Energy & voltage in circuits
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is electric current?
- the rate of flow of electric charge
- it can only flow in a complete circuit
Which way does electric current flow in metallic conductors & why?
- towards the positive terminal & away from the negative terminal
- this is because the charges are carried by electrons which have a negative charge. Therefore, the electrons are attracted towards the positive terminal & repelled away from the negative terminal
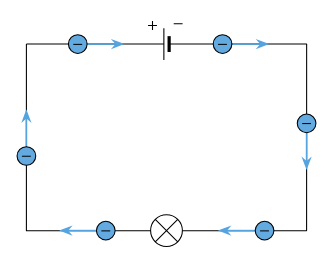
What is conventional current?
when the electric current flows towards the negative terminal & away from the positive terminal
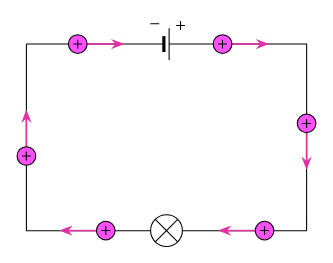
How is current measured?
with an ammeter
What are the units for current?
amps (A)
What is voltage?
what pushes the current around the circuit (“electrical pressure”)
How is voltage measured?
with a voltmeter
What are the units for voltage?
volts (V)
What is resistance?
anything in an electrical circuit which slows down the current
more components = higher overall resistance
What are the units for resistance?
ohms (Ω)
What is the effect of voltage on current?
current & voltage are directly proportional so if one increases / decreases the other will do the same
What is the effect of resistance on current?
current & resistance are inversely proportional so if one increases / decreases the other will do the opposite
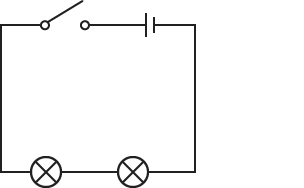
What is a series circuit?
-a circuit where there is only 1 path for the current to flow
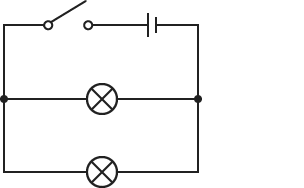
What is a parallel circuit?
a circuit where there is more than 1 path for the current to flow
How is current distributed across a series circuit?
the current is the same everywhere
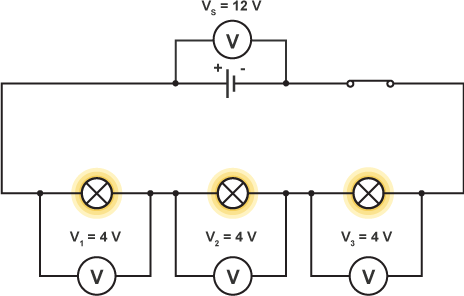
How is voltage distributed across a series circuit?
voltage is shared between all the components in a series circuit so that the sum of the voltages is equal to the supply voltage
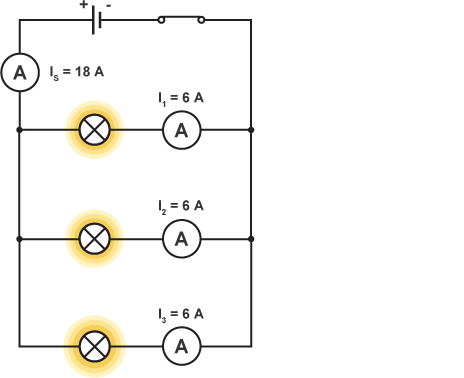
How is current distributed across a parallel circuit?
the current equally splits into the different paths of the circuit & then joins again before it goes into the power supply
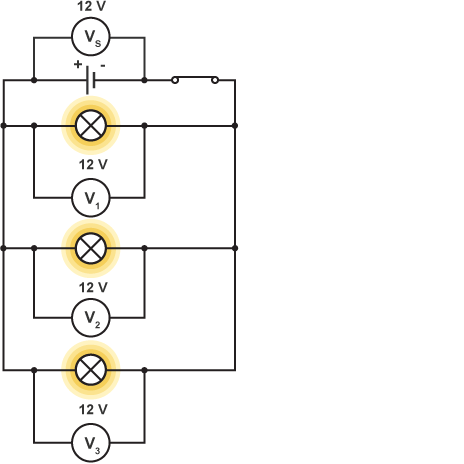
How is voltage distributed across a parallel circuit?
the voltage is the same for each component
What are the advantages & disadvantages of series circuits?
- cheap & easy to assemble as they require less wires
- uses less power
- if 1 component breaks the whole circuit stops working
- cells do not last long
What are the advantages & disadvantages of parallel circuits?
- components can be switched on / off independently
- if 1 component breaks the current can still flow through other parts of the circuit
- bulbs maintain a similar brightness
- cells last longer
- uses more power
- more expensive & difficult to assemble as they require more wires
What effect does the number of components in a circuit have on current?
more components = lower current
What does ohms law state?
that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage, provided its temperature remains constant
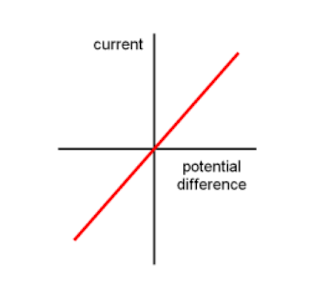
How does current vary with voltage in wires?
- as current increases the voltage across the wire increases
- this obeys ohms law
How does current vary with voltage in resistors?
- as current increases the voltage across the resistor increases
- this obeys ohms law
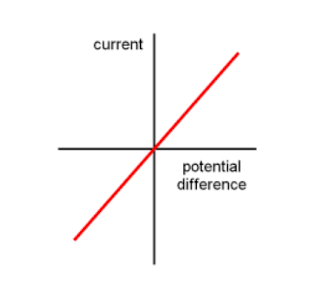
How does current vary with voltage in metal filament lamps?
- as current increases, the temperature of the metal filament lamp gets hotter which increases the resistance → as shown by the curve on the graph, meaning that voltage decreases
- this does not obey ohms law as the temperature does not remain constant
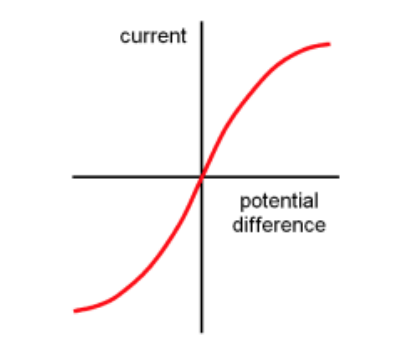
How does current vary with voltage in diodes?
- current increases when the voltage rises above the threshold value
- steep gradient on the graph shows that only small amounts of voltage needs to be applied to increase the current
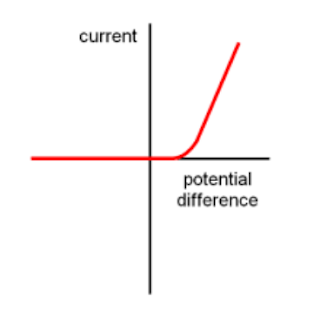
What is a thermistor?
A temperature-dependent resistor where
in hot conditions, resistance drops
in cold conditions, resistance goes up
thermistors make useful temperature detectors, e.g. car engine temperature sensors, fire alarms, thermostats
What is a light dependent resistor (LDR)?
a resistor that changes its resistance depending on how much light falls on it
What is a diode?
- a circuit component that allows current to flow through them in only 1 direction when the voltage is above the thresh-hold value
- they have high resistance in the reverse direction
What is a light emitting diode (LED)?
- a diode that emits light when current flows through them forward
- they are used for traffic lights, numbers on digital clocks & remote controls
- they have no filament that can burn out (unlike light bulbs)
What is the formula linking voltage, current & resistance?
voltage = current × resistance
V = I × R
What is the formula linking charge, current & time?
charge = current × time
Q = I × t
What is the formula linking energy, charge & voltage?
energy transferred = charge × voltage
E = Q × V