A&P Lab Exam Review (Digestive System)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are the 6 main regions of the large intestine?
Cecum
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Rectum
(a) What are the 2 flexures called? What abdominopelvic regions are they located in?
Right colic (hepatic) flexure – between ascending & transverse colon; in right hypochondriac region.
Left colic (splenic) flexure – between transverse & descending colon; in left hypochondriac region.
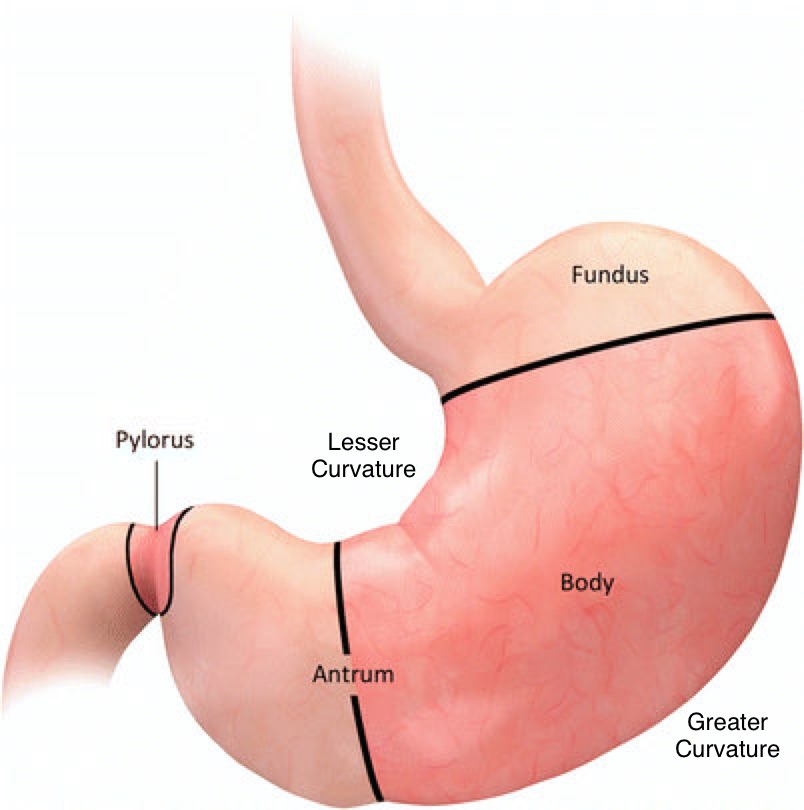
Name and identify the gross anatomy of the outside stomach: corpus, greater curvature, lesser curvature, pylorus, fundus.
Fundus – dome-shaped region superior & left of esophagus entry.
Corpus (body) – large central region.
Greater curvature – long, lateral/inferior border.
Lesser curvature – shorter, medial/superior border.
Pylorus – distal part leading to duodenum (pyloric antrum → pyloric canal → pyloric sphincter).
What epithelium is found in the small intestine?
Simple columnar epithelium with microvilli and goblet cells.
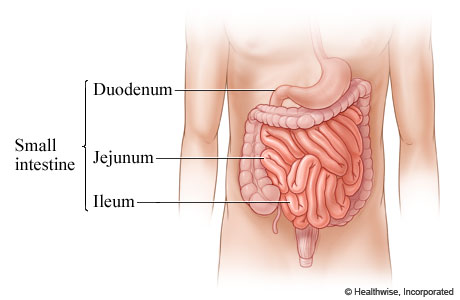
Name and identify the 3 regions of the small intestine.
Duodenum
Jejunum
Ileum
What abdominopelvic region is the liver in? What about the pancreas, and stomach?
Liver – mostly right hypochondriac and part of epigastric.
Pancreas – mostly epigastric, extending into left hypochondriac; retroperitoneal.
Stomach – mainly epigastric and left hypochondriac.
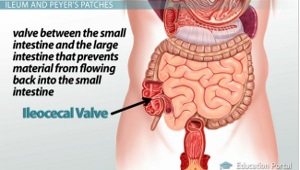
Name the valve that separates the small intestine from the large intestine. Be able to identify it
Ileocecal valve (at junction of ileum and cecum).
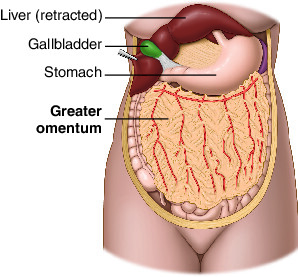
Where does the greater omentum attach to? Identify it.
Hangs from greater curvature of the stomach and proximal duodenum, then drapes over intestines and attaches to transverse colon.
What enzymes digests the following molecules: proteins, starch and fats.
Proteins – proteases: pepsin (stomach), trypsin, chymotrypsin, peptidases.
Starch (carbs) – amylases (salivary amylase, pancreatic amylase).
Fats (lipids) – lipases (lingual, gastric, especially pancreatic lipase; bile aids by emulsifying).
Describe the function of HCl and gastric juices secreted in the stomach.
HCl -
Lowers pH (very acidic).
Activates pepsinogen → pepsin.
Denatures proteins and kills many microbes.
Gastric juice -
(HCl + pepsinogen + mucus + intrinsic factor, etc.)
Chemically digests proteins.
Mucus protects stomach lining.
Intrinsic factor needed for vitamin B12 absorption in small intestine.
Identify the following digestive system anatomy: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus.
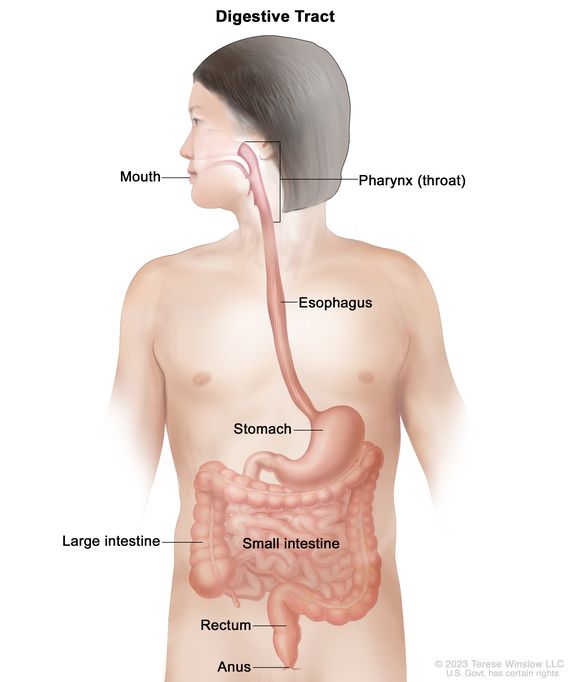
(a) What epithelium is found in each of these areas?
Mouth (oral cavity) - Epithelium: nonkeratinized stratified squamous.
Pharynx (oropharynx, laryngopharynx) - Epithelium: stratified squamous.
Esophagus - Epithelium: stratified squamous nonkeratinized.
Stomach - Epithelium: simple columnar (mucous cells and gastric glands).
Small intestine - Epithelium: simple columnar with villi & microvilli.
Large intestine - Epithelium: mostly simple columnar with many goblet cells; anal canal transitions to stratified squamous.
Rectum - Epithelium: simple columnar transitioning to stratified squamous near anal canal.
Anus (anal canal) - Epithelium: stratified squamous (keratinized near opening).
(b) What digestive process happens in these organs? (e.g. ingestion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion, deglutition, absorption, etc.)
Mouth (oral cavity) - Processes: ingestion, mechanical digestion (chewing), chemical digestion of carbs (salivary amylase) and some lipids (lingual lipase), start of deglutition.
Pharynx (oropharynx, laryngopharynx) - Processes: deglutition, propulsion of bolus.
Esophagus - Processes: deglutition, peristalsis (propulsion)
Stomach - Processes: mechanical digestion (churning), chemical digestion of proteins and some lipids, limited absorption (alcohol, some drugs).
Small intestine - Processes: main site of chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients; segmentation and some peristalsis.
Large intestine - Processes: absorption of water, electrolytes, vitamins; compaction of feces; defecation.
Rectum - Processes: storage of feces, defecation.
Anus (anal canal) - Processes: defecation.
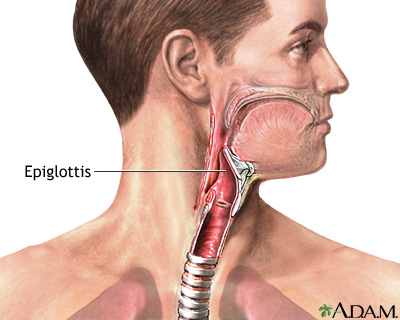
Describe the function of the epiglottis. Identify it.
Elastic cartilage flap that covers the laryngeal inlet during swallowing, preventing food/liquid from entering the trachea and directing it into the esophagus.
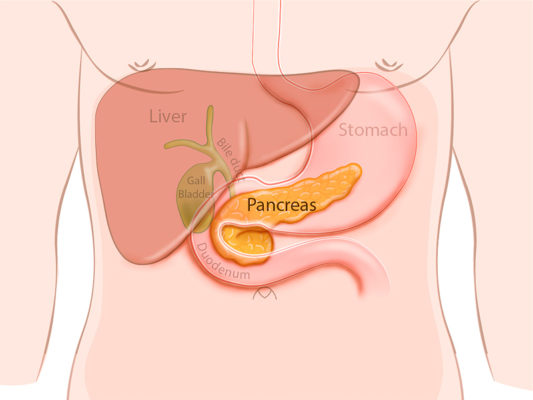
What function does the pancreas serve in the digestive system? Identify it.
Exocrine pancreas (acinar cells) secretes pancreatic juice containing:
Digestive enzymes (amylase, lipase, proteases, nucleases).
Bicarbonate to neutralize acidic chyme.
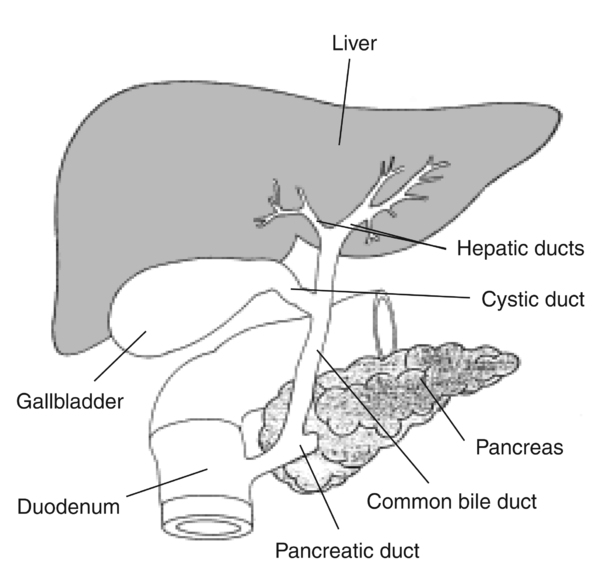
Biliary tree/pancreas: be able to identify the common hepatic duct, cystic duct, pancreatic duct (and sphincter) and common bile duct.
What is the wave-like contraction of muscle that propels food down the digestive tract?
Peristalsis.
What is hydrolysis? What molecule uses this process in the digestive system?
a. Hint: we used these molecules to eat up macromolecules in the digestion lab
Chemical process where water is used to break bonds in larger molecules, splitting them into smaller units.
In digestion, digestive enzymes catalyze hydrolysis of carbs, proteins, and fats using water.
Digestion can be broken down into 2 main types. Name them and describe how they work.
Mechanical digestion -
Physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces (chewing, churning in stomach, segmentation in intestines).
Chemical digestion -
Enzymatic breakdown of macromolecules into monomers (e.g., proteins → amino acids, starch → glucose).
What is the process that happens when carbs, fats, and proteins move from the digestive tract and into the blood or lymphatic system for use by the body?
Absorption.