Set 4: The Alvarez Hypothesis
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Iridium
Platinum group metal
Foram

Iridium anomaly
Aristarchus
Heliocentric in 3rd century BC
Alfred Wegener
Continental drift
Gregor Mendel
Genetics
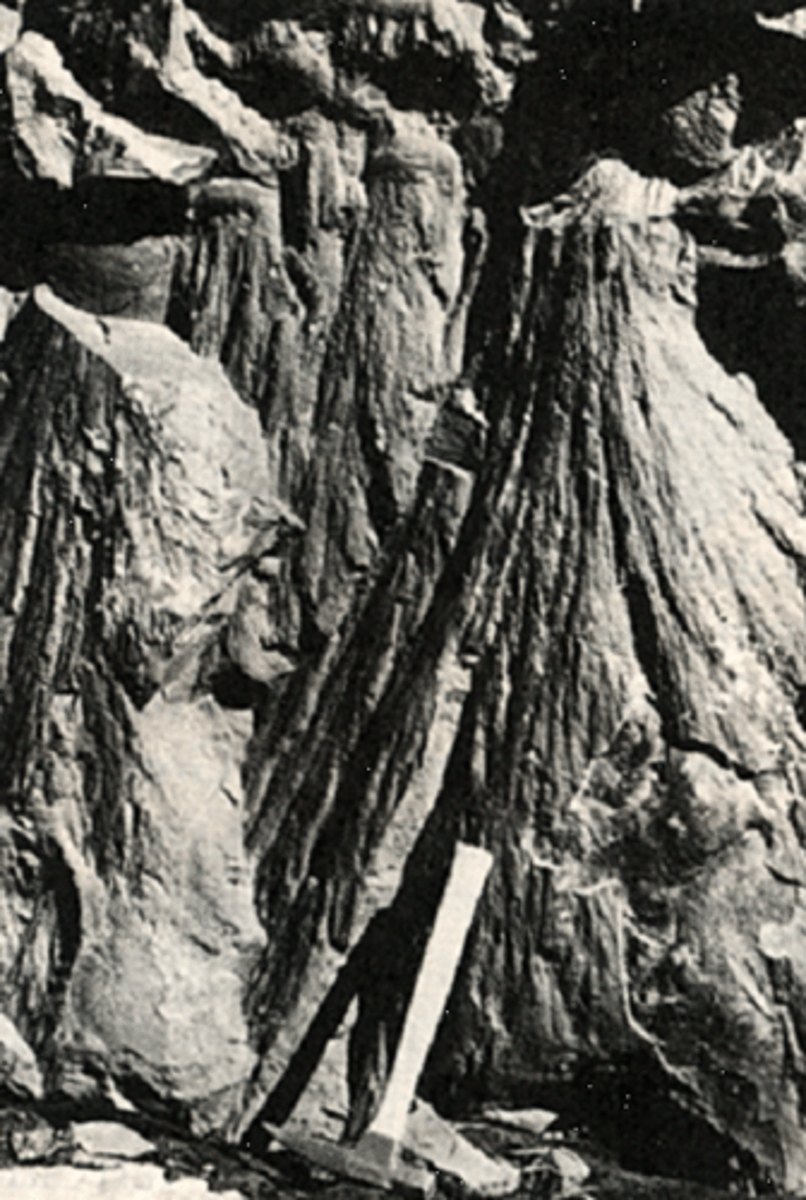
Shatter cones
Fossil shock waves, horsehair texture

Shocked quartz
>= 2 sets parallel deformation features, only at craters and nuclear sites
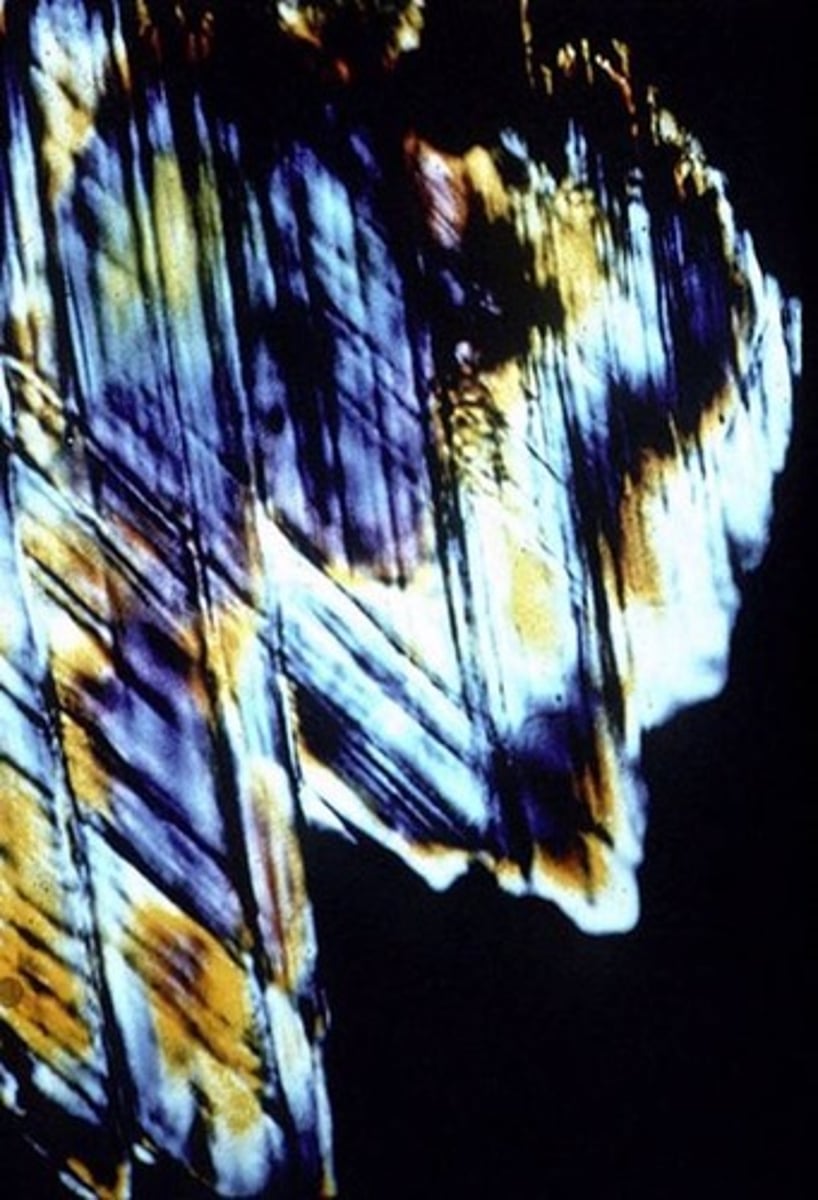

Spherules
Tiny 'glass raindrops' that turn to clay
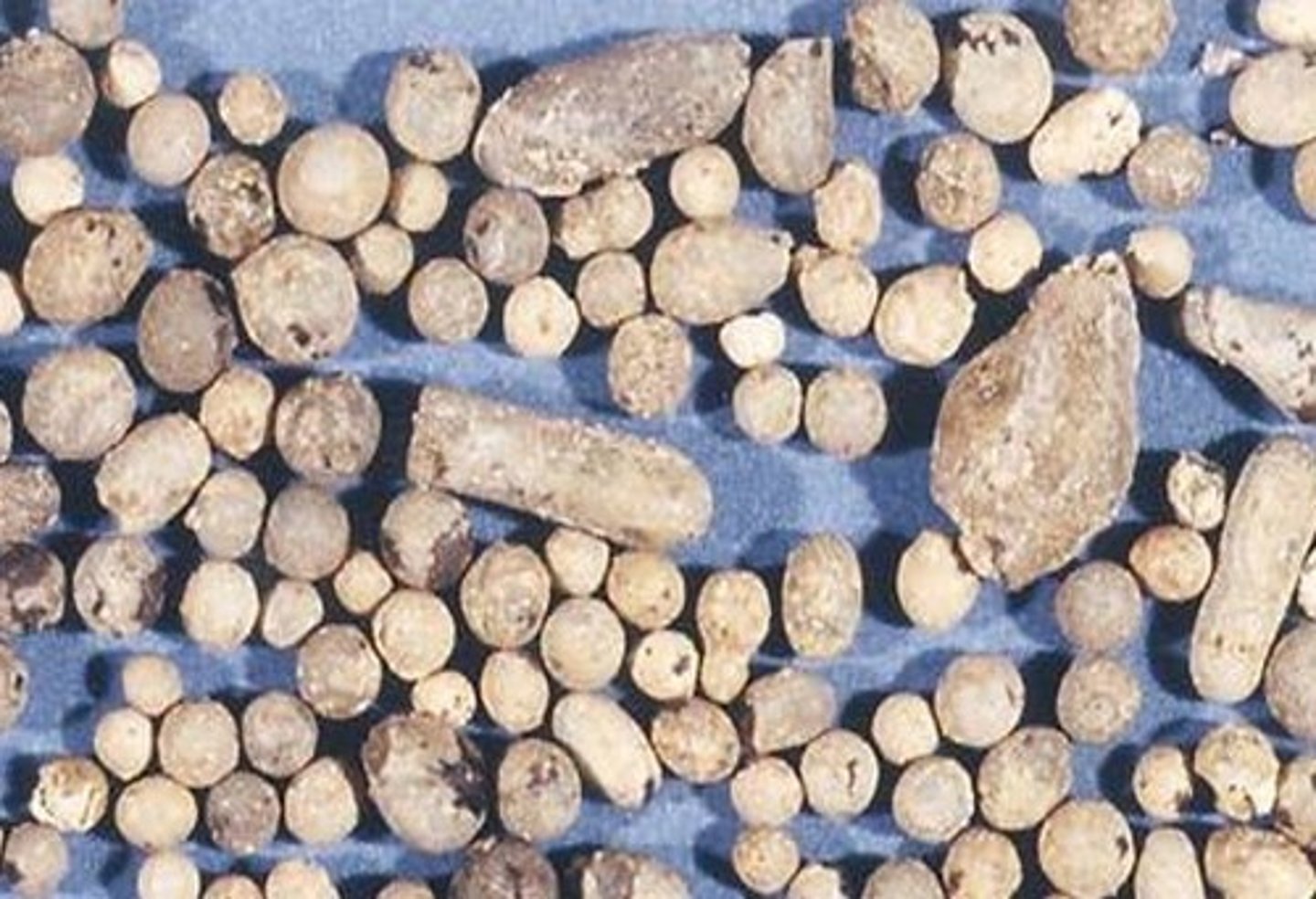

Tektites
Large, teardrop shaped 'glass raindrops'
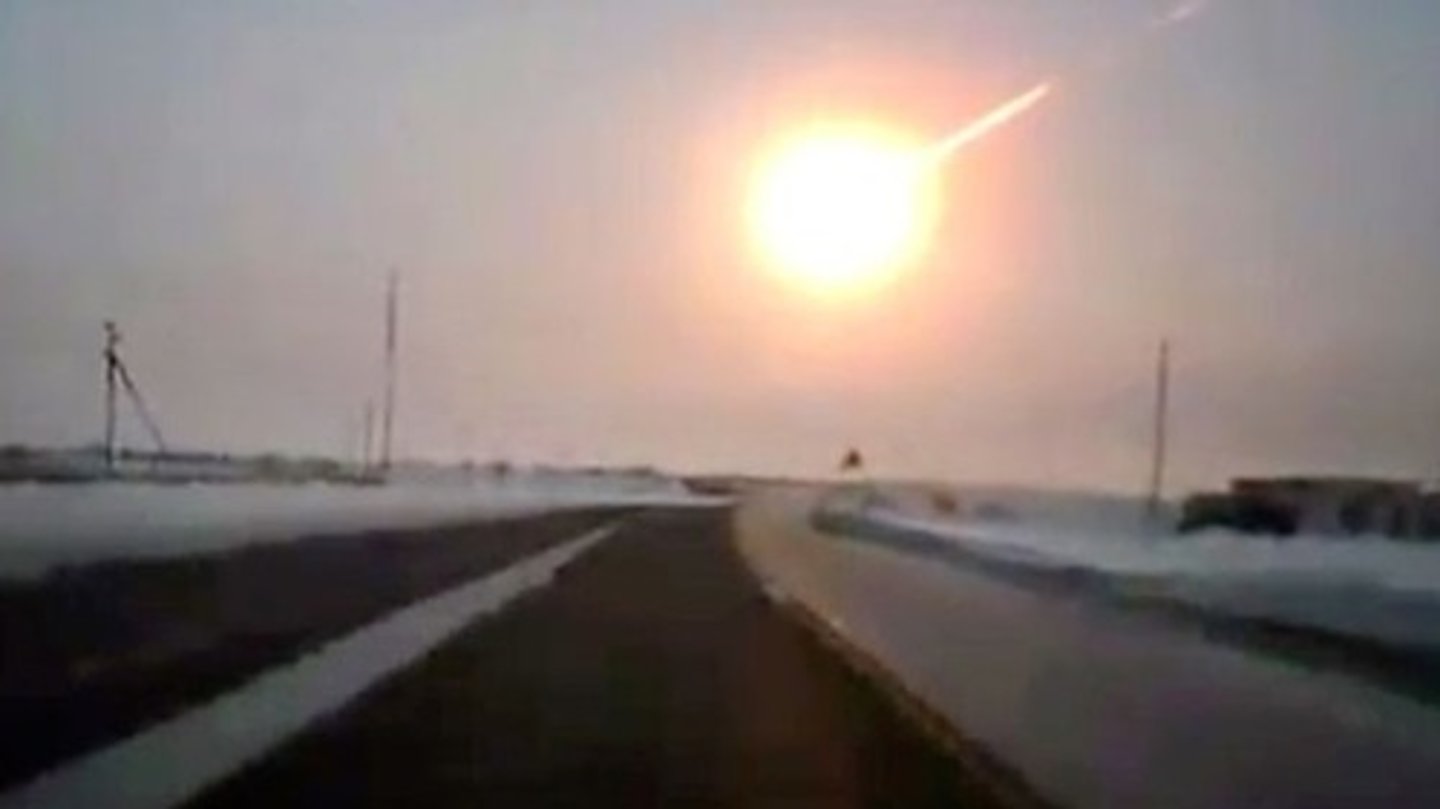
Chelyabinsk
Siberia 2013, dust plume wrapped the Earth

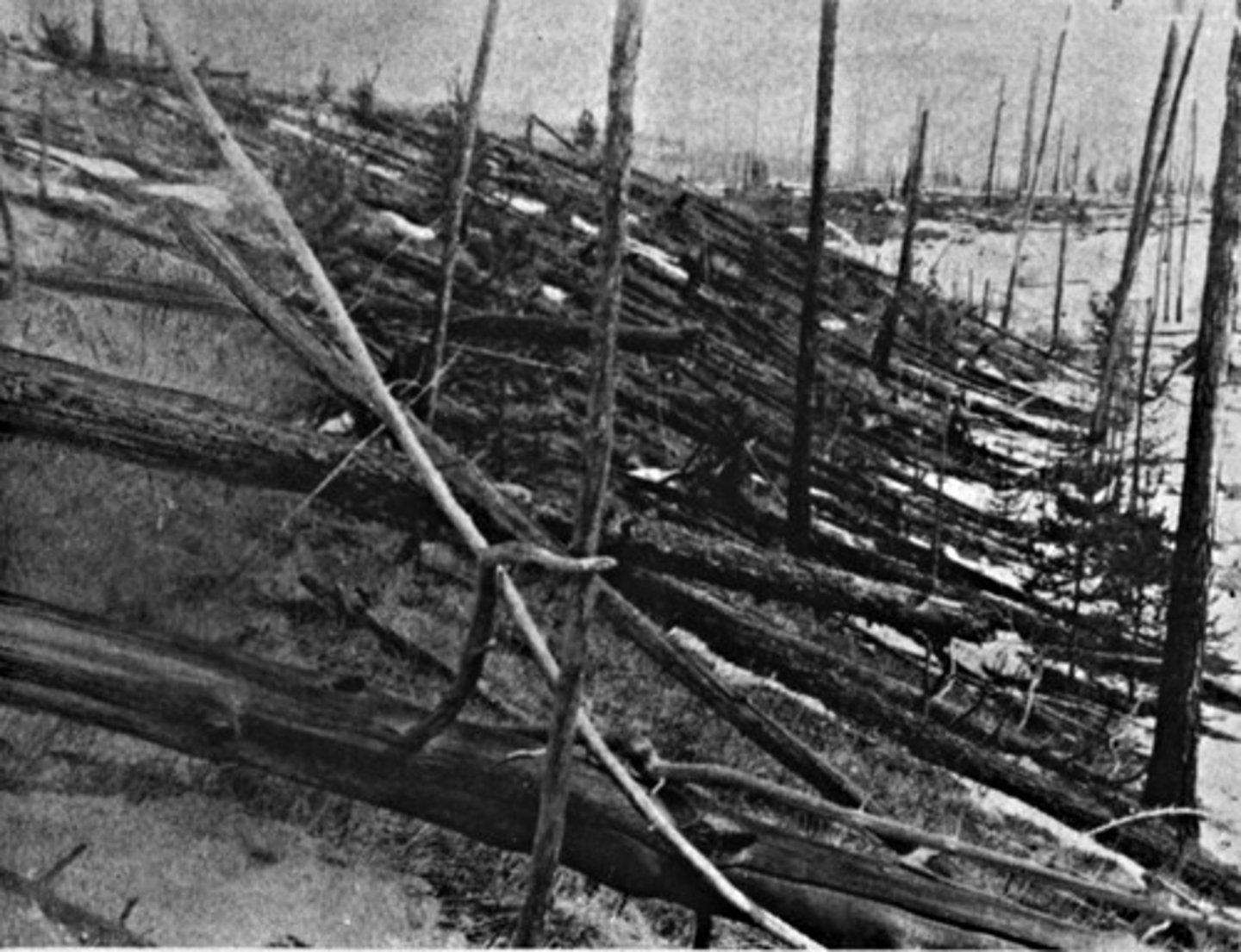
Tunguska
Siberia 1908, flattened forests

TC3
Tracked from sky to ground in Sudan

Coesite and stishovite
High pressure forms of quartz found at impact sites
Walter's question
How much time in K-T boundary clay
Discovered K-T shocked quartz
Bruce Bohor
Earth's iridium
Mostly in the core
Luis Alvarez
Physicist

About 10 km diameter
The K-T asteroid

Proposed killing mechanism
Dust blocks the sun and photosynthesis
Alvarez Hypothesis, Part 1
Bolide impact occurred precisely at the K-T.
Alvarez Hypothesis, Part 2
The impact caused the K-T extinctions.
1980
Alvarez Hypothesis published in Science

Formed by impact
The Moon
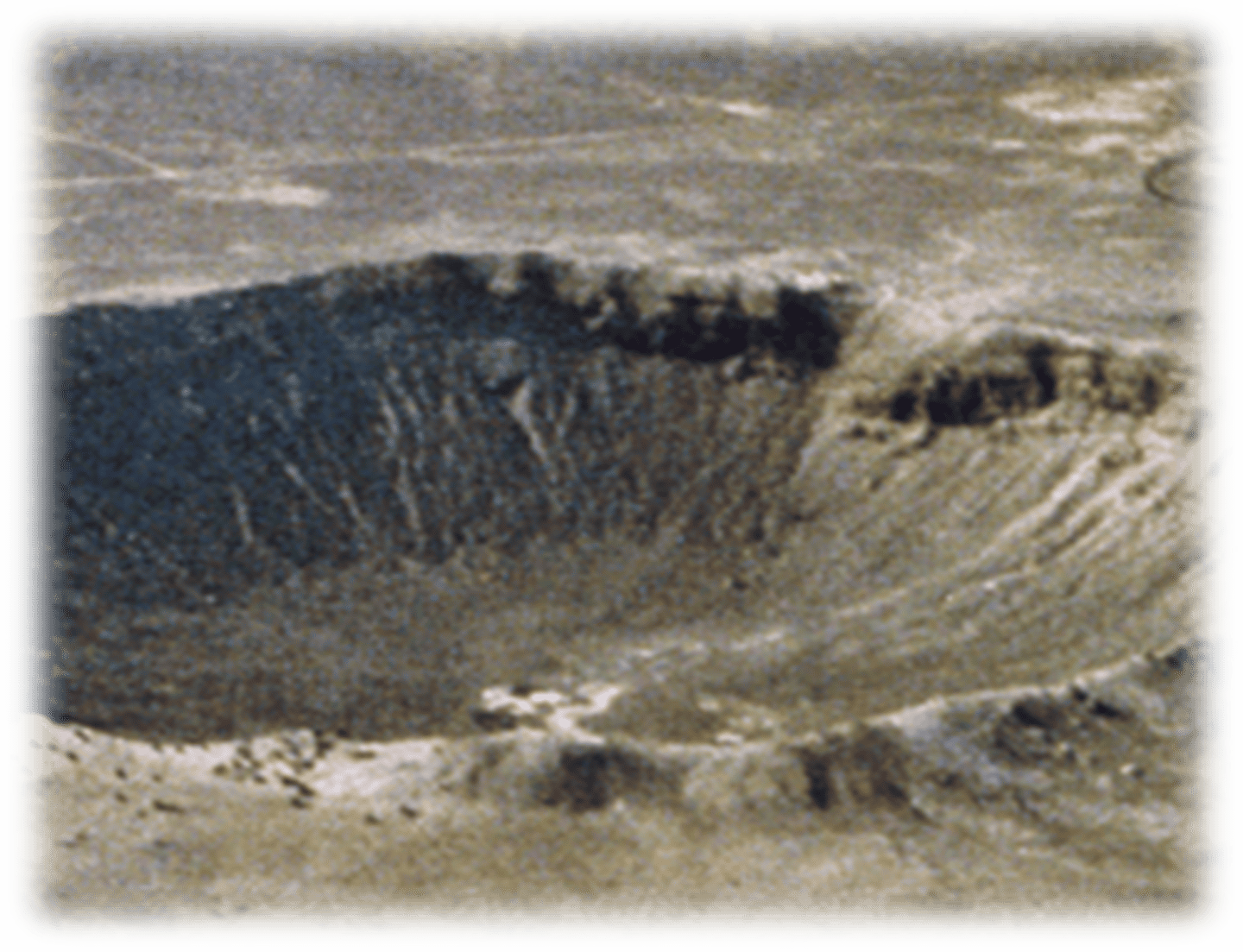
Meteor Crater, Arizona
Gene Shoemaker's starting point

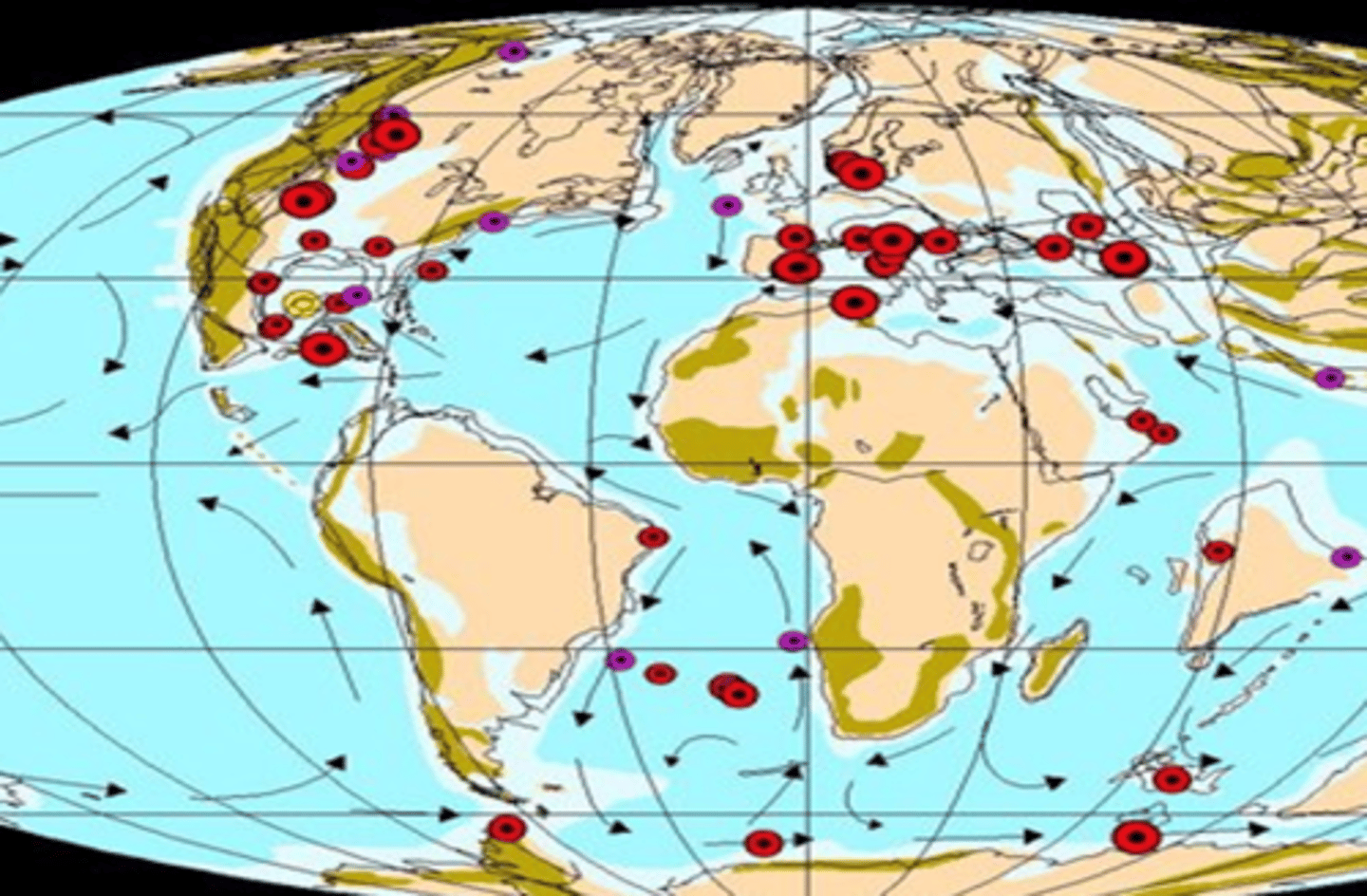
World's only globally distributed rock layer from a single event
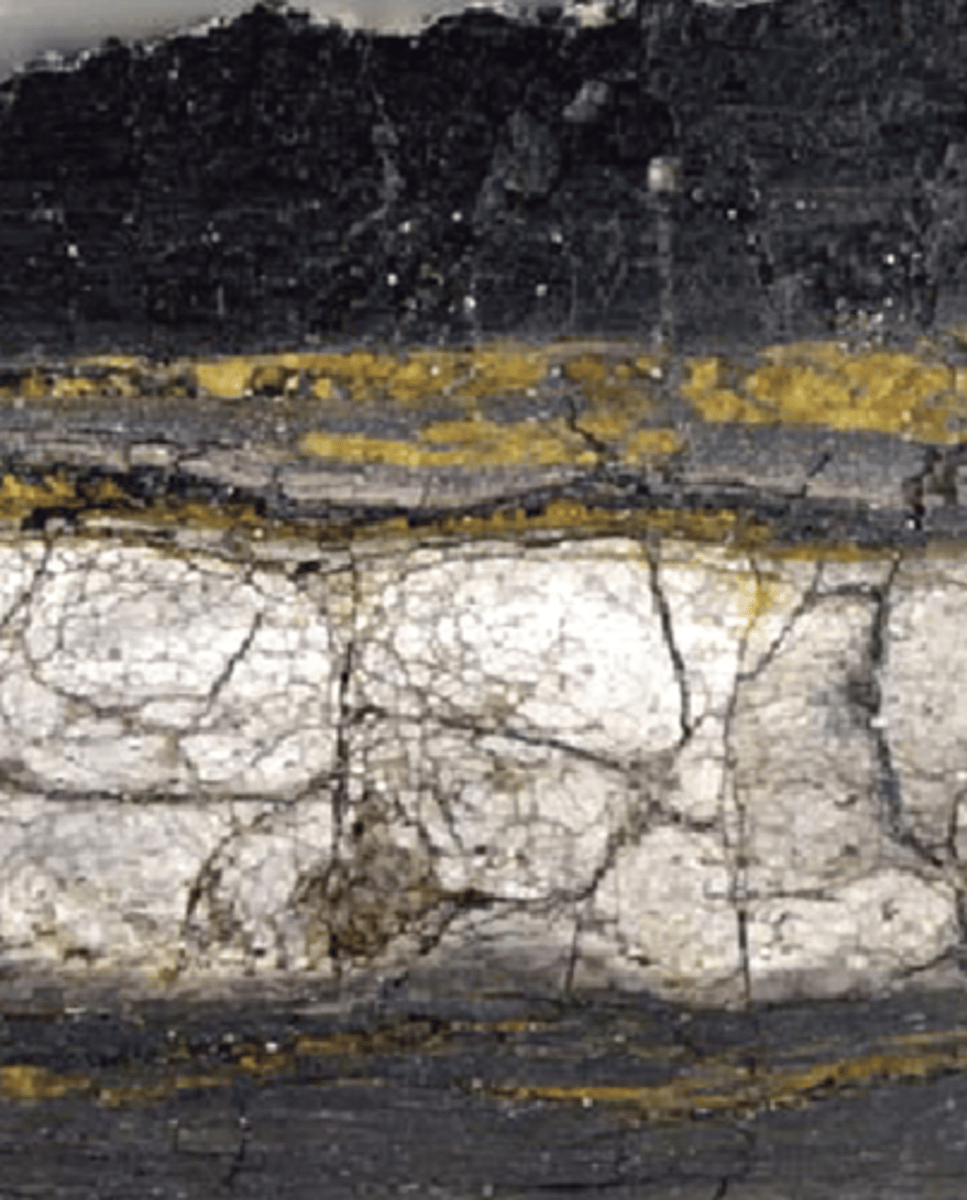
The K-T boundary layer

Global iridium anomalies
Volcanic "spherules"
angular, not rounded
Volcanic iridium
from non-explosive (basaltic) volcanoes
Deccan Traps
Massive lava flows from India
Peak of Deccan eruptions
Hundreds of thousands of years before and after the K-T
Major effect of Deccan eruptions
Short global warming episodes, biodiversity increased
Granite and quartz
K-T impactor struck a continent
Double boundary layer
North America only

Lead of Chicxulub discovery team
Alan Hildebrand
First noted Chicxulub gravity and magnetic anomalies
Penfield and Camargo (1981)
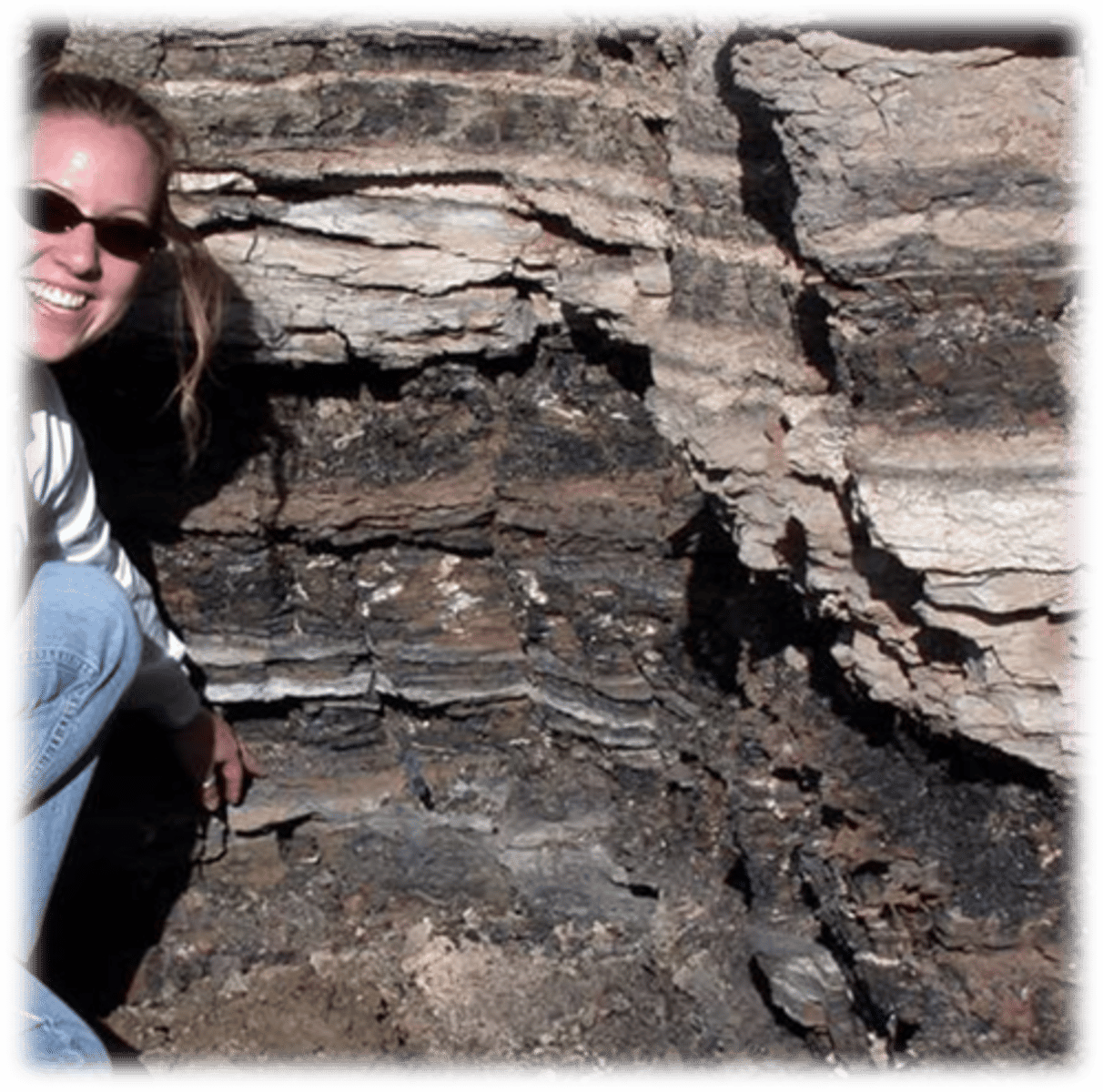
Global, regional, and local events revealed in one place
West Bijou Creek K-T section

Chicxulub gravity field
Cenotes
Chixculub ring from space shuttle

Same isotopes, 3 different elements
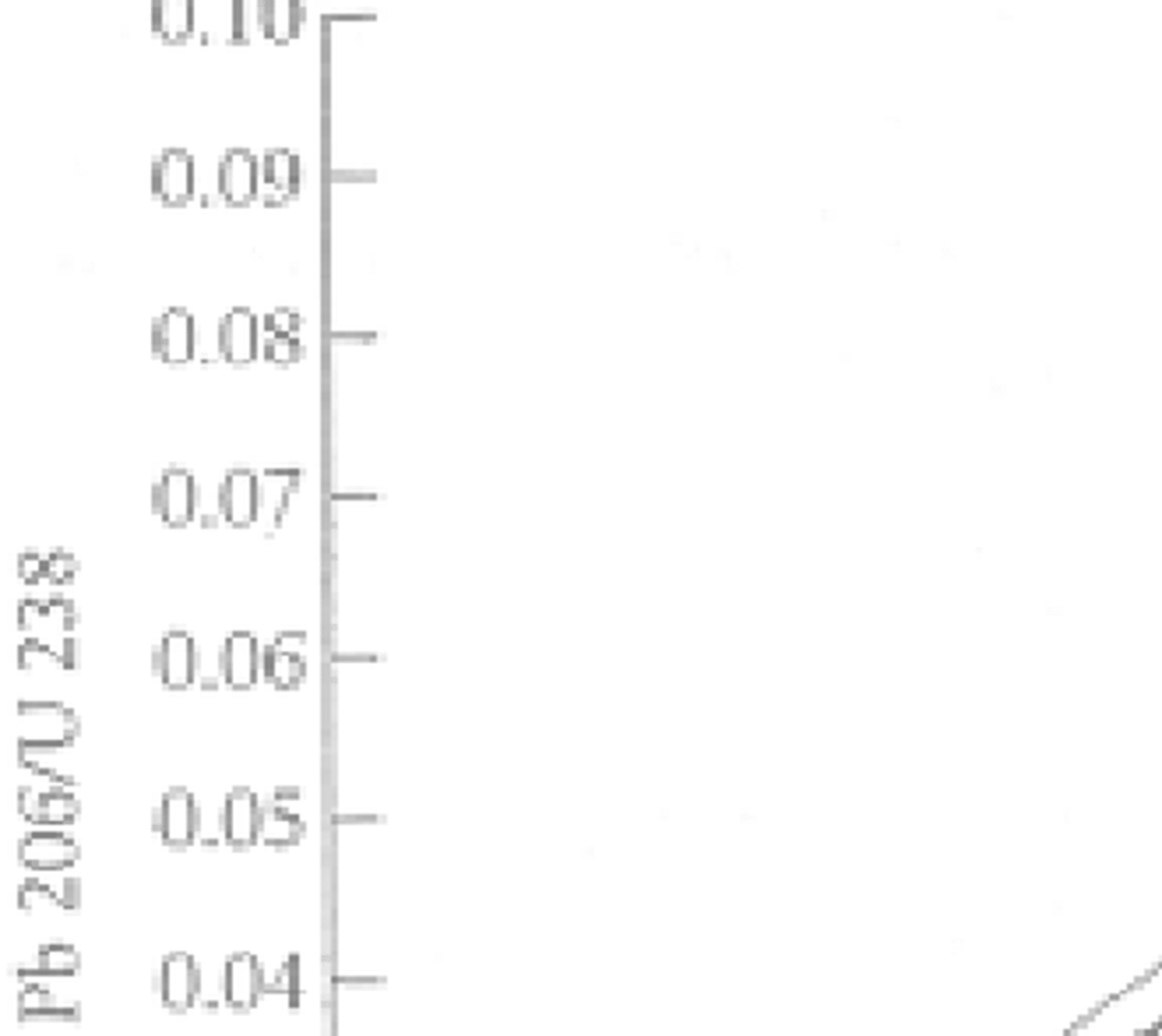
Impact glass in Haiti and Chicxulub
Same age within 32,000 years
Chicxulub and North Dakota K-T ashes
Same lead loss line and age
Zircons from Chicxulub and N America K-T boundary

Signor-Lipps effect
Observed extinction may precede true extinction
Least Signor-Lipps effect
Superabundant microfossils, forams and pollen
Most Signor-Lipps effect
Rare, large fossils (dinosaurs)
Overcome Signor-Lipps effect
Heavy sampling and statistics
The key question for Part 2 of Alvarez Hypothesis
Sudden or gradual extinction
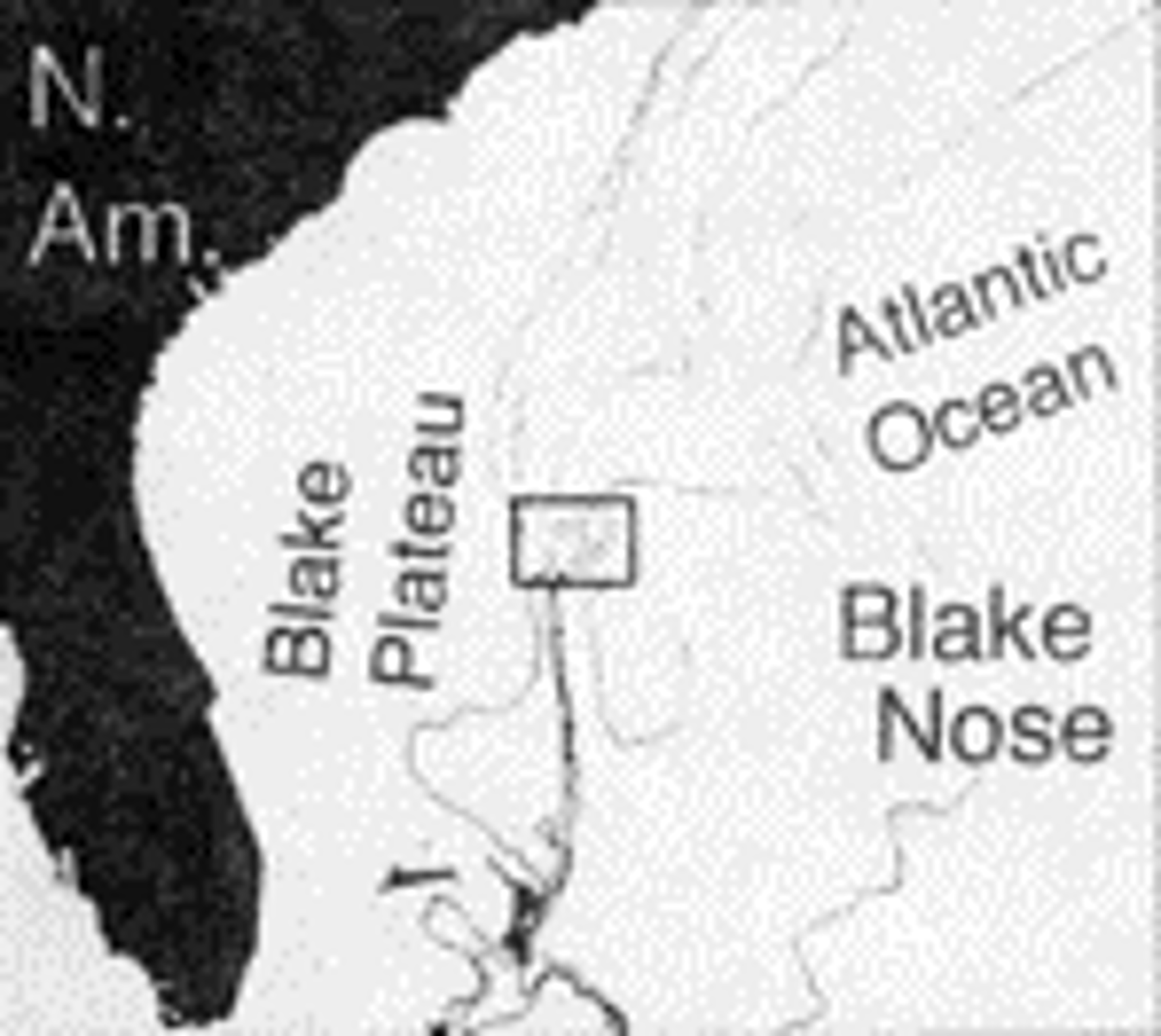
Blake Nose, Florida
Complete K-T boundary, abrupt foram extinction
Cretaceous forams
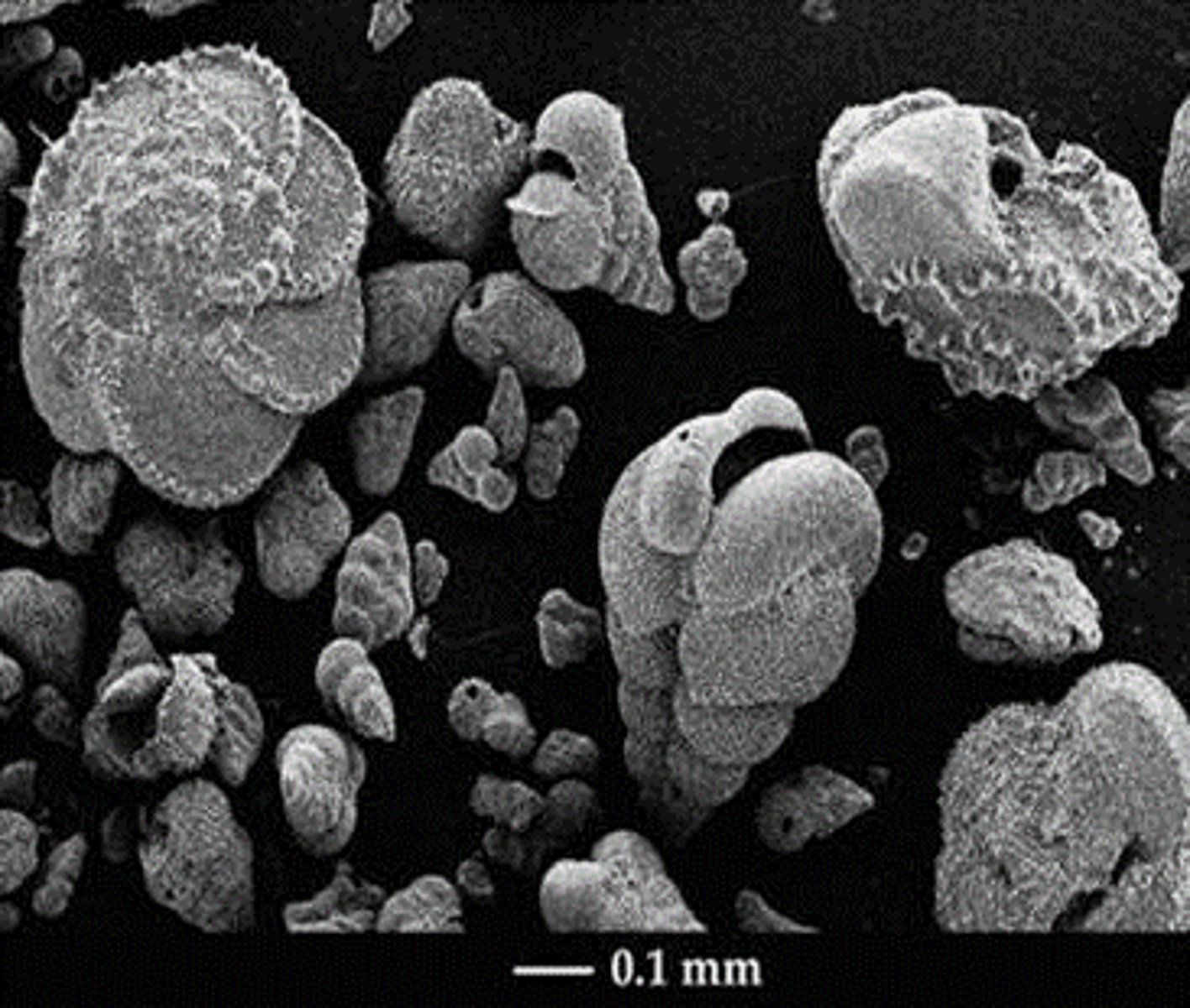

Post K-T forams
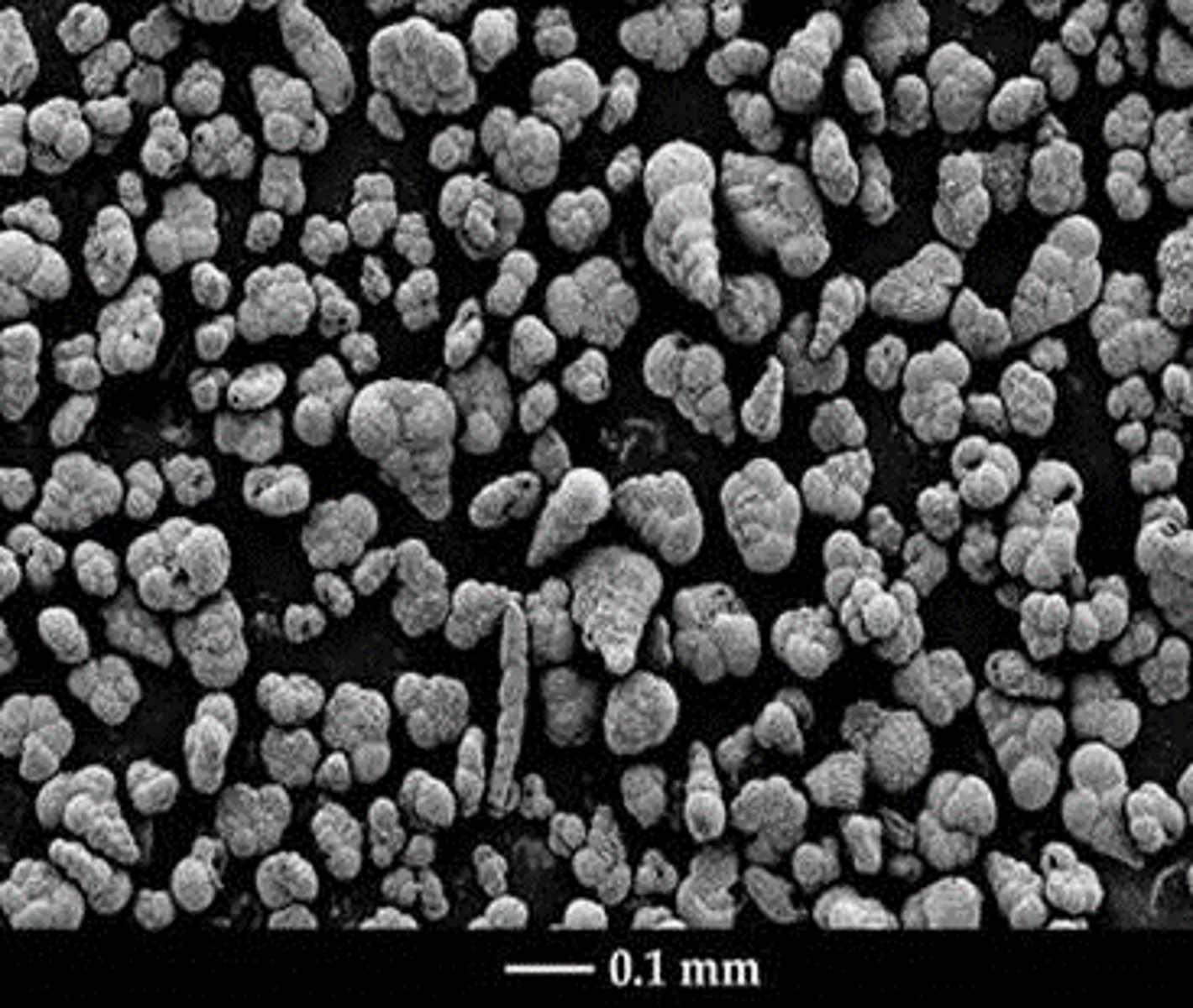

60%
North Dakota plant extinction
K-T plants with confidence intervals
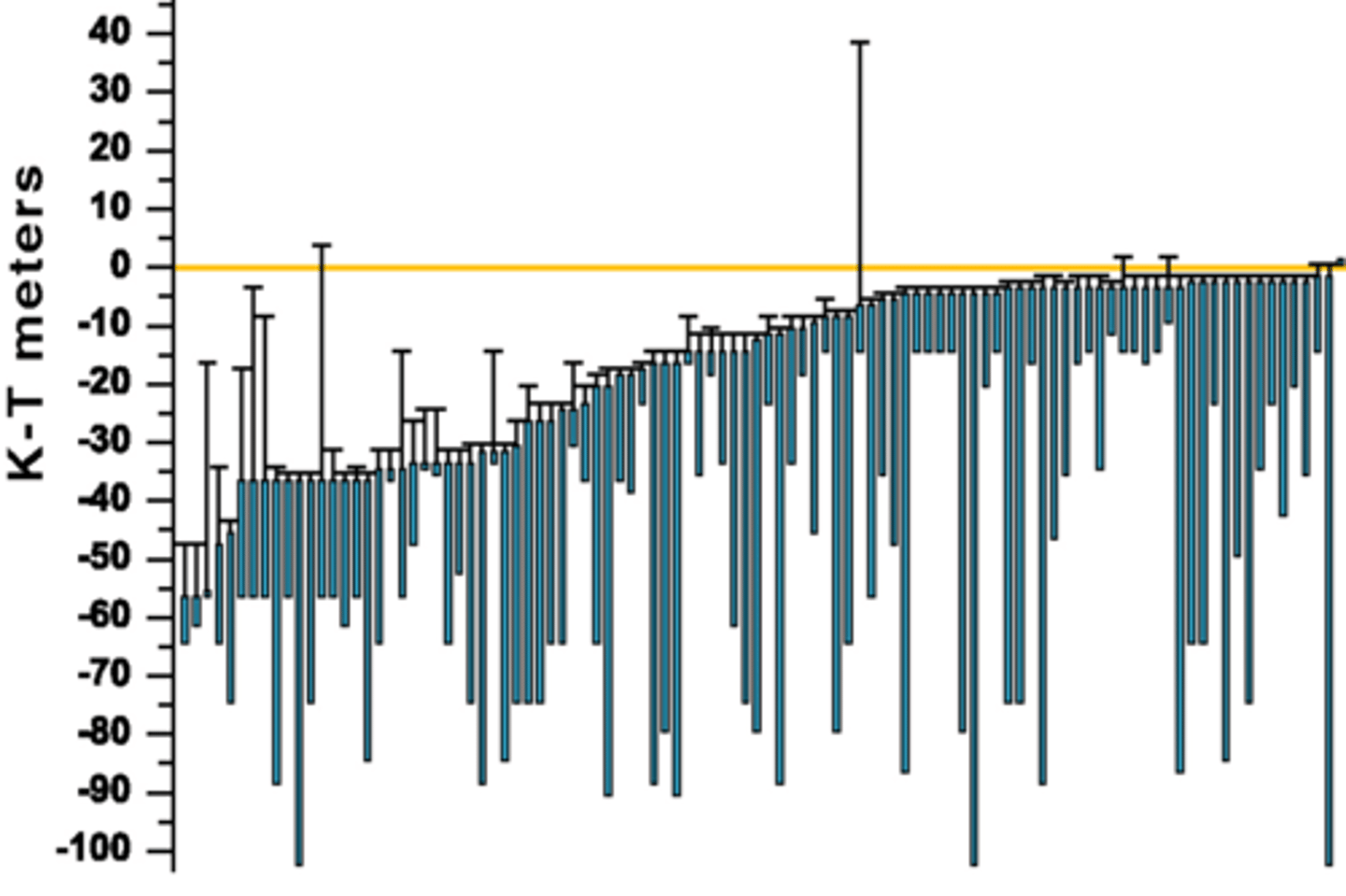
No survival known
Cretaceous leaf miners
How to study insect diversity and extinction without insect fossils?
Insect feeding marks on fossil leaves
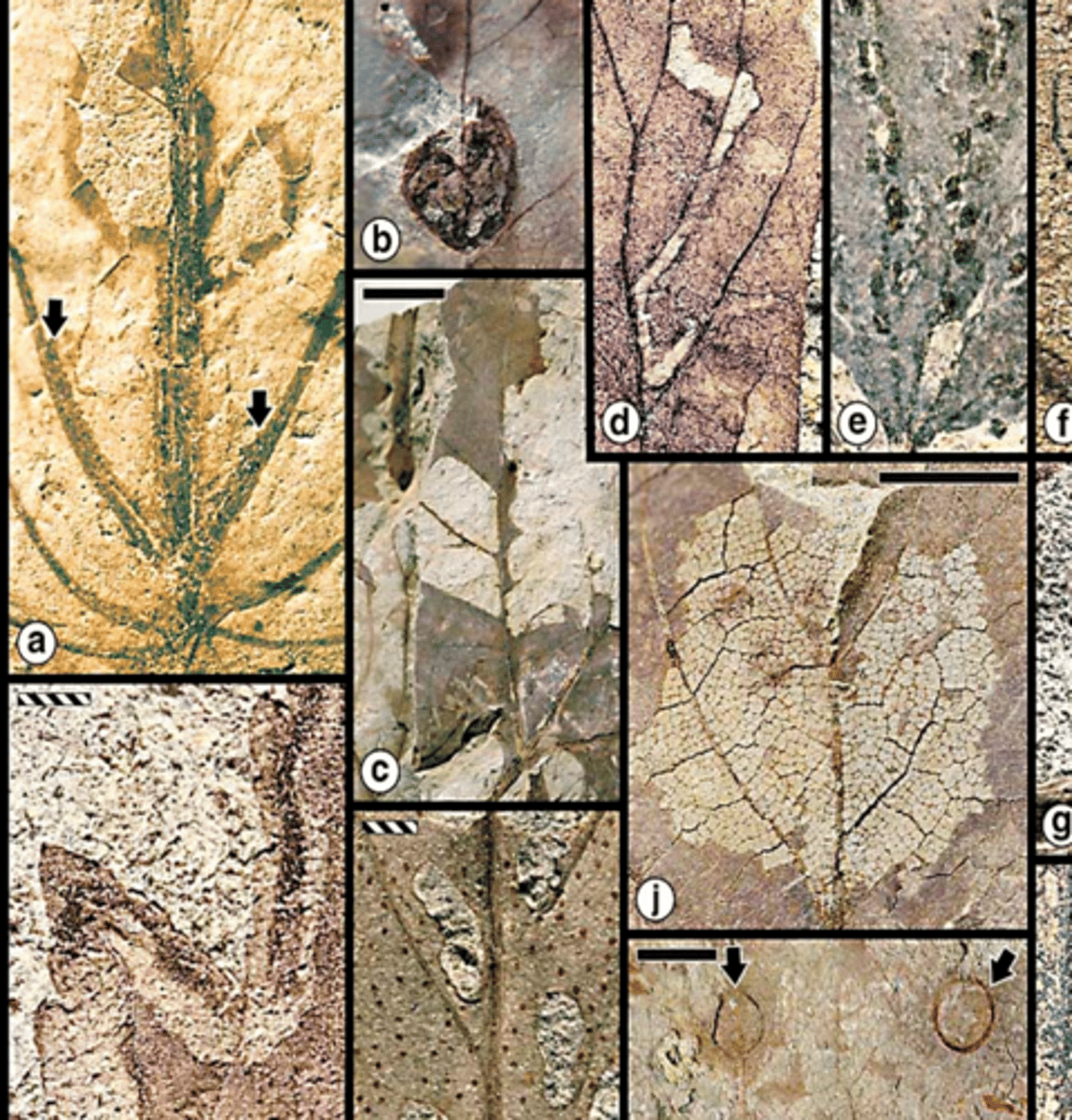

Second reason insects died
Host plants went extinct
Only detailed record of the end of the Mesozoic on land
Hell Creek Formation
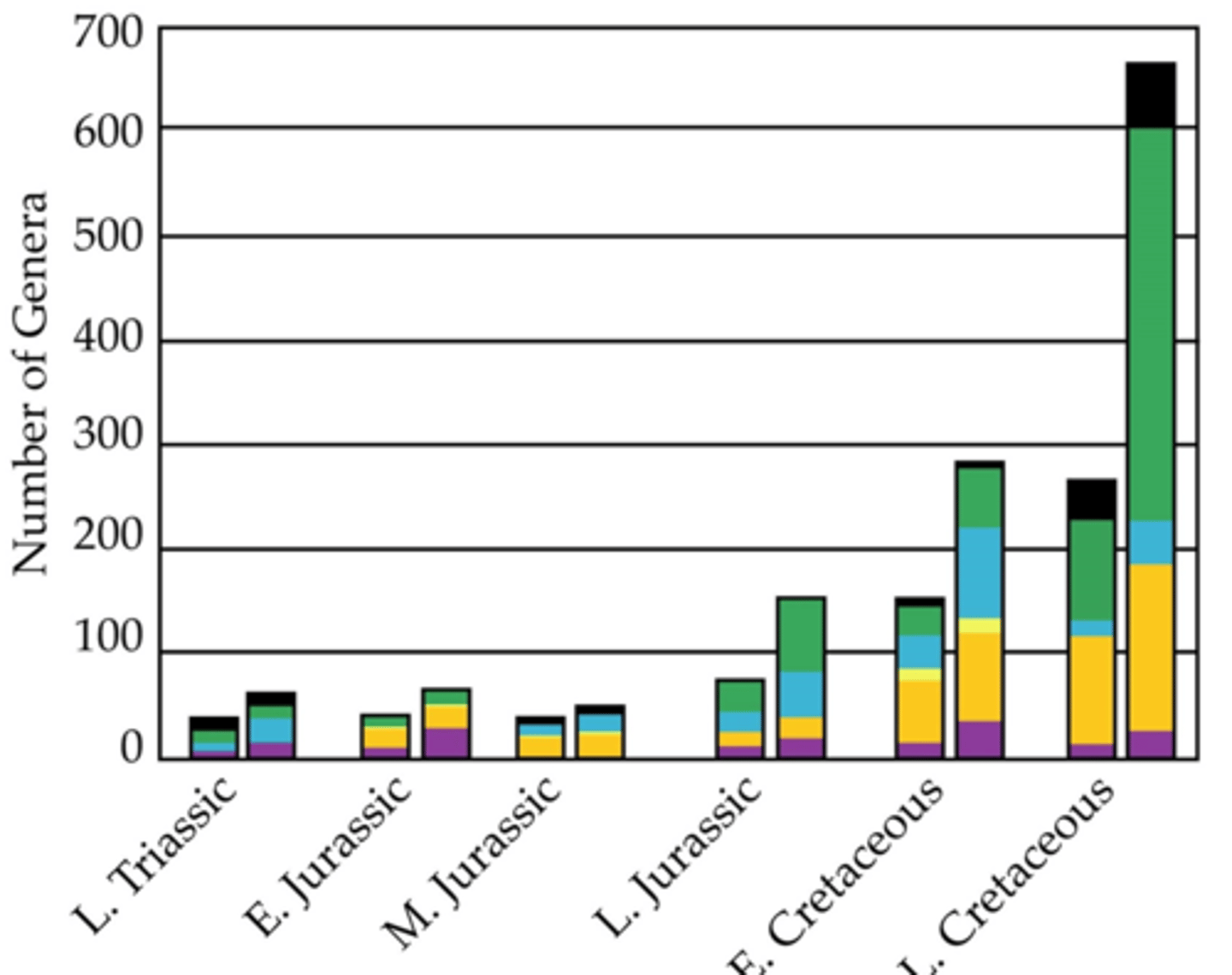
Quantified global dinosaur diversity and sampling
David Fastovsky
Dinosaur diversity and sampling, whole Mesozoic
Dinosaur diversity and sampling, last ~35 my of Cretaceous
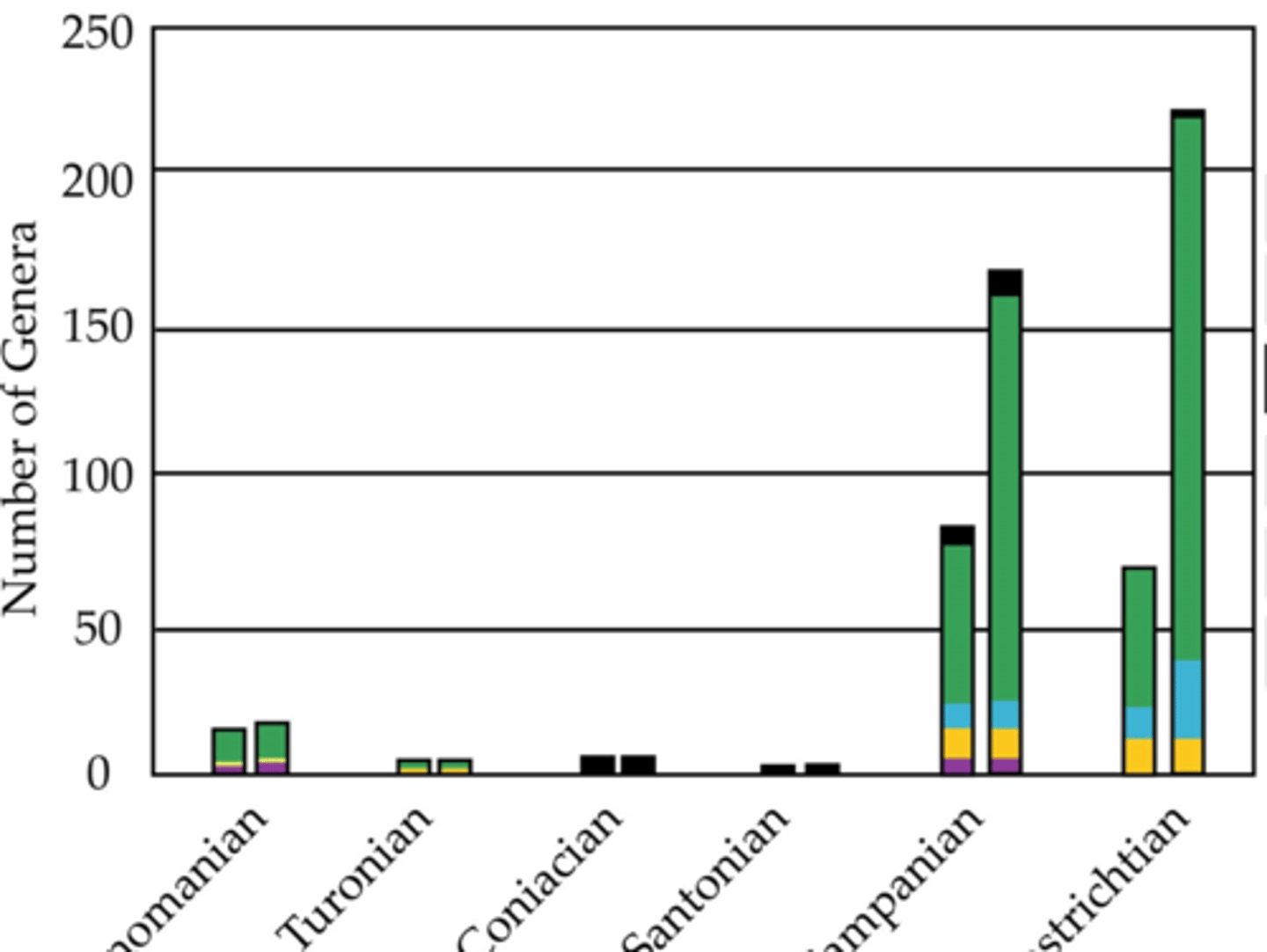
Dinosaur diversity, last ~19 my of Cretaceous
Quantified vertebrate diversity in Hell Creek Formation from 10,000 fossils
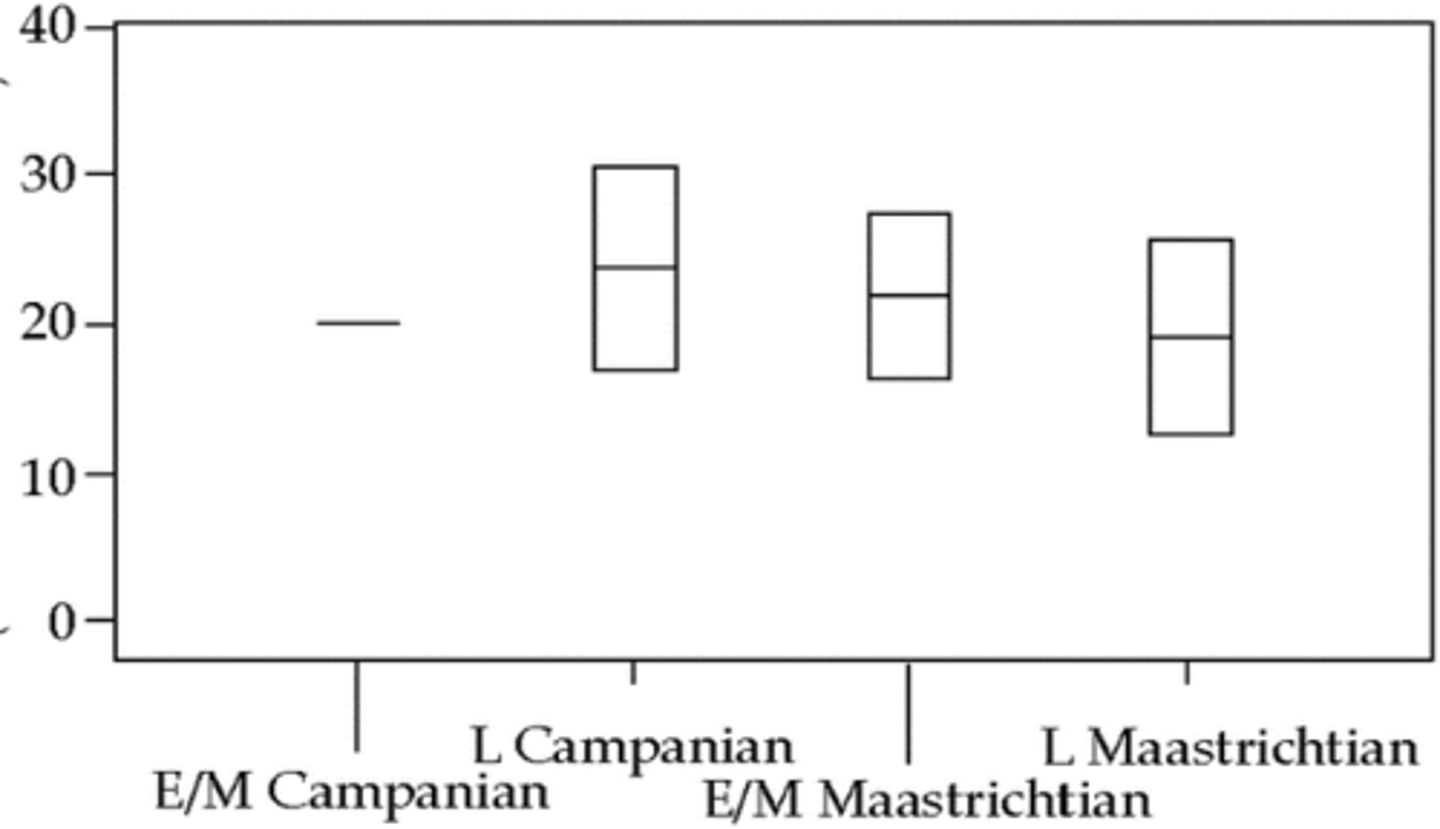
Dean Pearson

Vertebrate diversity, last 0.7 my of Cretaceous
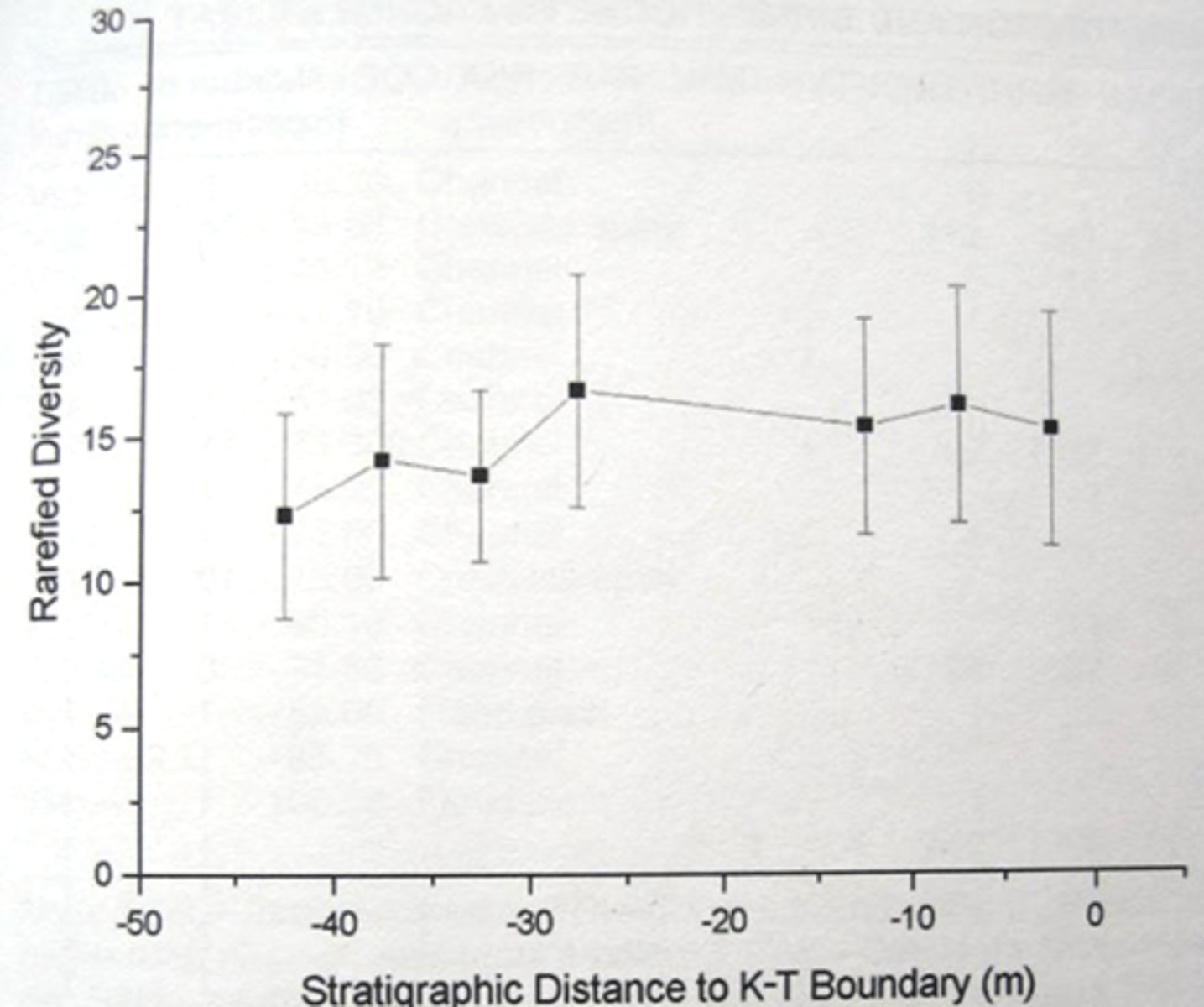
No Bone Zone
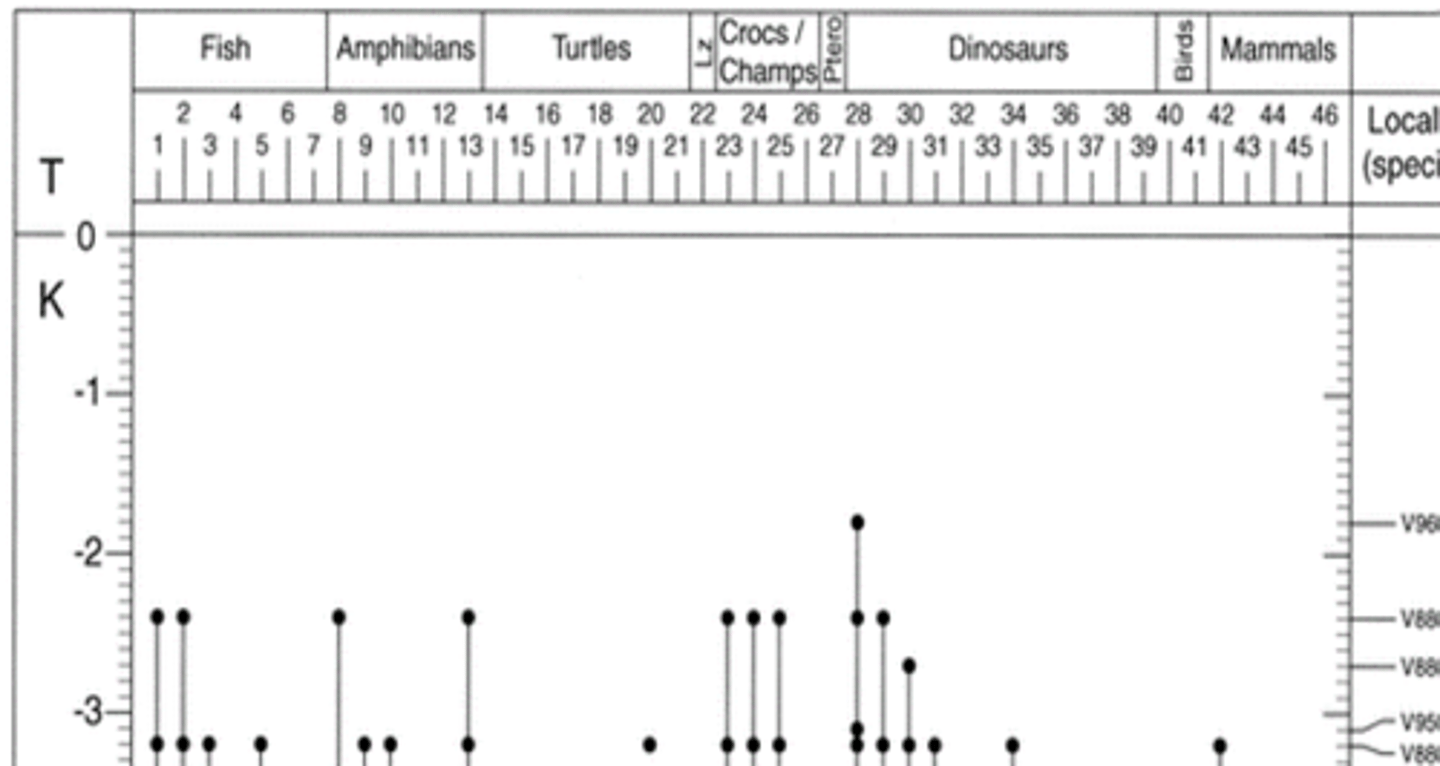
Youngest dinosaur known
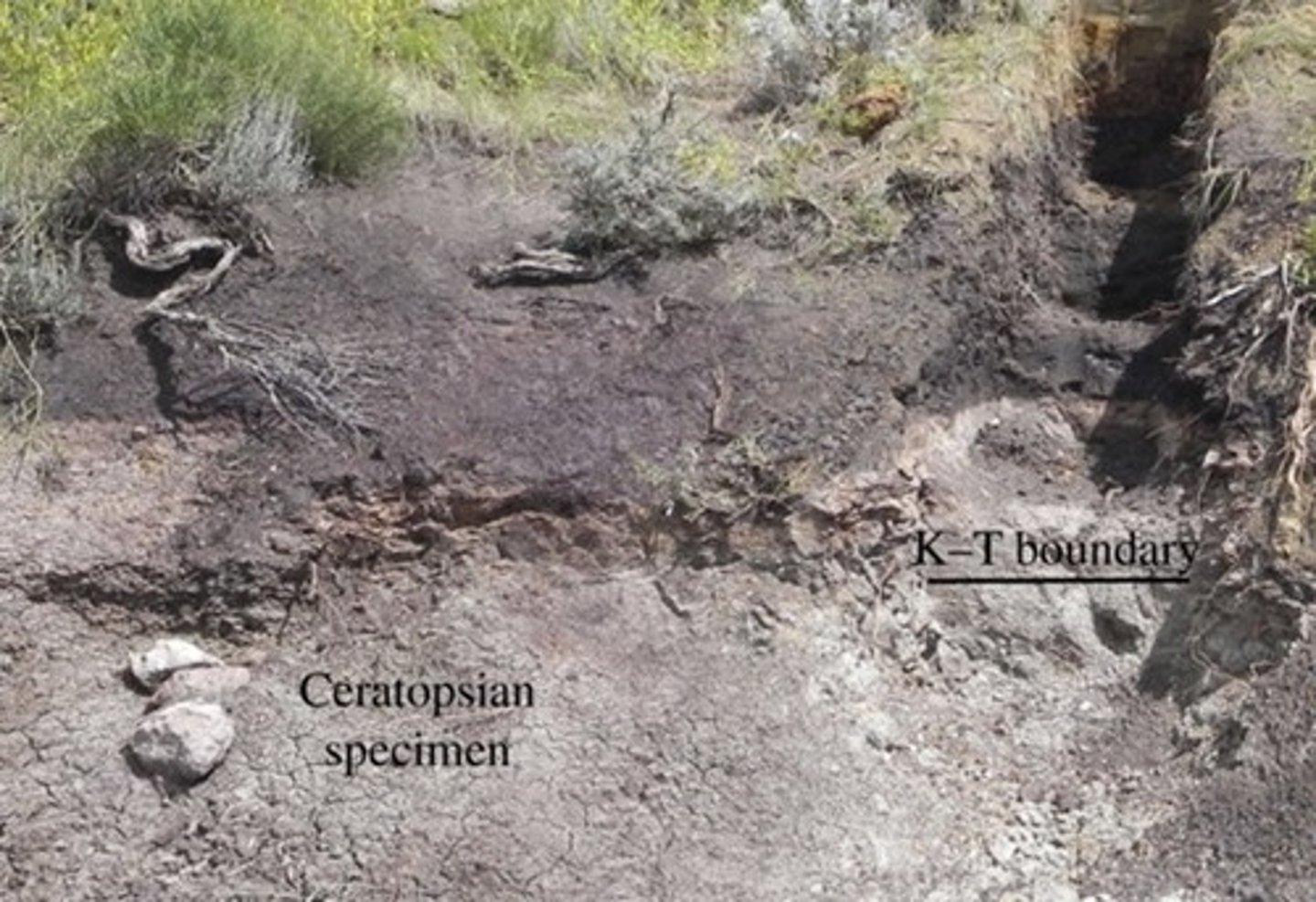

Evidence we have seen for pre K-T decline or gradual extinction of any group
0
Number of mass extinctions currently attributable to impacts
1
Fossil vs. modern extinction rates
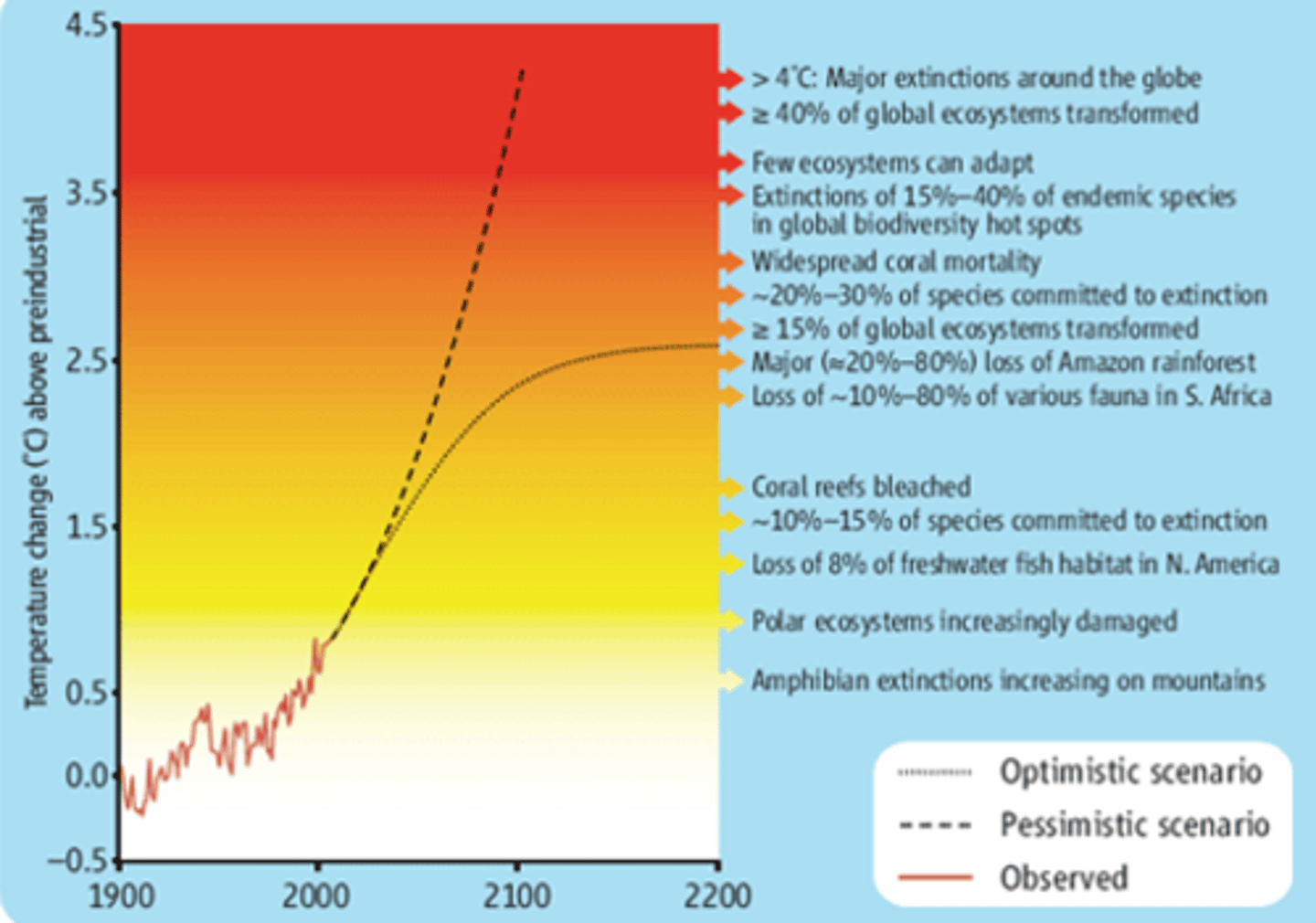
Where extinction risk is increasing
Climate change impact scenarios
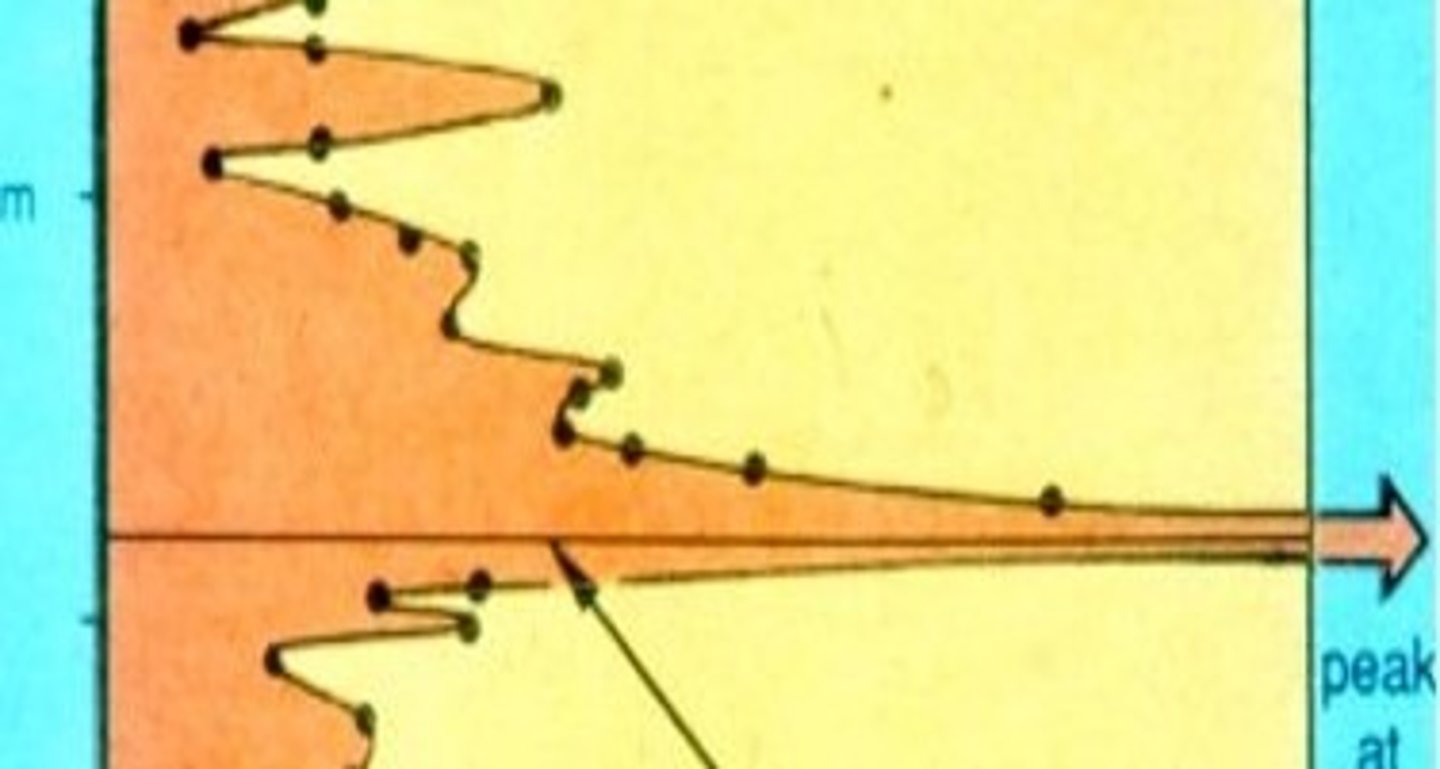
Shoemaker data

Shoemaker-Levy 9
