Lecture 16 - Neutrons and Activation
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 243 - Radiation Safety. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Are neutrons charged or uncharged? How does this affect their penetration ability
Neutrons are uncharged particles, which allows them to penetrate materials more effectively than charged particles like protons or electrons, as they are not repelled by atomic nuclei.
Are neutrons direction or indirectly ionizing?
Neutrons are indirectly ionizing particles, as they do not ionize atoms directly but can cause secondary ionization through interactions with other particles.
What materials attenuate gamma particles?
Materials such as lead, concrete, and steel are effective at attenuating gamma particles due to their dense atomic structure, which absorbs and scatters the high-energy radiation.
what materials attenuate neutrons?
Materials such as hydrogen-rich substances
such as water, plastics
can lead attenuate neutrons?
no
what type of collision occurs between neutrons and protons?
A neutron-proton collision results in an elastic collision, where kinetic energy and momentum are conserved
neutron stops completely, proton goes forward
neutron mean lifetime
14 minutes 47 seconds
are neutrons essential for all nuclei?
no
H-1 can exist without
what are neutron stars
neutron stars are the remnants of massive stars that have undergone supernova explosions, consisting almost entirely of neutrons and exhibiting incredibly high density and strong gravitational fields.
what are two ways a nucleus can be activated to become radioactive?
Photoactivation
photon hits nucleus and activates it
Neutron activation
neutrons hit nucleus and activate it
how are photoactivation and neutron activation related?
photoactivation can cause neutrons to be ejected, which can the participate in neutron activation
what is photoneutron production?
The process by which high-energy photons interact with a nucleus to produce neutrons, typically requiring energy above 10 MeV.
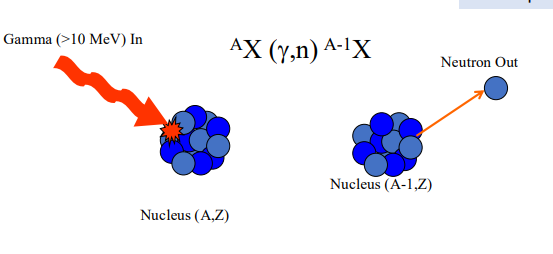
what is the energy requirement for photoneutron production?
E > 10 MeV
what are fast energy neutrons called
fast neutrons
what energies of LINAC generate fast neutrons
about 2 MeV
what energy do room scattered fast neutrons have?
100-400 keV.
what are low energy neutrons called?
thermal neutrons
why are they called thermal neutrons
They are called thermal neutrons because they are in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings, having low kinetic energy similar to that of the surrounding atoms.
energies of thermal neutrons
0.04 eV
what two things can (gamma, n) reactions be?
photoactivation
neutron production
what parts of the LINAC can be made radioactive (activated) by photon irridation?
wedges and compensators
how are wedges and compensators designed to reduce radioactive activation
they are designed with materials with low activation cross sections
after prolonged use of high energy photons (during commissioning), what should be done before entering the treatment room?
wait 10 minutes to let activation products decay before entering room
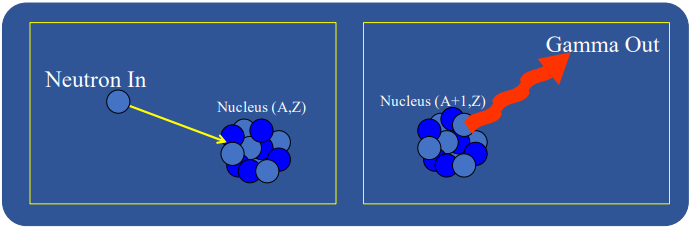
describe the process of neutron capture (n,y)
a fast neutron scatters loosing energy until it becomes a thermal neutron
thermal neutron is captured by certain nuclei
a gamma ray is emitted as the nucleus transitions to a higher energy state.
resulting nuclide is radioactive
Do neutrons scatter more or less than photons?
Neutrons scatter more than photons due to their larger mass and different interaction mechanisms with matter.
what do neutron attenuation and scatter depend on?
the neutron’s energy
what are the three steps of shielding neutrons
slow neutrons
absorb neutrons
absorb gamma rays
how are neutrons slowed
fast neutrons are slowed when scattered off materials which in hydrogen
water, plastics, concrete
how are neutrons absorbed
with boron and cadmium
why are boron and cadmium used to absorb neutrons
they have high cross section due to resonance energies and other quantum mechanic principles
how are the resulting gamma rays absorbed
the normal way: with lead
what are put into vaults to shield from neutrons
long mazes
neutron door
what are neutron doors made out of
borated paraffin
paraffin = plastic = water = slow neutrons
borated = boron = capture neutrons
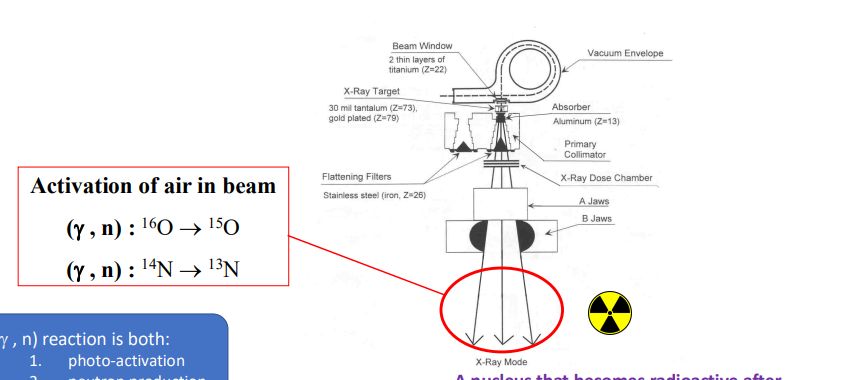
describe how photoactivation can occur in the air
are doses to radiation therapists from neutron activation high
no
especially now with dynamic wedges and MLCs, therapists wont have to touch the activated materials
what can cause an increased buildup of radioactive gases in treatment vaults
improper air ventilation
how many air changes are needed to limit build-up of radioactive gases in the room
5-10 air changes per hour
what type of radiation treatment creates most activation products?
IMRT - intensity modulated radiation therapy
when should machine service personnel be aware of neutron activation
when dismantling or working inside the accelerator head
exposure may be >1 mCi
what oxygen product may be created in electron mode
Ozone
what is the estimated skin dose from positrons for a therapist entering the room immediatly after a treatment for 5 minutes?
0.15-0.20 uSv
assuming 80 treatment fields per day, what is the annual dose a radiation therapist will recieve?
