Bio9 - Lung volumes
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Pharynx
Trachea
Bronchus
Bronchioles
Larynx
Alveolar duct
nasal cavity
alveoli
from up to down
nasal cavity,Pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, bronchioles, alveolar duct, alveoli
upper respiratory tract
Nasal cavity, pharynx, and larynx
Lower respiratory tract
Trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli
Inside the nasal cavity are curved shelves of bone called ?
lined with what?
conchae
ciliated respiratory epithelium
iliated respiratory epithelium, which secretes mucus and fluid, helps with what?
warm, filter, and humidify air
what part consists of C-shaped rings of cartilage
trachea
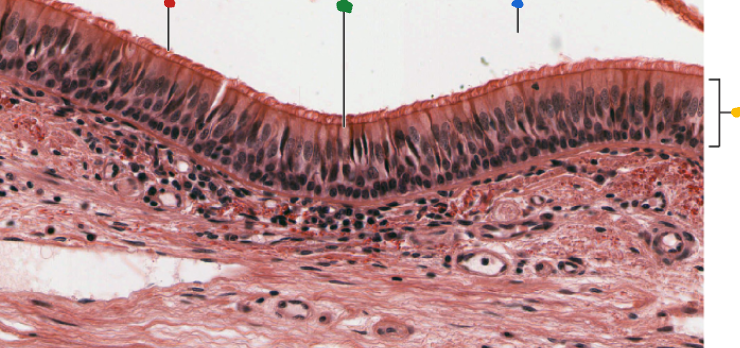
red
cilia
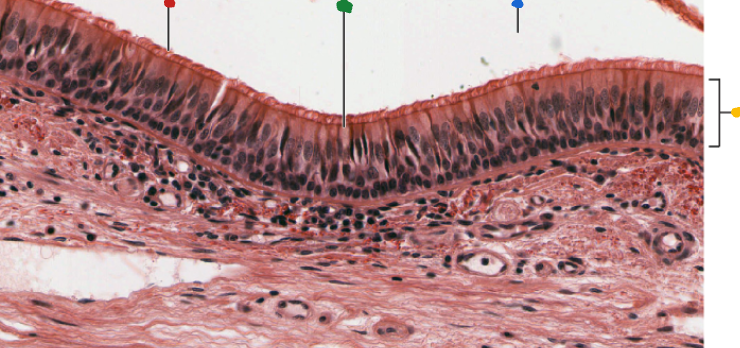
green
goblet cell
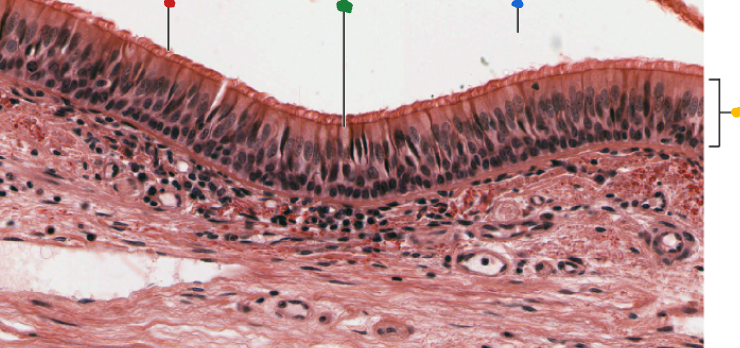
blue
lumen
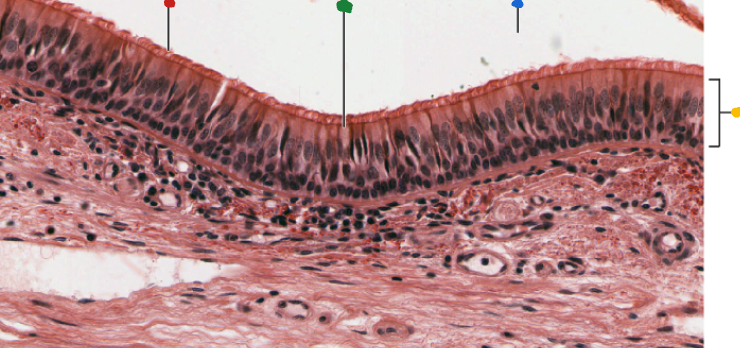
Yellow
Respiratory epithelium
How might the cilia and mucus secretions in the respiratory epithelium act as a barrier against infection?
Trap and remove infectious particles from airways using mucous
Inspiration
Diaphram, External intercostals
Expiration
Abdominals, internal intercostals
Why is it healthier to breathe through the nose rather than through the mouth?
The nose creates a more turbulent flow than breathing through mouth
Conducting Zone
nose to terminal bronchioles
higher resistance, larger branches
Respiratory zone
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli.
lower resistance, smaller branches
Broncioles
less cartilage, more smooth muscle
Bronchi
more cartilage, less smooth muscle
Volume increases, surface area inceases, pressure = ?
(like a soggy balloon)
decreases
Boyles law
describes the relationship between the pressure/volume of a gas at constant temperature
P1V1=P2V2
Compliance
how much pressure is required to produce change in volume
c=dv/dp
1
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
2
Tidal volume (VT)
3
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
4
Residual volume (RV)
Residual volume (RV)
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after exhalation
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
Max amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inhalation
Tidal volume (VT)
volume during normal/quiet breathing
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation
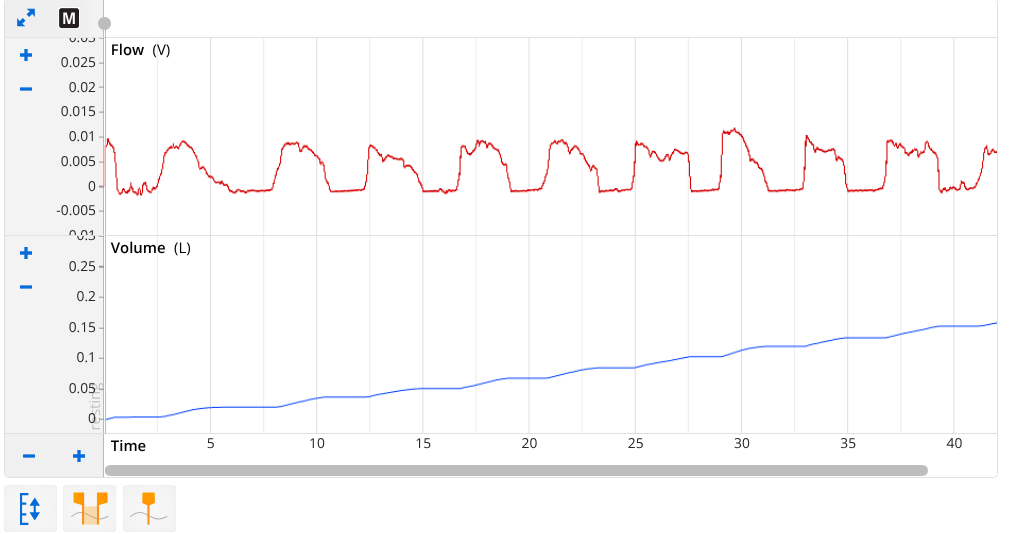
pneumotachometer/Spirometry
blue = ?
rate of airflow
airflow during expiration
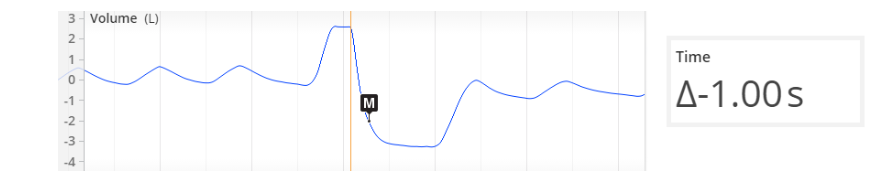
FEV1/FVC ratio - What could a low FEV1/FVC ratio indicate?
(need pic)
obstructive lung disease
pressure exerted by a gas is directly proportional to temperature, if the volume of the gas is held constant?
amantons law
IRV + V
IC
V + ERV
EC
ERV + RV
FRC
IRV + V + ERV
VC
IRV + V + ERV + RV
TLC