface receptor that helps recognize antigens and activate B cells to differentiate into plasma cells.
Antibody
Immunoglobulin molecule that binds antigen via its Fab region and interacts with the immune system via its Fc region.
Antigenic Determinant (Epitope)
Specific part of an antigen recognized by an antibody or T-cell receptor.
Antigen Presenting Cell (APC)
Cells that process and present antigen to T cells via MHC; includes dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells.
Complement System
Group of ~20 plasma proteins secreted by hepatocytes and monocytes that aid antibody responses and inflammation; activated by classical or alternative pathways.
Classical Pathway
Complement activation initiated by antibodies (IgG/IgM) bound to antigen; involves C1 complex.
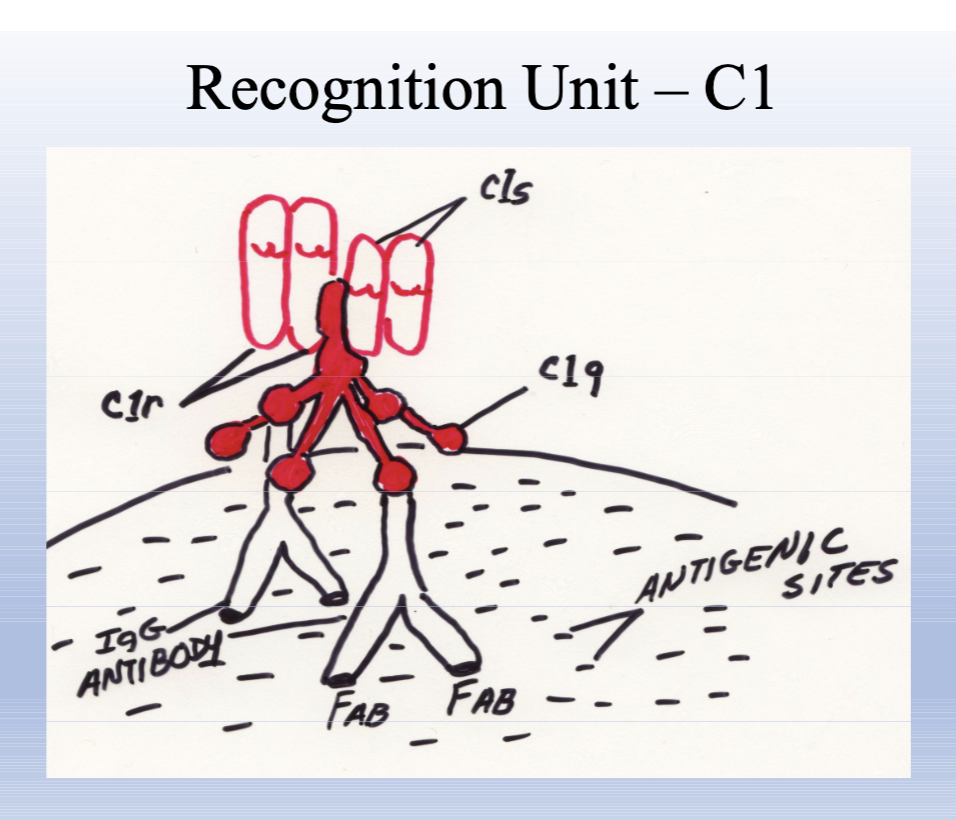
Recognition Unit - C1 complex (C1q, C1r, C1s)
Activation Unit
Membrane Attack Unit
Each unit contain certain # of complement proteins, all needed for lysis of the target cell
Alternative Pathway
Antibody-independent complement activation triggered by the microorganism itself or substances secreted. (bee venom, snake bites, etc.)
C1 Complex (C1q, C1r, C1s)
Recognition unit of the classical pathway; C1q binds antibody Fc to 2 IgG or one IgM; activates C1r and C1s.
C3 Convertase
Enzyme complex (C4-C2) formed in classical pathway to cleave C3 into C3a and C3b.
C3a
Anaphylatoxin that promotes inflammation by triggering mediator release.
C3b
Opsonin that also participates in forming C3 convertase and immune adherence.
C5 Convertase
Complex (C4-C2-C3b) that cleaves C5 into C5a and C5b.
C5a
Anaphylatoxin promoting inflammation and neutrophil recruitment.
Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
C5b together with C6-9 forms a pore in target cell membranes causing lysis.
Immune Adherence
Mechanism by which opsonized cells bind phagocytes via C3b sites, promoting phagocytosis.
Immune Mechanisms of Tissue Injury
Hypersensitivity Type 1-3 all require a specific Ab against an exogenous(foreign) or endogenous(self) antigen
Hypersensitivity Type I
Immediate Hypersensitivity, IgE-mediated reaction with mast cell degranulation; e.g., urticaria, asthma, angioedema.
Hypersensitivity Type II
Cytotoxic antibody reactions; IgG/IgM bound to cell surfaces; complement-mediated lysis or phagocytosis.
Hypersensitivity Type III
Immune complex-mediated; circulating antigen-antibody complexes deposit in tissues causing inflammation.
Hypersensitivity Type IV
Delayed-type cell-mediated hypersensitivity; T cells activate macrophages; granulomas; contact dermatitis.
Fever (Pyrexia)
Elevated body temperature due to infection/inflammation, mediated by pyrogens acting on the hypothalamus via PGE-2.
Pyrogen
Substance that causes fever; exogenous (endotoxins) or endogenous cytokines that raise the hypothalamic set point.
Septic Shock
Endotoxic shock from endotoxin (LPS) from gram-negative bacteria; massive cytokine release causing hypotension and organ dysfunction.
Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
Innate immune receptors on macrophages and dendritic cells recognizing microbial components; trigger cytokine production.
IL-1, IL-2, IL-6, TNF
Cytokines that stimulate hypothalamic PGE-2 and mediate fever and inflammation.
PGE-2
Prostaglandin that mediates fever by acting in the hypothalamus.
Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) Roles
Process and present antigen to T cells via MHC, initiating adaptive immunity.
Primary Antibody Response
Initial response to antigen; lag of about 7-10 days; IgM appears first, followed by IgG; antibody levels rise and then fall.
Secondary Antibody Response
Faster and stronger response upon re-exposure; predominately IgG with higher and longer-lasting levels.