Unit 6 Muscular System
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
connect muscle to bone and aid in body movement
skeletal muscle
Heart muscles only, enervated by autonomic nervous system
cardiac muscle
Located in vessels/organs, enervated by autonomic nervous, affected by hormones and neurotransmitters
Smooth muscle
Five key functions of muscle tissue
provides movement of the body
Stabilize body position/posture
Regulate volume in organs
Moving substances within body
Production of heat
Four properties of muscle tissue
electrical excitability
Contractually
Extensibility
Elasticity
Steps of neuromuscular junction
Brain sends an action potential towards a muscle
Impulse passes through multiple neurons until it arrives at the muscle
Synaptic vesicles filled with ACH arrive at axon terminals
Vesicles release chemicals via exocytosis
Chemicals will travel across synaptic draft
Receive at motor end plate
Chemicals travel down sarcolemma to the t-tubules
Calcium travels to actin and frees myosin head binding sites
Myosin attaches to troponin to form a cross bridge
Myosin performs a power stroke
Myosin head releases from troponin after contraction
what are the 3 sources of ATP
creatine phosphate
Anaerobic cellular respiration
Aerobic cellular respiration
Smallest in diameter, fewest myofibrils, least powerful of muscle fibers, dark red in appearance (heavy in myoglobin), heavy on mitochondria/ATP
Slow oxidative fibers
Intermediate in diameter, large amounts of myoglobin (pink in appearance), generates ATP through aerobic respiration, more power contractions
Fast oxidative fibers
Largest in diameter, white in appearance, most myofibrils, low myoglobin, most powerful contractions, fatigues most quickly, uses glucose to produce ATP
Fast glycolytic fibers
Groups of muscle fibers that allow stimulation of multiple muscles
Motor units
Total tension a muscle fiber can produce depends on
Frequency of stimulation
Activation of voluntary motor units, brings blood flow to muscle, generates an impulse but lingers
Muscle tone
Oxygen storage for muscle tissue, fibers are redder if there is more myoglobin
Myoglobin
The attachment site where the muscle fibers connect to a fixed/less moveable bone
Origin
The point where the muscle attaches to a bone/structure that moves when the muscle contracts
Insertion
How are muscles named
Location, shape, relative size, function, direction of fibers, number of origins, location of attachments
Study of muscles
Myology
Muscle tension without shortening the muscle
Isometric contraction
Muscle tension is constant and also shortens
Isotonic contraction
Flat connective tissue that functions as a tendon
Aponeurosis
Stimulates skeletal muscle
Somatic motor neurons
Branch out to enervate different muscle fibers, where the nerve and muscle meet to exchange the signal at neuromuscular junction
Axon terminal
Contractile proteins
Actin and myosin
Membrane of the muscle fiber
Sarcolemma
Plasma of a muscle cell that stores ATP/energy
Sarcoplasm
Contains/transports calcium within cell
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Thick filament
Myosin
Thin filament
Actin
Action only portion of a sarcomere that gets smaller with contraction
I band
Midline of a sarcomere, myosin only crosses this line
M line
Area of myosin only that gets smaller with contraction
H zone
Area of overlap between actin and myosin that gets bigger during contraction
A band
Gap where the neuron meets the muscle
Synapse
Divides the two cells from each other
Synaptic cleft
Chamber that contains the neurotransmitter
Synaptic vesicle
Most easily seen contraction, 20-30x a second
Unfused tetanus
80-100 stimuli per second
Fused tetanus
Muscle shortens pulling on another structure to produce movement
Concentric isotonic contractions
Length of the muscle is increasing during contraction, controlled movement against tension
Eccentric isotonic contraction
Muscle in charge of the major force in the movement
Prime mover
Opposing muscle working in reverse
Antagonist
Supporting muscles that aid prime movers and help add force
Synergists
Specific synergists to support origin site of the muscle for stabilization
Fixator
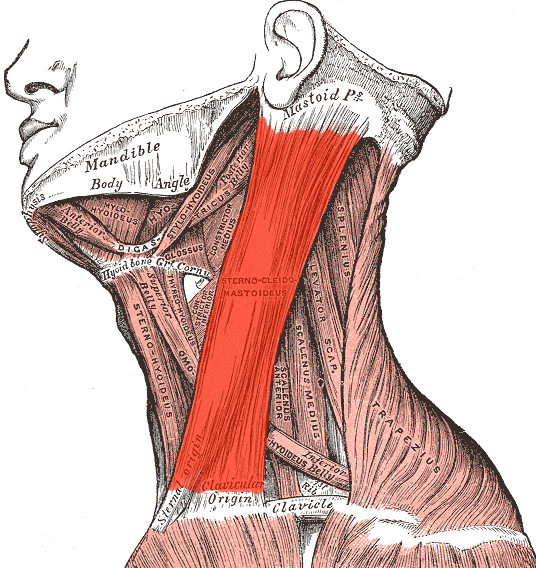
sternocleidomastoid
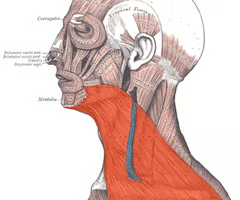
tenses skin of neck
platysma
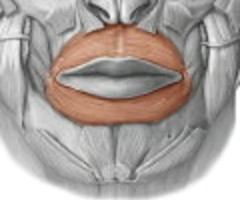
closes and protrudes lips
orbicularis oris
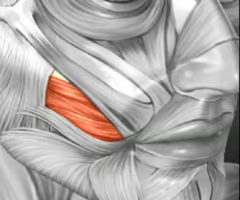
compresses cheek, holds food between teeth during chewing
buccinator
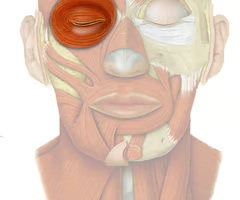
Closes eyelids; used in blinking, winking, and squinting
orbicular oculi
retracts and elevates corner of mouth

zygomaticus
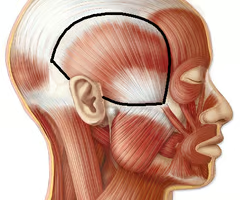
Elevates and retracts mandible; assists in side to side movement of mandible
temporalis
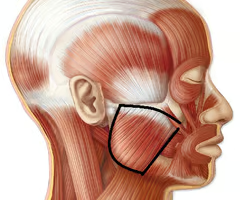
elevates mandible and closes jaw
masseter
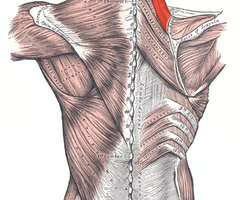
elevates and adducts scapula
levator scapulae
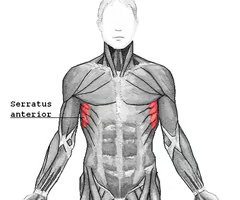
pulls scapula anteriorly and downward
serratus anterior
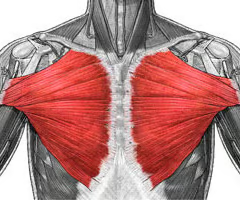
chest muscle
pectoralis major
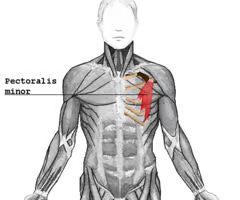
insertion: coracoid process of scapula
pectoralis minor
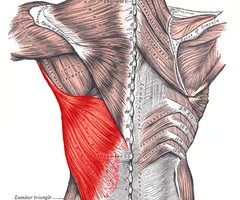
extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
latissimus dorsi
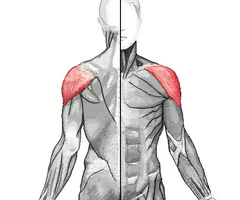
shoulder
deltoid
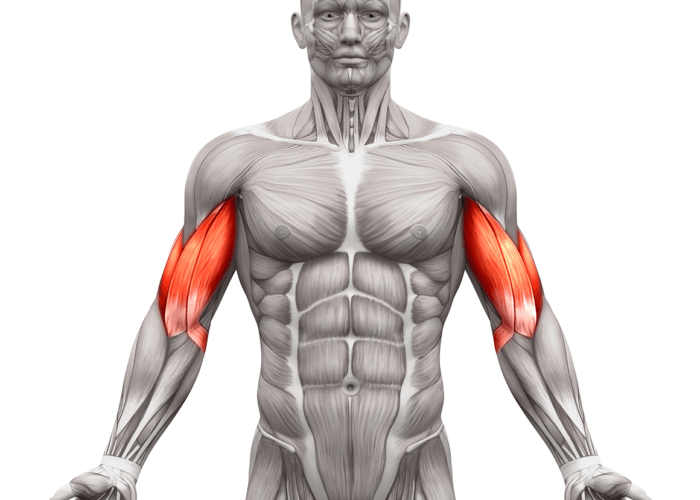
origin: scapula
action: flexes forearm at elbow
biceps brachii
origin: humerus
insertion: radius
action: flexes forearm at elbow
brachioradialis
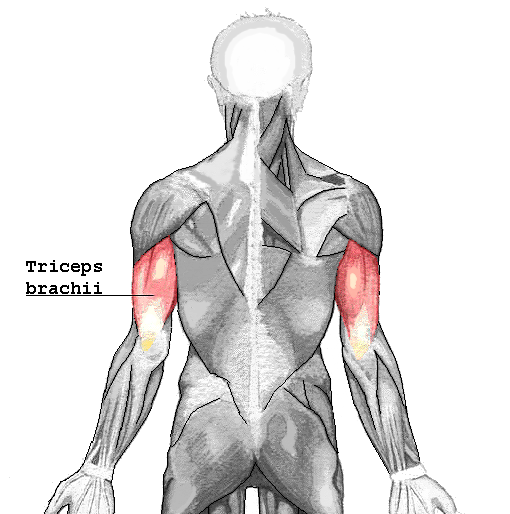
origin: humerus
insertion: ulna
action: extends forearm at elbow
triceps brachii
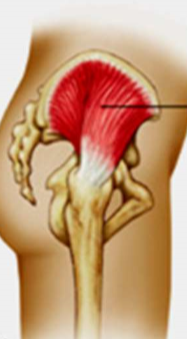
gluteus medius
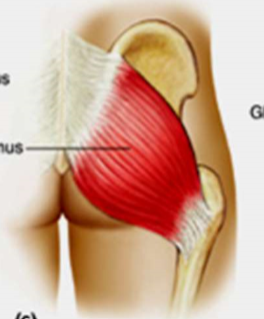
gluteus maximus
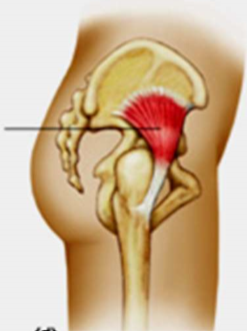
gluteus minimus
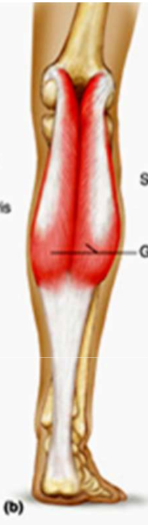
back of knee/calf muscle
gastrocnemius
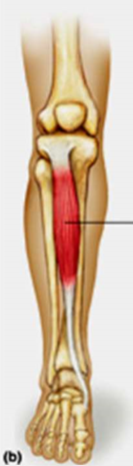
origin: tibia
insertion: tarsal bone
action: dorsiflexion
tibialis anterior
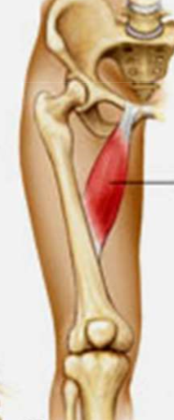
origin: pubic bone
insertion: femur
action: adducts
adductor longus
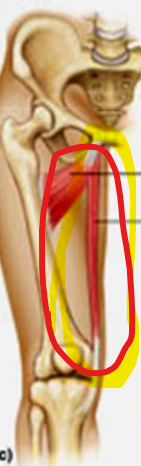
gracilis
bicep femoris
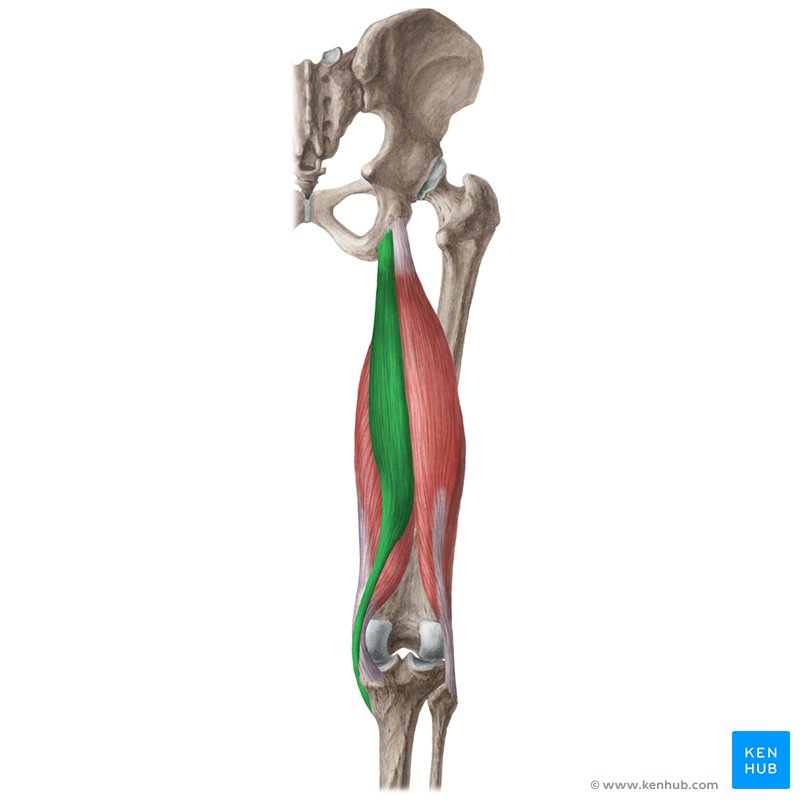
semitendinosus
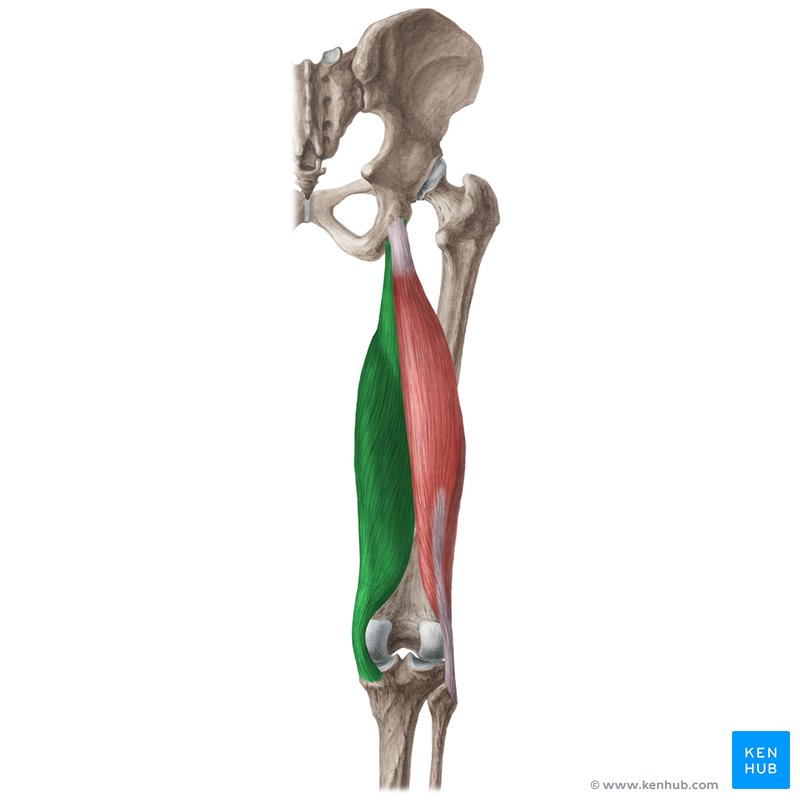
semimembranosus
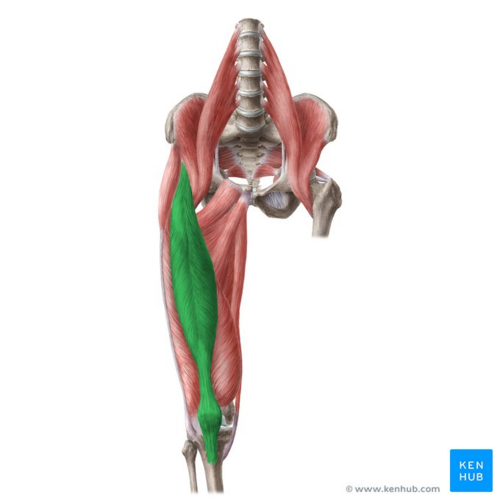
rectus femoris
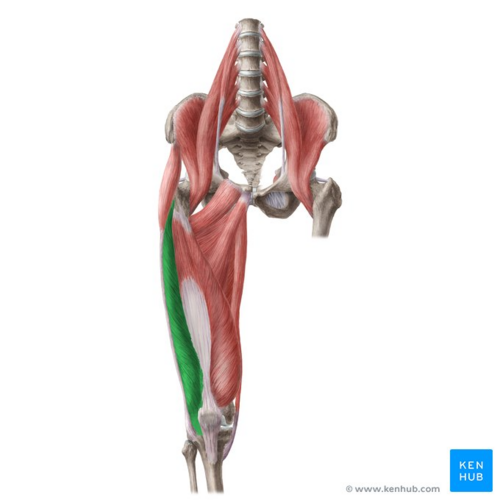
vastus lateralis
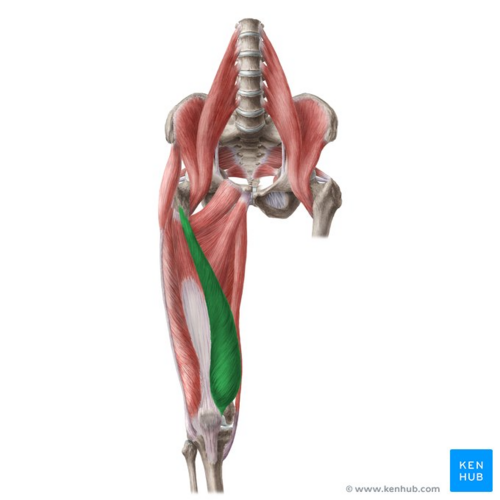
vastus medialus
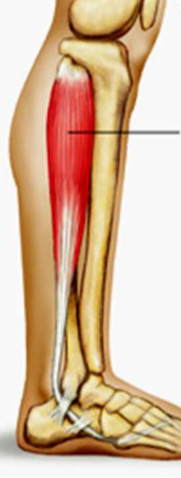
action: plantar flexion
fibularis longus
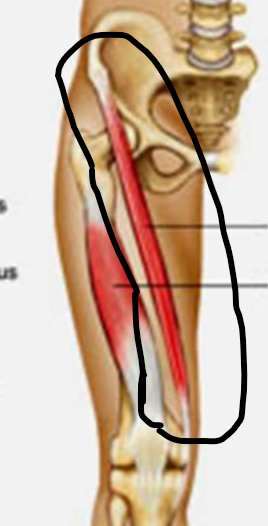
sartorius