Biology Study Set: Imprinting Defects & Syndromes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
The proband is clinically suspected to have Angelman syndrome. FISH testing for 15q11 deletion was negative. The BEST next step in testing would be to draw blood from the affected individual, his mother, and ?
c. paternal aunt
3 multiple choice options
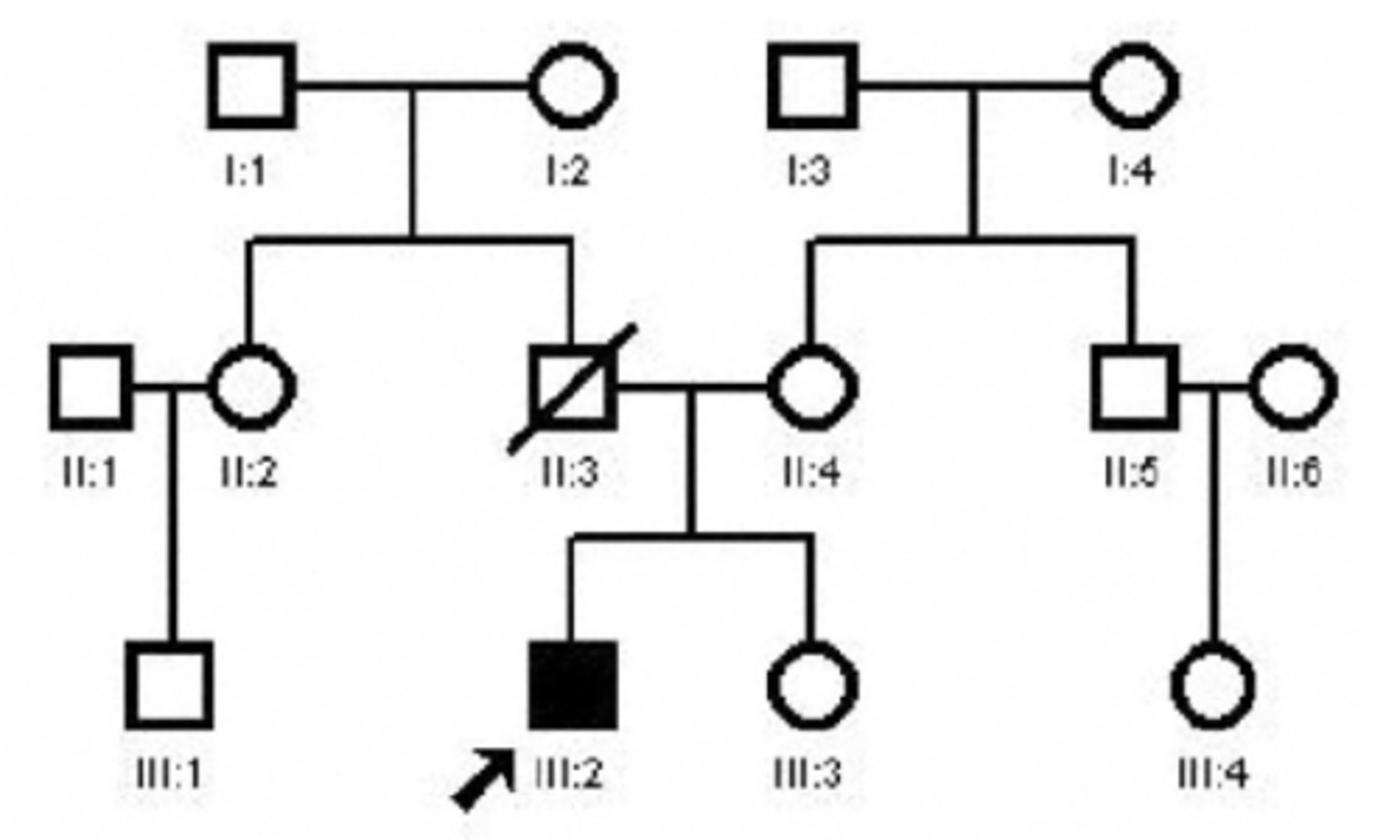
The parents of a 3-year-old girl are concerned about their daughter's developmental delay. Parents report that delays were first noted in early infancy. She only recently began to walk with the aid of a reverse walker. She has no speech and communicates with gestures and vocalizations. She is a happy and easily excitable child. On physical exam, her height and weight plot at the 25th percentile, however, her head circumference is less than the 3rd percentile and is at the 50th percentile for a 15-month-old. She ambulates with support but has a wide based ataxic gait. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this child's features?
Angelman syndrome
3 multiple choice options
What are the two most common Angelman syndrome mechanisms?
a. Maternally inherited deletion and paternal Uniparental disomy
b. Maternally inherited deletion and UBE3A mutation
c. Imprinting center defect and paternal uniparental disomy
d. imprinting center defect and UBE3A mutation
b. Maternally inherited deletion and UBE3A mutation
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is false regarding Angelman syndrome?
A. Can be due to a small deletion being present in the q arm of chromosome 15
B. Can be due to uniparental disomy of the maternal copy of chromosome 15
C. Can be due to a small deletion being present in the maternally derived chromosome 15
D. Angelman patients can be male or female
B. Can be due to uniparental disomy of the maternal copy of chromosome 15
Concerning genomic imprinting, which of the following statements is false?
A. Angelman syndrome affected patients are always due to uniparental disomy for chromosome 15
B. Prader-Willi and myotonic dystrophy syndromes exhibit features of genomic imprinting
C. Deletions in chromosome 15 can cause Prader-Willi syndrome
D. Lack of inheritance of a maternally derived chromosome 15 may cause Angelman syndrome
A. Angelman syndrome affected patients are always due to uniparental disomy for chromosome 15
Concerning Angelman and Prader-Willi syndromes, which of the following statements is false?
A. Lack of inheritance of paternal genes from chromosome 15 can cause Angelman syndrome
B. Uniparental disomy for chromosome 15 can cause Angelman syndrome
C. Uniparental disomy for chromosome 15 can cause Prader-Willi syndrome
D.Although Prader-Willi syndrome patients can become obese after the age of 2, they tend to gain weight poorly in the first years of life
A. Lack of inheritance of paternal genes from chromosome 15 can cause Angelman syndrome
In which of the following syndromes is maternal uniparental disomy (UPD) a potential etiology?
a. Cornelia de Lange syndrome
b. Russell-Silver syndrome
c. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
d. Angelman syndrome
b. Russell-Silver syndrome
Array testing identified an abnormality on chromosome 15 in a pediatric patient with hyperplasia and short stature. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis and chromosomal abnormality?
a. Angelman syndrome; duplication
b. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome; deletion
c. Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome; duplication
d. Prader-Willi syndrome; deletion
d. Prader-Willi syndrome; deletion
A 34 year old woman, who is 11 weeks gestation, elects non-invasive prenatal screening. The results come back positive for a deletion at chromosome 15q11.2. After appropriate counseling she elects diagnostic testing for Angelman/Prader-Willi syndrome and subsequently undergoes amniocentesis at 16 weeks gestation. What is the most appropriate test to order?
a. Chromosome analysis
b. FISH
c. MS-PCR
d. Microarray
c. MS-PCR
What percentage of children with BeckwithWiedemann syndrome would be expected to have an affected parent?
a. 80%
b. 50%
c. 30%
d. 15%
d. 15%
Which of the following is true?
A. Genetically imprinted loci are only located on chromosome 15
B. Some genes may be expressed differently when inherited from one sex versus the other
C. Imprinting is not involved in hydatidiform molar pregnancies
D. Prader-Willi syndrome can be caused by deletions in maternal chromosome 15q11-q13
E.None of the above are true
B. Some genes may be expressed differently when inherited from one sex versus the other
Which of the following is true about Prader Willi syndrome?
a. It is seen when the maternal genes in 15q11-15q13 are absent or non-functional
b. About 75% of cases are caused by paternal deletions of 15q11-15q13
c. The same genes imprinted in Prader Willi syndrome are imprinted in Angelman syndrome\
d. Prader Willi syndrome shows anticipation
b. About 75% of cases are caused by paternal deletions of 15q11-15q13
3 multiple choice options
A 39 year old woman undergoes prenatal diagnostic chorionic villus sampling because of advanced maternal age. Unexpectedly, both direct and cultured chromosomal analysis shows mosaic trisomy 15 (88% normal; 12% trisomy 15). Ultrasound assessments show no demonstrable malformations and the family elects to continue the pregnancy. At birth, cytogenetic assessment of the newborn is normal (46,XX). However, by 5 months of age the clinical diagnosis of Prader-Willi syndrome is made. Of the following, which is the most likely mechanism by which this girl's Prader Willi syndrome arose?
a. duplication of proximal 15q
b. deletion of proximal 15q
c. imprinting mutation
d. uniparental disomy
d. uniparental disomy
What two imprinting conditions are associated with chromosome 11?
a. Prader-Willi syndrome
b. Angelman syndrome
c. Beckwith Weideman syndrome
d. Russell-Silver syndrome
c. Beckwith Wiedeman syndrome
d. Russell-Silver syndrome
What two imprinting conditions are associated with chromosome 15?
a. Beckwith Weideman syndrome
b. Prader-Willi syndrome
c. Russell-Silver syndrome
d. Angelman syndrome
b. Prader-Willi syndrome
d. Angelman syndrome
Most common cause of Russell-Silver syndrome?
Loss of methylation on PATERNAL chrm 11p15.5
~35-50% of cases
___________ UPD is associated with 7-10% of Russell-Silver cases
MATERNAL UPD
Chrm 7
A clinical diagnosis of Russell-Silver syndrome is achieved with how many features?
4 of 6
1. Small for gestational age
2. Post-natal growth restriction
3. Relative macrocephaly at birth
4. Protruding forehead
5. Body asymetry
6. Feeding difficulties
What skull/head findings are associated with Russell-Silver syndrome?
Relative macrocephaly at birth
Protruding forehead
Delayed fontanelle closure
Triangular facies
About ~50% of Beckwith-Weideman cases are caused by?
Loss of methylation on MATERNAL chrm 11p15.5
About 20% of Beckwith-Weideman cases are caused by?
PATERNAL UPD of chrm 11p15.5
Beckwith-WeideMAN = too much paternal DNA
About 5% of Beckwith-Weideman cases are caused by?
Mutations in the maternal CDKN1C allele
If a child is suspected of having Beckwith-Weideman syndrome, what is the first list of testing?
Methylation analysis (MS-PCR)
Then do CNV testing at 11p15.5 for chrm 11 abnormality
If a child is suspected of having Beckwith-Weideman syndrome and the MS-PCR is positive but CNV testing at 11p15.5 is negative, what is the next line of testing?
Paternal UPD (SNP array)
If a child is suspected of having Beckwith-Weideman syndrome and the MS-PCR testing is negative, what is the next line of testing?
CDKN1C sequencing
Also need to test mother to confirm
What two syndromes are on your differential for Beckwith-Weideman?
Soto syndrome - AD, de novo
-frontal bossing
-sparse hair
-ID
Simpson-Golabi Behmel synd- XL
-heart defect
-polydactyly
-DD
What prenatal findings are associated with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
Polyhydramnios
Macrosomia (increased birth weight)
Omphalocele
Premature birth
What features are present in neonates with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
Macroglossia (englarged tongue)
Hypoglycemia
Earlobe creases / ear pits
What features are presents in infants/children with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome?
Generalized overgrowth
Hemihypertrophy (asymmetric overgrowth)
Wilms' tumor (until age 7)
Hepatoblastoma (until age 4)
*Normal intellect*
Which imprinting disorder is expected to have normal intellect?
a. Russell-Silver syndrome
b. Beckwith-Wiedemann
c. Angelman syndrome
d. Prader-Willi
b. Beckwith-Weidemann
About 70% of Angelman syndrome cases are caused by?
MATERNAL deletion of chrm 15q11.2
AngelMAN - too much paternal because maternal is deleted
Andel man - maternal deletion
About 10-15% of Angelman syndrome cases are caused by?
Mutations in the maternal UBE3A allele
**30% of UBE3A mutations found in AS patients are inherited
About 5% of Angelman syndrome cases are caused by?
PATERNAL UPD of chrms 15
AngelMAN = too much paternal DNA
What are the 3 clinical criteria seen in more than 80% of Angelman syndrome cases?
1. relative microcephaly
2. seizures before age 3
3. abnormal EEG
What other features are seen in Angelman syndrome?
-Sleep problems
-Autism spectrum disorder
-Inappropriate laughter and aggression
-Motor delay/tremor (increased deep tendon reflex)
-Language delay
About 60-70% of Prader-Willi syndrome cases are caused by?
PATERNAL deletion of chrm 15q11.2
PraDer -> Paternal Deletion
About 10-30% of Prader-Willi syndrome cases are caused by?
MATERNAL UPD
What are the features of Prader-Willi seen in the neonatal period?
Hypotonia with poor suck
What are the features of Prader-Willi seen in the first month-age 2 years?
Hypotonia
Poor appetite & suck
Developmental delay
What are the features of Prader-Willi seen in from age 6-12?
Developmental delay
Excessive eating leading to obesity
What are the features of Prader-Willi seen from age 13 to adulthood?
Cognitive impairement
Mild intellectual disability
Excessive eating & hyperphagia
Hyperthalmis hypogonadism
Distinct behaviors (manipulative, OCD, temper tantrums)
What two imprinting conditions are caused by maternal UPD?
1) Prader-Willi (chrm 15)
2) Russell-Silver (chrm 7)
* the two WITHOUT (men) in the name*
*also have deletion/loss of methyl of paternal chrm*
What two imprinting conditions are caused by paternal UPD?
1) Angelman syndrome (chrm 15)
2) Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome (chrm 11)
*the two WITH (men) in the name*
*also caused by deletions/loss of methyl on maternal chrms*