COMP ORG FINALS UNIT 6-8 (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
UNIT 6 - – Embedded System
2
New cards
Embedded System
* A computer system that performs a specific function for controlling a machine or other systems requiring control, and an electronic system in the device.
* it is a system with a built-in microprocessor and a program that drives the microprocessor to perform a specific function
* it is a system with a built-in microprocessor and a program that drives the microprocessor to perform a specific function
3
New cards
Embedded hardware
consists of a microprocessor/microcontroller, equivalent to a CPU, memory, input/output device, network device, sensor, driver, etc
4
New cards
Embedded software
consists of an operating system (OS) that directly controls hardware and manages the software, system software, and application software.
5
New cards
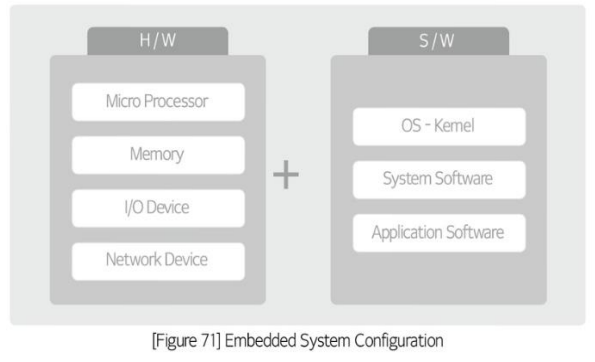
EMBEDDED SYSTEM CONFIGURATION
6
New cards
* Low cost
* Low performance
* Resource constraints
* Stability
* Resilience
* Low performance
* Resource constraints
* Stability
* Resilience
Characteristics of embedded system
7
New cards
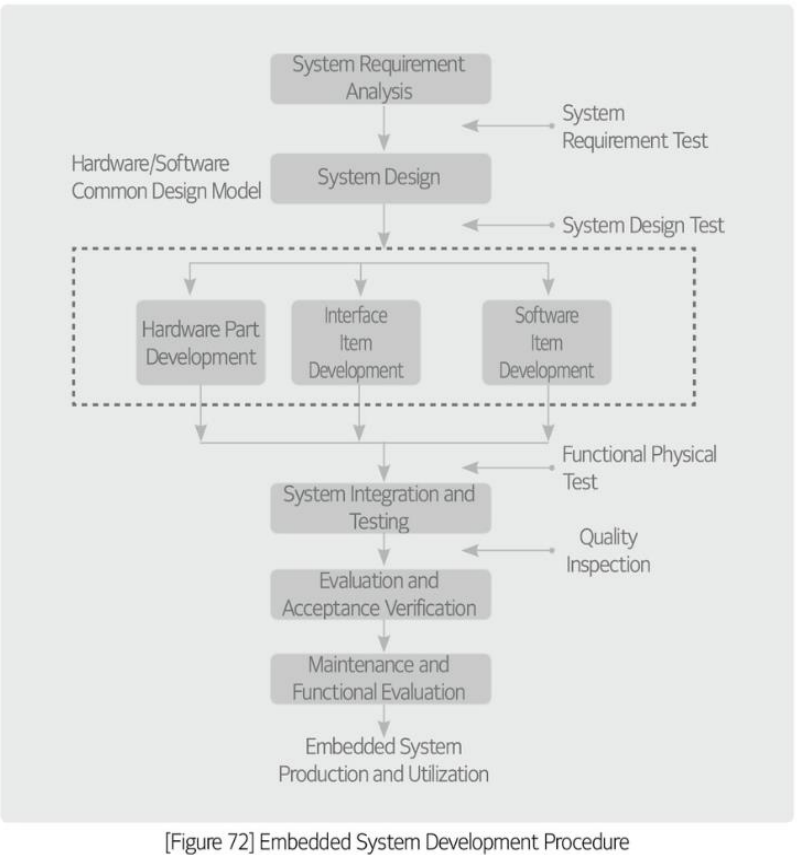
Embedded system development process
8
New cards
Early microprocessor units (MPUs)
____were made in a single chip, in which registers data processing, arithmetic logic unit (ALU) for mathematical operation, and flags for storing result values were integrated into a chip.
9
New cards
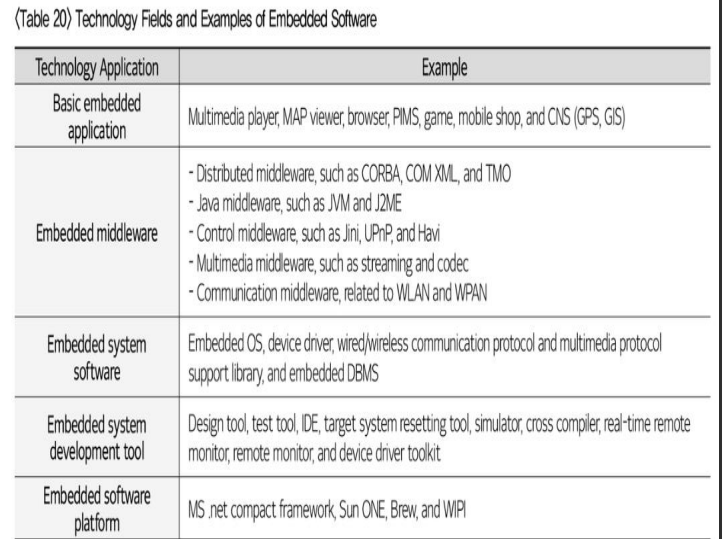
Embedded software
___ refers to software installed in embedded systems
10
New cards
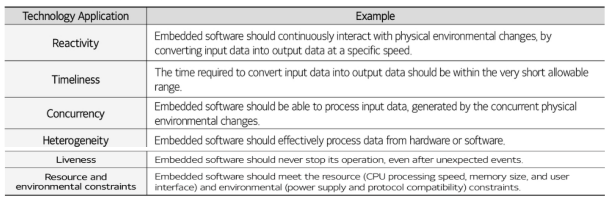
Characteristics of embedded software
11
New cards
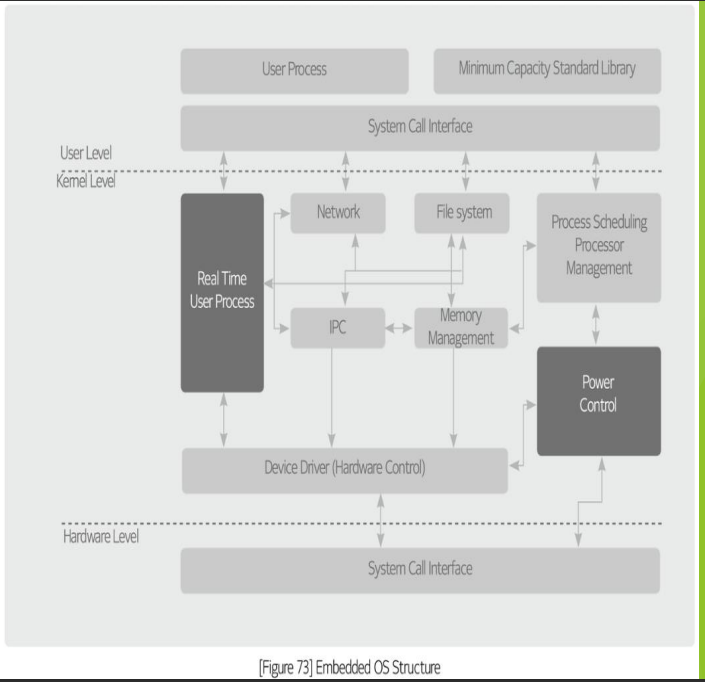
Embedded OS structure
12
New cards
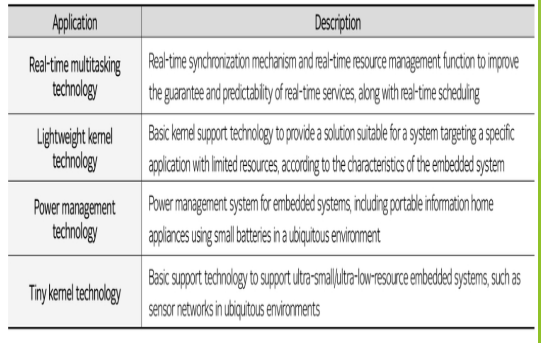
Technologies applied to embedded
13
New cards
Real-time OS (RTOS):
Mainly focuses on controlling application programs or hardware affected by a limited amount of time. The leading operating systems include VxWorks, VRTX, QNX, and pSOS
14
New cards
Non real-time OS:
Mainly focuses on development convenience, scalability, and diverse operating environments. The leading operating systems include Linux series, embedded Window XP. and Windows CE
15
New cards
Linux
___is installed in about 65% of all embedded devices and is still growing very fast, at an annual average of 17%
16
New cards
17
New cards
UNIT 7: Information System Implementation
18
New cards
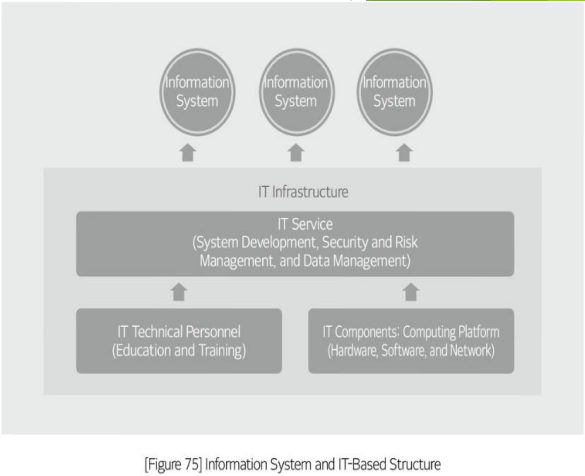
Information system
* uses information technology (IT) to perform business procedures, such as providing necessary information, or business processing required by enterprise
* creates a system that enables IT personnel to provide IT services by using IT components, such as hardware and software, to perform organizational business procedures.
* creates a system that enables IT personnel to provide IT services by using IT components, such as hardware and software, to perform organizational business procedures.
19
New cards
* web system architecture
* client-server system architecture
\
* client-server system architecture
\
types of structures for an information system:
20
New cards
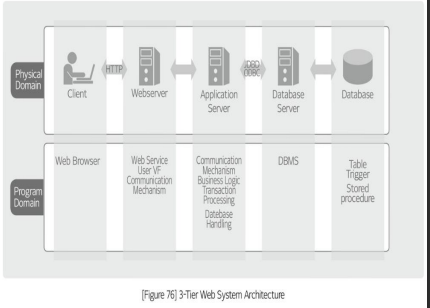
WEB SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
21
New cards
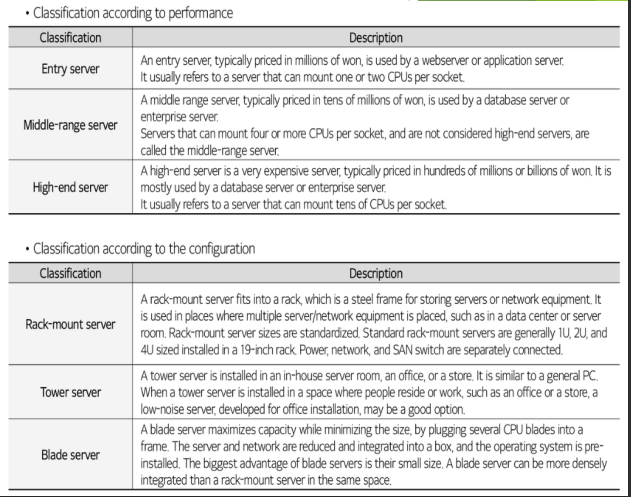
server
* A ___is the most fundamental component required when implementing an information system.
* A__ is a hardware platform that runs server application programs and is classified in various ways, according to performance and type as follows.
* A__ is a hardware platform that runs server application programs and is classified in various ways, according to performance and type as follows.
22
New cards
Storage
* ___is classified into enterprise or mid-range storage, according to processing capacity, It provides large storage space, high performance, and high availability, compared to general disk arrays.
23
New cards
OS
An__ is defined as system software that operates and manages an application platform and that provides an interface between an application program and the platform.
24
New cards
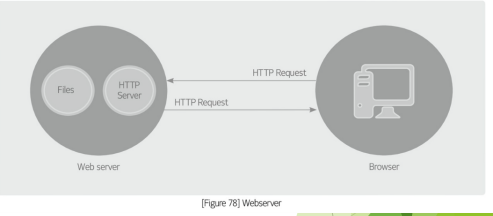
webserver
A __ provides media content, such as HTML and text, images, and video, to web clients, like web browsers. It provides data through the HTTP protocol to enable a web browser to present information. Leading webserver products include Apache, Nginx, and IS (see \[Figure 78}).
25
New cards
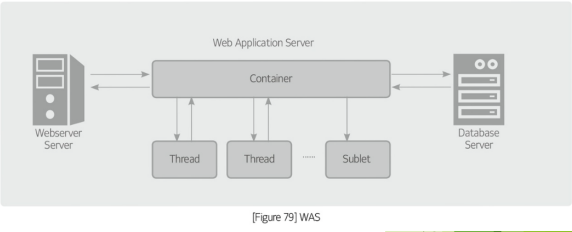
Web application server (WAS)
A ___ is a middleware that enables the stable transaction processing of web client requests and helps develop the distributed systems.
26
New cards
Transaction processing (TP) monitor
A___ is transaction management middleware that supports the distributed transaction processing and monitors transactions, which are the minimum processing units between active sessions and systems in various protocols, in order to maintain them consistently
27
New cards
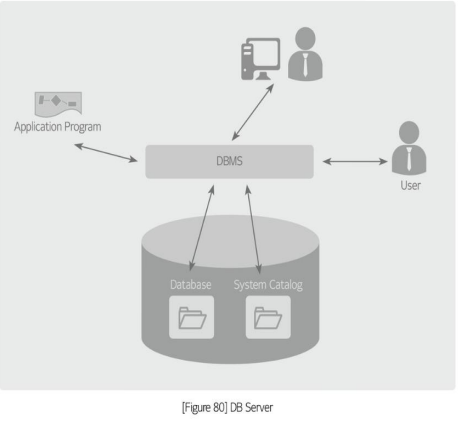
DB server (Database management system, DBMS):
A ___ server provides the database type, database management technology, and query language for the access to and modification of structural data.
28
New cards
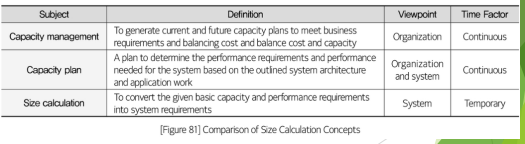
Concept of size calculation
System sizing is to estimate or calculate a system's size using a mathematical methodology, based on actual work and applications.
29
New cards
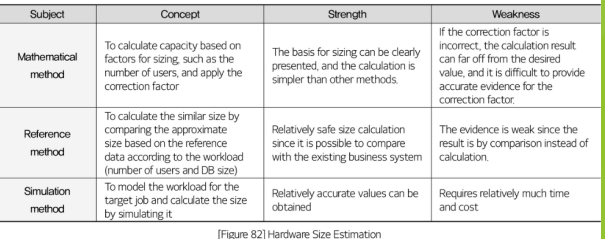
. Concept of size calculation
Sizing is a matter of prediction, and the calculation method significantly affects the accuracy of the calculation. Hardware size calculation methods are generally classified into the mathematical calculation,
30
New cards
. Size calculation targets
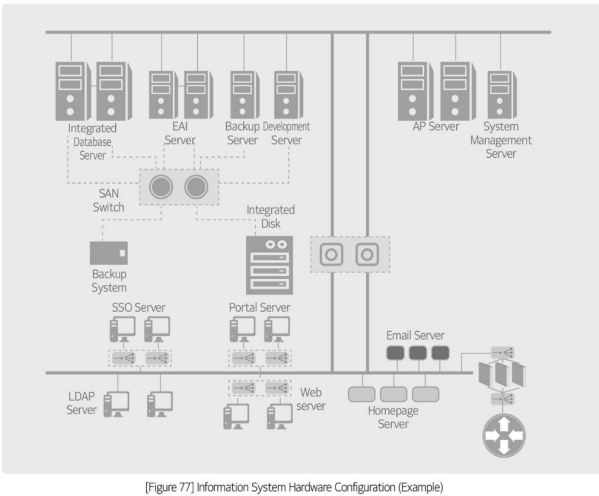
the target for sizing includes not only hardware, but also software or network. As shown in \[Figure 83\], the size calculation target in the capacity calculation guidelines is hardware, which is defined as servers, not PCs or other peripherals.
31
New cards
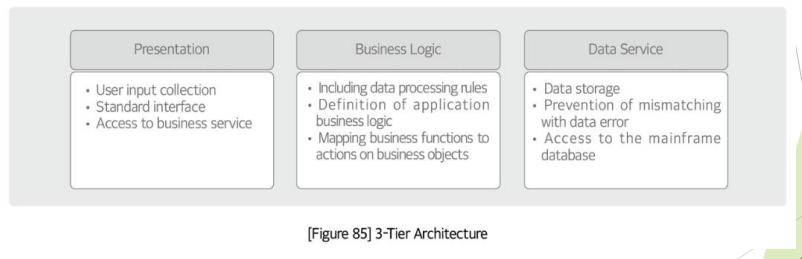
3 tier Architetcture
32
New cards

validate basic data and task analysis
33
New cards
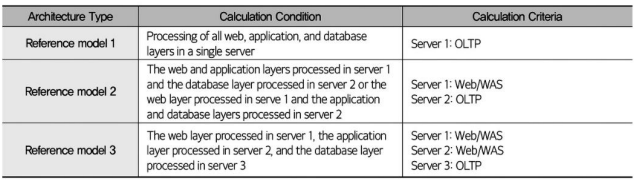
reference model
34
New cards
hyper converged infrastructure (HCI)
__ is a concept that overcomes the limitations of Cl by eliminating the expensive external storage
35
New cards
UNIT 8: Fault Response Technology
36
New cards
High Availability (HA)
___refers to an uninterrupted service. However, it is not easy to make a system, that consists of numerous parts and software, 100% availabl
37
New cards

Availability Calculation Formula
38
New cards
* Hot standby (Active-standby)
* Mutual takeover (Active-active)
* Concurrent access
* Mutual takeover (Active-active)
* Concurrent access
HA configuration type
39
New cards
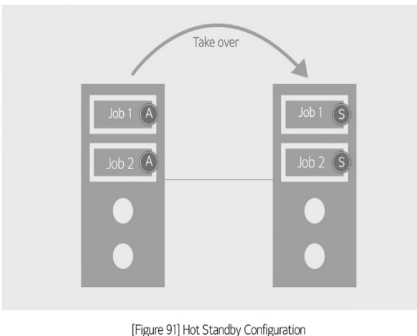
Hot standby (Active-standby)
the simplest structure of HA clustering implementation. It consists of an active server and a standby server that are normally in a standby state. The standby server is powered on, and the operating system is running.
40
New cards
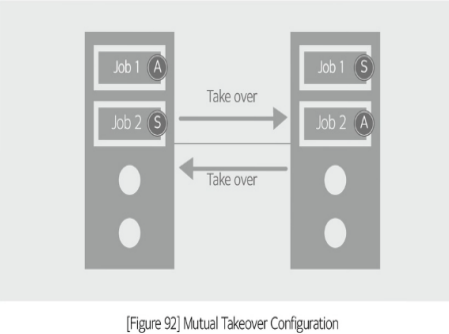
Mutual takeover (Active-active)
is the case of two or more systems operating with separate servers. When a server fails, its services are switched to the designated server (takeover) to continue the services
41
New cards
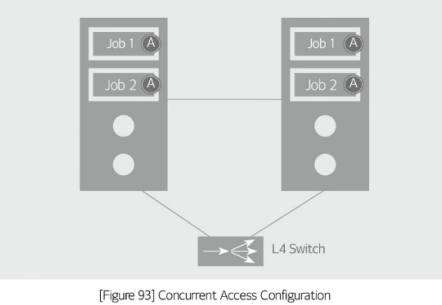
Concurrent access
a structure in which multiple systems process tasks in parallel in order to provide availability. Al servers operate in an active state. Even if a server fails, the service continuity can be guaranteed without a fail-over.
42
New cards
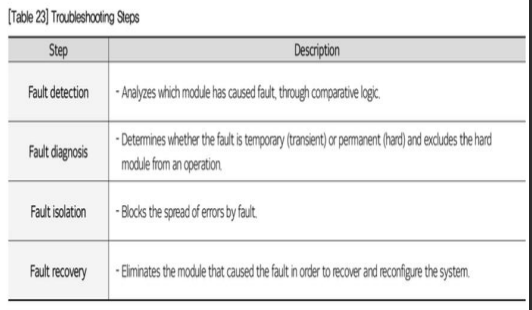
fault-tolerant system
* A ___can continuously perform the functions specified in the design, even if a system part fails.
* it cannot use certain functions when a component fails
* When components continue to fail, the unavailable functions gradually increase, and the system shuts down when a critical failure occurs.
* it cannot use certain functions when a component fails
* When components continue to fail, the unavailable functions gradually increase, and the system shuts down when a critical failure occurs.
43
New cards
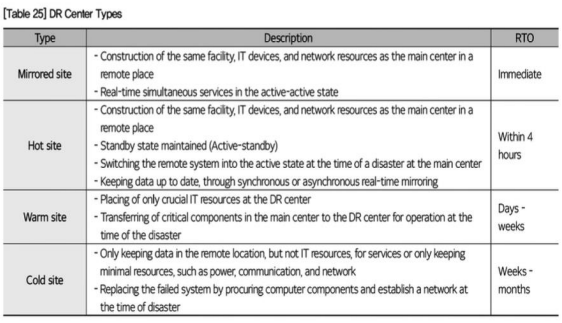
Disaster Recovery System
an overall plan and system to minimize the impact of a disaster on a business, by locating al or part of the information system infrastructure in a location different from the disaster point, then quickly recovering from a disaster when it occurs.
44
New cards
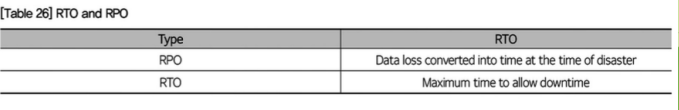
* Recovery Time Objective (RTO)
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
* Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
The most important factors to consider when implementing a Disaster Recovery (DR) system are __ and _