Proponents & Laws - 1st Sem Chemistry
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Democritus
In 400-300 BCE, he proposed that matter is made of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms separated by a void, a concept that forms the basis of modern atomic theory.
Aristotle
He rejected atomism, asserting that matter is a continuous substance, infinitely divisible and composed of four fundamental elements—earth, air, fire, and water.
Robert Boyle (1627-1691)
He published the The Sceptical Chymist. Defined the "element" as the simplest composition of matter that cannot be broken down further by any chemical means. Suggested that atoms of elements combine to form different "compounds."

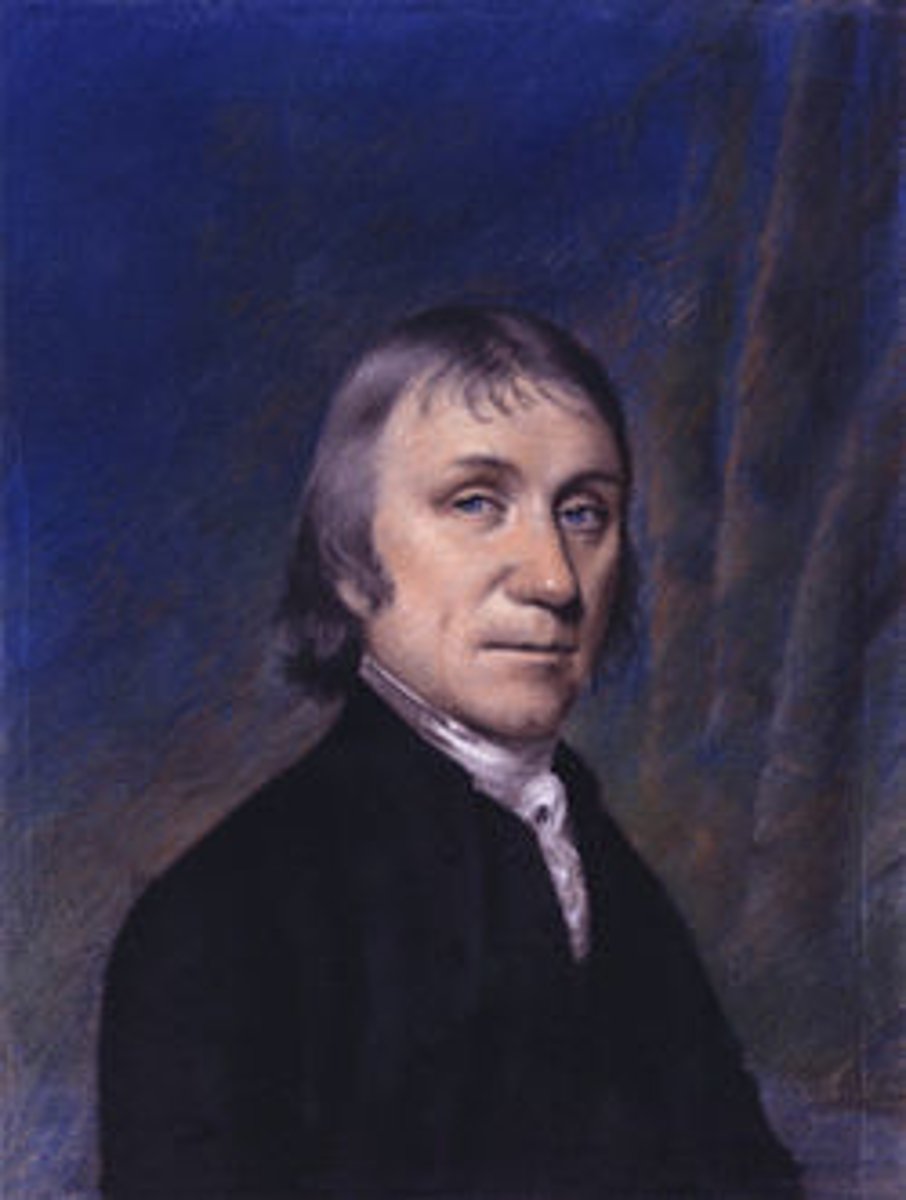
Joseph Priestly (1733-1804)
Isolated oxygen gas, which he called "dephlogisticated air" by heating mercury (II) oxide (HgO).

Phlogiston theory
An early 18th-century scientific theory that proposed that all combustible bodies contained a fire-like element which was released during combustion, fermentation, and metal rusting.
Phlogiston
A fire-like element released during combustion, fermentation, and metal rusting.
Antoine Lavoisier (1743-1794)
Known for proving the law of conservation of mass by burning a diamond in a sealed jar and showing the total mass stayed constant. Also studied combustion and respiration, heating mercury in a sealed container to produce mercury oxide and identify the gas supporting combustion and respiration, which he named oxygen. Measures the amount of the substances before and after a chemical reaction in a closed vessel.

Father of Modern Chemistry
Lavoisier is also known as the "_____."
Law of Mass Conservation
First formulated by Lavoisier in the 18th century and is the foundation of balancing chemical equations. The law states that in a chemical reaction, the mass of substances produced is equal to the mass of substances reacted.
mass (before reaction) = mass (after reaction)
Reactants -> Products
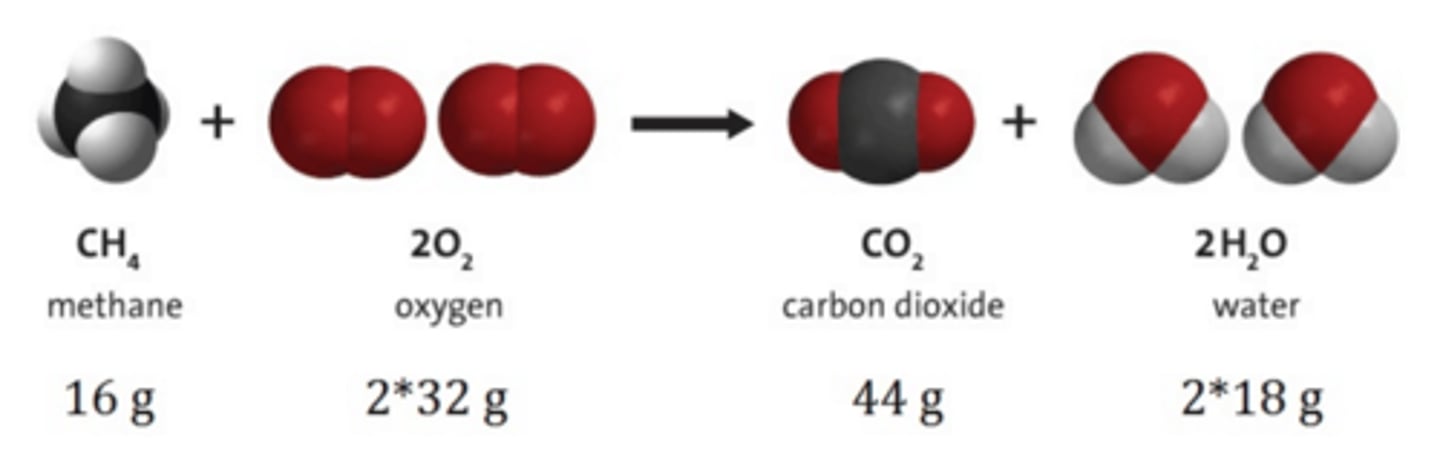
Law of Definite Composition/Law of Definite Proportion
States that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same fixed ratio by mass, regardless of its source or method of preparation. In other words, the composition of a pure compound is constant and does not depend on where it is obtained or how it is made.
Law of Multiple Proportion
States that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in a simple whole-number ratio.
Matter is made up of extremely small particles called atoms; Atoms of the same element are identical, and are different from those other elements; Compounds are formed when atoms of different elements combine in certain whole-number ratios; Atoms rearrange only during a chemical reaction to form a new compound
Enumerate the four (4) postulates of Dalton's atomic theory:
Dalton 1807
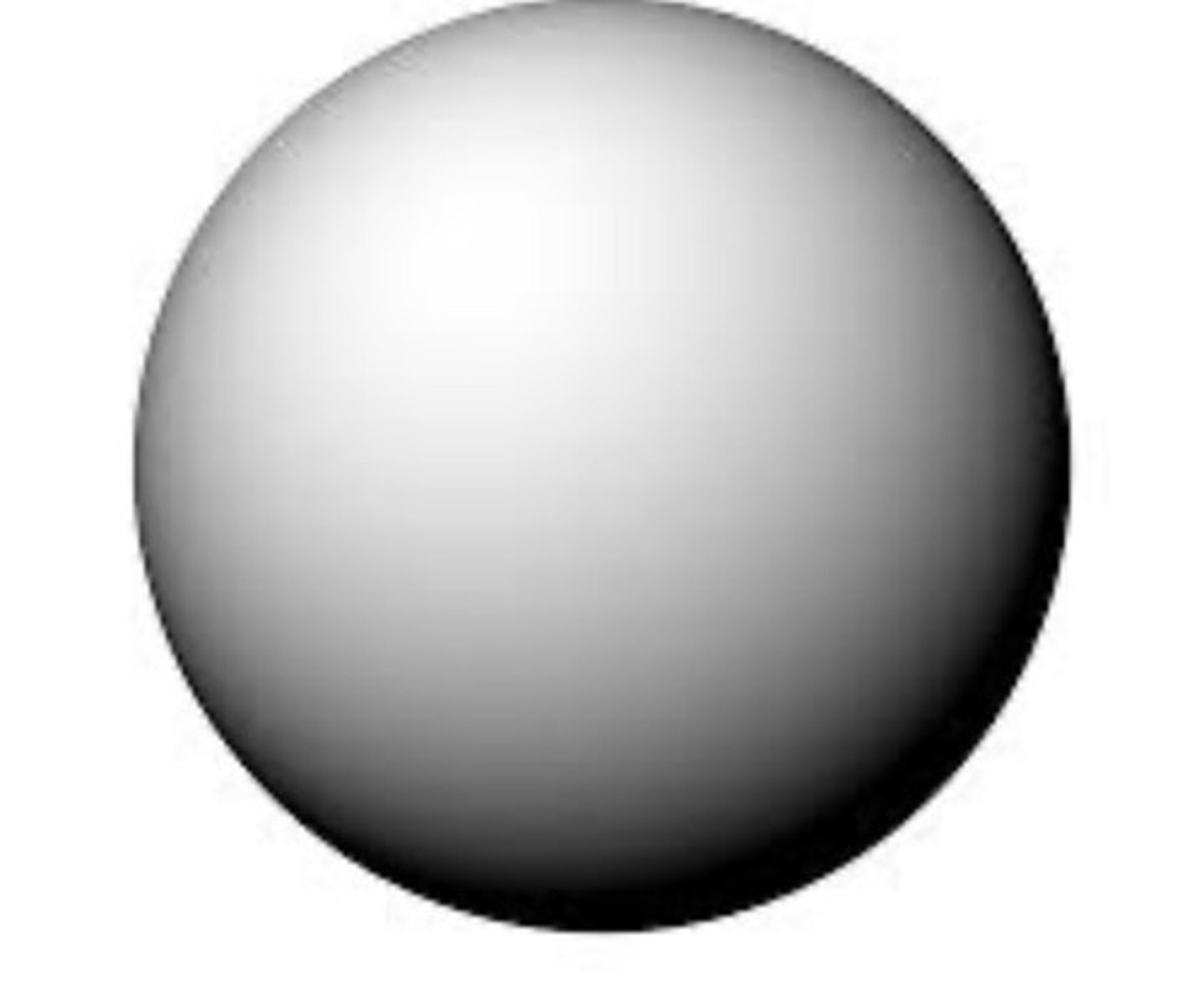
State the year and proponent of the solid sphere model.

Thomson 1897
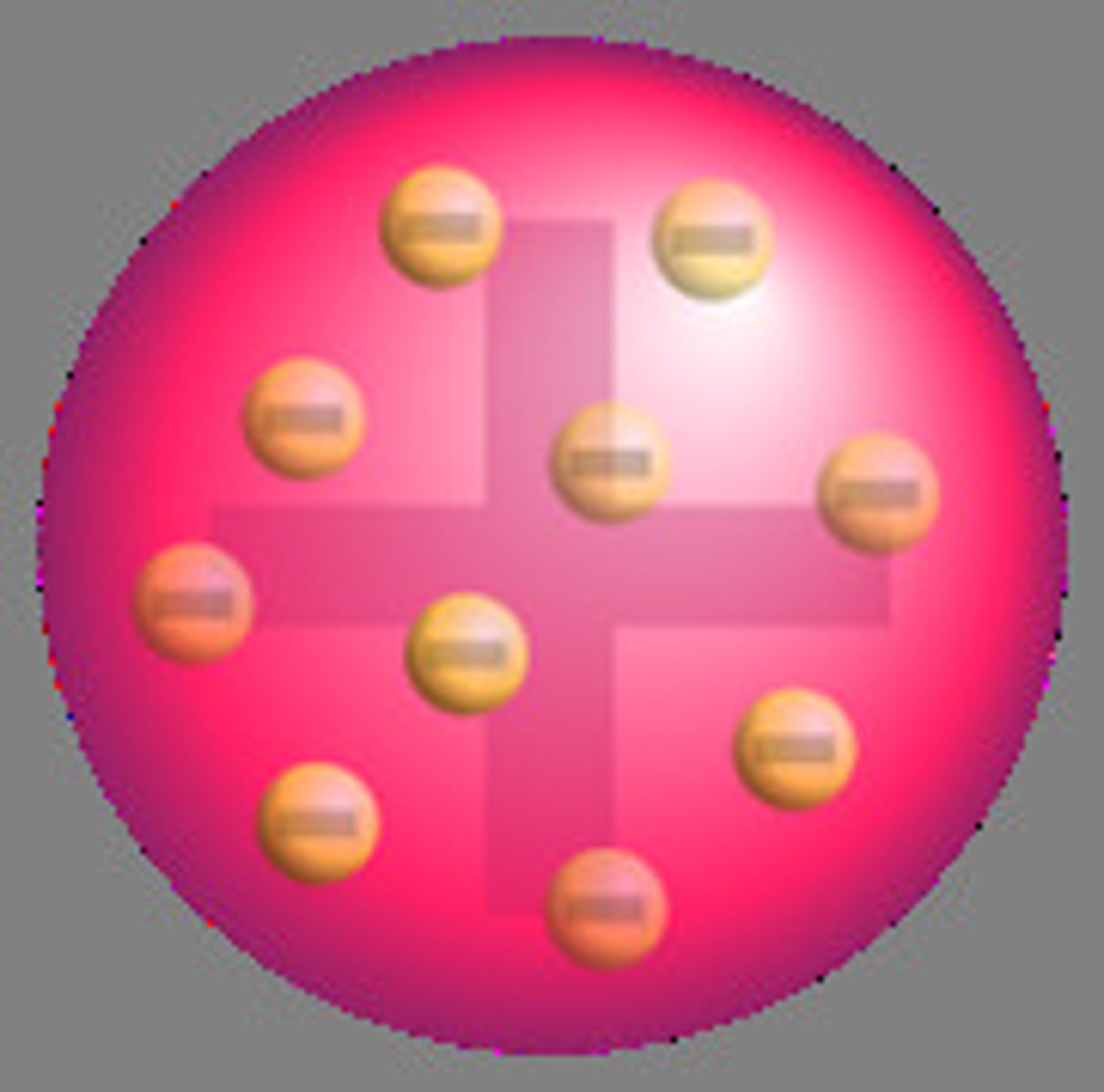
State the year and proponent of the plum pudding model.
Rutherford 1911
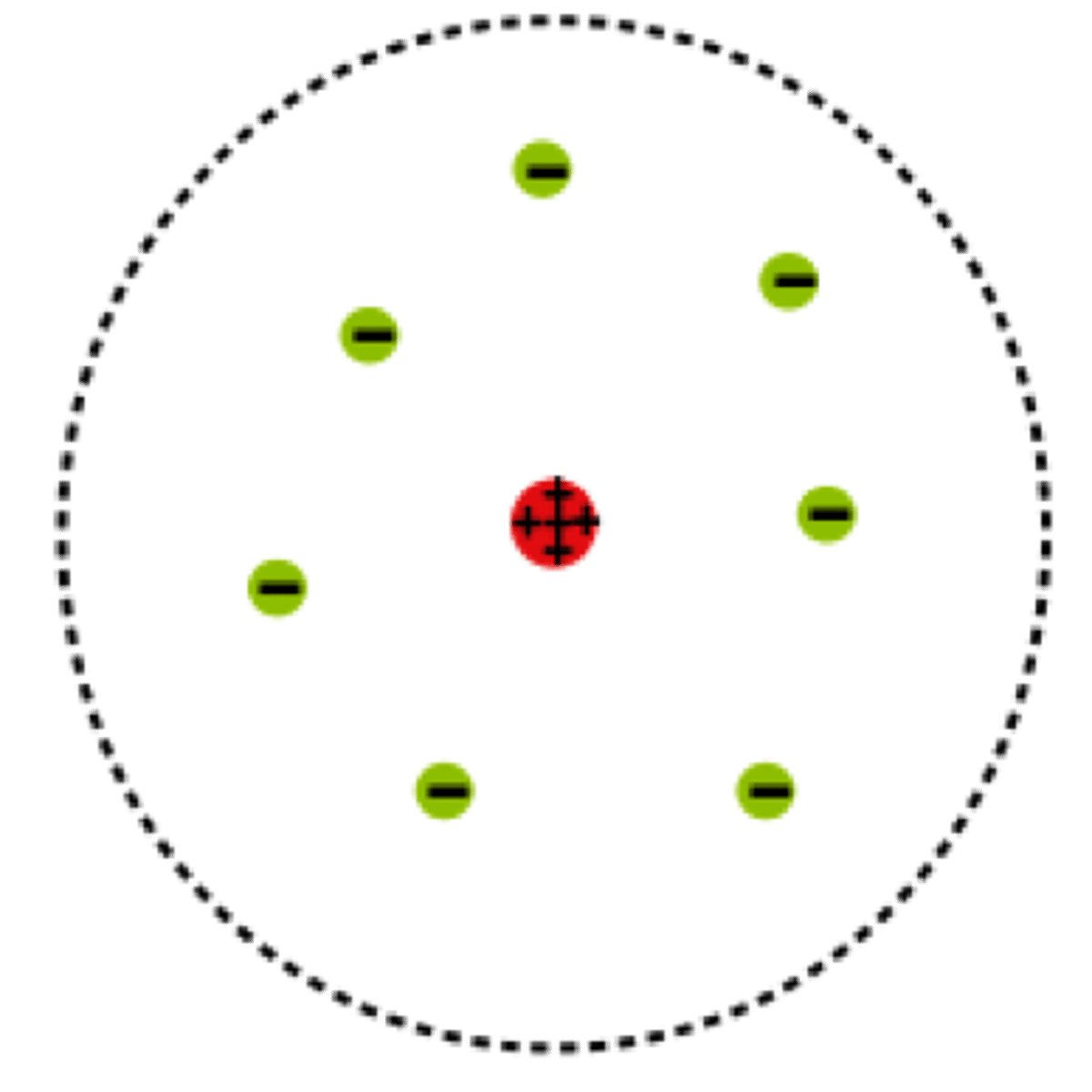
State the year and proponent of the nuclear model.
Bohr 1913
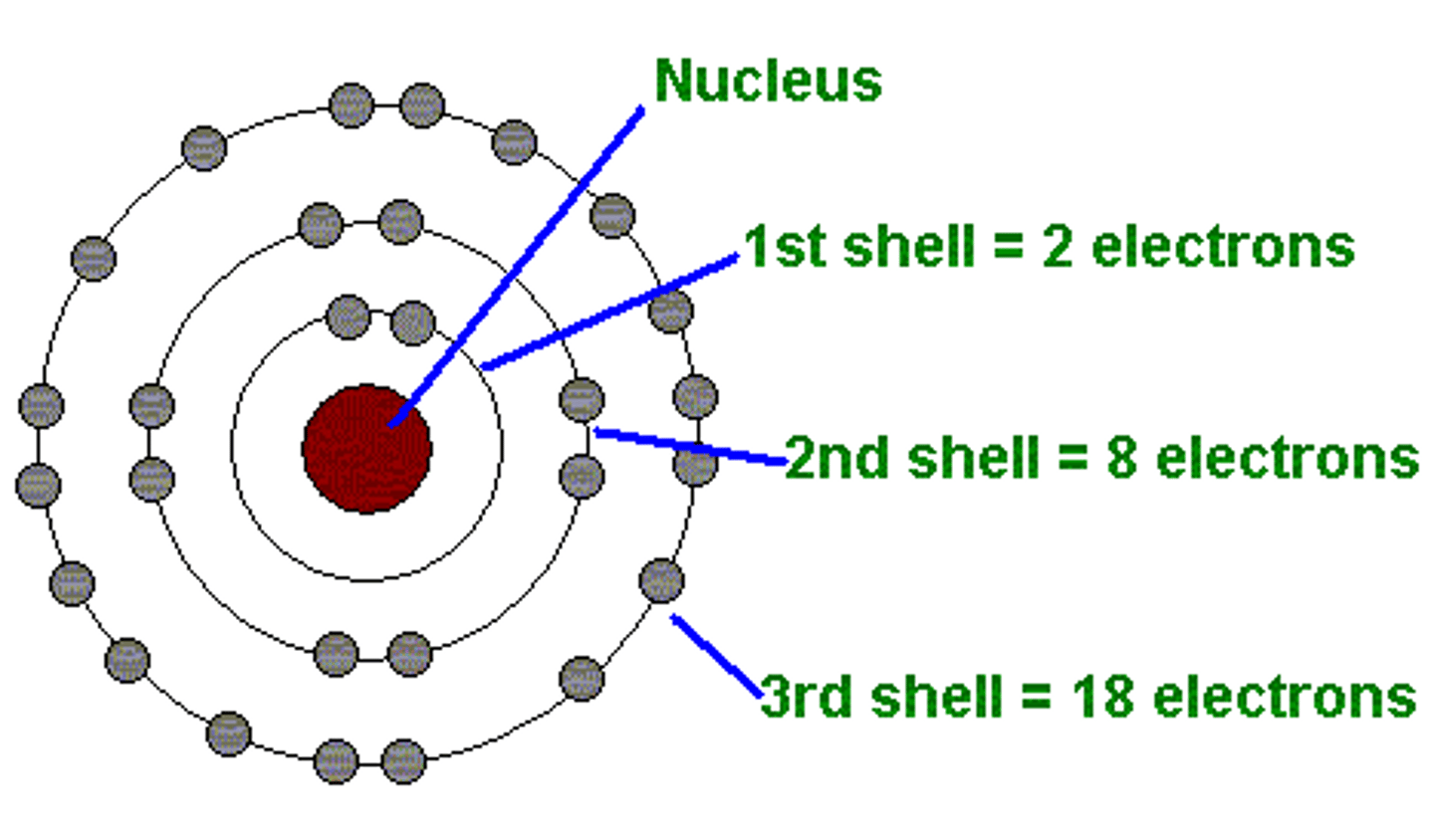
State the year and proponent of the planetary model.
Schrodinger 1926
State the year and proponent of the quantum model.
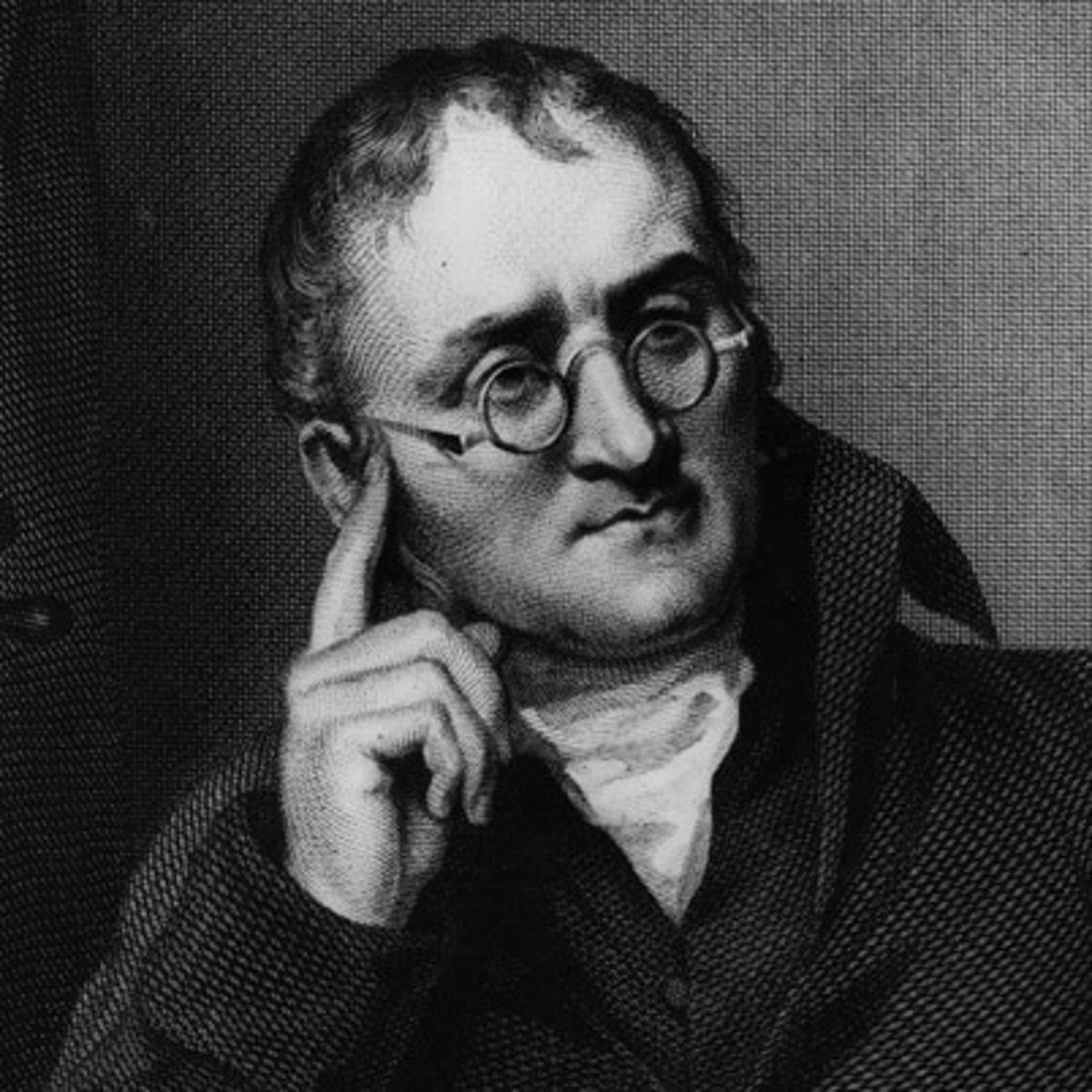
John Dalton
- Experimented on Law of Chemical Combination
- Discovered the invisible atom
- Proposed the Billiard Board model

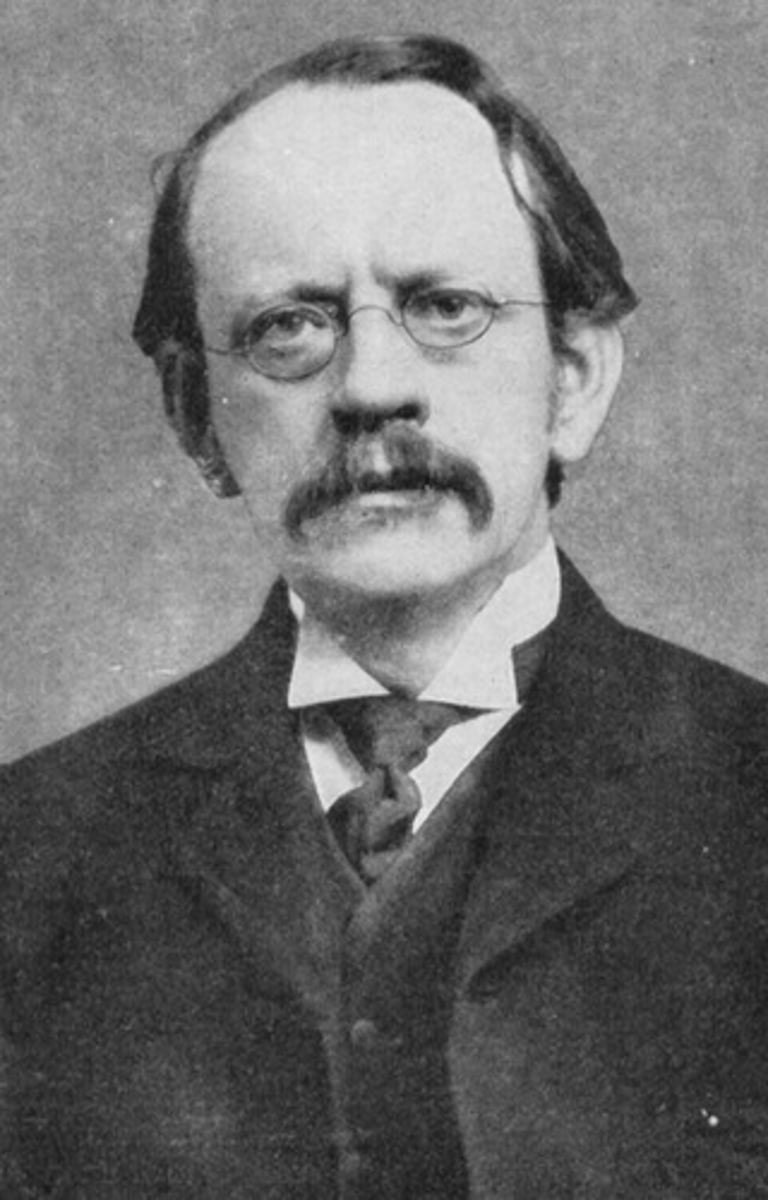
J.J. Thomson
- Experimented on the cathode ray tube (proved atom is divisible)
- Discovered the electron
- Proposed the plum pudding model

Eugen Goldstein
- Experimented on canal rays
- Discovered the positive rays (precursor to protons)
- Did not propose a model
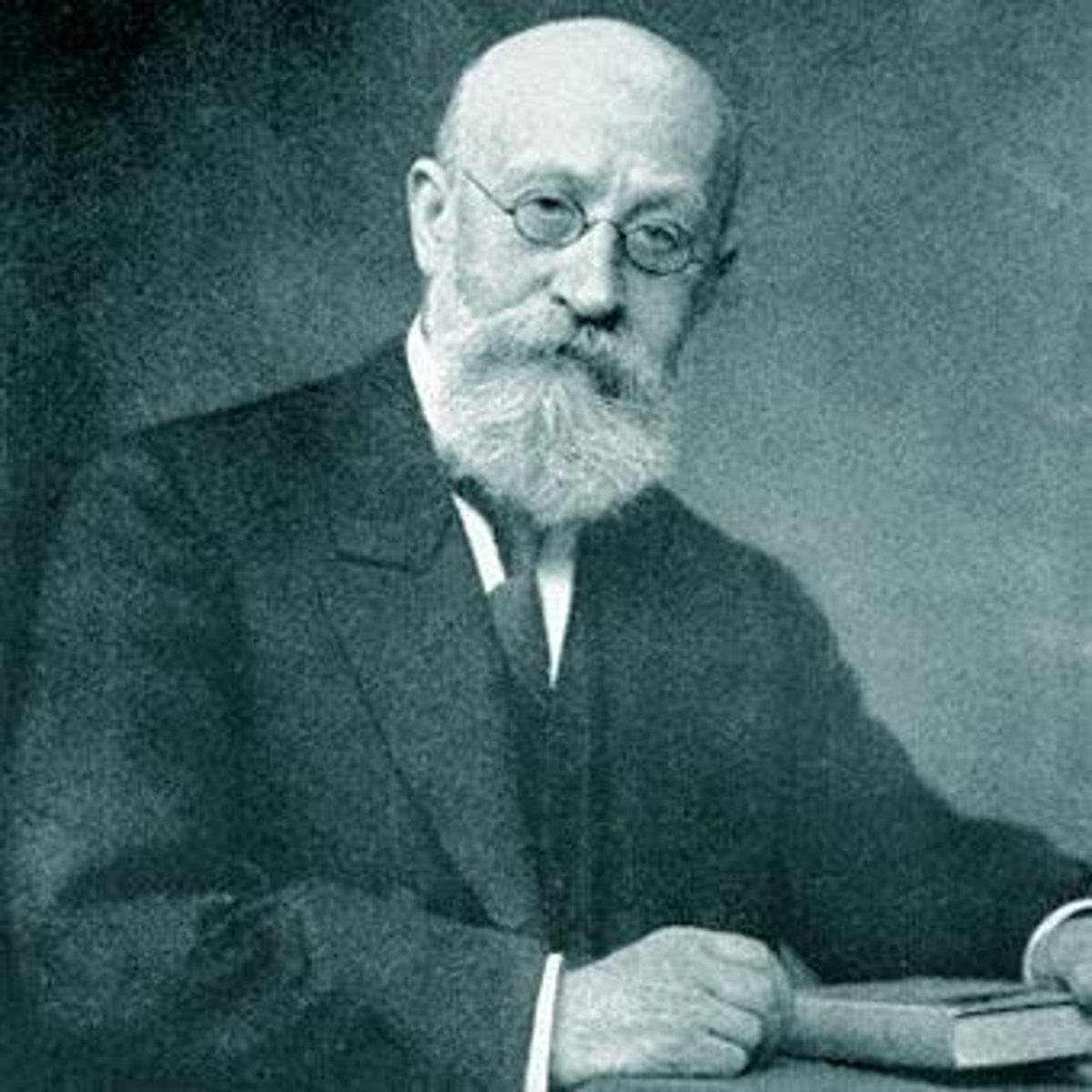

Ernest Rutherford
- Gold foil experiment and alpha bombardment of nitrogen
- Discovered the nucleus and proton
- Proposed the nuclear model
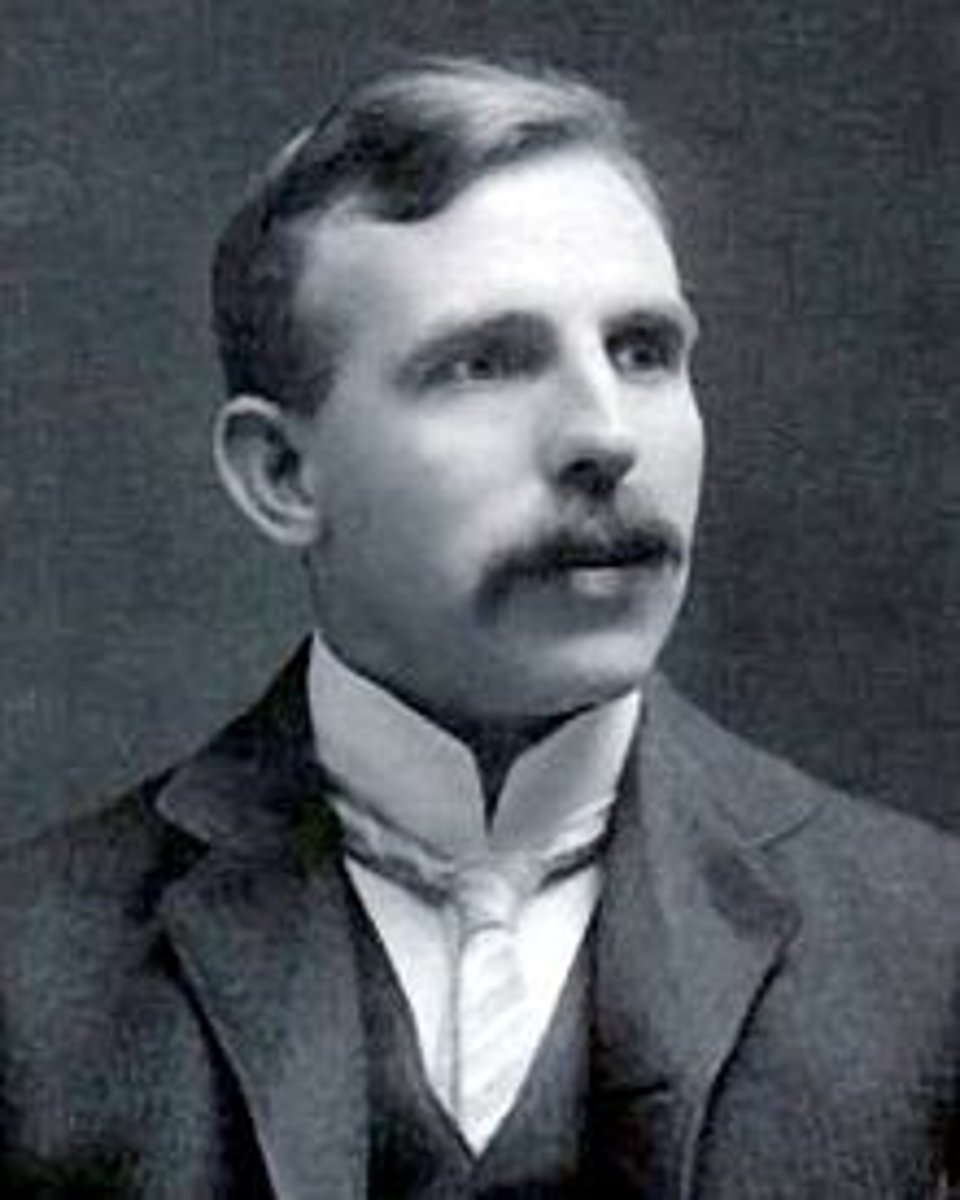

Niels Bohr
- Hydrogen spectrum studies
- Discovered the energy levels
- Proposed the Planetary model

James Chadwick
- Experimented on beryllium + alpha particles
- Discovered the neutron
- Did not propose a model

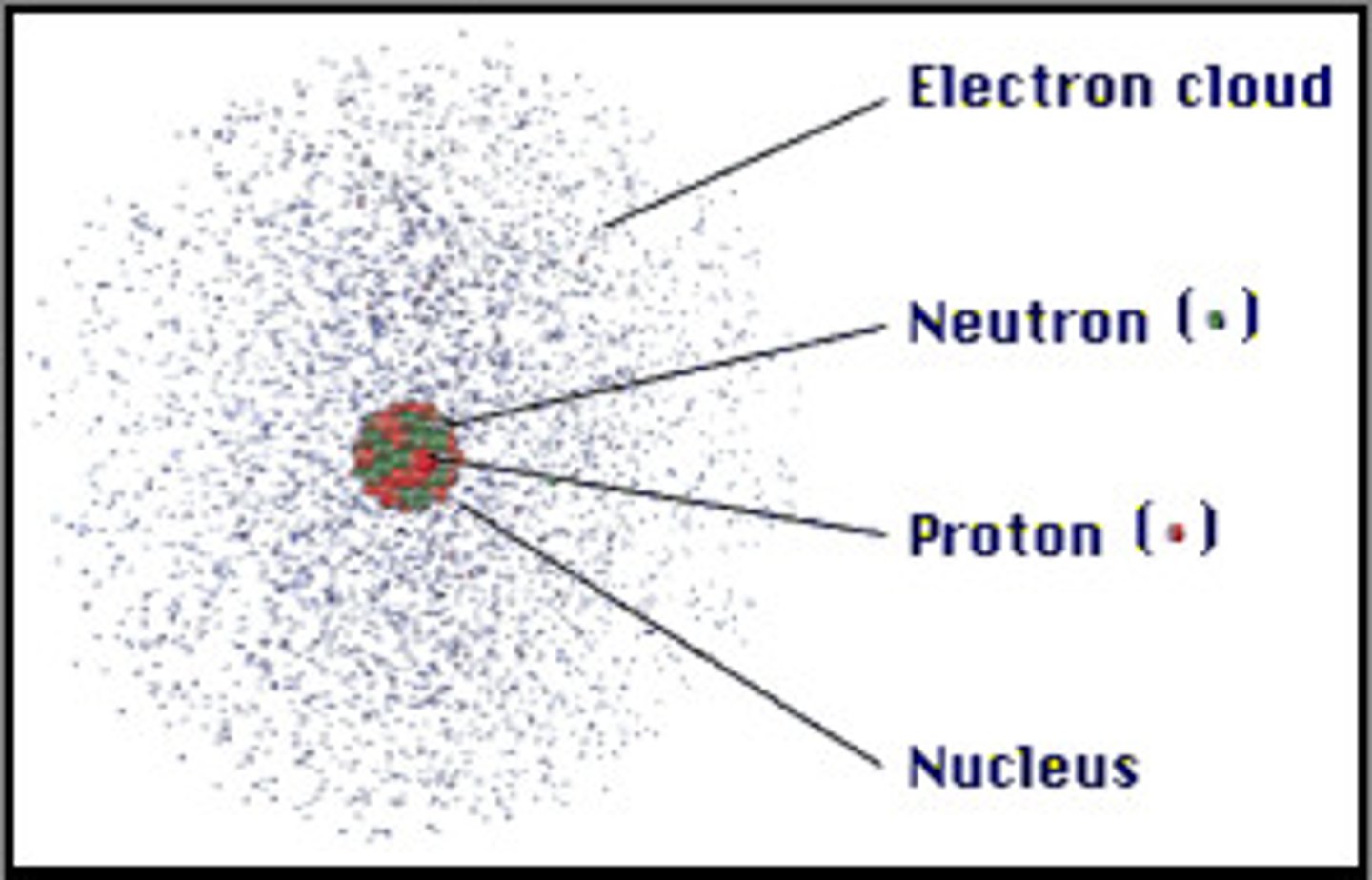
Schrodinger and Heisenberg
- Experimented on quantum mechanics/wave-particle
- Discovered the electron clouds (orbitals)
- Proposed the Quantum Mechanic Model