Electrical Safety and Symbols
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/79
Earn XP
Last updated 8:39 PM on 11/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
1
New cards
Class I
Earthed equipment. Fuses are also present so that if there is a short-circuit current will pass to earth causing the fuse to blow.
2
New cards
Class II
Double-insulated equipment
3
New cards
Class III
Power supplied by a safety/separated extra low voltage (SELV) source.
4
New cards
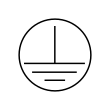
Class I Electrical Equipment (Appliance Class)
& Protective Earth/Ground
& Protective Earth/Ground
5
New cards
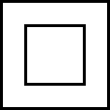
Class II Electrical Equipment (Appliance Class)
6
New cards
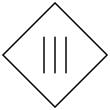
Class III Electrical Equipment (Appliance Class)
7
New cards

Danger (Generic Caution)
8
New cards

Biological Hazard (Hazardous Organisms)
9
New cards

Flammable (Chemical)
It can also indicate a chemical may be pyrophoric, self-heating, self-reactive, or emit flammable gas
It can also indicate a chemical may be pyrophoric, self-heating, self-reactive, or emit flammable gas
10
New cards

Electrical Hazard / Electrocution Risk / Exposed Wires
11
New cards
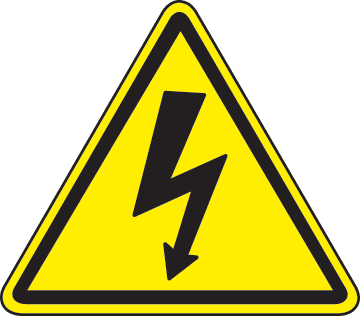
High Voltage / Electrocution Risk
12
New cards

Poison
13
New cards

Radioactive
14
New cards

Laser Hazard / Laser Operating
15
New cards

High-Level Ionising Radiation
16
New cards

Carcinogen
17
New cards

Non-Ionising Electromagnetic Radiation
18
New cards

Explosive (GHS01)
19
New cards

Flammable (GHS02)
20
New cards

Oxidising (GHS03)
21
New cards

Compressed Gas (GHS04)
22
New cards
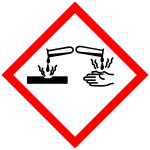
Corrosive (GHS05)
23
New cards

Toxic (GHS06)
24
New cards

Harmful (GHS07)
25
New cards

Health Hazard (GHS08)
Inhalational, Ingestion, Topical
Inhalational, Ingestion, Topical
26
New cards

Environmental Hazard (GHS09)
27
New cards
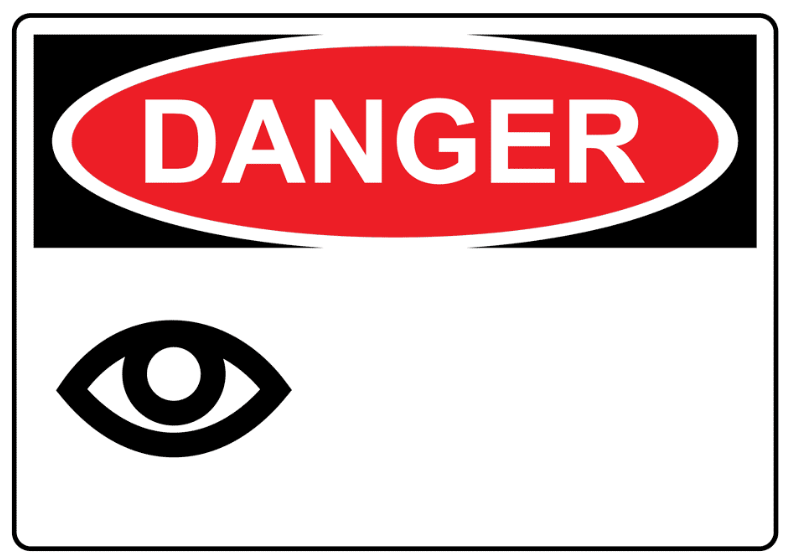

Eye Irritant
28
New cards

Cardiac-Protected Electrical Area
Body-Protected Electrical Area
Body-Protected Electrical Area
29
New cards
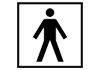
Type BF (Body Floating)
30
New cards
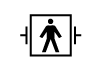
Type BF (Body Floating) Defibrillator Safe
31
New cards

Type CF (Cardiac Floating)
32
New cards

Type CF (Cardiac Floating) Defibrillator Safe
33
New cards

Place of Manufacture
34
New cards

Date of Manufacture
35
New cards

Do not use if packaging damaged
36
New cards

Sterilised via Ethylene Oxide
37
New cards

Sterilised via Asepsis
38
New cards

Expiry Date
39
New cards

Sterilised via Irradiation
40
New cards
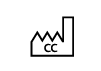
Country of Manufacture
41
New cards

The Conformitè Europëenne
European Conformity
Manufacturer deems product safe by EU safety, health and environment protection standards
European Conformity
Manufacturer deems product safe by EU safety, health and environment protection standards
42
New cards
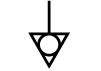
Equipotential Earth Point
43
New cards

Sterilisation via Dry Heat
44
New cards

Alternating Current
45
New cards

Temperature Limit Range
46
New cards
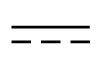
Direct Current
47
New cards

MRI Safe
48
New cards

MRI Conditional
49
New cards

Not MRI Safe
50
New cards
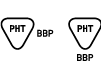
Contains PHT and BBP
51
New cards

Water Resistance Rating
52
New cards

Contains Latex
53
New cards

Serial Number
54
New cards
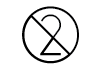
Single Use
55
New cards

Batch Code
56
New cards

Catalogue Number
57
New cards

Expiry Date
58
New cards

Sterile Fluid Path
59
New cards

Drops per ml
60
New cards
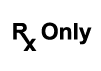
Prescription Only
61
New cards

Certified to British Standards (Kitemark)
62
New cards
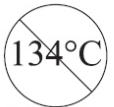
Not for Autoclave
63
New cards

Waterproof
64
New cards
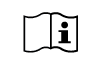
Consult Instructions for Use
65
New cards
Type B
Class I, II or III. Low leakage current 0.5 mA Class I and 0.1 mA class II
66
New cards
Type BF
Type Body Floating: Similar to type B (Class I, II or III. Low leakage current 0.5 mA Class I and 0.1 mA class II) but safer because patient is isolated
67
New cards
Type CF
Type Cardiac Floating: Lower current leakage, 0.05 mA for class I and 0.01 mA for class II, protects against microshock
68
New cards
Body Protected Area
Type BF allowance for a 0.5mA current leakage.
A body protected patient area includes all full height walls and doors bounding an area where patients are stationed. Dividers such as bed curtains, desks, or partial walls do not separate a body protected area from a common area. Certain types of medical equipment cannot be used within these areas.
A body protected patient area includes all full height walls and doors bounding an area where patients are stationed. Dividers such as bed curtains, desks, or partial walls do not separate a body protected area from a common area. Certain types of medical equipment cannot be used within these areas.
69
New cards
Residual Current Device (RCD)
A type of fuse or circuit breaker which cuts power in the case of a short-circuit or current overload
70
New cards

What is this for?
Uninterrupted Power Supply
71
New cards
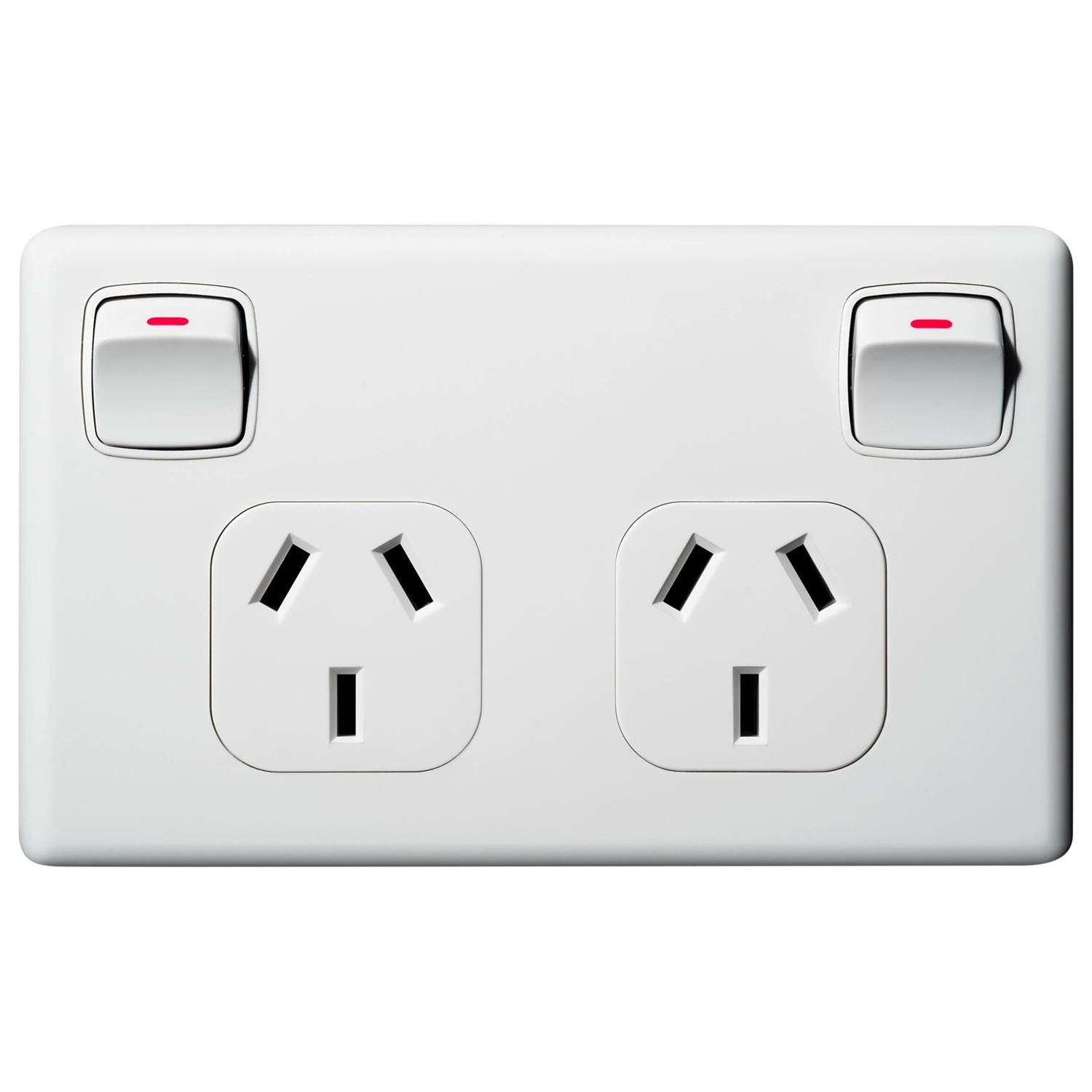

What is this for?
Normal Power Supply
72
New cards

What is this for?
Essential Power Supply
73
New cards
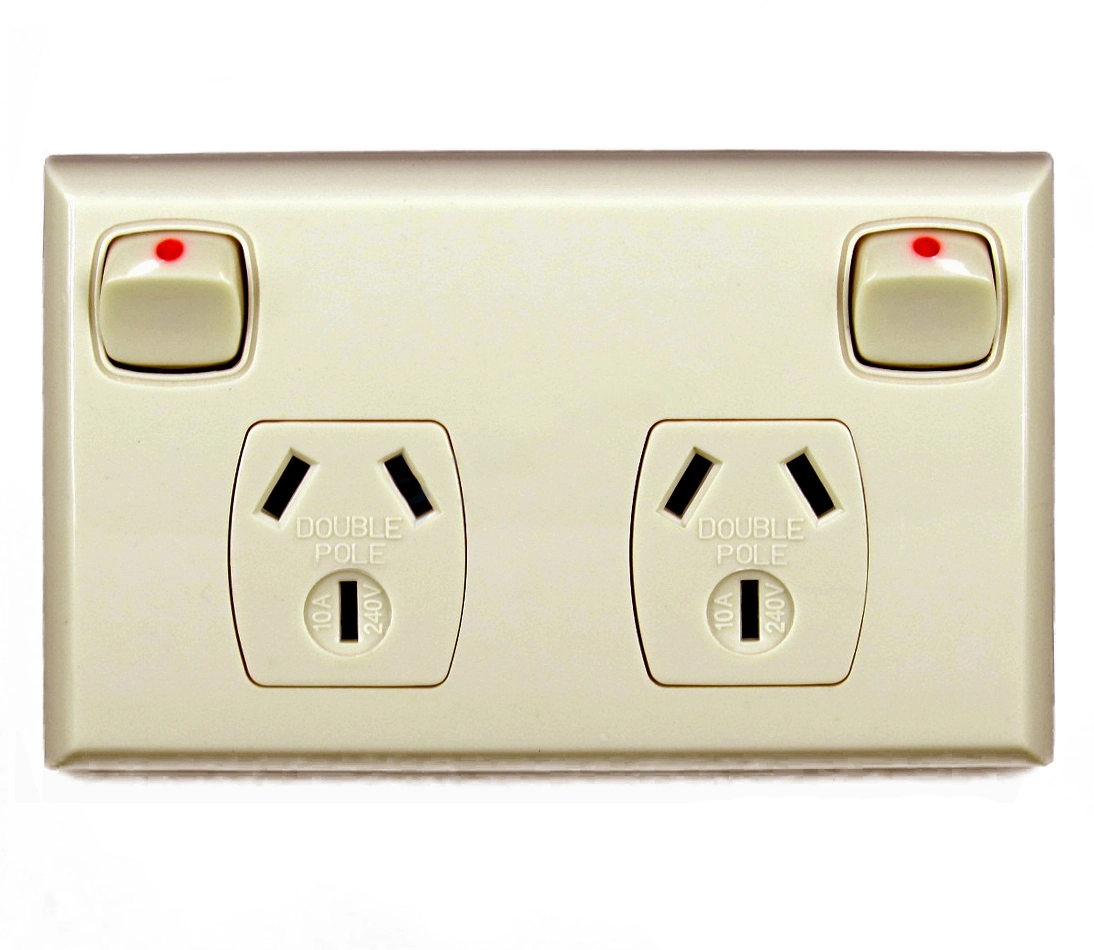

What is this for?
Cleaning Purposes Only
74
New cards
Earthed Equipment
Equipment with a direct connection to ground/earth reducing risk of electrocution
75
New cards
Double Insulated Equipment
Electrical equipment that does not require earth/ground. Two separate layers of insulation reduces risk of electrocution.
76
New cards
Uninterrupted Power Supply
Power supply that will continue in case of power grid failure via battery as local generators activate. For anaesthetic machine, diathermy, essential anaesthetic volumetric/syringe pumps.
77
New cards
Diathermy Pad Placement
Must be placed on intact skin, over fatty/muscle body parts (thigh, abdomen), same side as operative area, placed flat.
Must not be used if creased, placed on bony protuberances, on hair, or on metal implants - burn risks.
Skin must be checked on removal for signs of burn/irritation.
Must not be used if creased, placed on bony protuberances, on hair, or on metal implants - burn risks.
Skin must be checked on removal for signs of burn/irritation.
78
New cards
Monopolar vs Bipolar Diathermy
Monopolar: Alternating current travels from surgical electrode to diathermy pad (dispersion plate).
Bipolar: Alternating current enters and exits the electrodes of the handheld device.
Bipolar: Alternating current enters and exits the electrodes of the handheld device.
79
New cards
Importance of Electrical Safety
Electrical safety standards, safe practice and regular biomedical servicing reduces risks of:
Electrocution (patient and staff)
Equipment failure
Electrical fire - particularly in an environment containing flammable materials and rich oxygenation
Electrocution (patient and staff)
Equipment failure
Electrical fire - particularly in an environment containing flammable materials and rich oxygenation
80
New cards
Cardiac Protected Area
Type CF allowance for a 0.05mA current leakage.
These areas include strict controls to allow for cardiac applied equipment to be used. Cardiac applied equipment directly involves contact with the heart and is associated with a significantly higher risk of electrical complications (i.e., microshock electrocution).
These areas include strict controls to allow for cardiac applied equipment to be used. Cardiac applied equipment directly involves contact with the heart and is associated with a significantly higher risk of electrical complications (i.e., microshock electrocution).