Integumentary System Health Assessment
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
annular
circular ring-like arrangement
confluent
joining or running together
discrete
separate lesions
grouped
clustered together
gyrate
rings or convolutions
polycyclic
formed from circles
macule
<1 cm, flat, nonpalpable, circumscribed, discolored
patch
>1 cm, flat, nonpalpable, irregular shape, discolored
papule
<1 cm, raised, palpable, firm
nodule
>1 cm, raised, solid
plaque
large flatter elevation of skin, can be formed by papules coalescing
vesicle
<1 cm, circumscribed elevation of epidermis containing clear fluid
bulla
>1 cm, circumscribed elevation of the epidermis containing clear fluid
pustule
small circumscribed elevation of the epidermis filled with purulent fluid
wheal (hives/urticaria)
raised lesion consisting of dermal edema
scale
irregular formation of exfoliated, keratinized cells, irregular shape and size
crust
dried serum, blood or exudate, slightly elevated
lichenification
thickened epidermis with accentuated skin lines caused by rubbing
scar
thin or thick fibrous tissue, following dermal injury (burn)
fissure
linear break in skin through epidermis and dermis
excoritation
hollowed-out area of all or portion of epidermis with depressed appearance (eczema)
erosion
localized loss of epidermis, heals without scarring (herpes)
ulcer
loss of epidermis and dermis, variations in size (decubitus)
atrophy
depression resulting from loss of epidermis and/or dermis (striae)
burrow
narrow, elevated channel produced by a parasite (scabies)
telangiectasia
superficial dilated blood vessel (rosacea)
petechiae
<1 cm circumscribed deposit of blood, deep red or reddish purple, variable shape that fades over time, non-blanchable
purpura
>1 cm circumscribed deposit of blood, deep red or reddish purple, variable shape, fades over time, non-blanchable
ecchymosis
>3 mm variable size, larger than petechiae, purple or purplish blue, fading to green, yellow and brown with time. Non-blanchable
spider angioma
central body sometimes raised, surrounded by erythema and radiating legs, most common on the face and chest. Seen in pregnancy and liver disease
spider vein
varying size and shape, bluish color; most common on the legs near veins and anterior chest
cherry angioma
1-3mm, bright or ruby red, may turn purple with age. Common on trunk and extremities
list the primary lesions
macule, patch, papule, nodule, plaque, pustule, vesicle, bulla, wheal
list the secondary lesions
scale, crust, lichenification, scar, fissure, excoriation, erosion, ulcer, atrophy
what are the vascular skin lesion
spider angioma, spider vein, cherry angioma
define epidermis
outermost, avascular layer of the skin composed of 4-5 layers
define dermis
composed of a thin upper layer, the papillary dermis, and a thicker lower layer, the reticular dermis
what is the subcutaneous layer
layer of connective tissue and fat that binds the dermis to underlying tissue
what provides the first line of defense for the body
the skin
what is the hair shaft composed of
dead protein
what are the two types of sweat glands
eccrine glands and apocrine glands
what do the eccrine glands do
regulate body temp through water secretion and evaporation
what controls the eccrine sweat glands
hypothalamus
What do apocrine glands do?
release clear and odorless secretions under cholinergic and hormonal control
Where are apocrine glands found?
places that have hair- scalp, axillary, groin
list the functions of the skin
prevent fluid loss
provide a barrier to invading organisms
relaying sensations
regulate body temp
synthesize vitamin D
excrete sweat, urea, and lactic acid
what are the primary papulosquamous disorders
pityriasis rosea, lichen planus, seborrheic keratosis
what are the secondary papulosquamous disorders
seborrhea, psoriasis
wha do papulosquamous disorders consist of
papules or plaques with scales
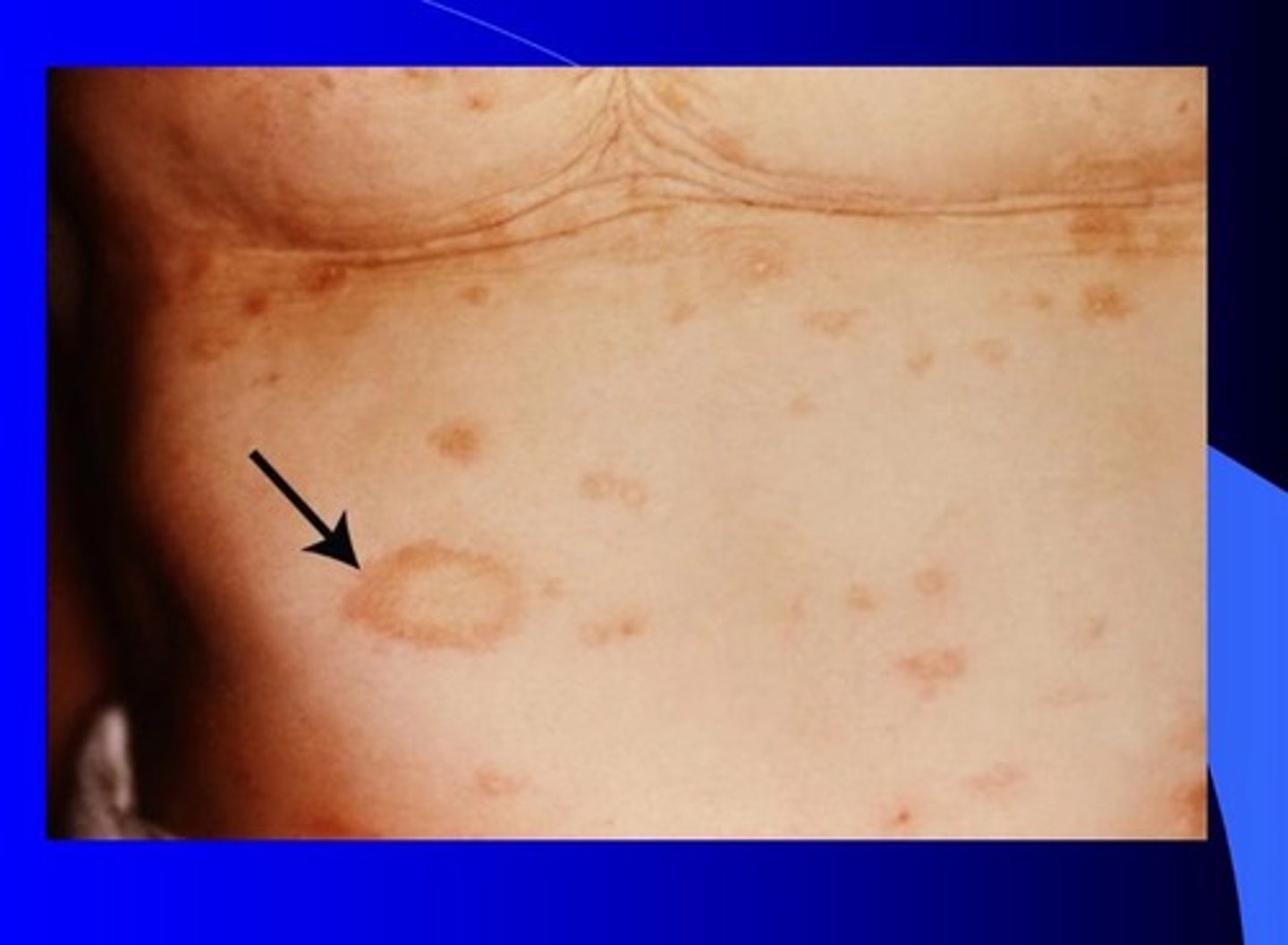
what is the first sign of a pityriasis rosea rash
herald patch (usually on the trunk)
the distribution of pityriasis rosea follows what type of arrangement
christmas tree
what papulosquamous disorder is shown in this picture
Pityriasis rosea (herald patch)
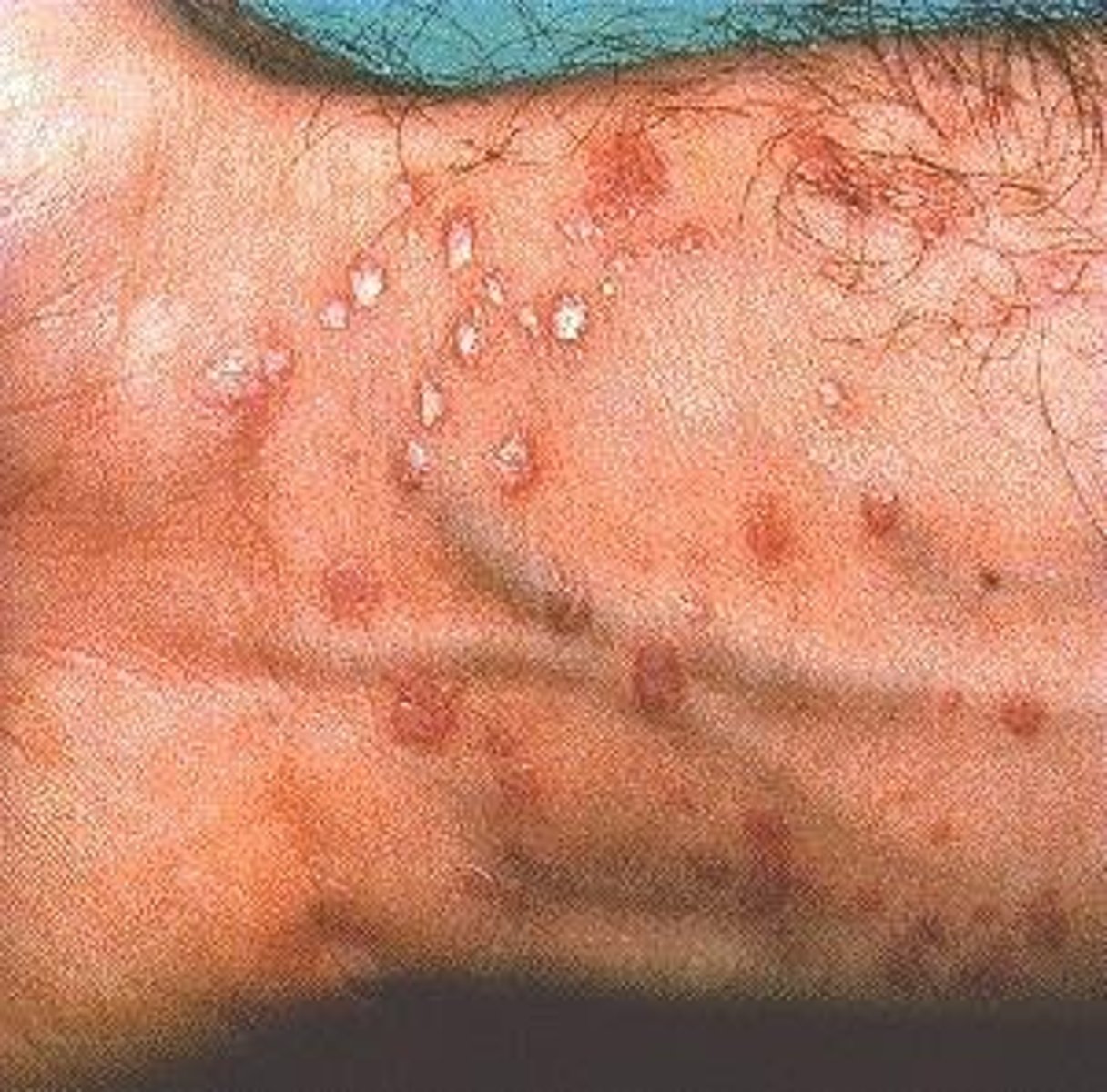
this rash is periodic, lacy, with purple papules or plaques that is common during winter months. It occurs when the immune system attacks the cells of the skin
lichen planus
what rash is shown
lichen planus
what is seborrheic keratosis
an asymptomatic flat, light tan lesion that can become raised with increased pigment and karotic surface
describe psoriasis
plaques present in the epidermis, scales shed easily, common on the knees, elbows, and buttocks
what is seborrheic dematitis
Dry or oily scales common on the head. flakes easily
what is vitiligo
macular, flat. Progressive loss of pigmentation
what is tinea versicolor (pityriasis versicolor)
scaly patches of hyper or hypopigmented skin, accompanied by itching
what is xanthoma
flesh to yellow-colored asymptomatic plaques around eyes/eyelids or extensor surfaces of knees and elbows
xanthoma is indicative of abnormal ____ _____
lipid metabolism
what are café au lait spots
tan to brown asymptomatic macular lesions that vary in appearance and size from increased melanin
what is café au lait spots associated with
developmental and congenital conditions- neurofibromatosis
what is acanthosis nigricans
hyperpigmented area usually in the axillae, neck and groin areas. Macular lesions with velvety texture
what is acanthosis nigricans associated with
insulin resistance (evaluate for diabetes)
what is the most common symptom associated with dermatitis
pruritus
people with atopic dermatitis (eczema) have a hx of ____ or chronic ____
asthma/allergies
describe the presentation of atopic dermatitis
recurrent, itchy rash and erythematous scaly patches and flax
on flexor surfaces of extremities, neck, and face
what labs are elevated in pts with atopic dermatitis
eosinophil or serum IGE
varicose veins results in this
stasis dermatitis
this rash has a red base with satellite pastels when left in contact with feces or urine
diaper dermatitis
this is known as cradle cap
seborrheic dermatitis
list the physical exam findings of seborrheic dermatitis
greasy scales, macules, papules, and patches
list the vesiculobullous disorders
impetigo, herpes simplex, varicella, herpes zoster, erythema multiforme, dyshidrosis
describe the presentation of impetigo
erythematous papules that have honey-colored crust. Highly contagious, caused by staph
describe presentation of herpes simplex
cluster of multiple vesicles - painful erosion of the vesicle with ulcer formation
what is the hallmark of varicella
lesions present and in all stages simultaneously
list the stages of varicella
red papule --> vesicle --> pustule --> ulceration --> crusted lesion
what two disorders are caused by the varicella zoster virus
herpes zoster (shingles)
varicella (chicken pox)
what is the hallmark for shingles
presents along a dermatome and is usually unilateral
herpes zoster
viral disease affecting the peripheral nerves, characterized by painful blisters that spread over the skin following the affected nerves, usually unilateral; also known as shingles
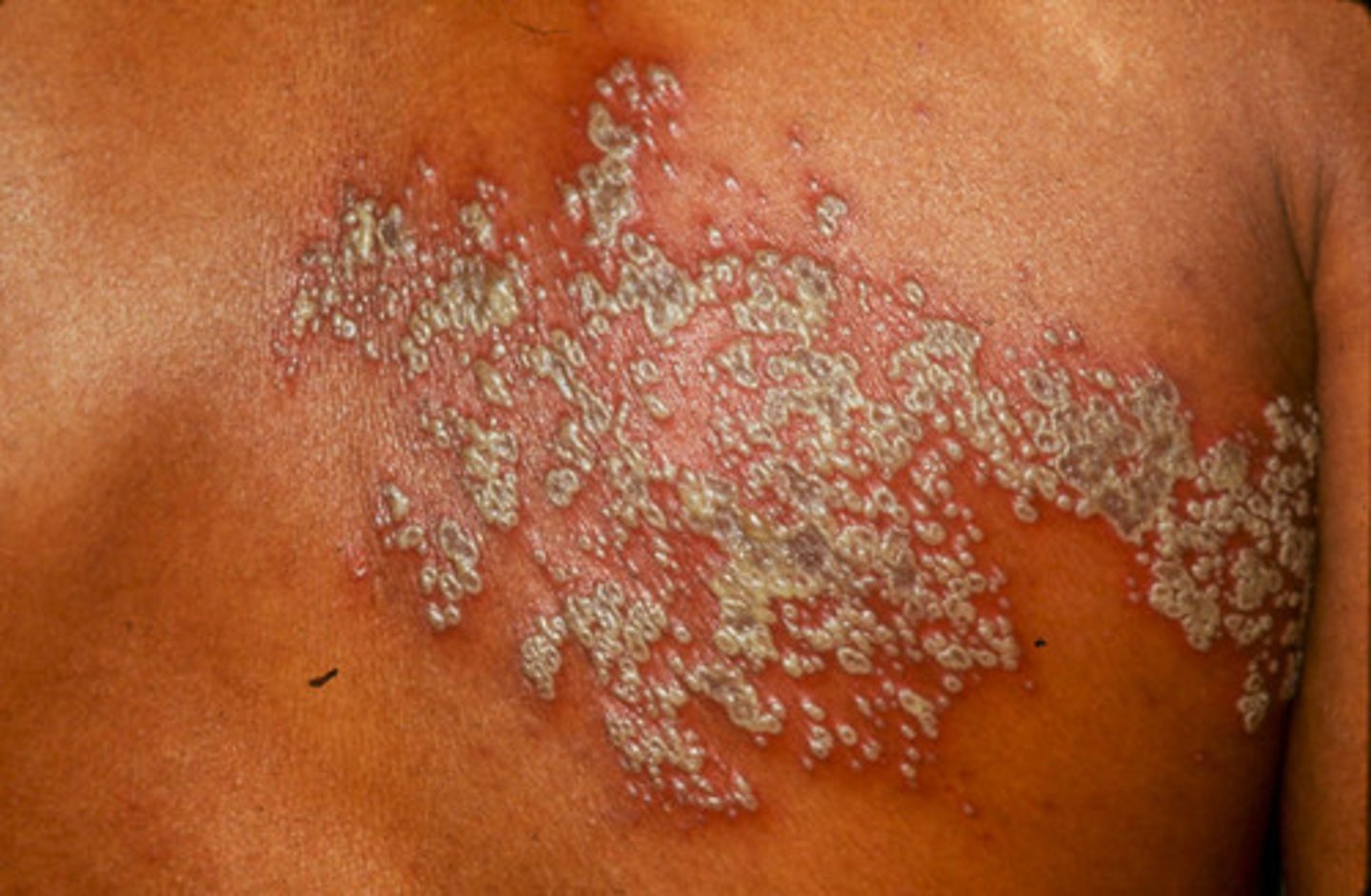
describe the presentation of erythema multiforme minor
flat, reddened macules and/or plaques. Lesions may have a target appearance or the bull's-shaped lesions with 3 zones of color
what can the erythema multiforme minor lesions progress to
vesicles or bulla
what causes erythema multiforme minor
herpes virus
what causes erythema multiforme major
infection like herpes virus or mycoplasma
or response to medicine
what lab changes might you see in a patient with erythema multiforme
decreased WBC and RBC
Increased sed rate, BUN and creatinine
what is dyshidrosis
vesicular disorder that typically affects the hands and feet
what is dyshidrosis associated with
excessive moisture or sweating of the hands/feet
small vesicles that itch and burn which crust over
list the inflammatory disorders
acne vulgaris, rosacea, cellulitis, boil/abscess, folliculitis
what are the 4 components of rosacea
facial flushing, papules or pustules, rhinophyma, dry eyes
how can rosacea be differentiated from acne
no comdeones present
what usually causes boils or abscesses
staphylococcal infections of hair follicles or sebaceous glands
what typically causes cellulitis
staph or strep infections
what is folliculitis
inflammation of hair follicles, typically associated with staph
list the types of hyperplasia disorders
verruca (warts), corns & calluses, molluscum, skin tag, epidermal inclusion cyst
what is the difference between a corn and a callus
callus is thick skin with indistinct borders, painless
corn has distinct borders and is painful
true/false: molluscum is contagious
true
describe molluscum
white or flesh-colored firm dome-shaped papule with a small dimple center
describe epidermal inclusion cysts
lesions with a cheesy discharge and a foul odor
nodular and firm
subcutaneous lesions and tender
what is tinea pedis
fungal infection on the soles of the feet and webs of the toes. scaly rash with maceration