GCSE Economics paper 2
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
economic growth
growth in GDP( value of output) over time
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value added of goods and services produced in the country in a year
rate of growth =
change in gdp/ original gdp * 100
GDP per capita
GDP divided by population
Boom
A period of rapid economic growth and high unemployment
recession
a period when the country's GDP falls for 2 or more consecutive quarters
determinants of economic growth
1. investment - increased investment in capital makes businesses produce more goods and services
2. changes in technology - makes capital more effective increasing the quantity it can produce
3. education and training - this increases the skill of the labour meaning a country and output more
4. labor productivity - more output per worker over a period of time
5. size of the workforce - increases the amount a country can produce
6. discovery of natural resources- stimulates economic growth
Benefits of economic growth
- rise in living standards: GDP per capita increases when the rate of growth is higher than the rate of growth of the population
-A reduction in poverty: higher tax revenue ~ increased budget for benefits and training
- increased in education and training
- rise in employment
Costs of economic growth
- environmental costs
- air pollution
- global warming
- congestion
- loss of non-renewable resources
- lower quality of life
- inequality
- inflation
employment
the use of labour in an economy to produce goods and services
unemployment
occurs when workers are willing and able to work at the current wage rates are unable to find employment
claimant count
The method of measuring unemployment according to the number of people who are claiming benefits
Labour Force Survey
A measure of unemployment based on a survey using the ILO definition of unemployment
level of unemployment
The number of people in the working population who are unemployed.
unemployment rate =
number of unemployed/ workforce * 100
seasonal unemployment
unemployment caused by a fall in demand during a particular season.
frictional unemployment
unemployment caused by time lags when workers move between jobs
structural unemployment
unemployment caused by a permanent decline if an industry or industries
cyclical unemployment
unemployment caused by a lack of demand in the economy
aggregate demand
the sum of all the demand in the economy
Benefits of unemployment
- workers need frictional unemployment to allow the movement of jobs
- wage rates are low since there is a surplus of workers available
- decrease in inflation due to the Philips curve
costs of unemployment to the government
- labour resources are wasted
- lower tax revenue
- increased spending on benefits
- increased in budget deficeit
distribution of income
How incomes are shared out between individuals and households
income
the reward for the service provided by a factor of production including labour
Wealth
The market value of all assets owned by a person, group or country at a specific point in time. Wealth is a stock of assets
types of income
-wages
-rent
-interest
- profit
- state benefits
Gross Income
income received before any taxes are taken or benefits given
reasons why income is unevenly distributed
- income-earning assets are distributed unevenly
- difference in wages
- reliance on benefits
- age
-gender
Distribution of wealth
How wealth is shared out between individuals and households.
reasons why wealth is distributed unevenly
- inheritance
- savings
- purchase of property
- enterprise
cost of living
The price level of goods and services bought by the average family
inflation
a sustained rise in the general price level over time
Price stability
When the general level of prices stays constant over time, or grows at an acceptable low rate
rate of inflation
the annual percentage rate of change in the price level, as measured, for example, by the CPI
CPI
method used to calculate the rate of inflation
How is CPI calculated?
1. Fix the basket
2. Find the prices
3. Compute the basket's cost
4. Choose a base year and compute the index
5. Compute the inflation rate
What causes inflation
- increase in demand
- rise in cost
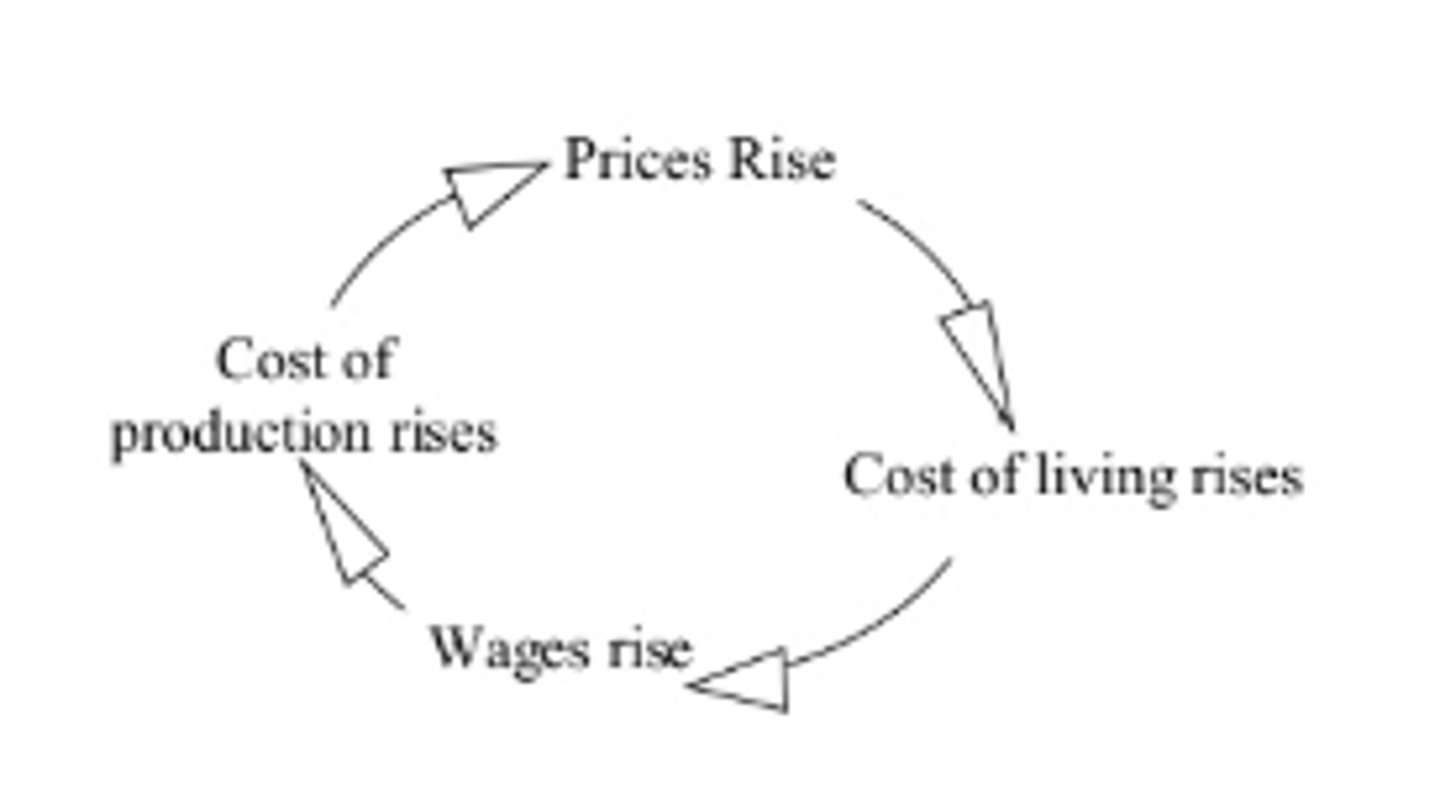
wage-price spiral
the process by which rising wages cause higher prices, and higher prices cause higher wages
consequences of inflation for consumers
- loss of consumer confidence
- shoe leather costs( consumers take more time and effort looking around for the best prices)
- real income may fall since the cost of living will increase
- debtors gain since their value of debt decrease
consequences of inflation for producers
- menu costs must be regularly updated
- wages will increase meaning a greater cost for firms
- uk economy will be less competitive causing unemployment
- creditors lose money during times of inflation
Government spending
the total amount of money spent by the government in a given period of time
direct tax
a tax on income or wealth
Government revenue
the source of finance for government spending
Examples of government spending
Health ,Education , Transport , Welfare, Defence, Foreign Relations/Affairs, Trade
examples of Direct Taxes
- income tax
-National insurance contributions
- cooperation tax
- inheritance tax
- capital gains tax
Indirect taxes
a tax on spending, often defined as a tax on goods and service
examples of indirect taxes
-VAT
- exercise duties
- gambling duties
Balanced budget deficit
when tax revenue = gov spending
Budget deficit
when gov spending > than tax revenue
Budget surplus
when gov spending < than tax revenue
Fiscal policy
A policy that uses government spending and taxation to affect the inflation of a country as a whole
Objectives of Fiscal policy
- economic growth
- low unemployment
- price stability
- a balance in the balance of payments
multiplyer effect
a process by which an original change in incomes in the economy leads to a total change in incomes which is a multiple of the original change
expansionary fiscal policy
when the government decreases taxes to increase demand
contractionary fiscal policy
when the government increases taxes to decrease demand
what are the function of taxes
- government source of revenue
- control over demand
regressive tax
A tax for which the percentage of income paid in taxes decreases as income increases
progressive tax
A tax for which the percentage of income paid in taxes increases as income increases
Laffer Curve
a supposed relationship between economic activity and the rate of taxation that suggests the existence of an optimum tax rate that maximizes tax revenue.
deflation
a sustained drop in the price level
disinflation
a reduction in the rate of inflation
Hyperinflation
A very rapid rise in the price level; an extremely high rate of inflation.
Increase in government spending( Fiscal Policy)
increase in spending ~ increase in people spending ~ increase in demand ~ demand pull inflation
reduction in taxes ( Fiscal policy)
increase in disposable income ~ increase in aggregate demand since people can buy more things ~ demand pull inflation
A decrease in government spending( Fiscal Policy)
decrease in employment ~ due to Philips curve, a decrease in employment leads to a decrease in inflation
increase in taxes( fiscal policy)
decrease in disposable income ~ decrease in aggregate demand ~ disinflation
Income and wealth redistribution
Government action, using mainly taxation and benefits, to reduce inequalities of income and wealth
inheritence tax
a state tax collected on the property left by a person to his or her heir(s) in a will
monetary policy
A policy that aims to control the total supply of money in the economy to try to achieve the government's economic objectives, particularly price stability.
Objectives of Monetary Policy
- economic growth
- low unemployment
- price stability
-A balance in the balance of payments
Bank rate
The interest rate that the Bank of England uses when it lends money to other banks. Financial services providers take account of the Bank rate when they decide how to set interest rates on their own products.
interest rate policy
The use of interest rates to try to achieve the governments economic objectives
Interest rates
cost of borrowing credit for saving
Increase in interest rates( monetary policy)
credit for saving increases ¬ people spend less and save more ¬ aggregate demand decreases ¬ inflation rate decreases
decrease in interest rates(monetary policy)
cost of borrowing decreases ¬ more people will have money to spend ¬ increase in aggregate demand ¬ demand pull inflation
monetary policy lag time
long( 9months - 2 years)
fiscal policy lag time
short
supply side policy
Policies that increase the ability of an economy to supply more goods and services
reducing direct taxes(supply side policy)
- increases incentive to work
- if cooperation tax is high, firms may be unwilling to invest
reducing benefits( supply side policy )
- decrease in incentive to work if benefits are too high
encouraging enterprise( supply side policy )
- new businesses benifit from tax reductions and subsidies too encourage people to set up work
education and training( supply side policy )
the better trained the workforce, the the more able it is to produce goods and services
supply side time lags
very long
externality
the impact of one person's actions on the well-being of a bystander
positive externality
beneficial side effect that affects an uninvolved third party
negative externality
the harm, cost, or inconvenience suffered by a third party because of actions by others
government policies to correct positive and negative externalities
- Taxation
- subsidies
- state provision
- legislation and regulation
- information and provision
Exports
Goods and Services sold to other countries
imports
goods and services purchased from other countries
`international trade
the exvhange of goods and services between cou tries
benefits of imports and exports for consumers
- lower prices for consumers
- more innovative and better quality goods
- Greater choice of goods
benefits if imports and exports for producers
- Access to larger market meaning an increase in potential buyers
-increased competition leading to greater efficiency
- specialization and lower average costs
- lager markets for buying inputs and lower average costs
European Union
An Economic and political group of countries that have free trade with each other
Free trade
Free movement of goods and services between countries without any restrictions
Balance of payments
record of all financial transactions between one country and the rest of the world
current account
the record of trade in goods and services, income flows and transfers between one country and the rest of the world
trade in goods
export - imports of goods
trade in services
exports - imports of services
income flows
earnings on investment from abroad for example interest that foreigners earn on an investment in the UK and that UK nationals earn on investment abroad.
transfers
transfers do not reflect any actual trade. They cover the transfer of money or goods and services without any requirement of payment: for example, foreign or money sent home by relatives working abroad