CHEM322 Reactants and Reactions
1/74
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
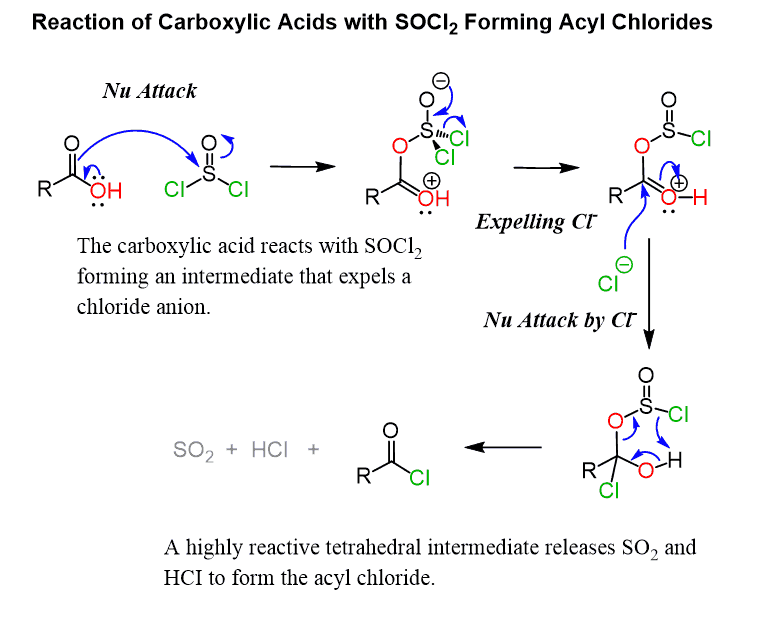
SOCl2
only reacts with carboxylic acids
replaces an alcohol group with a chlorine
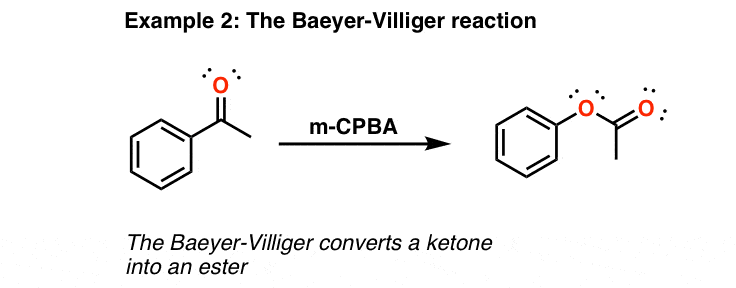
mCPBA
forms epoxides
forms esters from ketones (Baeyer-Villiger)
forms carboxylic acid from aldehydes
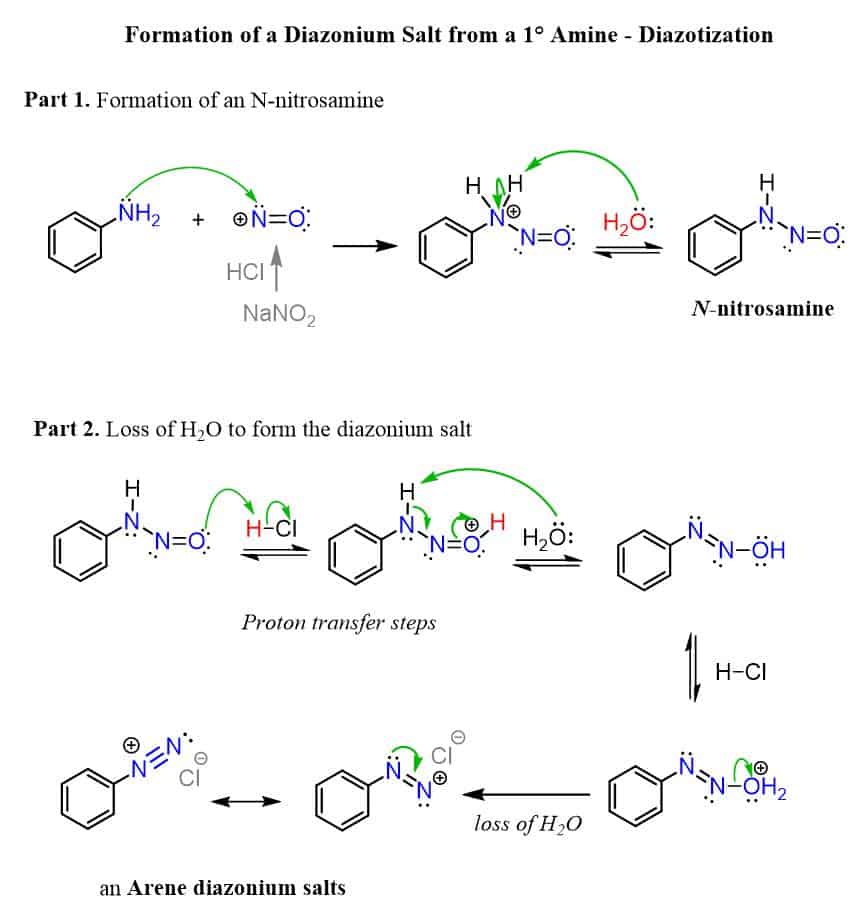
HNO2 , HCl
performs a nucleophilic attack, then a deprotonation to form a diazonium salt
good for multistep synthesis; in a reaction, releases N2 (g), which is very stable
PCC
mild oxidizing agent
converts primary alcohols to aldehydes
converts secondary alcohols to ketones without further oxidation
does NOT work on tertiary or quaternary
does not react with ketones or aldehydes
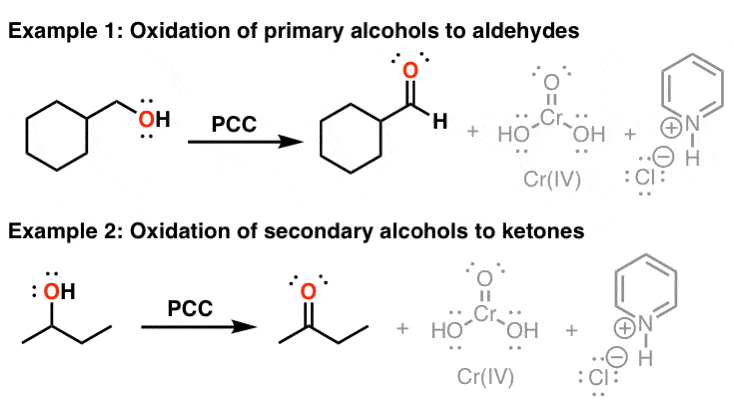
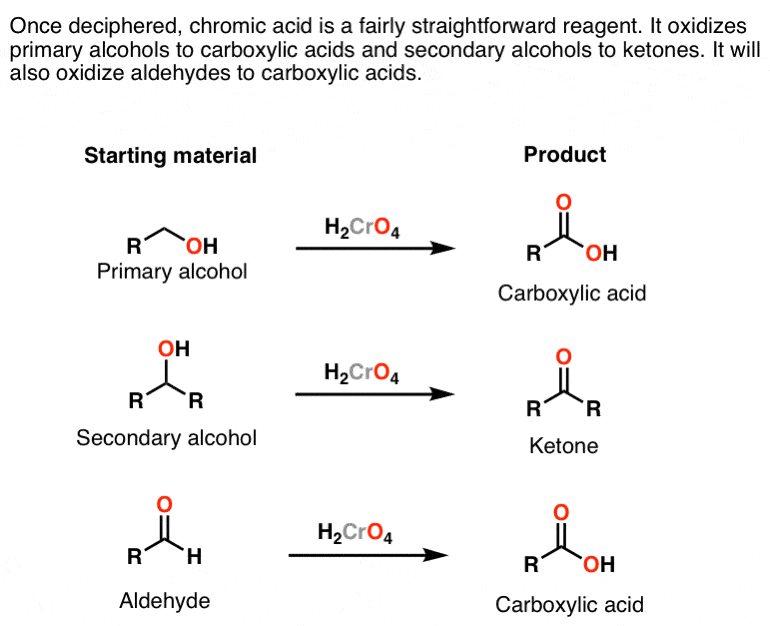
H2CrO4
strong oxidizing agent
converts primary alcohols to carboxylic acids
converts secondary alcohols to ketones
does not react with tertiary alcohols (all steps reversible) or quaternary
converts aldehydes into carboxylic acids
does not react with ketones
HgSO4, H2SO4 and H2O
forms a ketone from an alkyne (catalyzed hydration)
Hg2+ can make an epoxide
H2O breaks the epoxide
H+, H2O
converts alkenes to alcohols
converts alkynes to enols which rearrange to ketones
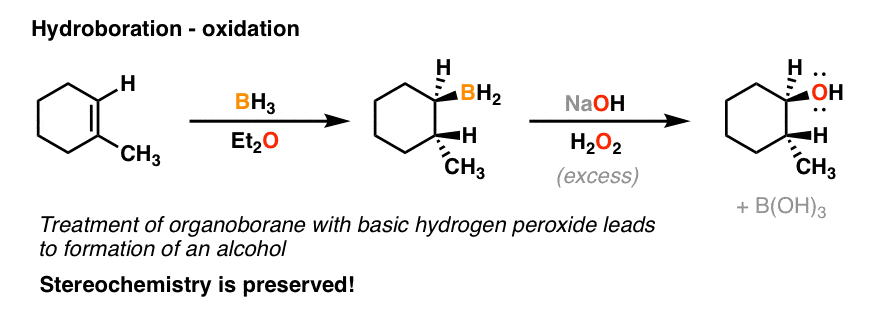
a) BH3 b) HOO-
performs concerted addition (anti-Markovnikov)
forms alcohol from an alkene (hydroboration/oxidation)
a) Hg(OAc)2 b) NaBH4
adds alcohol to most substituted carbon (Markovnikov)
Alkene hydration
EtOH (or CH3CH2OH), H+
performs alcohol addition
turns ketones into acetals/ketal (requires 2 EtOH)
turns double bonded oxygens into hemiacetals
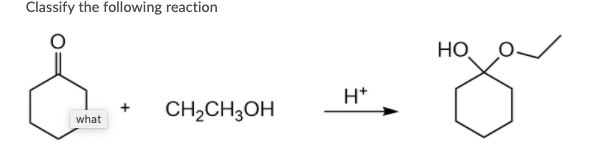
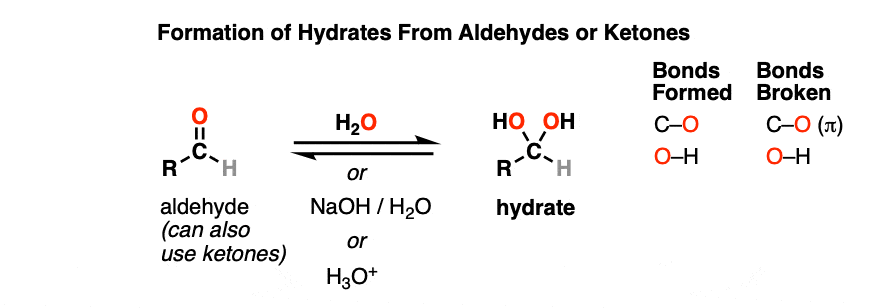
What can turn a ketone into a hydrate?
Water (H+, OH-)
can happen in acidic or basic conditions
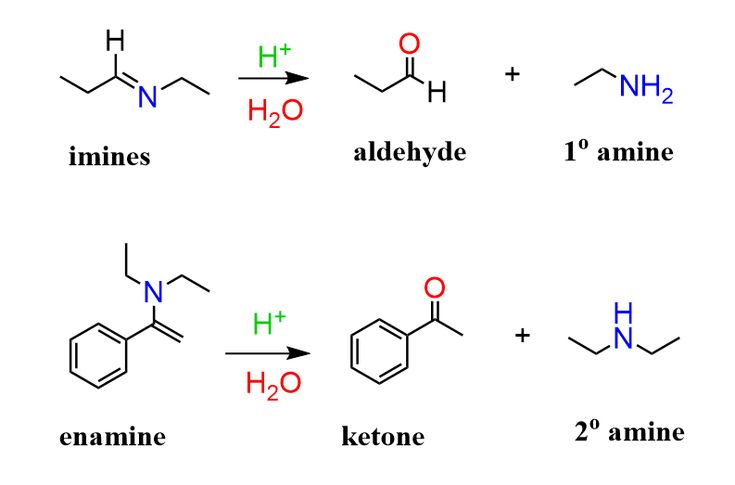
CH3CH2NH2 with H2O, H+
forms imine from an aldehyde or ketone and a primary amine (all steps reversible)
forms enamine from an aldehyde or ketone and a secondary amine (all steps reversible)
Opposite direction is hydrolysis (see picture)
a) Hb(Sia)2 b) HOO-
converts a terminal alkyne to a terminal aldehyde (hydroboration of alkynes)
Anti-Markovnikov
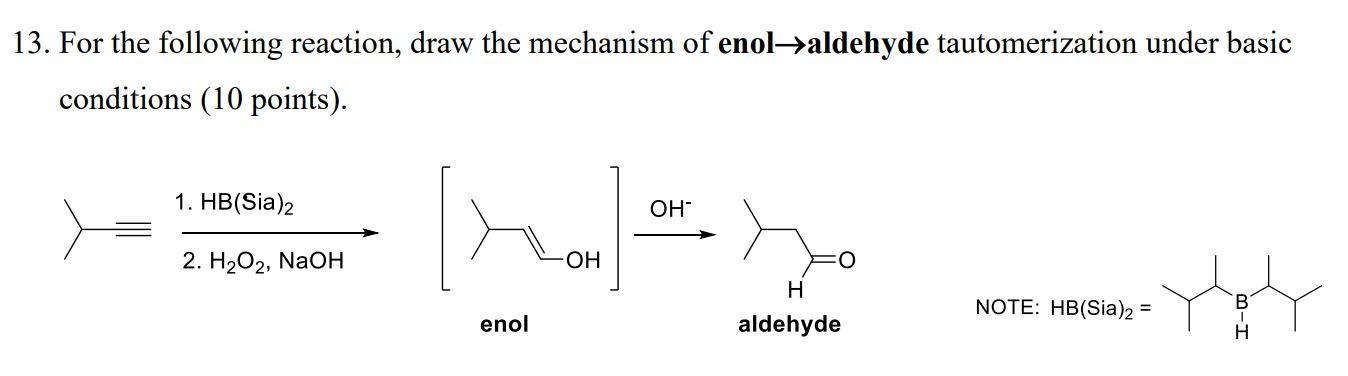
a) PPh3 b) Strong Base
Wittig reaction
AB + CD → AD + CB
concerted addition (1 step)
adds R group from PPh3 to original molecule
if symmetrical, stereochemistry does not matter
if not symmetrical: non-stabilized = Z alkene, stabilized = E alkene
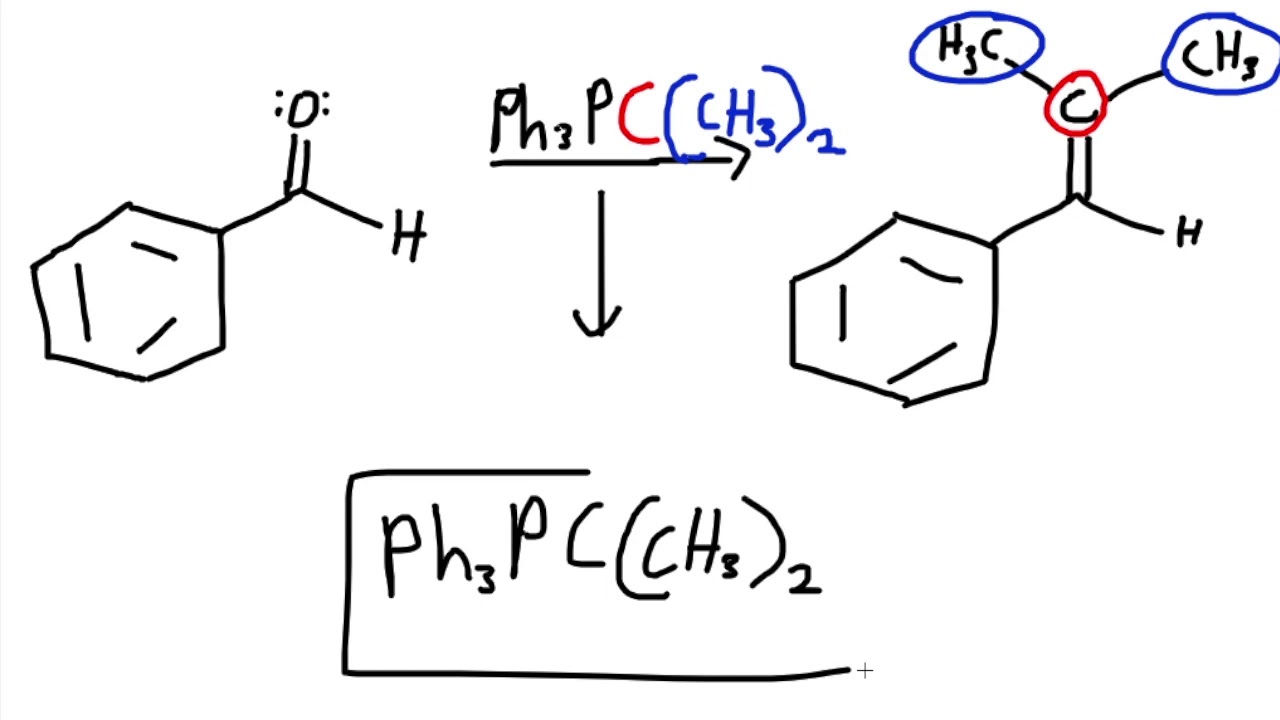
H2NNH2, base, heat
Wolff-Kishner reduction (same product as Clemmensen reduction)
reduces ketones to alkanes
under basic conditions
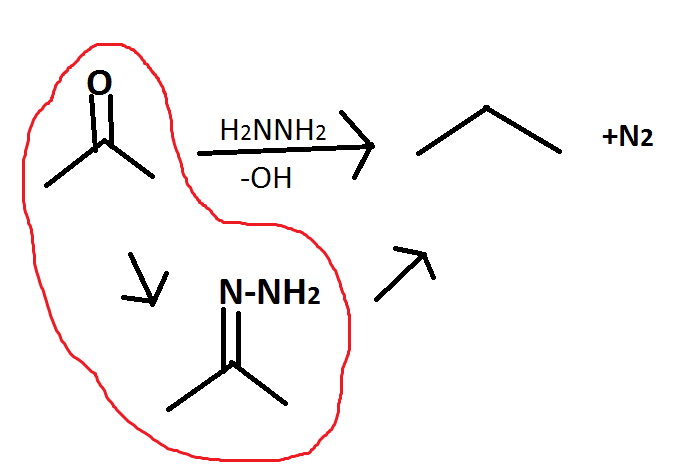
Zn/Hg, HCl, H2O
Clemmensen reduction (same product as Wolff-Kishner reduction)
reduces ketones to alkanes
under acidic conditions
P2O5
with two carboxylic acids, forms anhydride
What does a carboxylic acid and CH3CH2SH form?
a thioester
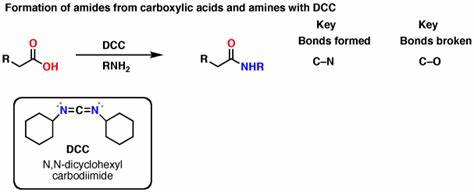
DCC, RNH2
forms amide from a carboxylic acid (DCC coupling)
stops amine from taking H+ from carboxyl
What reagent is used in decarboxylation?
Heat
Which alcohol position does NaBH4 and H+ work on in nucleophilic addition?
primary
Which alcohol position does LiAlH4, RMgBr, and H+ work on in nucleophilic addition?
secondary
Which alcohol position does RLi and H+ work on in nucleophilic addition?
tertiary
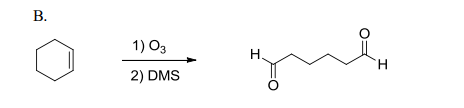
a) O3 b) DMS
splits pi bonds
add double bonded O to each side of original pi bond
can perform cycloaddition/reversion reactions
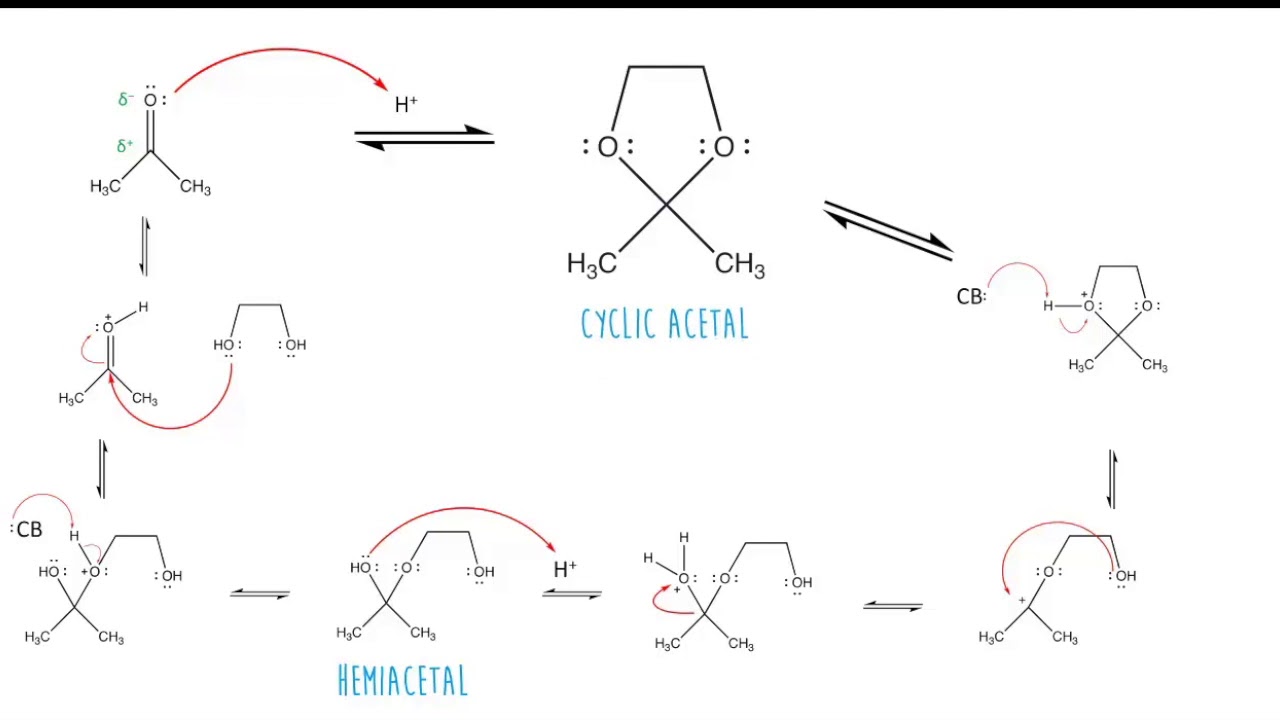
How are cyclic acetals formed?
When a ketone reacts with a diol
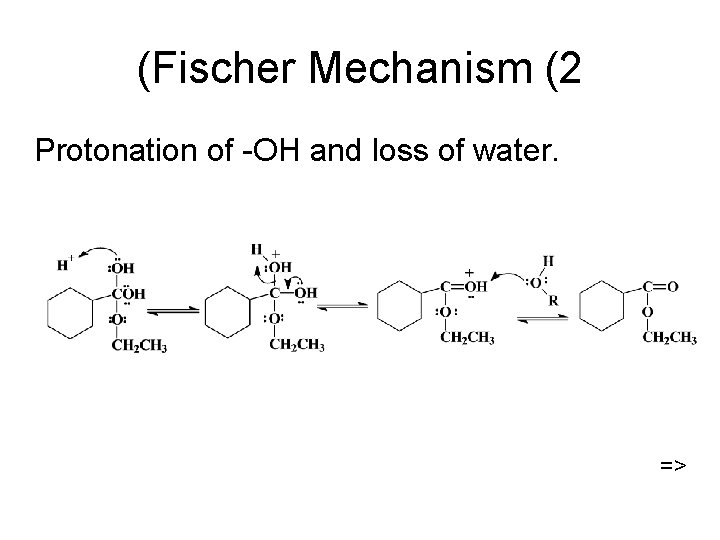
What type of reaction is the reverse of acid-catalyzed hydrolysis?
Fischer esterification
Are all steps of base catalyzed hydrolysis reversible?
No, the last two steps are one way
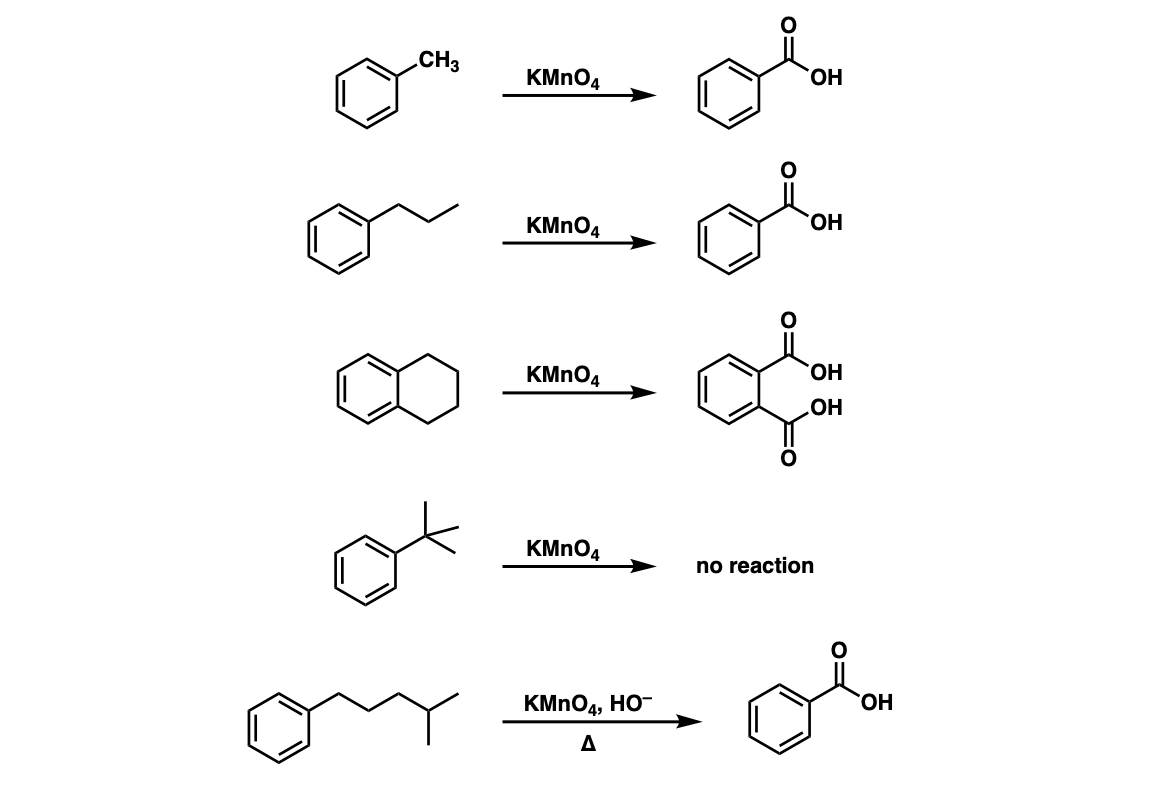
KMnO4, KOH, heat
permagnate oxidation
works on primary, secondary, tertiary
does not work on quartnerary
can form carboxylic acids on ‘benzylic’ positions (1 position away from aromatic ring)
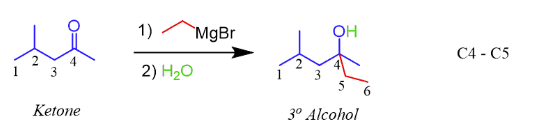
a) EtMgBr b) H+ with a ketone
1,2 addition
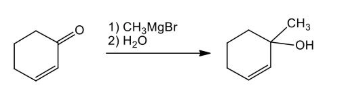
a) CH3MgBr b) H+ with an enone
1,2 addition
a) Et2CuLi b) H+ with an enone
1,4 addition (Michael’s addition)
a) Et2CuLi b) H+ with a ketone
no reaction
What does excess CH2CH3SH and a carboxylic acid form?
a thioester
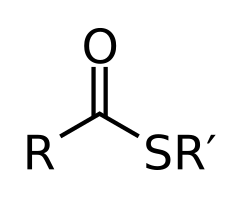
HgCl2, H2O
turns S-H carbon chain groups back into ketones or aldehydes
reverse reaction is thioacetal formation
a) LiAlH4 b) H+
converts aldehydes and ketones to alcohols
reduces amides to amines (acidic conditions)
forms aldehydes from esters
converts nitriles to primary amines
excess H2O, H+
acetyl hydrolysis
converts acetyl to ketone
What does H2CrO4 do with a ketone?
Nothing; no reaction
What does PCC do with a ketone/aldehyde?
Nothing; no reaction
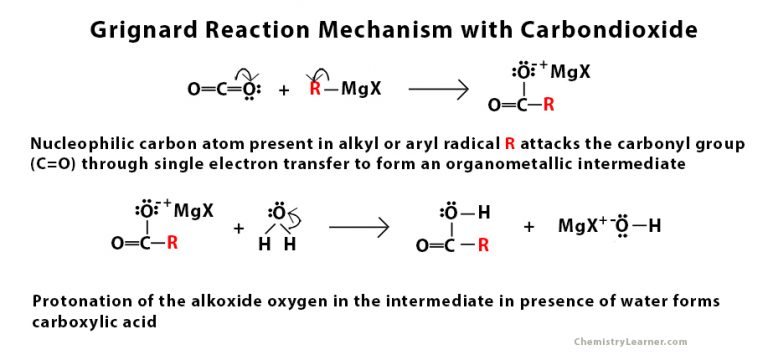
a) CO2 b) H+ with a Grignard
forms a carboxylic acid
What is the migratory rule (relating to Baeyer-Villager Oxidations)?
H > tertiary carbon > secondary carbon, Ph > primary carbon > methyl
-relevant when reacting mCPBA with asymmetrical ketones
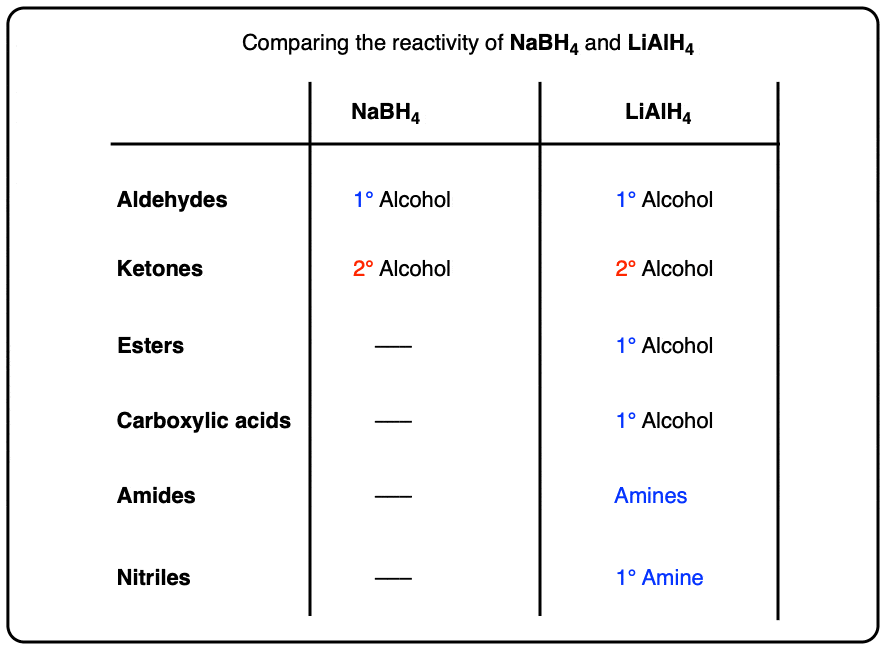
What are the differences between LiAlH4 and NaBH4
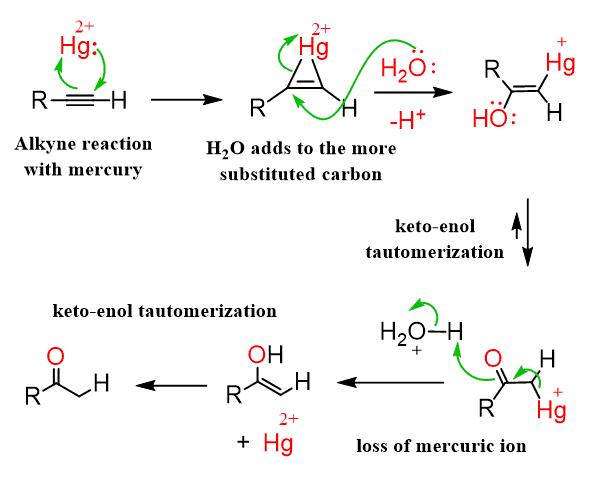
Hg2+, H2O
forms ketones and aldehydes
keto-enol tautomerization
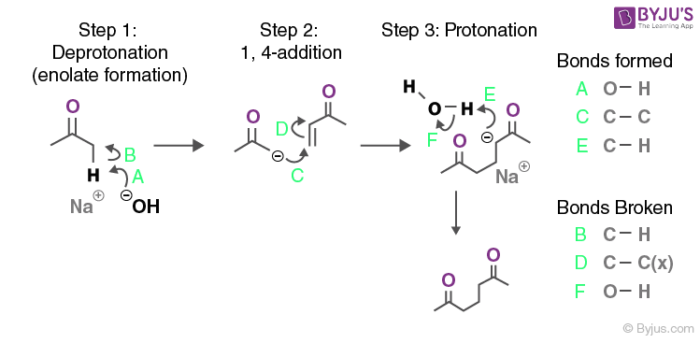
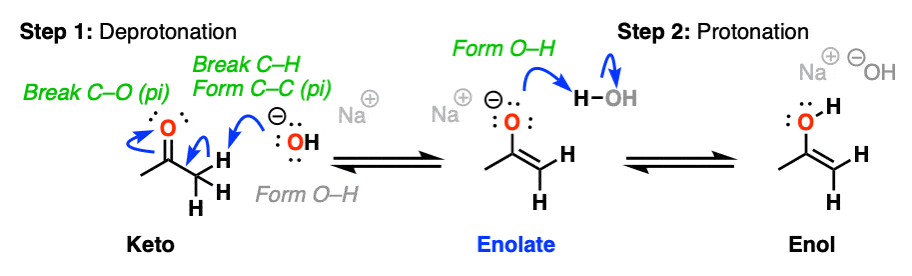
-OH, H2O
keto-enol tautomerization (base-catalyzed)
occurs via enolates
reversible
forms enols from ketones and vice versa
reacts with ketones and aldehydes
a) LDA
b) ketone or aldehyde
c) H+, cold
adds carbon chain
leaves OH group where double bonded O was
a) LDA
b) ketone or aldehyde
c) H+, hot
adds carbon chain
removes alcohol group to form carbon pi bond
a) enolate
b) H+
adds enolate at end of double bond
a) CH3CH2O-
b) Carbon chain with halogen
removes most acidic H
forms double bond where acidic H was
cation adds to double bond
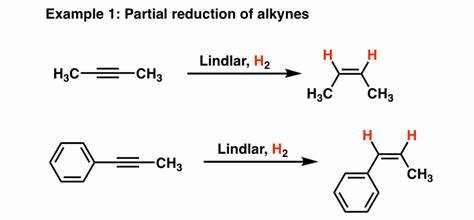
H2, Lindlars
makes z alkenes from alkynes
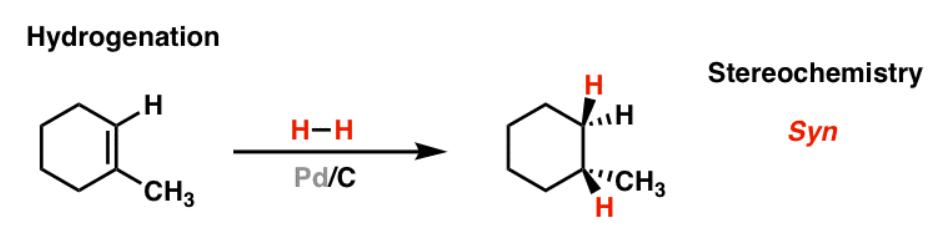
H2, Pd
removes pi bonds
reduces alkenes to alkanes
does NOT reduce ketones/aldehydes
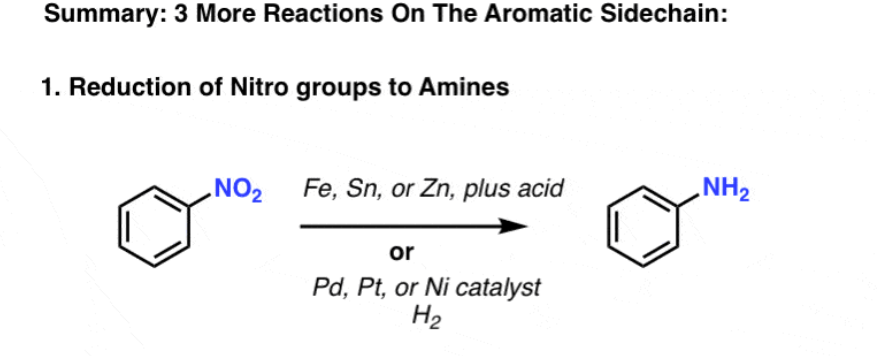
H2, Pt or Zn, HCl
nitro reduction
changes NO2 group to NH2
replaces O2 with hydrogens
reduces alkynes to alkenes
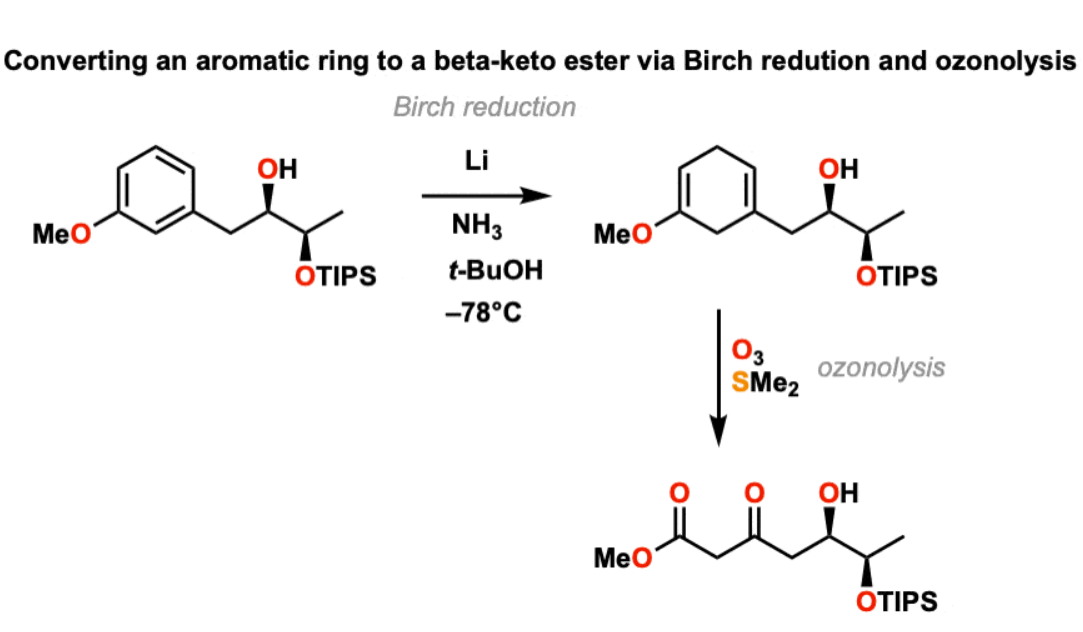
Li, NH3 (Birch’s reduction)
makes symmetrical pi system on aromatic ring
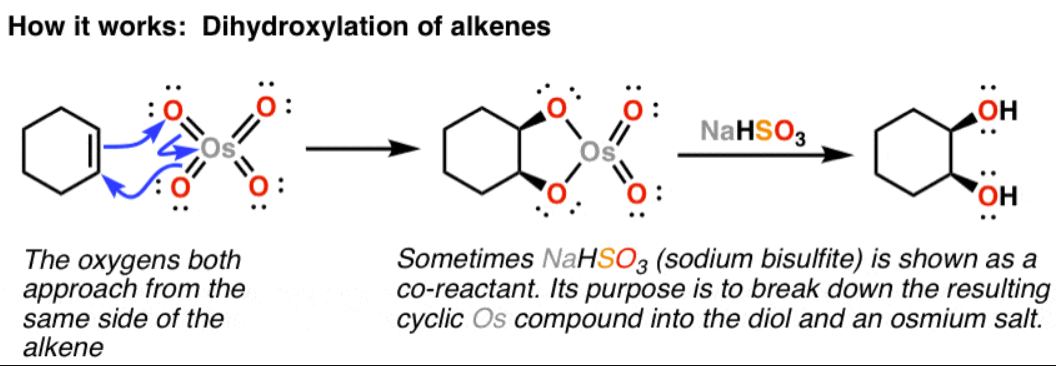
a) OsO4 b) HO- or NaOH, H2O
adds 2 alcohol groups onto either side of the double bond
reduces double bond to alkane
Li, NH3
makes E alkenes from alkynes
trans-conformations
Na, NH3 can also be used
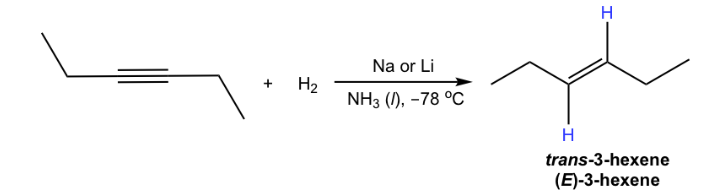
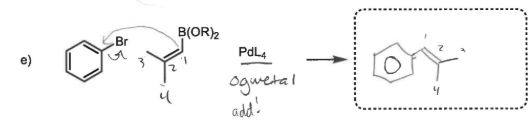
PdL4
replaces halogen with carbon chain containing double bond
organometallics
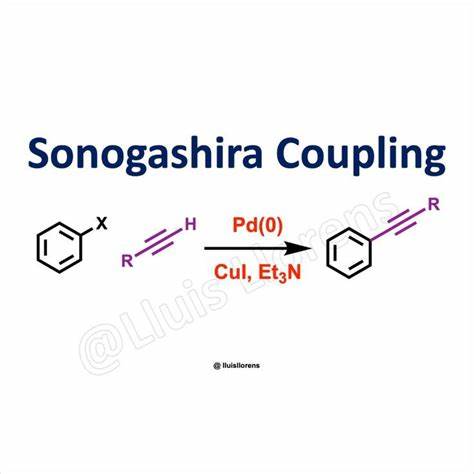
L2PdCl2, Cu/Et2NH (any base)
replaces halogen with carbon chain containing triple bond
organometallics
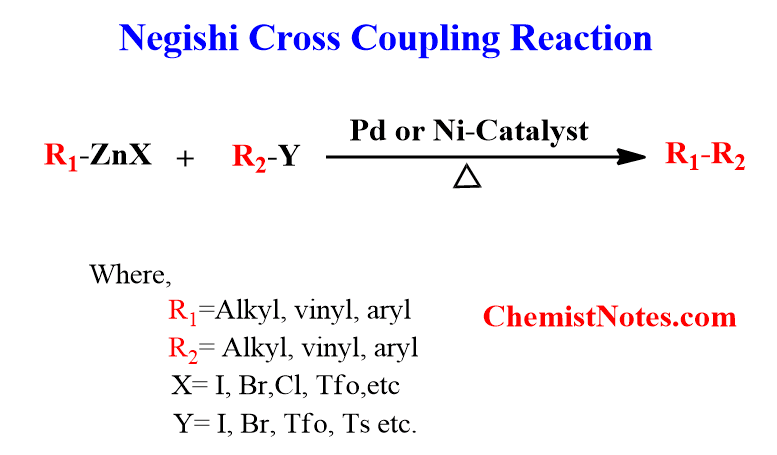
Pd2L4 or NiL4 (Negishi)
replaces halogen with carbon chain only with single bonds
organometallics
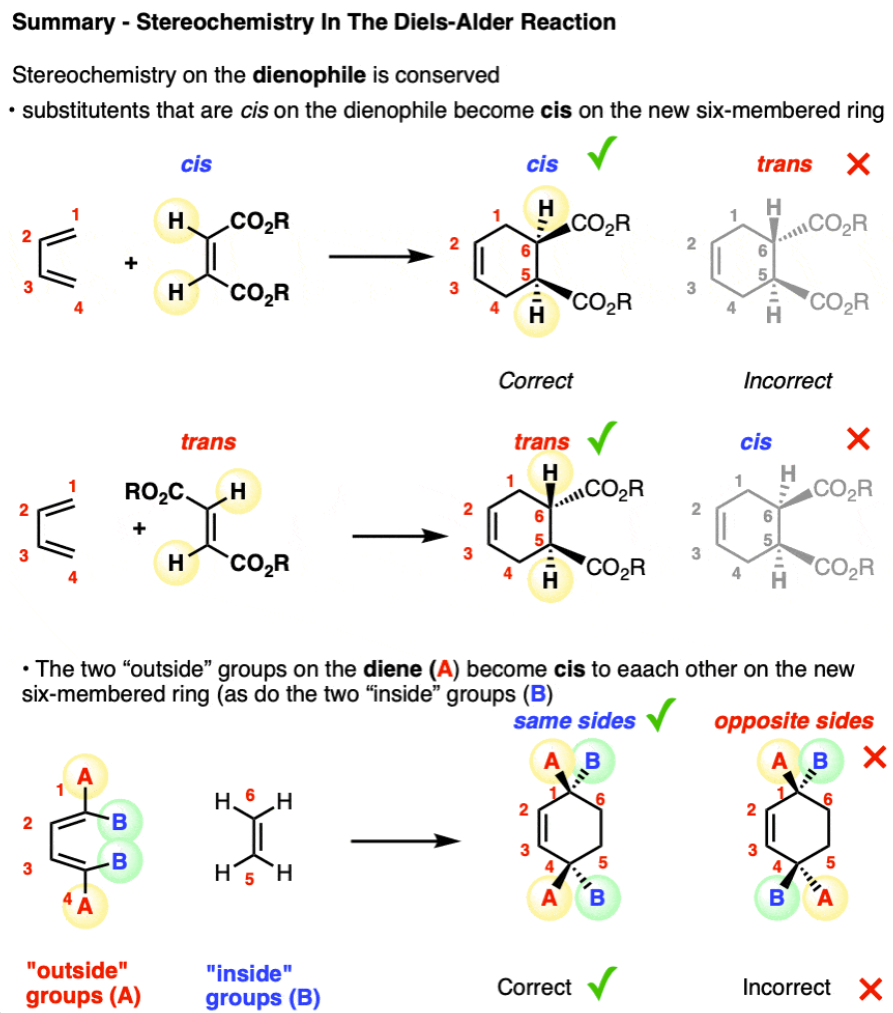
What are the three reactants in a Diels-Alder reaction?
dienophile
diene
heat
see image for stereochemistry explanation
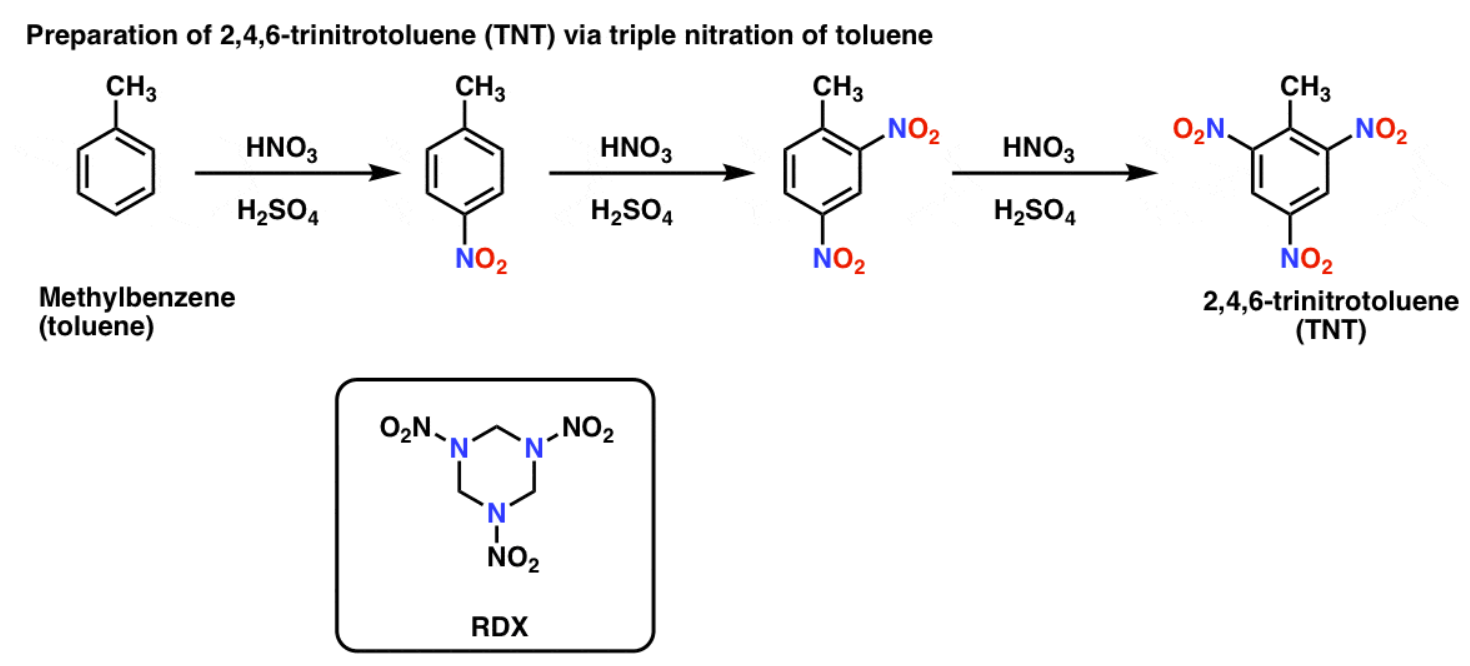
HNO3, H2SO4
adds NO2 group to sp2 hybridized carbon
What pi electron counts are associated with heat or light?
4n = light
4n + 2 = heat
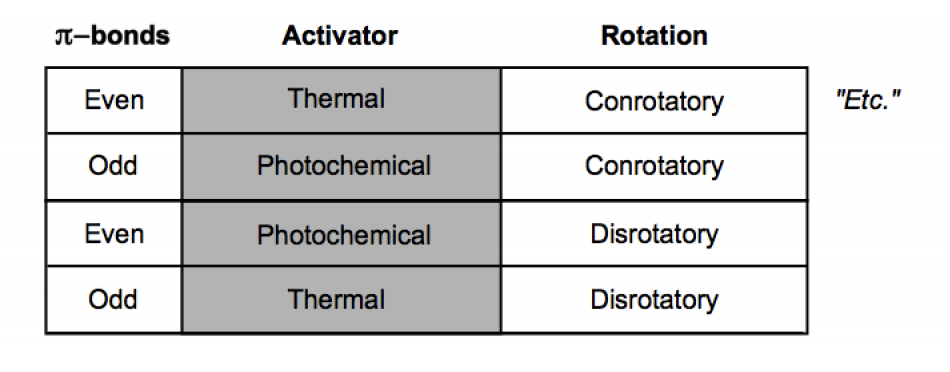
What pi electron counts and rotations are associated with heat or light?
4n, disrotatory (turn in different directions) = light
4n, conrotatory (turn in same direction) = heat
4n + 2, disrotatory (turn in different directions) = heat
4n + 2, conrotatory (turn in same direction) = light
What pi electron count is associated with aromatic or antiaromatic?
4n + 2 = aromatic
4n = antiaromatic
anything else is nonaromatic
rings must be conjugated to be antiaromatic/aromatic!
The ortho/para positions are associated with what type of groups?
EDG (electron donating groups)
The meta position is associated with what type of groups?
EWG (electron withdrawing groups)
SO3 , concentrated H2SO4
adds SO3H to para position only when dealing with EDGs
due to steric hindrance
dilute H2SO4, excess H2O
removes SO3
Br2, FeBr3
electrophilic aromatic substitution
adds to aromatic ring on sp2 carbon
other halogens can be used instead of Br (ie: Cl)
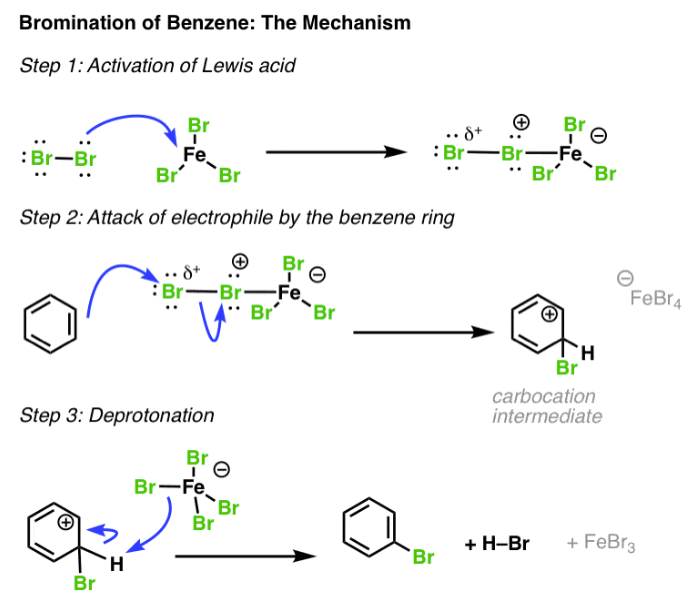
Cl2, AlCl3
will chlorinate and add any R group/carbon substituent, knocking off the Cl
if the Cl has no R group, it is the only one added
List the protecting groups
TIPS
TMS
TDS
TES
TBS
TBDPS
should all be paired with a leaving group (ie: halogen)
What is the function of protecting groups and how can they be removed?
expose other groups on the compound
deprotectors/removers: HF, TBAF, NaF
anything with fluorine
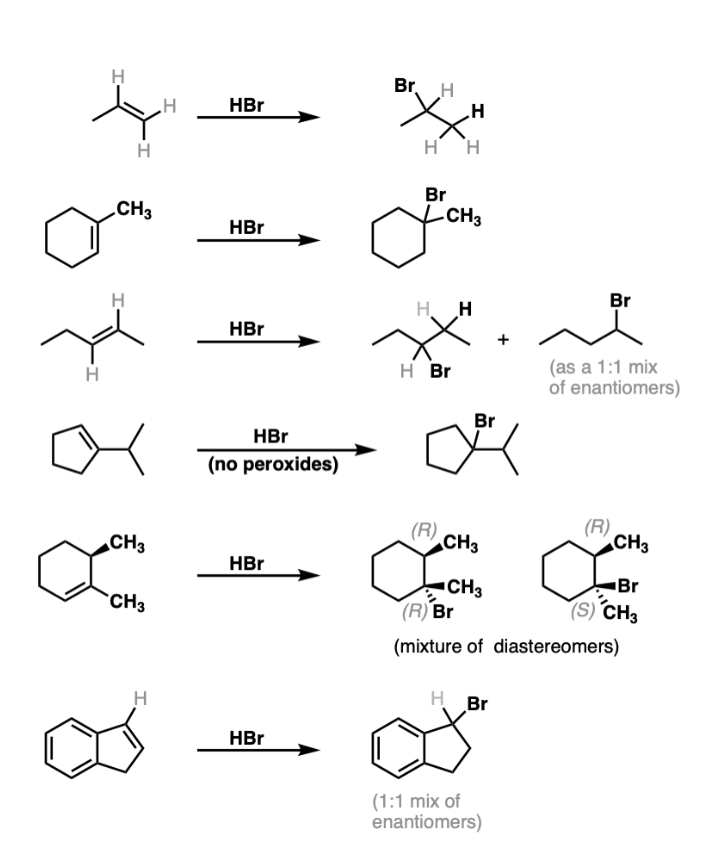
HBr
Markovnikov
adds Br (brominates) most substituted carbon in double bond
acts in absence of light or peroxides
Br2, light
adds Br to benzylic or allylic position
if performing allylic bromination, Br2 concentration must be low or else Br will be added on either side of the double bond
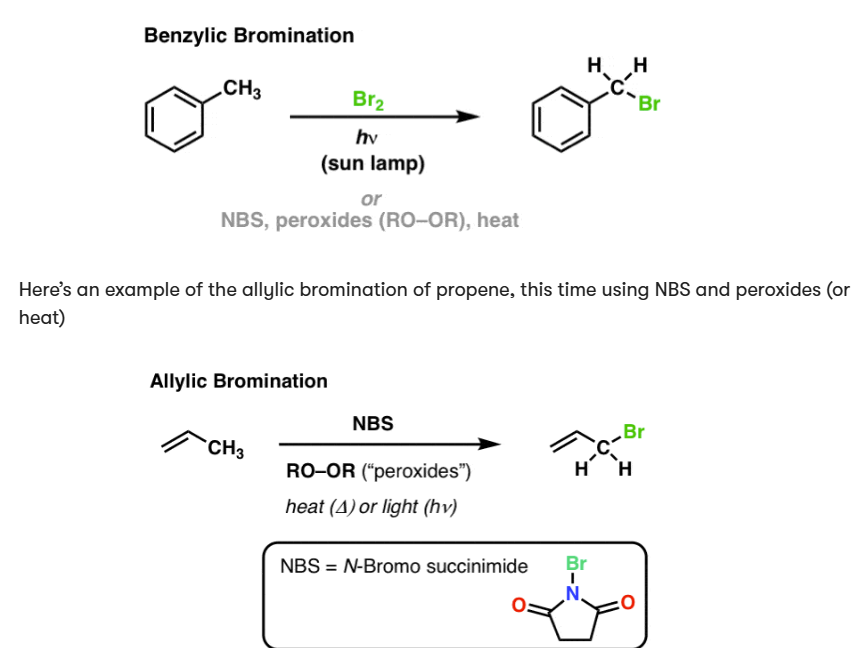
HBr, ROOR, light
anti-Markovnikov
Br attaches to least substituted carbon in a double bond
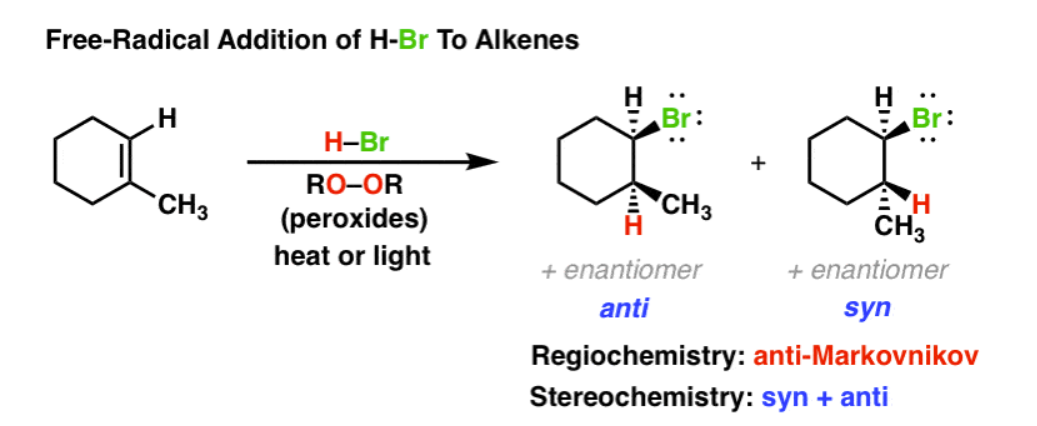
KOH (alc), heat
creates alkene from alkane
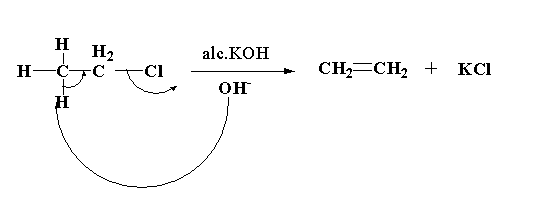
KOH, heat (200 degrees)
double elimination
dehalogenates
creates alkynes from alkanes
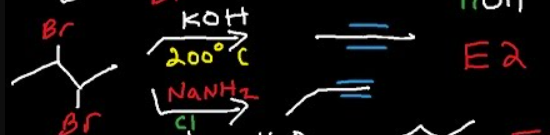
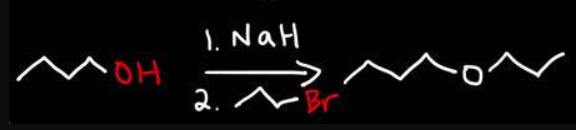
NaH
super base
stronger than NaOH
used to deprotonate alcohols
can be used in Williamson ether synthesis