Advanced Periodontal Instrumentation
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the explorer strokes?
assessment
contact with surface of tooth but without pressure application
fluid stroke, medium length
What are the root planing strokes?
light to moderate pressure
medium length strokes
What are the calculus removal strokes?
powerful (biting) strokes
moderate to firm pressure
short stroke length
What are the types of strokes?
vertical
horizontal
oblique
channeling
crosshatching (multidirectional)
What is the channeling stroke?
overlapping strokes on root surface that covers every mm of the tooth, going slower
short strokes, firm to light strokes
vertical or oblique direction
used for root planing to smooth things out
What does a channeling stroke utilize?
Utilizes the terminal 1/3 of the instrument blade
Utilizes a specific pattern based on length and width of deposit
What is the crosshatching stroke?
combination of vertical, horizontal, and oblique strokes
What are the 4 most common extra-oral fulcrums?
palm up
chin cupping
finger assisted
finger on finger: using non dominant
What are the things needed for fulcrum stability?
need a broad area of contact between the hand and patient's face
establish equal pressure of fulcrum to pressure exerted against tooth and blade
use extended grasp
What does a strong fulcrum look like?
palm up
fingers together and stationary
activation by shoulder
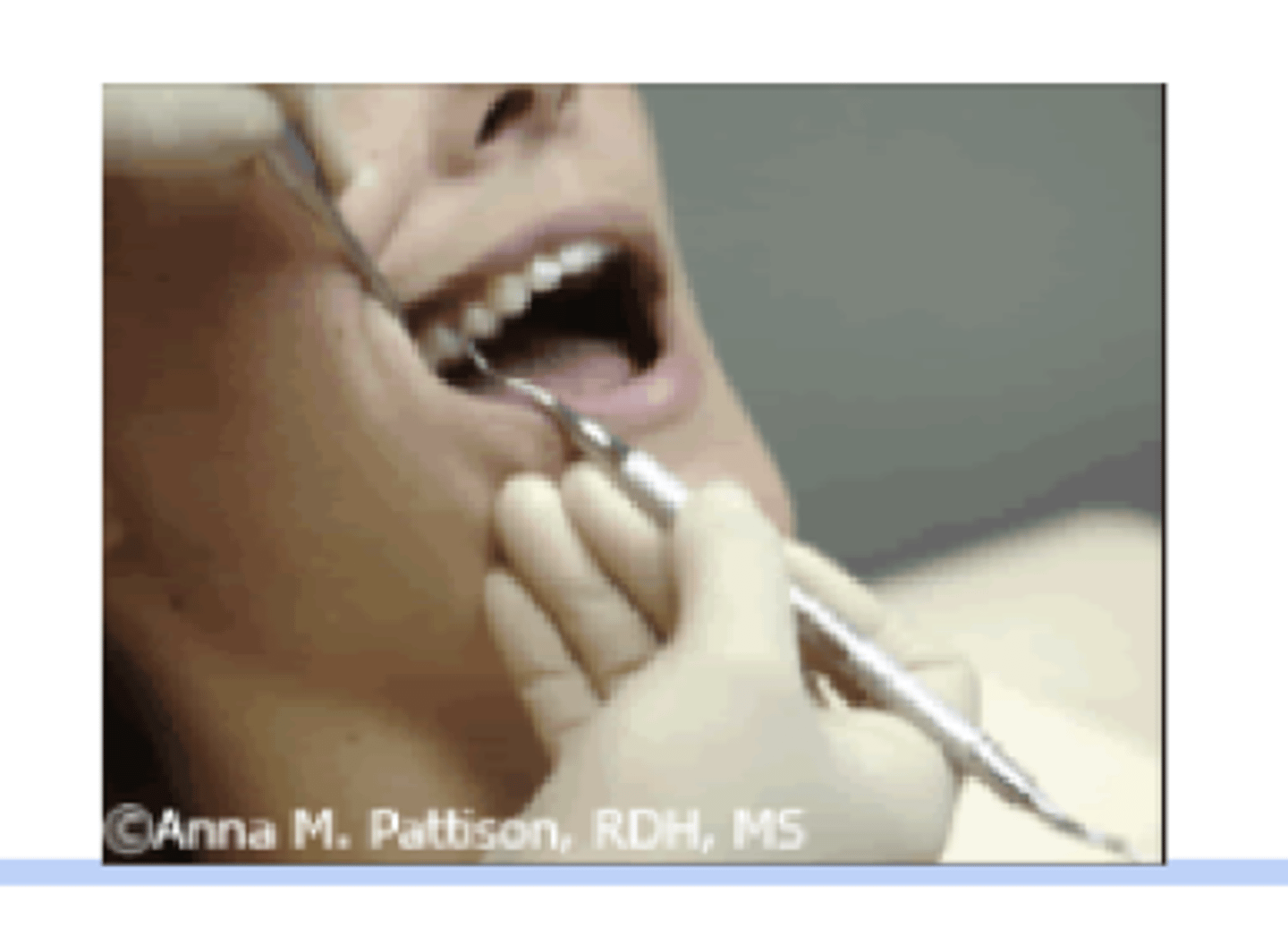
What are the benefits of an extra-oral fulcrum?
Allows your whole hand to activate a powerful stroke
Wrist kept in a neutral position
Gain improved ergonomics
What are the disadvantages of extra-oral fulcrums?
Misunderstandings or misinterpretations of the elements that comprise a properly established extraoral fulcrum
Some clinicians believe that they are too unstable and may result in slipping and injury to the patient
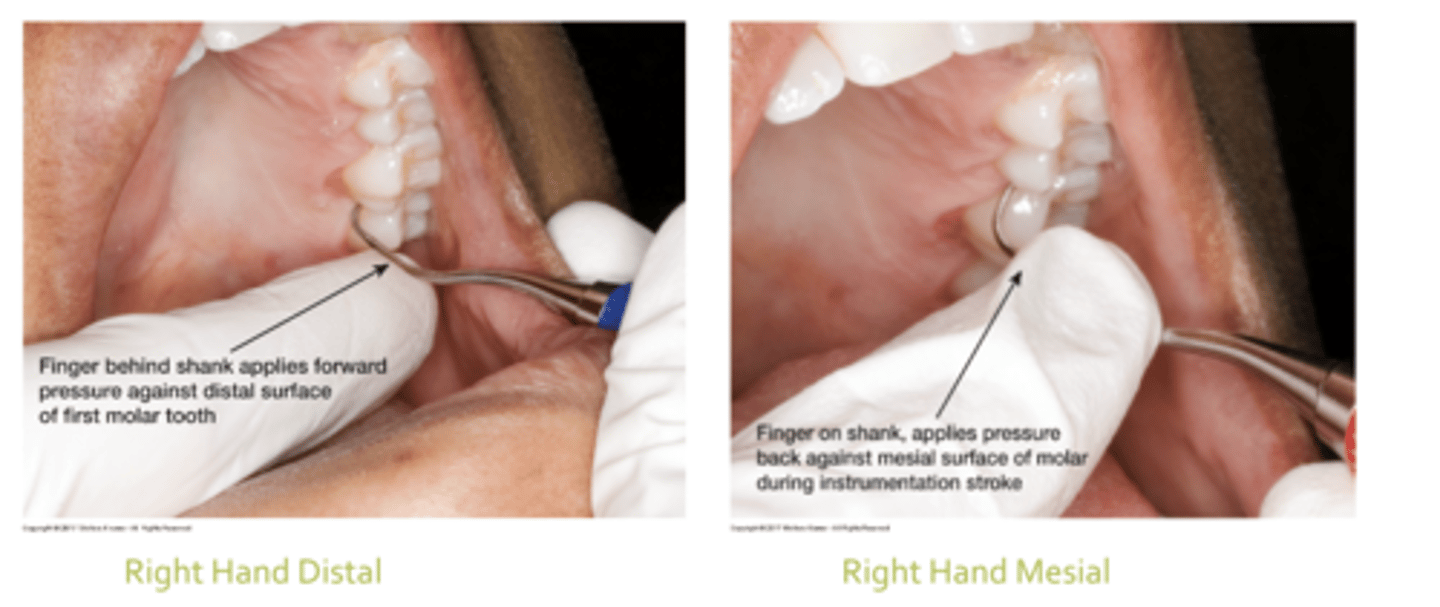
Where are your fingers going on the shank for distal and mesial?
distal behind
mesial on top
What are the benefits of standing dentistry?
Enhanced access
Increased operator visibility and direct vision
Easy movement around chair
Use larger muscle groups in upper torso and arms
Relieving stress on back
Allows stabilization and balance over both hips and feet
What should you do when standing?
Keep moving (to increase blood supply to legs)
Keep shoulders in line with body and forearms parallel to the floor
Keep working distance the same as in a seated position
Position patient's mandible as parallel to the floor as possible(when working on the mandibular arch)
Distribute weight evenly between both hips/legs/feet
What should you not do when standing?
Do not lean over the patient for a better view
Do not stand in one position for a long period of time (try sitting for maxilla and standing for mandible)
Do not stand with weight on one leg
What is the complementary approach of the ultrasonic?
1. Use ultrasonic at appropriate power to remove bulk of deposits
2. Follow with hand instruments for areas not accessible with ultrasonic
3. Finish with ultrasonic for debridement/flushing with thin tip -->
Irrigation
Reduce bacterial load