APHG Unit 3 (Cultural Geography) - Presser
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Culture
The beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
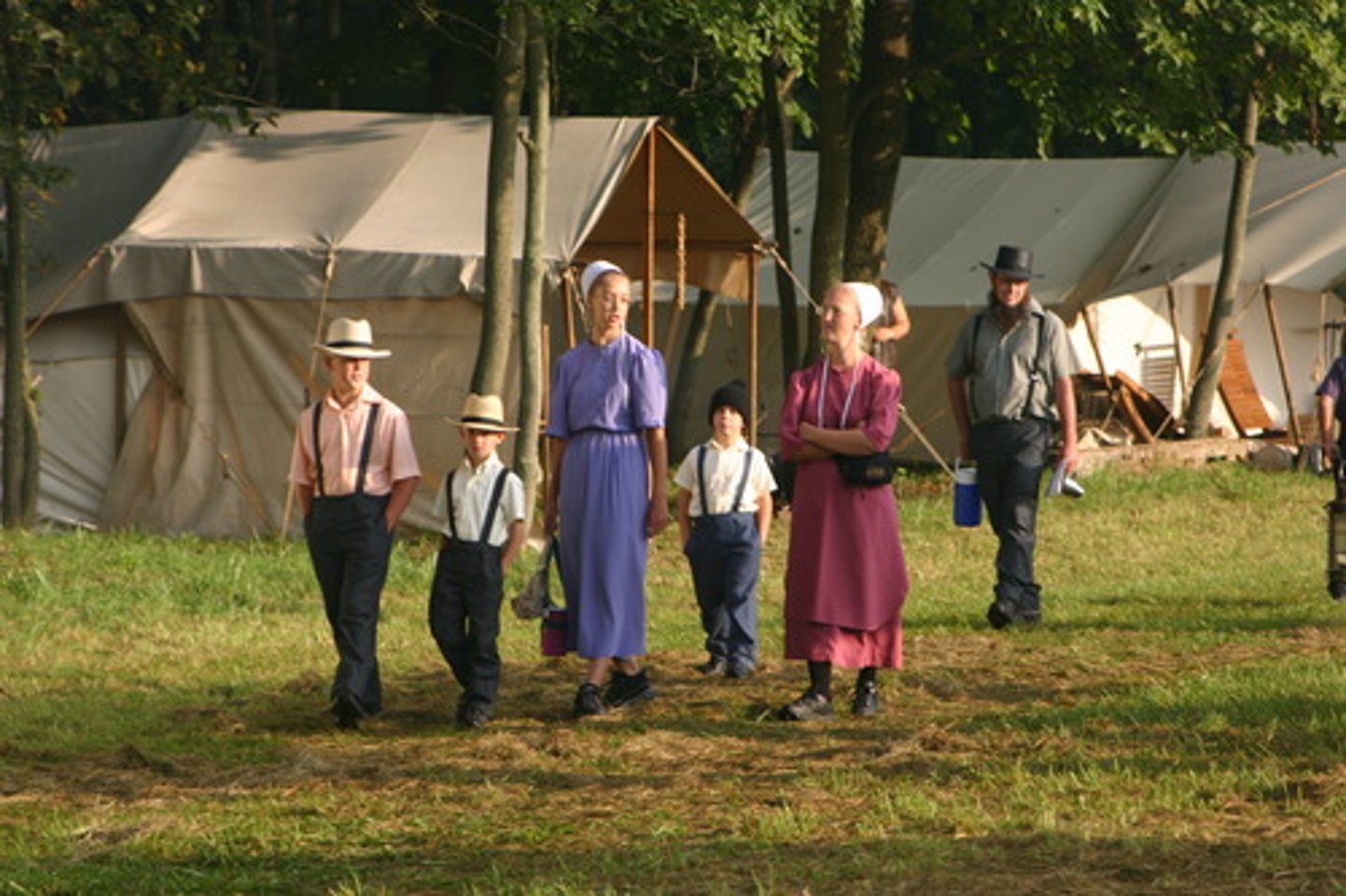
Traditional cultures / folk cultures
Small, homogenous groups of people that often live in rural areas are relatively isolated and are slow to change

Popular culture / global culture
Culture found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics.

Culture traits
The most basic elements of culture such as dress, food, or religious beliefs
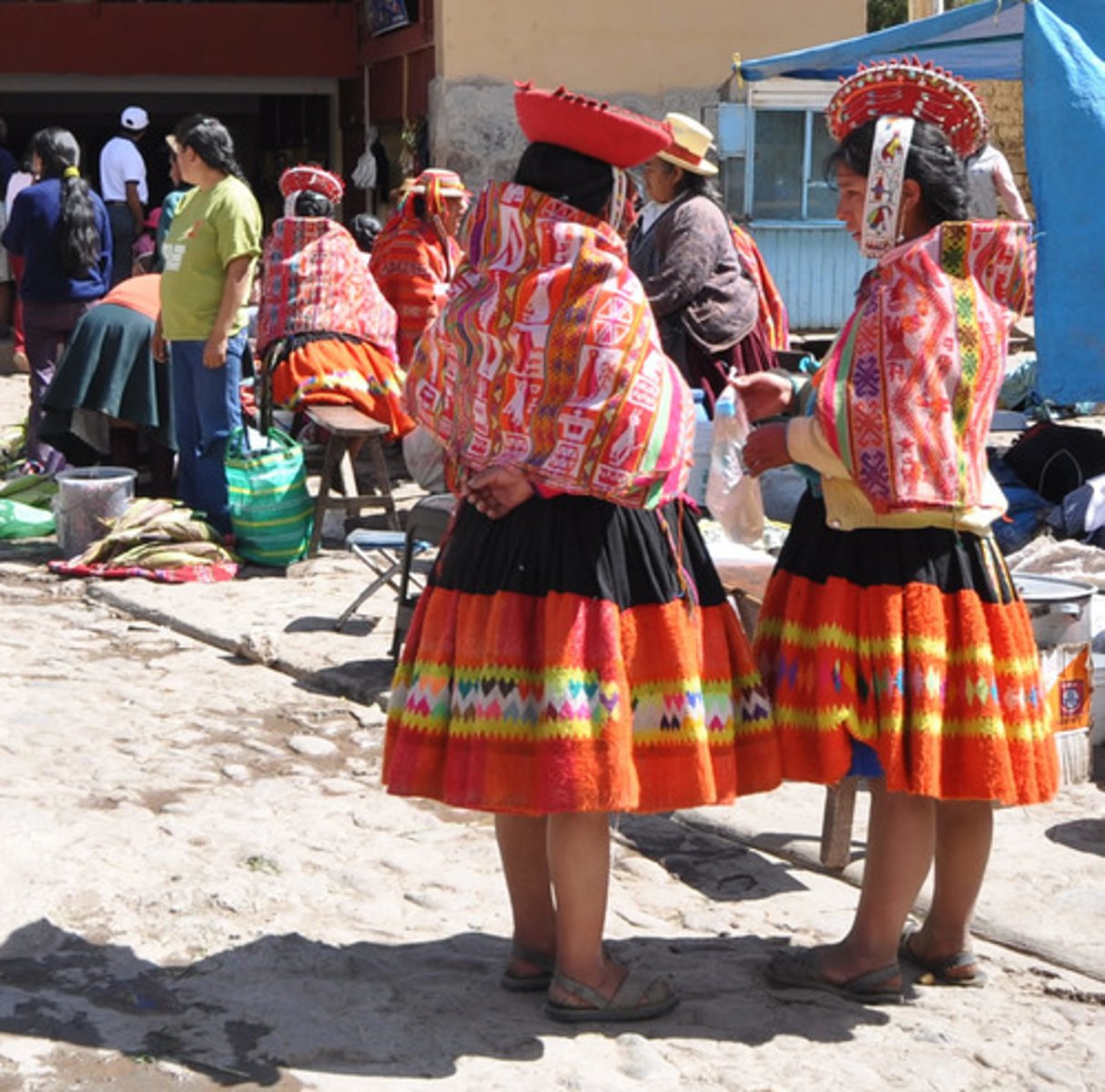

Culture complex
A related set of cultural traits, such as prevailing dress codes and cooking and eating utensils.

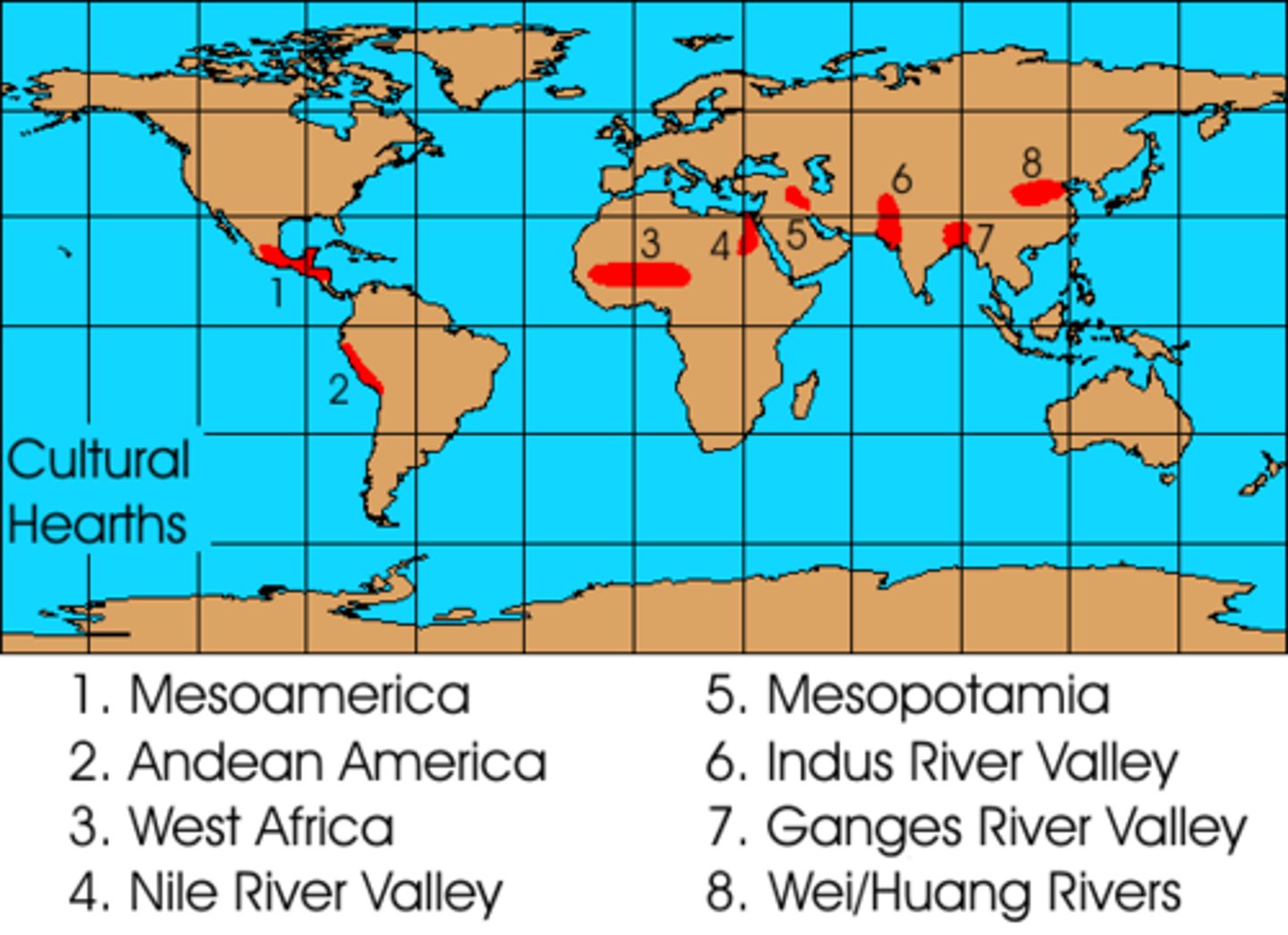
Cultural hearth
An area in which a unique culture or a specific trait develops
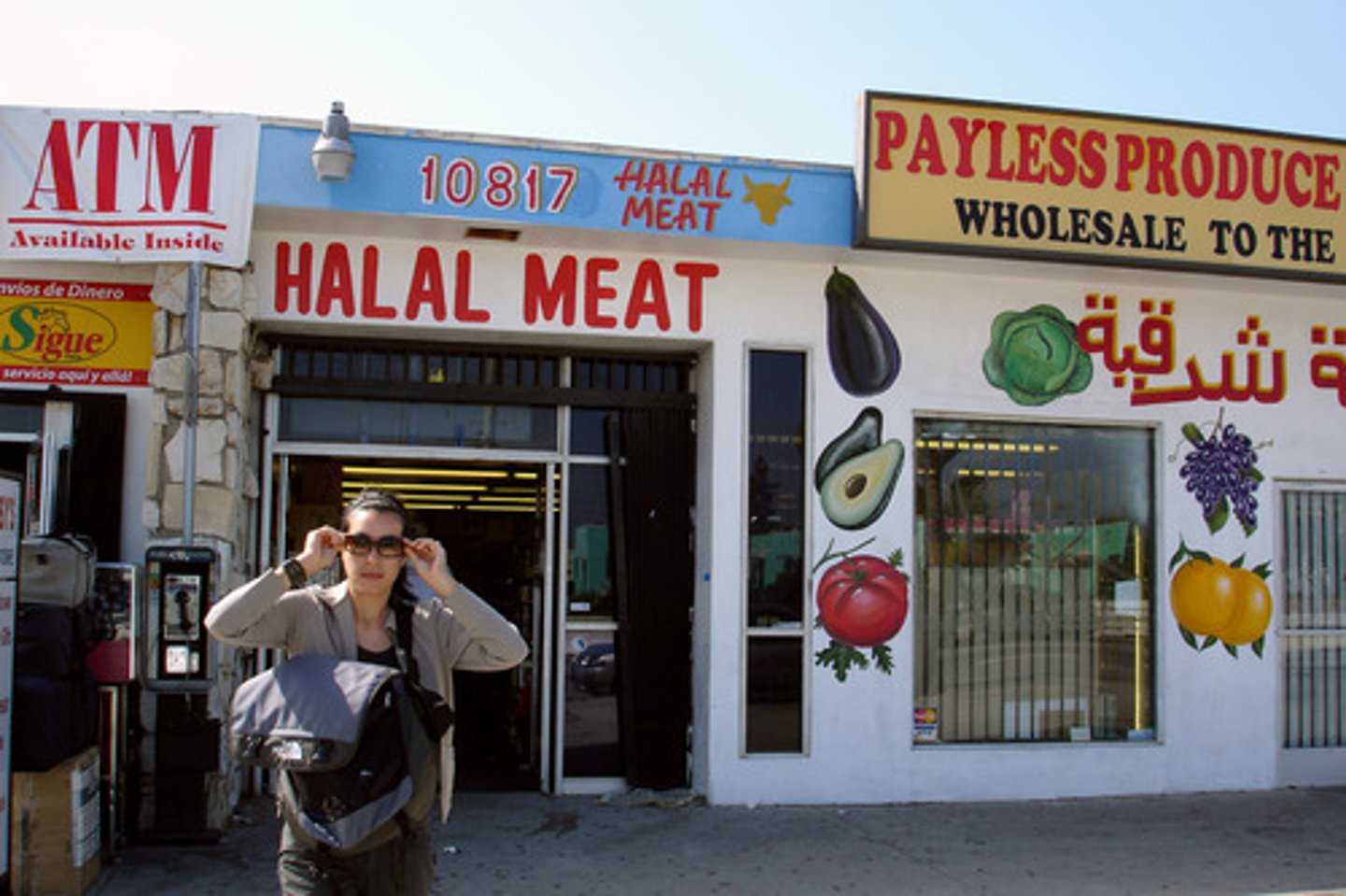
Taboo
Behaviors heavily discouraged by a culture

Sense of place
The feeling that an area has a distinct and meaningful character

Culture regions
Broad areas where groups share similar, but not identical cultural traits. Cajun Country is a great example: Primarily located in rural Southern Louisiana, the culture is defined by its French roots which are easily seen in their own distinct Cajun French dialect, societal norms, music, and food

Cultural landscape
The visible imprint of human activity and culture on the landscape

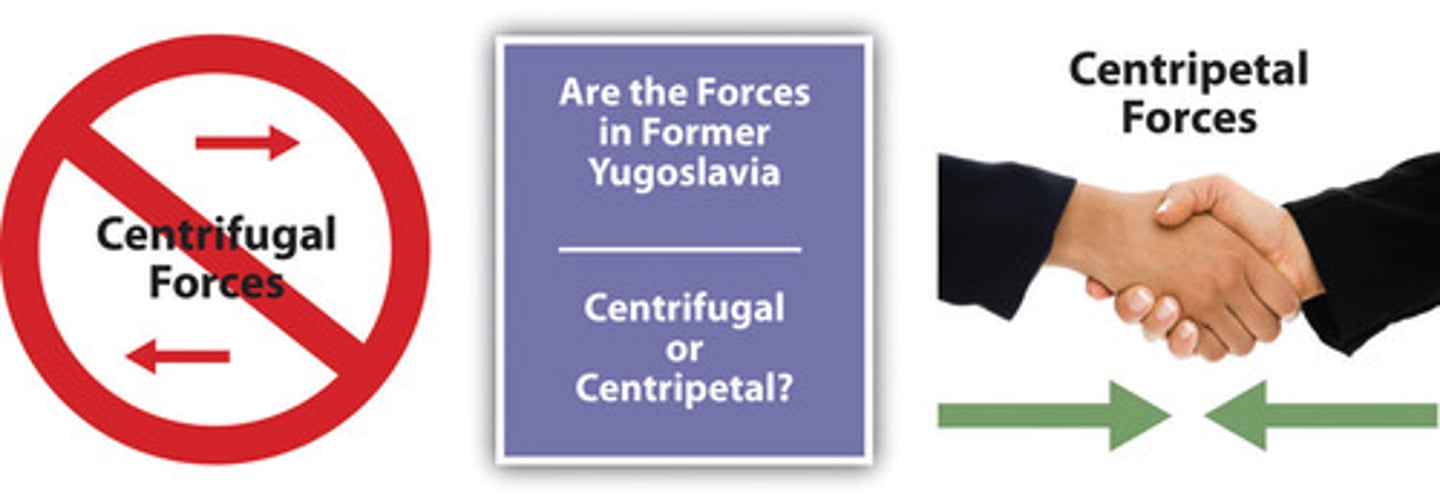
Centrifugal force
A force that divides people and countries. These forces can come in various forms. Think: ESPeN.
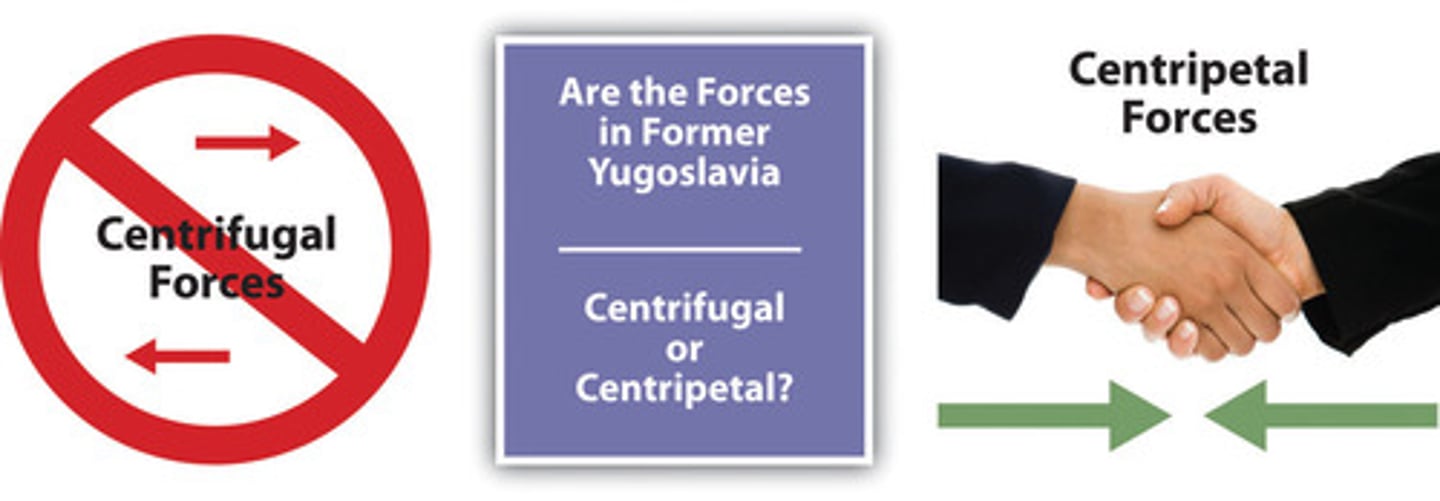
Centripetal force
A force that tends to unify people and enhance support for a state. These forces can come in various forms. Think: ESPeN.
Ethnic enclaves
Neighborhoods where people from similar cultures live together and assert cultural distinction from the dominant group; locations with a high concentration of one specific ethnicity.

Space-time compression
The increasing sense of connectivity that seems to be bringing people closer together even though their absolute distances remain the same; results from improvements in communication and transportation technologies.

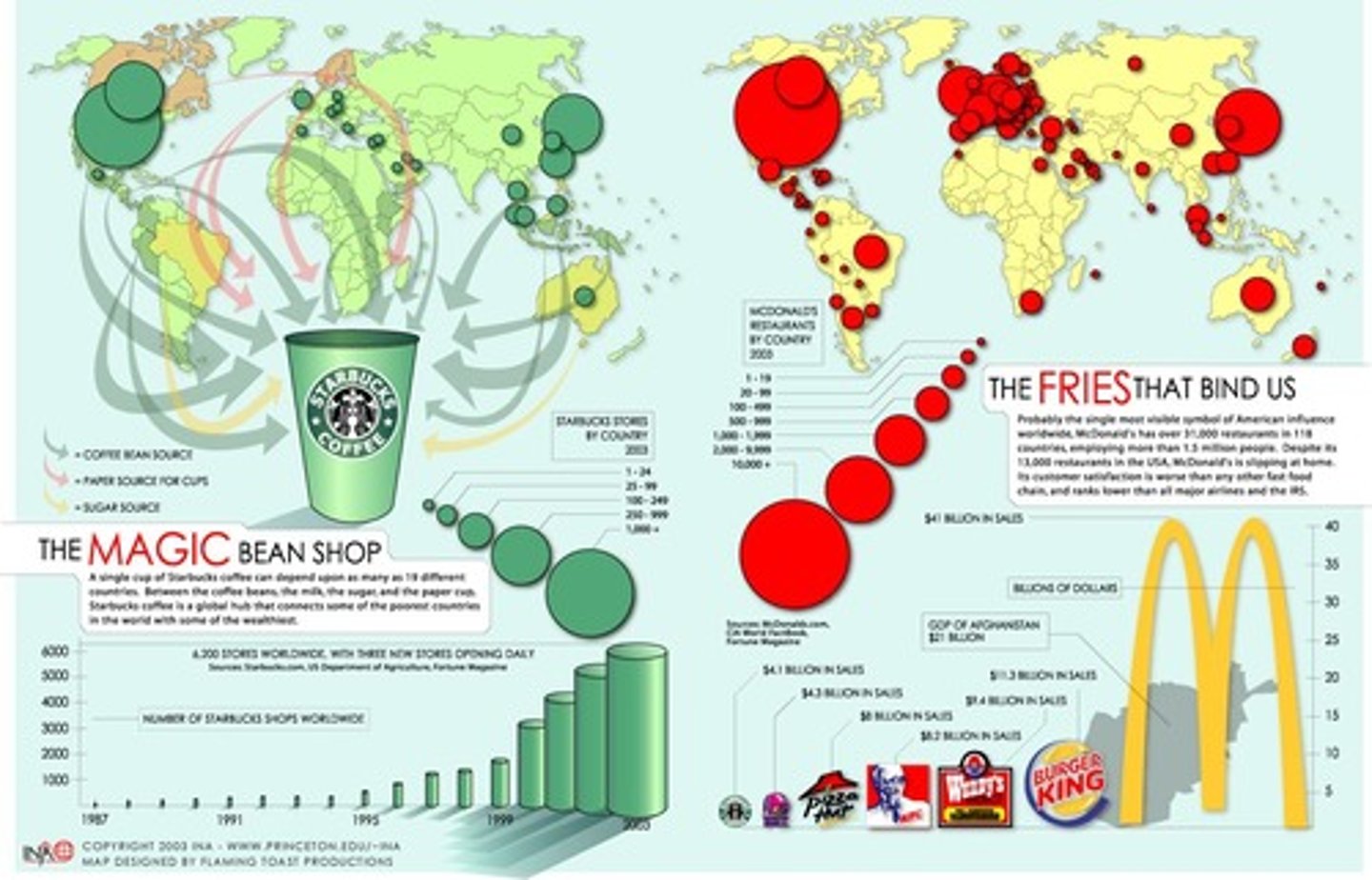
Globalization
A process by which regional economies, societies, and cultures have become integrated through a global network of communication, transportation, and trade

Cultural convergence
The tendency for cultures to become more alike as they increasingly share technology and organizational structures in a modern world united by improved transportation and communication.
Cultural divergence
The tendency for culture groups to disassociate from others in order to protect or preserve their culture from influence or change

Diffusion
The process of spread of a feature or trend from one place to another over time
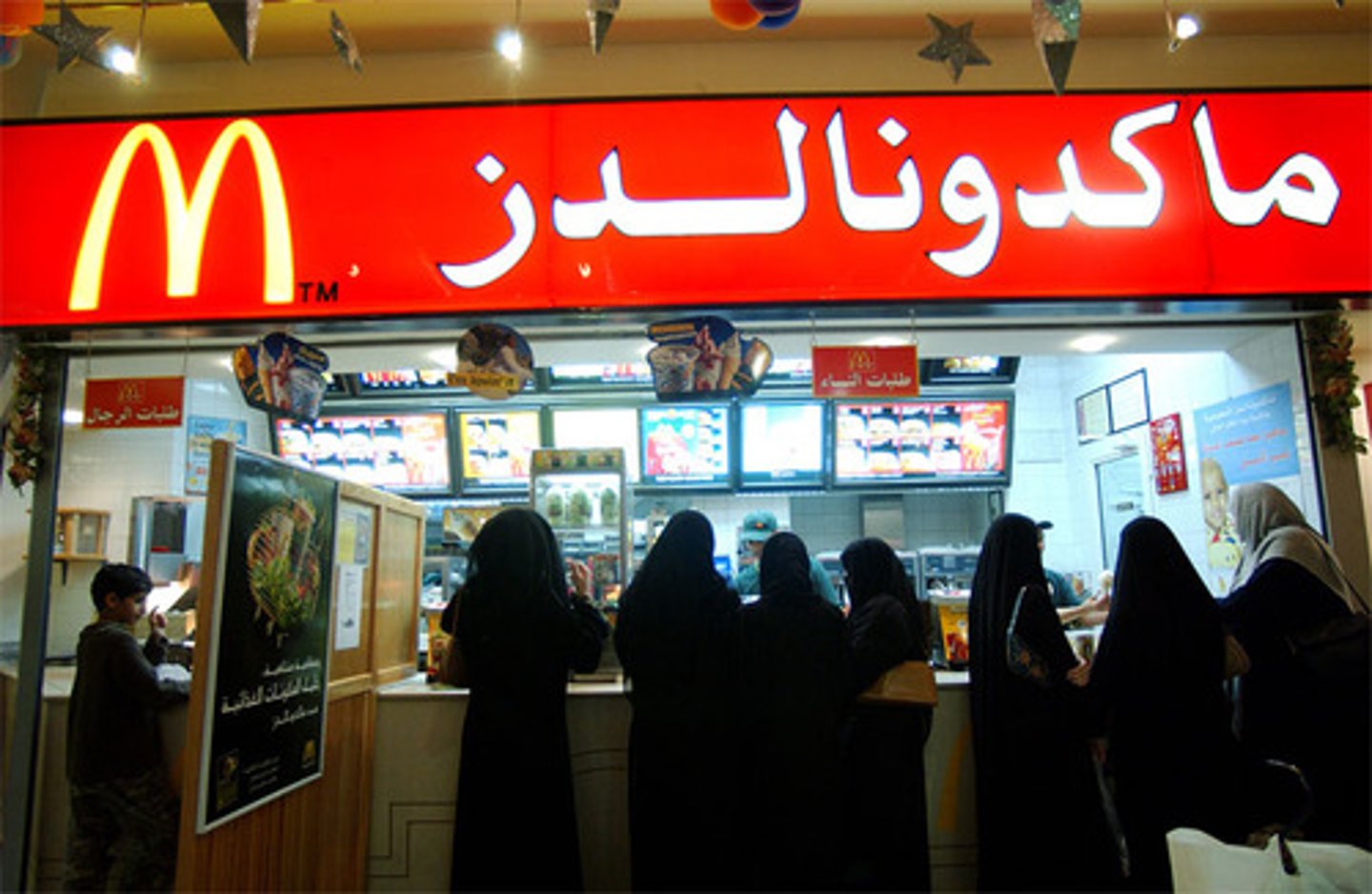

Relocation diffusion
The spread of a cultural trait by people who migrate and carry their cultural traits with them
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of cultural traits through direct or indirect exchange without migration

Three types of expansion diffusion
Hierarchical, contagious, and stimulus
Contagious Diffusion
The rapid, widespread diffusion of a feature or trend throughout a population.
Hierarchical Diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places of lesser status, prominence, or power.
Reverse hierarchical diffusion
When a trait spreads from areas of little influence to larger, more prominent areas. Think: the diffusion of Wal-Mart which first spread to small towns before opening stores in bigger cities and metropolitan areas.
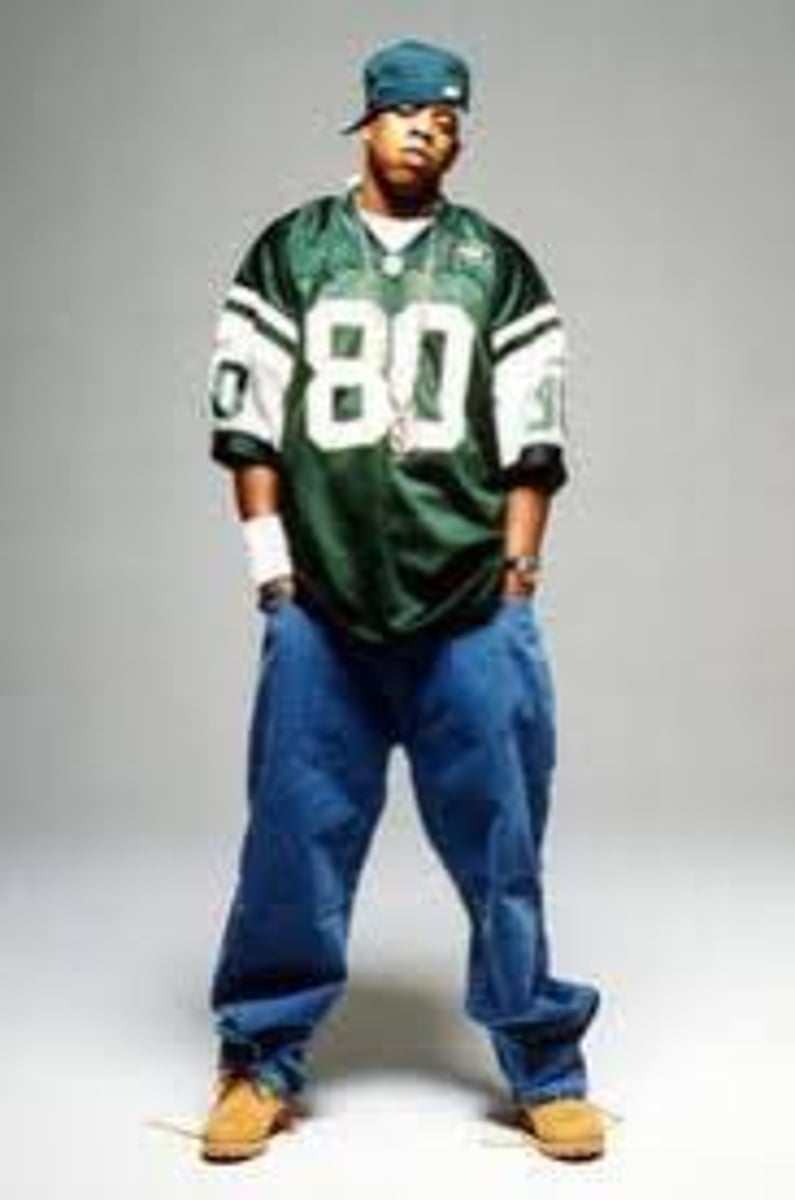

Stimulus Diffusion
Occurs when people in a culture adopt an underlying idea or process from another culture, but modify it. Think: Hip Hop was modified and adapted in different ways as it spread from its hearth in New York to other regions of the U.S.

Acculturation
When an ethnic or immigrant group moving to a new area adopts the values and practices of the larger group that has received them, while still maintaining major elements of their own culture

Assimilation
The process of less dominant cultures losing their culture to a more dominant culture.

Multiculturalism
The practice of valuing and respecting differences in culture; a perspective recognizing cultural diversity and promoting equal standing for all cultural traditions

Cultural relativism
The practice of judging a culture by its own standards

Ethnocentrism
Evaluation of other cultures according to the standards and customs of one's own culture; often includes the belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group over others.

Sequent occupance
The notion that successive societies leave their cultural imprints on a place, each contributing to the cumulative cultural landscape

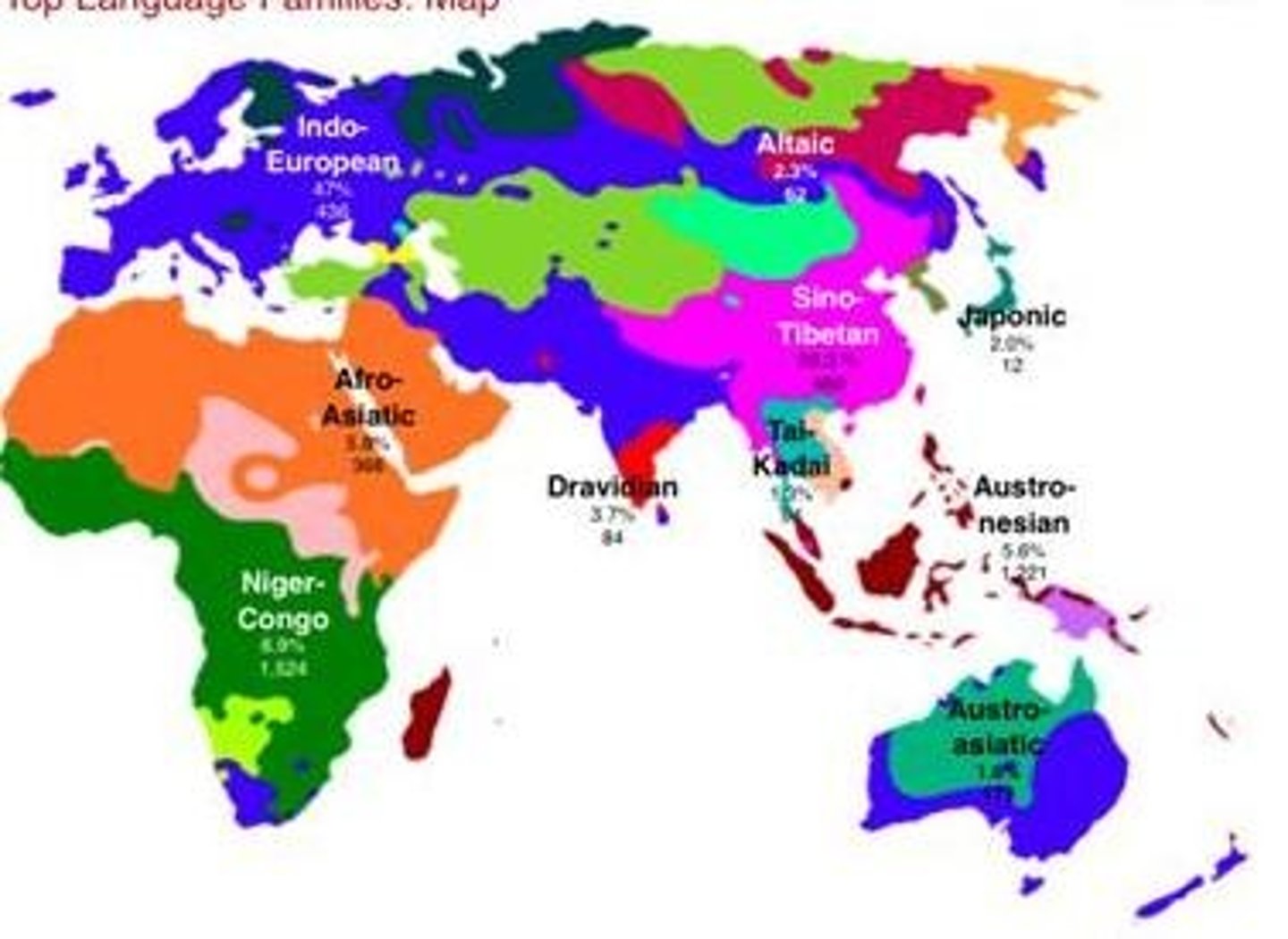
Language family
A collection of languages related to each other through a common ancestor long before recorded history.
Official language
The language adopted for use by the government for the conduct of business and publication of documents.

Extinct language
A language that was once used by people in daily activities but is no longer used (Hebrew was one of these languages until it was revived with the creation of Israel; Cornish is another example)
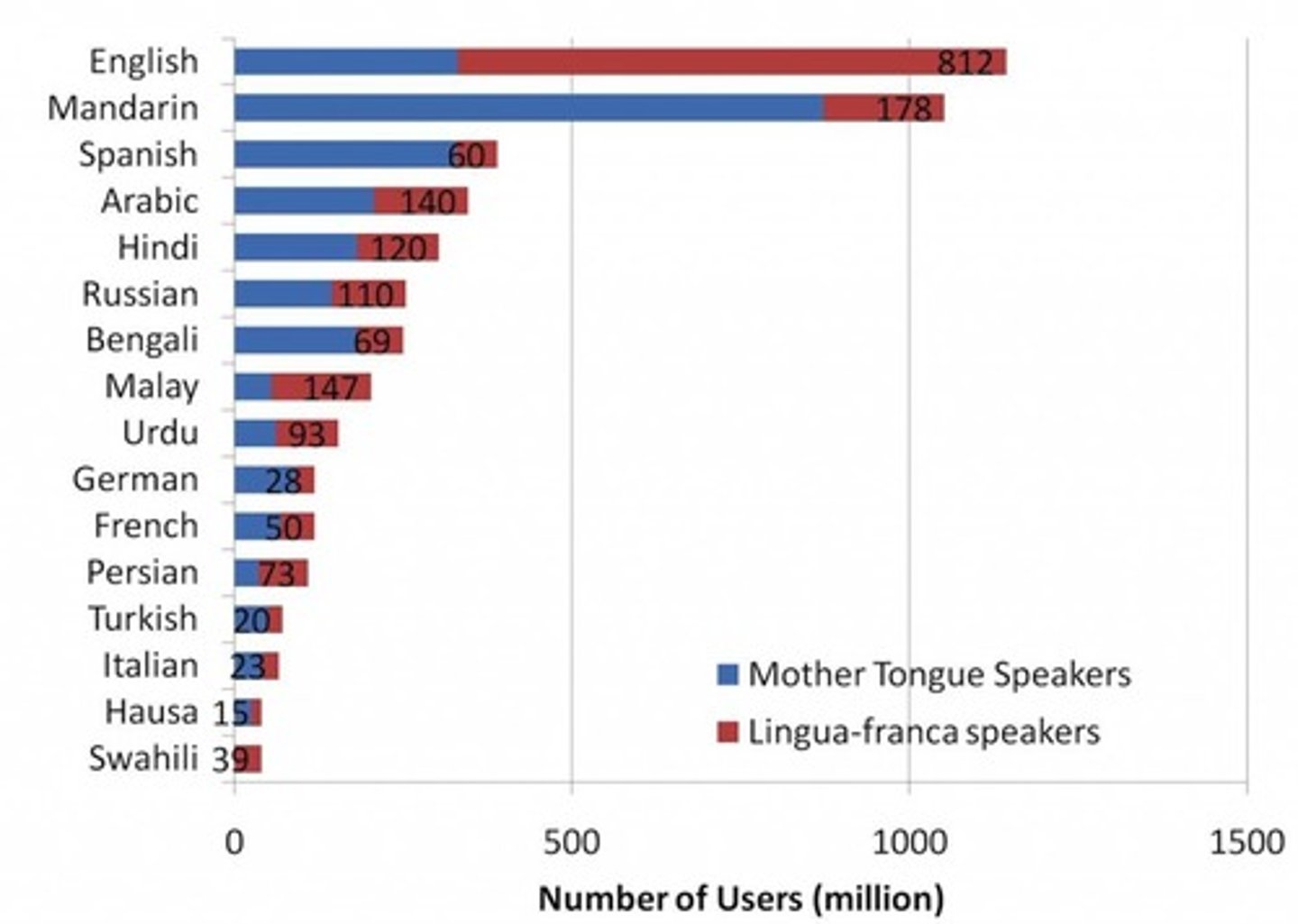
Lingua franca
A language that is adopted as a common language between speakers whose native languages are different.
Imperialism / colonialism
Domination by one country of the political, economic, or cultural life of another country or region

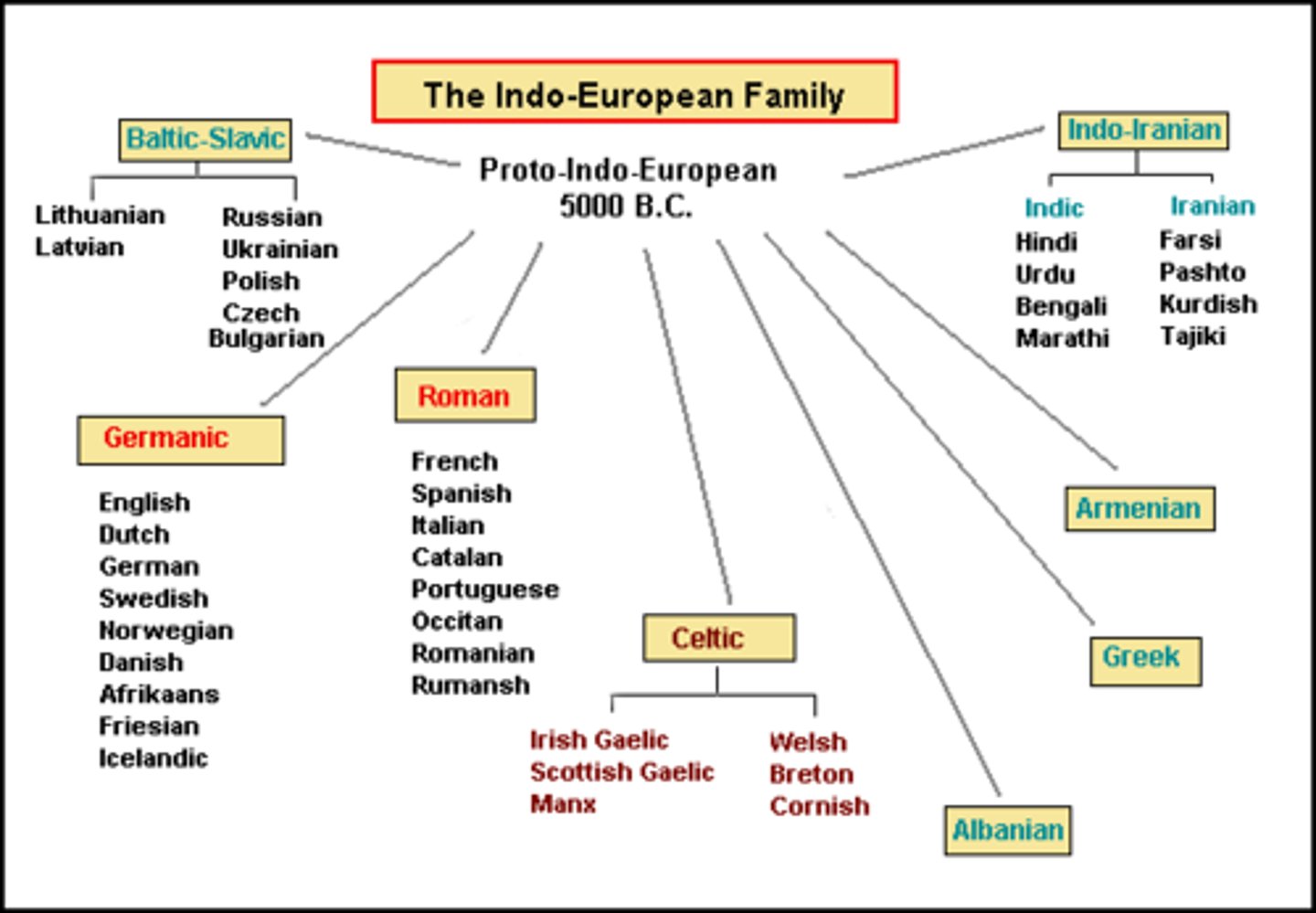
Indo-European
Relating to the family of languages spoken over the greater part of Europe and Asia as far as northern India; the world's most widely spoken family, spoken by over half of the world's population; includes the Romance languages as well as English, Russian, Hindustani, and German.
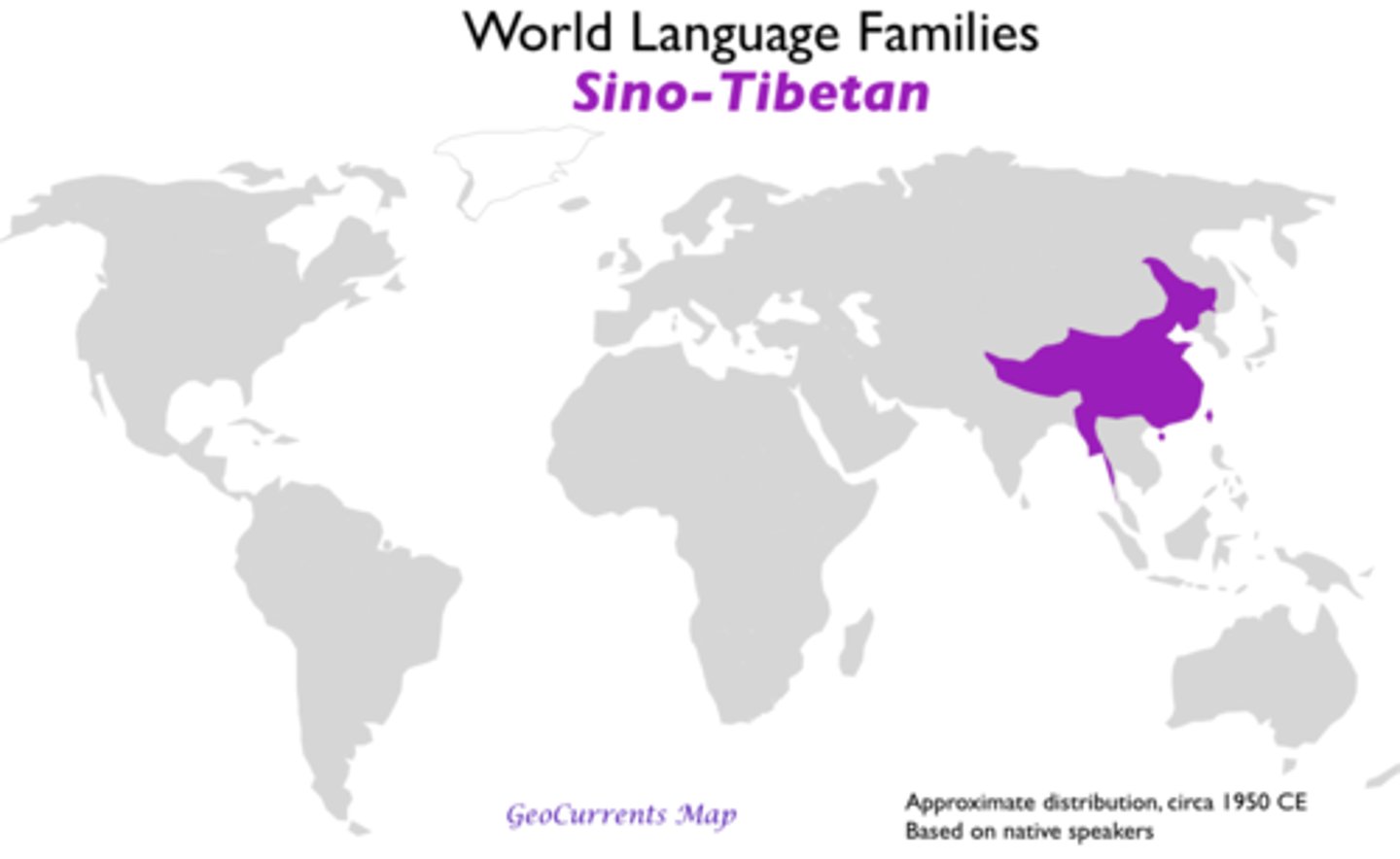
Sino-Tibetan
Language family that is dominant across most of Southeast Asia and China and is comprised of Chinese, Burmese, Tibetan, Japanese, and Korean.
Pidgin
A form of speech that adopts a simplified grammar and limited vocabulary of a lingua franca, used for communications among speakers of two different languages.
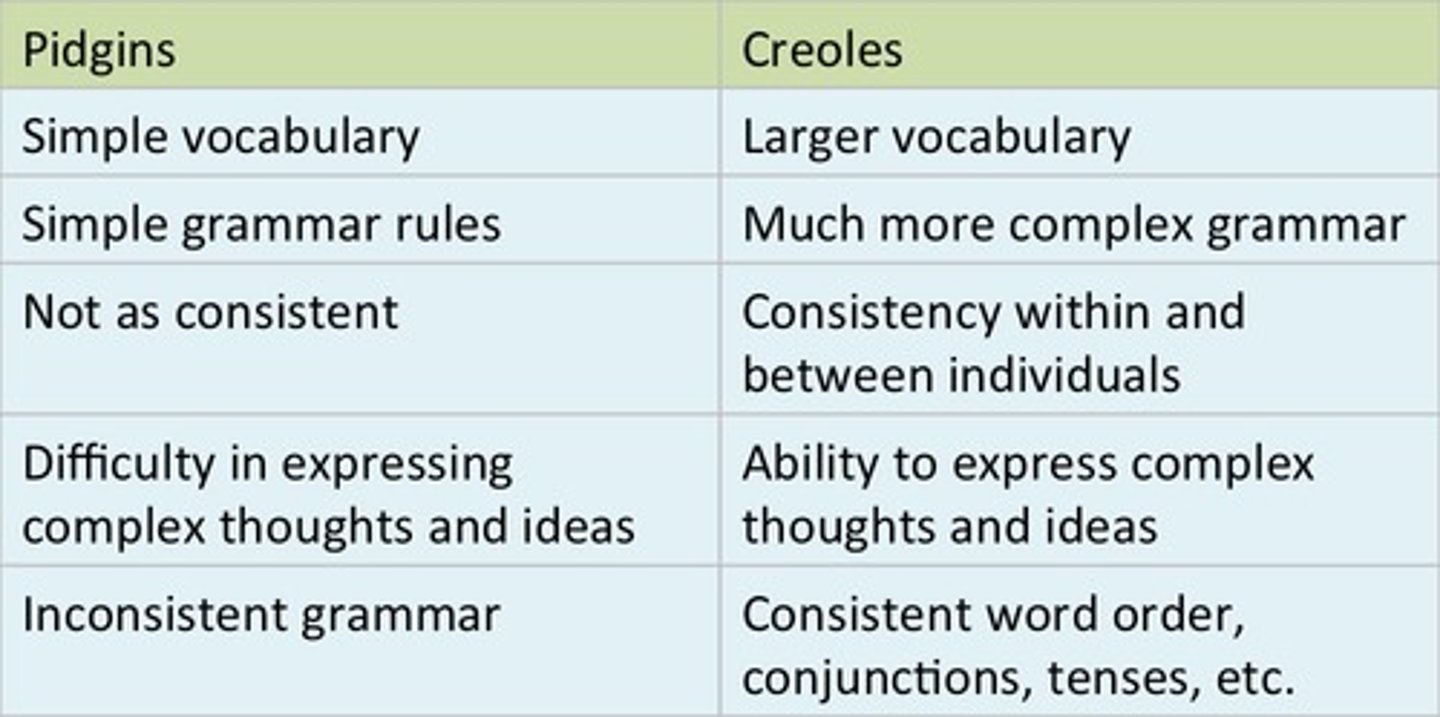
Creole
A pidgin language that evolves to the point at which it becomes the primary language of the people who speak it
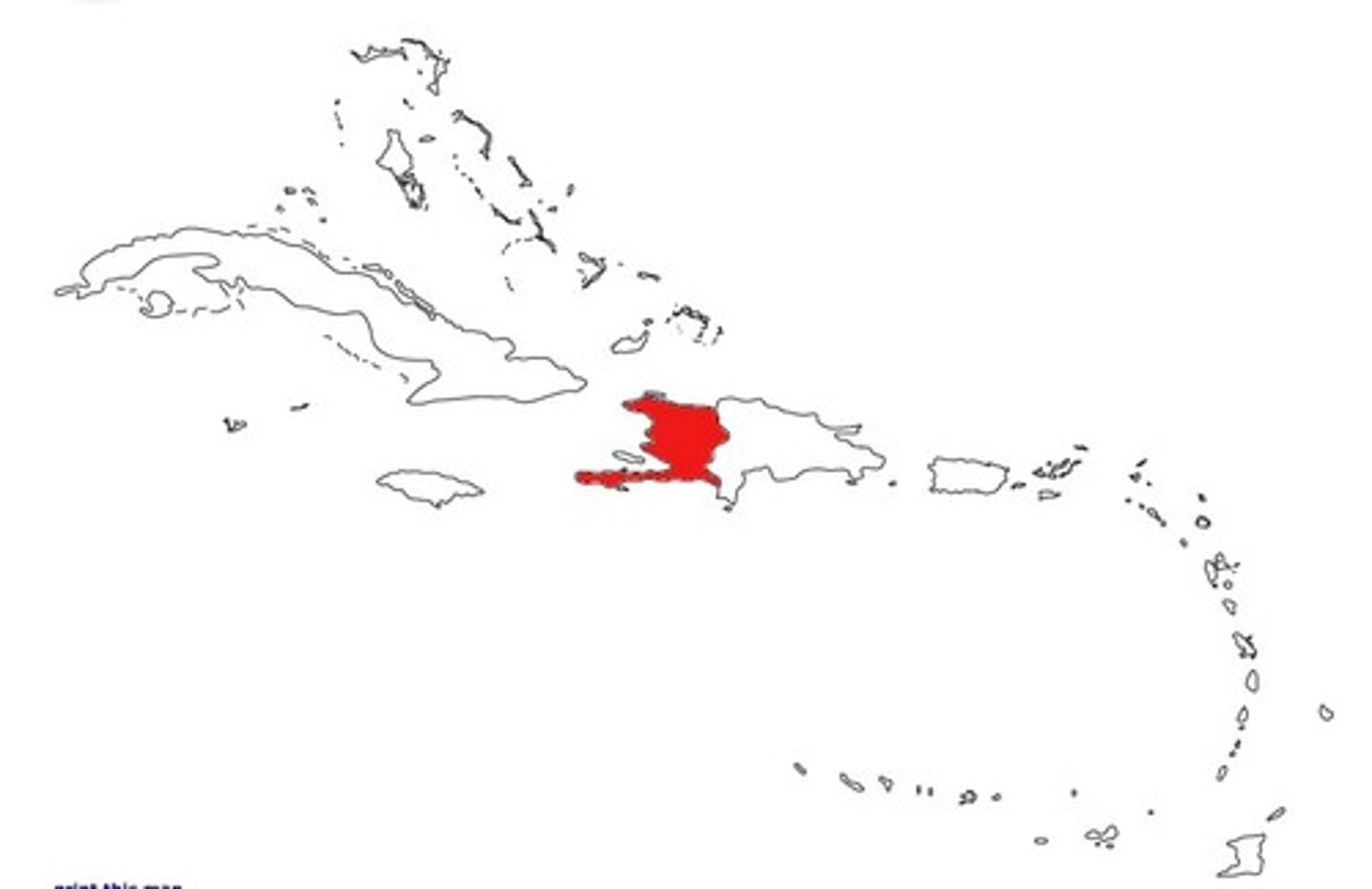
Syncretism
A blending of two or more cultural or religious traditions; Voodoo and Santeria blend Catholocism with traditional African faiths

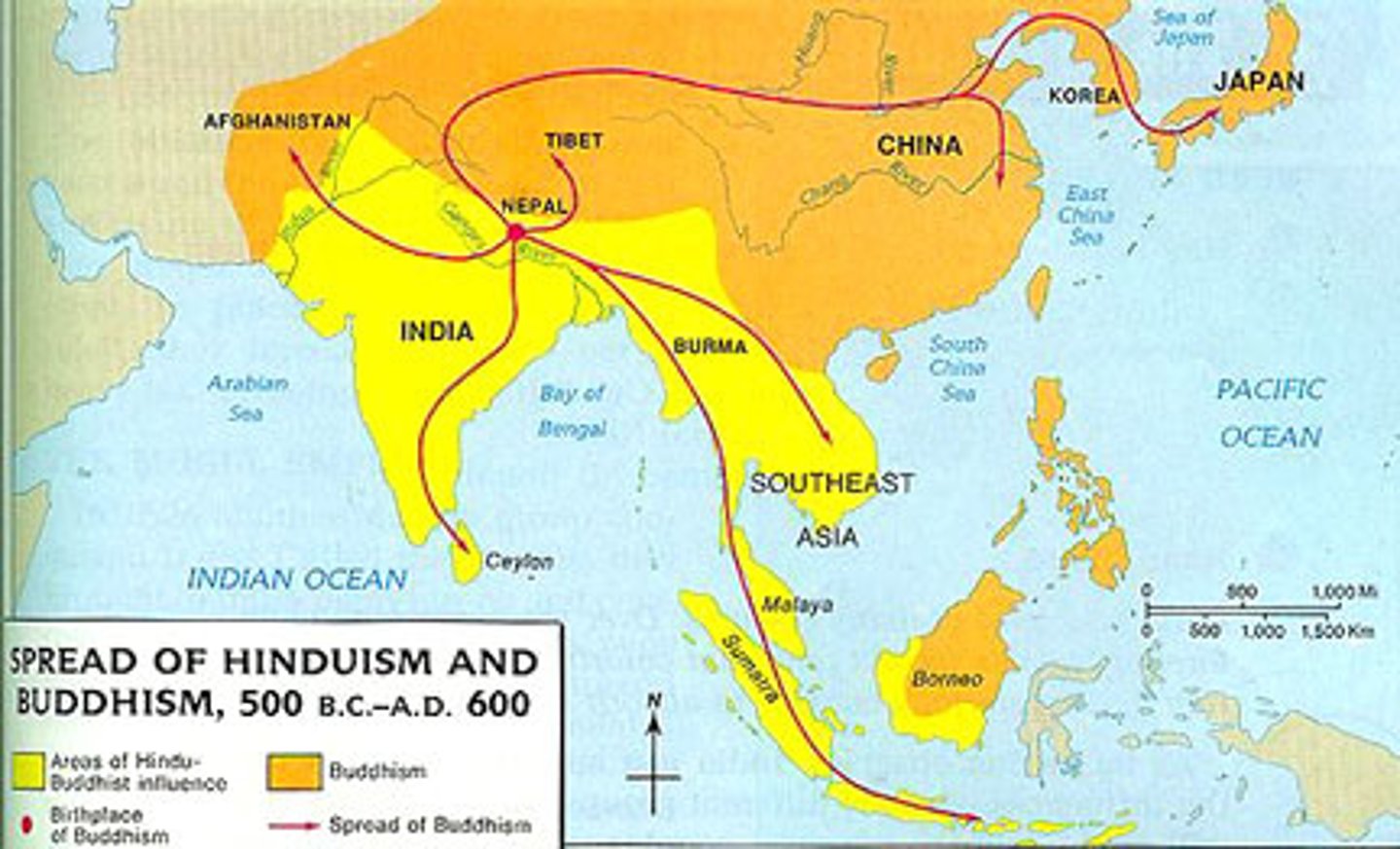
Universalizing religion
A faith that claim applicability to all humans and that seek to transmit their beliefs through missionary work and conversion (Examples: Christianity, Islam, Buddhism)

Ethnic religion
A religion that is identified with a particular ethnic or tribal group and that does not seek new converts (Examples: Judaism, Hinduism, Shintoism)

Christianity
A monotheistic system of beliefs and practices based on the Old Testament and the teachings of Jesus as embodied in the New Testament and emphasizing the role of Jesus as savior.

Judaism
A religion with a belief in one god. It originated with Abraham and the Hebrew people. Yahweh was responsible for the world and everything within it. They preserved their early history in the Old Testament.

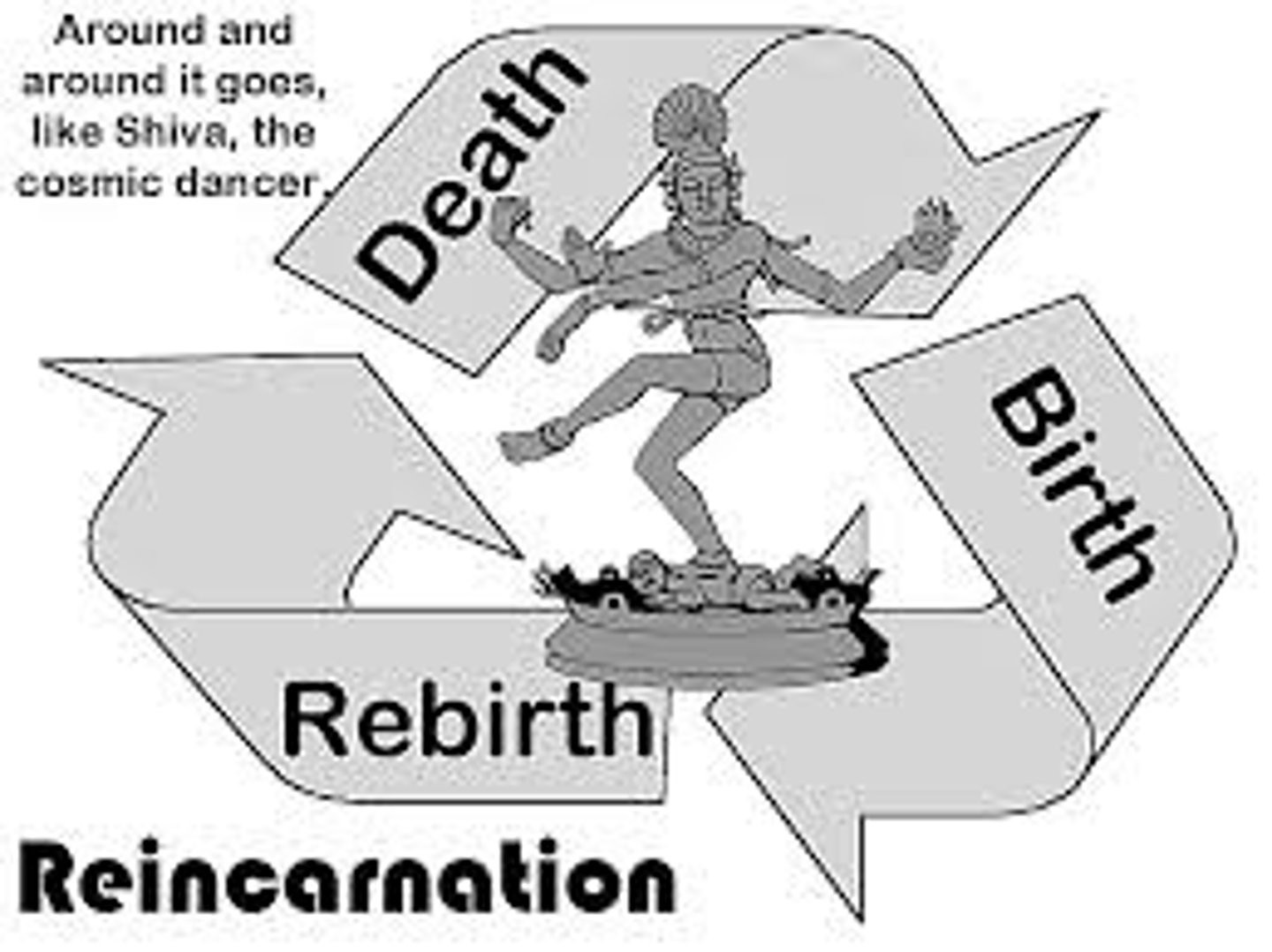
Hinduism
A religion and philosophy developed in ancient India, characterized by a belief in reincarnation and a supreme being who takes many forms; a ;polytheistic religion

Islam
A religion based on the teachings of the prophet Mohammed which stresses belief in one god (Allah), and the Five Pillars embodied in the Quran. Followers are called Muslims.

Mosque
A Muslim place of worship

Church
A Christian place of worship

Synagogue
A Jewish house of worship

Buddhism
The teaching of Siddhartha Guatama that life is permeated with suffering caused by desire, that suffering ceases when desire ceases, and that enlightenment obtained through right conduct and wisdom and meditation releases one from desire and suffering and rebirth

Jesus
A Jew from Galilee in northern Israel who sought to reform Jewish beliefs and practices. He was executed as a revolutionary by the Romans. He is the basis of the world's largest religion.

Muhammad
Arab prophet; founder of religion of Islam.

Abraham
Founder of Judaism who, according to the Bible, led his family from Ur to Canaan in obedience to God's command.

Reincarnation
In Hinduism and Buddhism, the process by which a soul is reborn continuously until it achieves perfect understanding
Old Testament
The forty-six books of the Bible that record the history of salvation from Creation until the time of Christ. Sacred to both Judaism and Chritianity

New Testament
The second part of the Christian Bible, containing descriptions of the life and teachings of Jesus and of his early followers

Quran (Koran)
The holy book of Islam

Arabic
A language that is the official language of several countries of North Africa and the Middle East, as well as the religion of Islam

Hebrew
Original language of the Jewish people and that of their sacred books.

Torah
A Hebrew word meaning "law," referring to the first five books of the Old Testament.

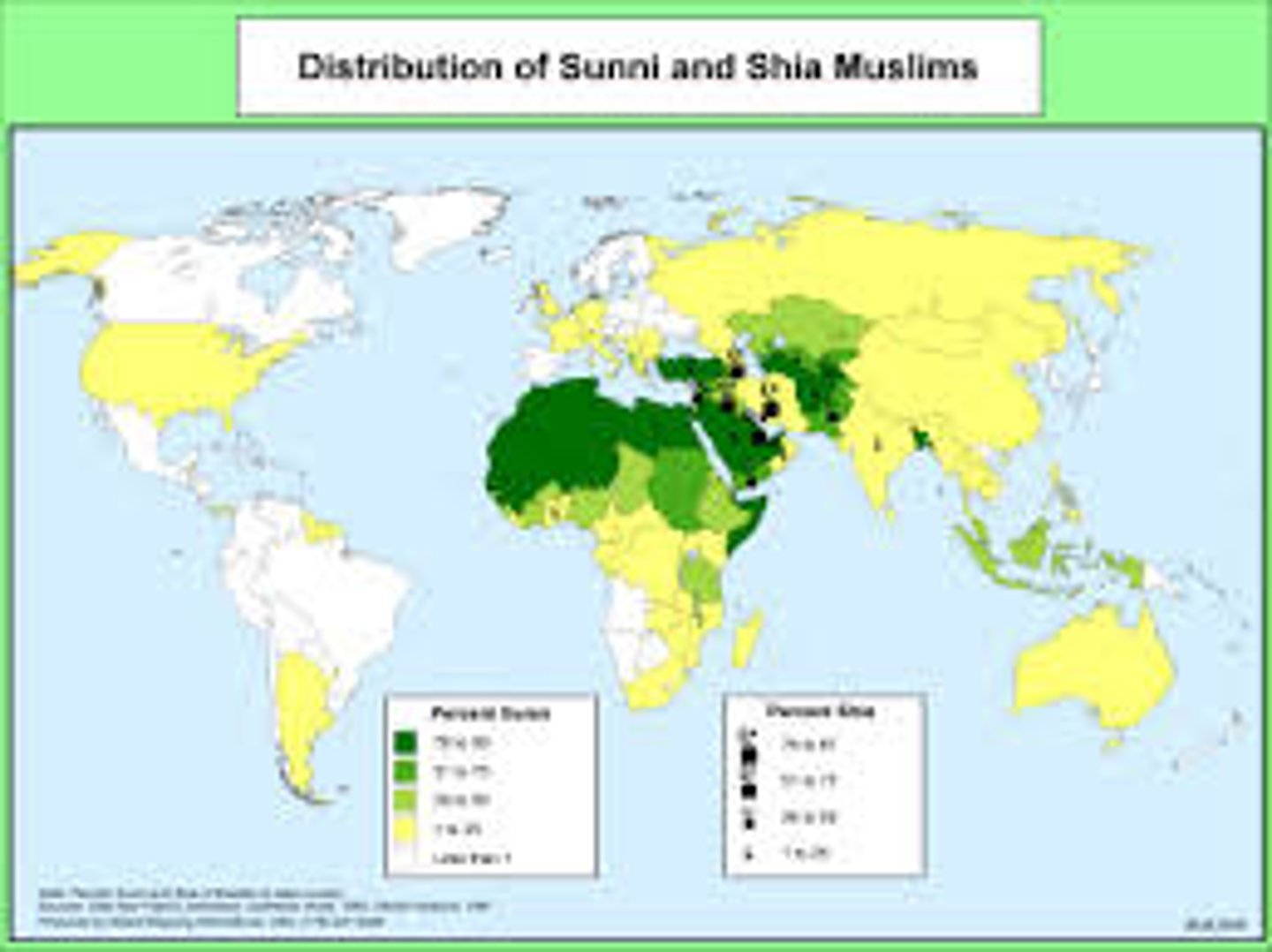
Shia Islam
A minority branch of Islam; dominant in Iraq and Iran; believed the successor to Muhammad should be a relative
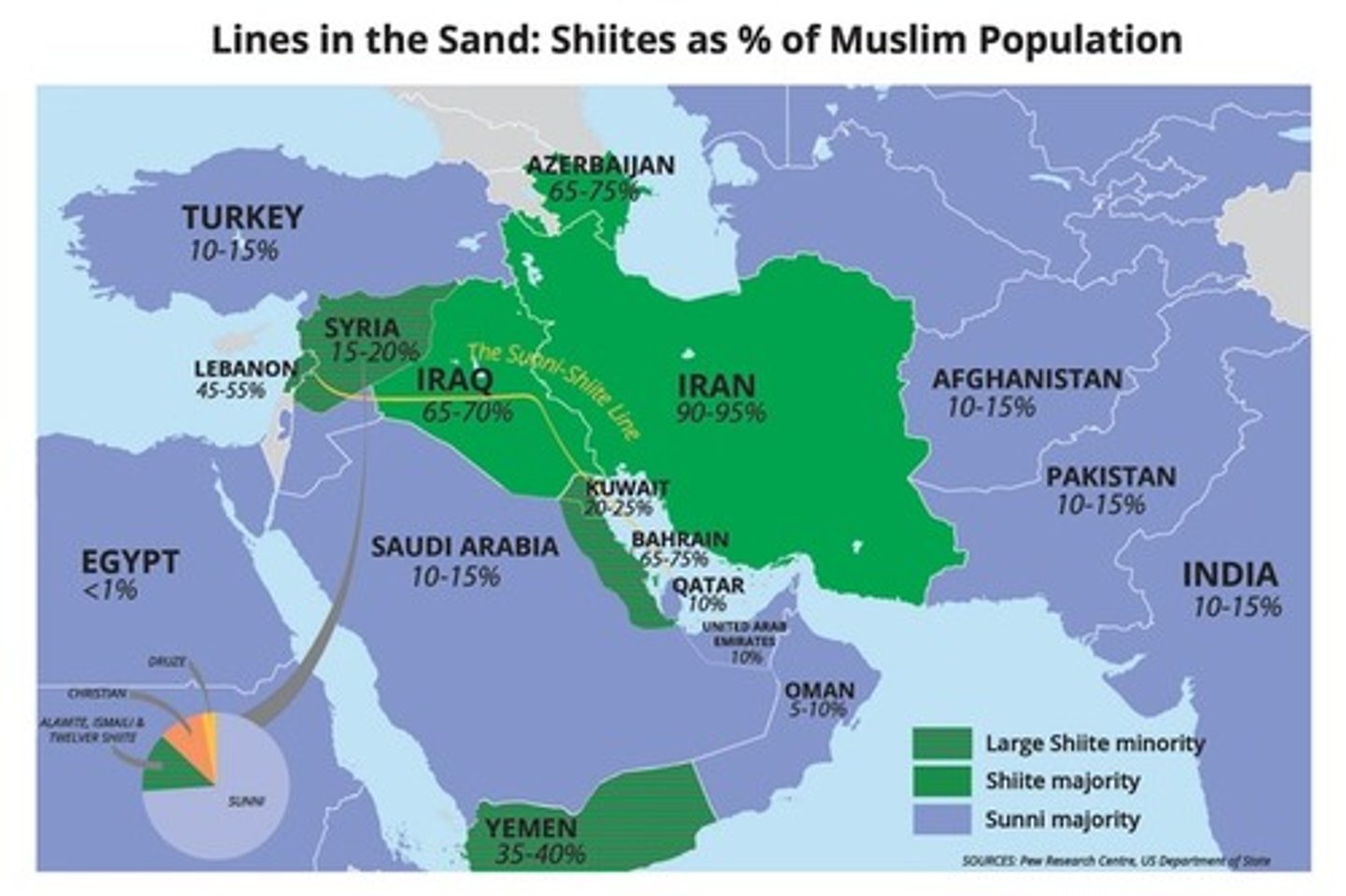
Sunni Islam
The dominant branch of Islam; believed successor to Muhammad should be a qualified leader and not necessarily a relative
Catholic Church
The Christian church of the West, based in Rome, that is under the authority of the pope and has a strict theological and cleric hierarchy

Protestant
A member or follower of any of the Western Christian churches that are separate from the Roman Catholic Church and follow the principles of the Reformation, including the Baptist, Presbyterian, and Lutheran churches.

Polytheism
Belief in many gods

Monotheism
Belief in one God

Sect
A relatively small group that has broken away from an established religion (Example: Christianity began as a Jewish sect)

Missionary
An individual who helps to diffuse a universalizing religion.

Syncretic religion
Combines two religious traditions into something distinctly new, while containing traits of both
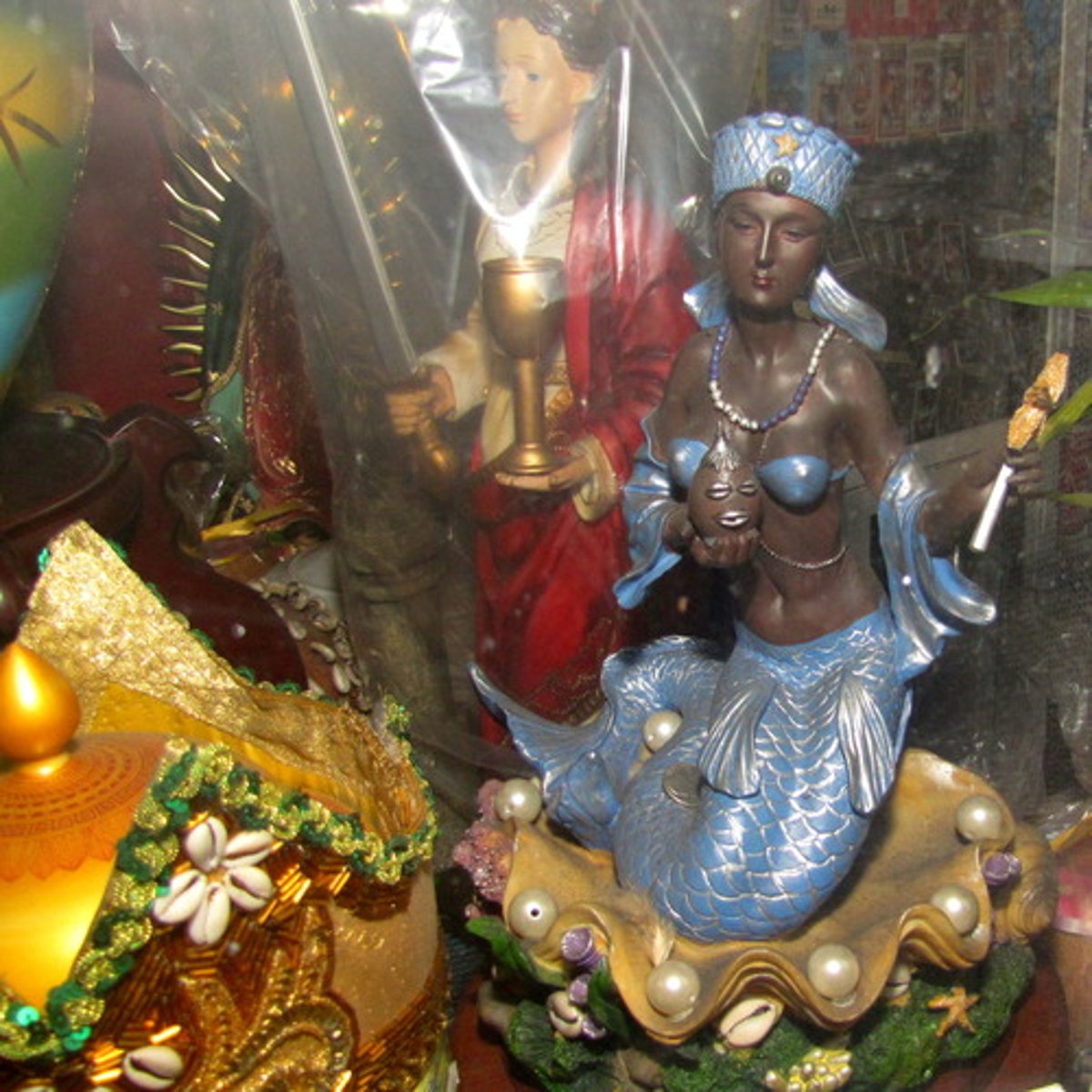

Santeria
Originating in Cuba, a religion that blends African traditions and Christian beliefs

Atheism
Belief that God does not exist

Race
Identification of a group of people through a perceived trait, such as skin color or physical chracteristics

Ethnicity
Identification of a group of people who share a cultural tradition of a particular homeland or hearth

Racism
Belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race.
Ethnic enclave
A place with a high concentration of an ethnic group that is distinct from those in the surrounding area

Genocide
The deliberate killing of a large group of people, in order to try to eliminate that group from existence.

Swahili
A creolized pidgin language based on Bantu and Arabic words; serves as a regional lingua franca throughout Eastern Africa
Glocalization
The process of firms standardizing their products globally, but adapting them locally (Example: McDonalds created the McCafe idea of a designer coffees and pastries to attract customers in France)
Caste system
A set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation and economic potential, but also his or her position in society
Isogloss
A line on a dialect map marking the boundary between linguistic features.
Dialects
Local or regional characteristics of a language based on pronunciation variation, distinctive grammar and vocabulary
Pilramage
A religious journey taken by a person to a sacred place of his or her religion
Toponyms
Place names
Cultural appropriation
The adoption of cultural elements belonging to an oppressed group by members of the dominant group, without permission and often for the dominant group's gain
Sharia Law
The system of Islamic law, based on varying degrees of interpretation of the Quran
Artifacts
Objects created by and used by humans
Mentifacts
Nonmaterial parts of a culture such as language, religion, artistic pursuits, folk stories, myths, etc.
Sociofacts
Institutions of a society (laws, government, sports teams, sports organizations, etc.)