Biotechy Ch 3/5
5.0(3)Studied by 41 people
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FOR MY FELLOW PEEPS IN BIOTECHY
Last updated 9:05 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
What is the definition of microbiology?
Study of eukaryotic and microbes (viruses, fungi, bacteria)
2
New cards
What are the domains of life and what organisms inhabit each domain?pg 69
Archaea, the Bacteria, and the Eukarya.
3
New cards
How are bacteria named and classified? What are the names of those classifications?
Based on their shape, Coccus, bacillus, diplo, strepto, and tetrad.
4
New cards
Know the microbial shapes?
coccus, bacillus, spirillum, diplo-, strepto-, tetrad-
5
New cards
Coccus-
sphere
6
New cards
Bacillus-
rod
7
New cards
Spirillum-
spiral
8
New cards
Diplo-
short rod-shaped bacteria that occur in pairs
9
New cards
Strepto-
pairs or chains
10
New cards
Tetrad-
group of 4 cells
11
New cards
What are the components found in the cell wall of bacteria and how do scientists visualize those components?
NAM, NAG and Peptidoglycan
12
New cards
What are two roles of microbiological media?
Selection and differentiation
13
New cards
Why would a scientist use antibiotic selection while growing bacteria?
Identify a successful bacteria transformation.
14
New cards
What type of culture would you use for long term bacterial storage?
Stab culture with solid media
15
New cards
Who was Koch and what contribution did he make to microbiology?
A microbiologists who worked with Pasteur and Lister. He contributed and set bacteriology on its way to being a modern science
16
New cards
What are Koch's postulates?
Four criteria designed to establish a causal relationship between a microbe and a disease.
17
New cards
How is a bacterial lawn different from colonies?
Will look like a hazy blanket of growth extending beyond the area that is streaked. While colonies only appear on the area that was streaked and usually looks like a small white circle.
18
New cards
What is a Kirby-Bauer test? What does it test?
Determines the sensitivity or resistance of pathogenic bacteria to various antimicrobial compounds in order to assist physicians in selecting treatment options for their patients.
19
New cards
Why would one disk have a greater zone of inhibition than another? What can this tell you about the bacteria's properties?
A larger zone of inhibition tells us that the bacteria are more sensitive to the antibiotic in the disc.
20
New cards
What would you expect to see if the chemicals used on a disk have no antimicrobial properties?
That the antibiotics were ineffective
21
New cards
How does gram staining help classify bacteria
Can identify whether or not a bacteria is present which would be gram positive (purple and thick wall) or negative (red/pink thin wall) if not present
22
New cards
What are colony forming units?
Unit to estimate the number of viable microbial cells in a sample
23
New cards
What are serial dilutions and when would you do one?
Used to quantify bacteria and Estimate the number of bacteria in a culture.
24
New cards
How do you determine the total magnification of the microscope?
Ocular magnification X objective magnification
25
New cards
Bacterial cell walls are made of\____ and \____. pg 71
Nam(N-acetylmuramic) and Nag(acetylglucosamine)
26
New cards
Microbiology is a field that studies:pg 69
Study of microorganisms and their effects on other living organisms
27
New cards
What does the gram status tell you about the bacteria's cell wall?
Gram positive (purple and thick wall) gram negative (red/pink thin wall)
28
New cards
What are the 3 ways that bacteria can transfer DNA and how?
Bacterial conjugation, natural transformation, and transduction
29
New cards
What are the 3 ways that a biotechnologist can transform a bacterial cell?
Transformation, conjugation and transduction.
30
New cards
Understand how the experiments by Griffith and Avery, MacLeod and McCarty demonstrated the principle of bacterial transformation.
Griffith and Avery: Can obtain non-virulent bacteria by experimentations on rates.
MacLeod and McCarthy: uptake and incorporated DNA by bacterial transformation
MacLeod and McCarthy: uptake and incorporated DNA by bacterial transformation
31
New cards
Know the features commonly found in a bacterial plasmid and their purpose(p.148): Ori, antibiotic resistance, promoter sequences.
Ori:(origin of replication) recognition sites for DNA polymerase:
Antibiotic resistance 'gene': provide a mechanism for scientist to separate bacteria containing recombinant plasmids from those that do not:
Promoter sequences: PROMOTER; provides a landing site for RNA polymerase so the gene can be transcribed, TERMINATOR; signals to stop transcribing
Antibiotic resistance 'gene': provide a mechanism for scientist to separate bacteria containing recombinant plasmids from those that do not:
Promoter sequences: PROMOTER; provides a landing site for RNA polymerase so the gene can be transcribed, TERMINATOR; signals to stop transcribing
32
New cards
What is a bacterial growth curve and what does it represent? Be prepared to draw and label one.
"is the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a certain period of time."
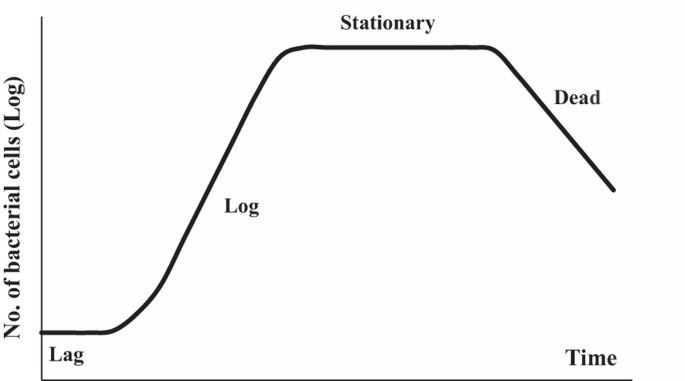
33
New cards
What features must be present in a plasmid that would be used to express a protein (148-149)?
origin of replication ("ori"), genes, promoter, and terminator.
34
New cards
What is a MCS and how is it used(p.149)?
Is a 'multiple cloning site'. It is used to open up a plasmid so that it is ready to receive the gene of interest.
35
New cards
What is an operon and what is it made up of (150)?
A naturally occurring control unit in bacterial chromosomal DNA. It consists of one promoter, multiple genes, and a single terminator.
36
New cards
What is the purpose of a miniprep (p. 156)?
Is the process of growing a small culture of bacteria and purifying the plasmid. (aka. DNA extraction)
37
New cards
What genes are commonly included in plasmids to transform bacterial cells?
Antibiotic resistance genes, transgenes and reporter genes are commonly found in plasmids.
38
New cards
Know what was expected for each plate during the bacterial transformation lab.
LB pGLO(negative): grow and no glow: LB/amp pGLO(negative): no grow and no glow: LB/Amp pGLO(positive): Grow because of transformation no glow: LB/amp/ara pGLO(positive): Grow and glow
39
New cards
What is transformation efficiency?
The number of bacteria that were successfully transformed per microgram