A&P Exam 3 Review Questions
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Georgia southern university, A&P 1 Exam 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the role of creatine phosphate in muscle energy metabolism?
Creatine phosphate is used in muscle contractions as a form of ATP or energy. It allows for a sudden burst of energy (around 10 to 15 seconds) in the muscle contraction when oxygen cannot be sufficiently delivered to the muscle during strenuous exercise.
Where is the trigger zone located in a neuron?
The axon hillock (located at the connection of the cell membrane and axon terminal) senses the electrochemical signals and creates an action potential(a plan of action). The action potential is then carried down the axon and to the dendrites which then passes through the synapse to another neuron.
-when a neuron receives a signal, the sodium channels at the axon hillock open
What happens when ATP breaks down?
Atp breakdown is causes by the addition of H20. H20 will break off a phosphate group within ATP, creatine ADP+Phosphate. During the breakdown, also known as catabolism, energy is released into the cell and used to perform a specific function.
Describe the structure and function of a neuromuscular junction.
The neuromuscular junction is where a neuron meets a muscle. The neuron attaches to a muscle through synaptic boutons on an end plate. The synaptic boutons release sodium into the synaptic cleft and then travel into the acetylcholine receptor on the junction folds. The action potential is then released and the muscle is contracted.
What is the difference between fast and slow twitch muscle fibers?
-Fast twitch muscles contract quicker and with greater force. They rely on anaerobic metabolism without oxygen so creatine phosphate and glycogen are used to create ATP as a quick energy source. Sprinting and weightlifting and leads to quicker fatigue
- Slow twitch muscles contracts slower and generate less force, its more for endurance and long-distance running. It uses aerobic metabolism, with the help of oxygen so ATp is produced over a longer period of time. It has a darker color than fast twitch muscles
What is tetanus in the context of muscle contraction?
Tetanus occurs when the muscle twitches tend to blend together. This is because the wave frequency is so high that there is little to no relaxation phase and causes continuous contractions.
-wave summation: twitches can tend to overlap, if another twitch begins building before the left is contracted it may cause a larger/stronger twitch.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum and what is its role in muscle contraction?
The SR is what houses calcium ions before they are used in muscle contractions. When the neurons trigger the SR to release the calcium through the axon hillock it travels and binds with troponin+tropomyosin at the cross bridge. After the muscle contraction has occurred and the action potential has played out, the Sarcoplasmic reticulum recollects the calcium for storage, leading to muscle relaxation.
What is the all-or-none law in relation to muscle fiber contraction?
The All or none law states that once a stimulus passes a certain threshold, it will fully contract. It does not matter if it barely passed the threshold or greatly exceeded, both situation will contract to the full extent. If a stimulus did not meet the threshold the muscle will not contract at all. However strength of the muscle contraction vary in severity because the number of motor units that pass the threshold will vary.
What type of muscle cells exhibit autorhythmicity?
Autorhythmicity is the heart's ability to control its own contractions. This is possible due to the presence of pacemaker cells that can fire action potentials on their own. They are self-excitable and able to depolarize the threshold. They also respond to signals from the autonomic nervous system from the connected jap junctions surrounding muscle fibers.
What is the role of microglia in the nervous system?
Microglia help protect the nervous system from infection by using phagocytosis (bacteria eating). Microglia eat diseased or damaged cells in healthy tissue. They also release signaling molecules to help regulate inflammation. They also remove unnecessary or weak synapses that are no longer needed, helping to maintain the most important neural networks.
Where are voltage-gated Ca++ channels found in a neuron?
The Calcium channels are located on the axon terminal in a neuron. The axon terminal is located at the end of the axon and is where the neurotransmitters release. When these channels open, calcium is allowed to enter and jump over the synaptic gab onto the next neuron, helping to transmit signals across neurons and to their goal destination.
What is the consequence of insufficient acetylcholine in a synapse?
Without enough acetylcholine there can be a disruption of communication between neurons, meaning it wouldn't reach the target muscle and subsequent contraction would not occur. The axon terminal releases acetylcholine as a chemical messenger to bind at the end plate connecting to a muscle, triggering depolarization. If there is not enough of this it would cause weak or ineffective muscle contractions. It can also cause complication in the neurons leading to alzhiemers and autonomic symptoms (heart rate, digestion, gland secretion)
Explain the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction.
It states that muscles slide when contracting or relaxing. When a skeletal muscle fiber contracts, thin filaments are pulled and slide past thick filaments. This only occurs when binding sites are exposed during calcium entry into the sarcoplasm.
What is the function of dense bodies in smooth muscle cells?
The thin filaments of smooth muscle fibers and anchored by dense bodies fastened to the sarcolemma (membrane). These are present on the Z bodies in a crossing diagonal lines and help maintain structure during muscle contractions. This also allows for longer, more sustained muscle contractions.
Which protein in a muscle cell binds with ATP?
ATP on the myosin binds with the myosin head in the actin. When the sliding filament theory occurs it causes the ATP to turn into ADP+Phosphate and the myosin head to pivot, causing a contraction. Once relaxed ATP is replaced and the cycle continues.
What is muscle hypertrophy?
Hypertrophy mean there is an excess amount of something, in this case that would be an increase of muscle size. This is causes by an enlargement of muscle fibers due to a higher intensity of physical training. Small tears appear in the muscles. The body them repairs and strengthens these muscles using satellite cells (specialized muscle stem cells) that fuse to the damaged cells and reinforces the structure.
-increasing myofibrils and volume of fluid
What is the primary reason muscles generate a lot of heat?
The conversion energy from atp during a muscle contraction causes a lot of heat to generate. Sustained muscle movement causes body temperature to rise. Also involving homeostasis when the body shivers, these are very small muscle contractions that produce friction causing heat.
Describe saltatory conduction.
Saltatory conduction involves the process of electrochemical signals traveling through a neuron. In saltatory conduction, the signal jumps from the nodes of ranvier (rings around the axon) for a faster transmission.
-continuous conduction is where the signal does not leap but rather travels through the entire neuron and onto the next instead of jumping.
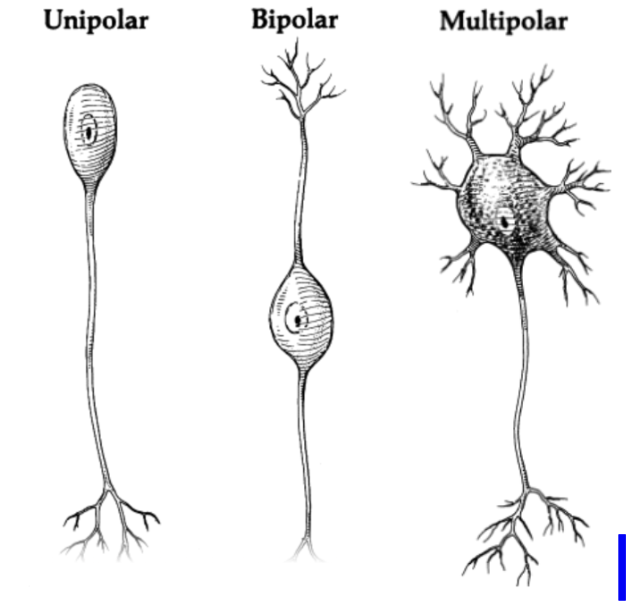
What is a unipolar neuron?
A unipolar neuron is where there is a single process from the cell body
Bipolar neuron: single dendrite and axon
Multipolar neuron: several dendrites and one axon
What is an IPSP and how does it affect a neuron?
Inhibitory post synaptic potential is where there is a hyperpolarization (too many negative charges enter the neuron) and makes the action potential less likely to occur and may stop the neuron from sending a signal to the other cells.
Which connective tissue layer covers the entire muscle?
The epimysium (dense, irregular connective tissue), it provides structural support and protection around the entire muscle, keeping the muscle fibers bundled together. The muscle is able to contract and move powerfully while also maintaining its shape and form.
-also separates muscle from tissue and other organs in the area, allowing for independent movement
What causes depolarization to end in a neuron?
Depolarization in a neuron ends with the closing and sodium channels (+) and the opening of potassium channels(+). When the potassium channels open the ions flow out of the neutron, making the action potential less positive with both + ions removed.
What is the role of astrocytes in the nervous system?
Astrocytes play a major role in the nervous system as they are the supporting cells for neurons. Hey help with the ion regulation, uptake/breakdown of neurotransmitters and help with the formation of the blood brain barrier (protects brain from harmful substances)
What are myofibrils?
Myofibrils are found inside muscle fibers and are composed of repeated sarcomeres. It contains the proteins myosin and actin for muscle contraction and part of the muscle sliding theory.
Where is the acetylcholine receptor found in a skeletal muscle cell?
It is found on the motor end plate where a neuron is connected to a muscle fiber (neuromuscular junction).
What type of channels are found at the axon hillock?
There are positive sodium and potassium channels that allow the neuron to send signals down the axon. These channels help with both polarization and depolarization when the threshold is reached. This is why the axon hillock is refers to as the trigger zone for action potentials.
Explain the function of the sodium-potassium pump.
The sodium potassium pump is used for transporting sodium (na+) out of the cell while also moving potassium (k+) into the cell. This is found in the membrane of the cell (neuron). They maintain an electrical gradient both in and outside the cell to maintaining the levels. This process uses a lot of ATP(energy).
What are the boundaries of one sarcomere?
The sarcomere is confined to the Z line at the end of each acetoin.
Describe the process of excitation-contraction coupling.
Excitation and contraction is where the muscle is stimulated and then contracts. Excitation is the electrical signal from the motor neuron (for a skeletal muscle to contract it must first be exited). The muscle must be stimulated to fire the action potential triggered by the nervous system. When calcium is releases and signals the Z bands begin sliding the muscle contracts.
What happens when ligand-gated Na+ channels open in a neuron?
When the neurotransmitter(ligand) binds to a protein, the channels open. When sodium channels open is a neuron it allows for sodium to flow into the cell as potassium flows out. This makes the neuron more positively charged and the neuron is more likely to reach the threshold.
Which glial cell forms the myelin sheath in the central nervous system?
An oligodendrocyte (oligo), a type of glial cell, forms the myelin sheath that wraps around the axon and can be used for signals to jump across.
-schwann cells for the myelin sheath in the PNS
What is the cell membrane of a muscle cell called?
The cell membrane of the muscle is called the sarcolemma
What is the difference between nuclei and ganglia in the nervous system?
-nuclei: collection of neuron cell bodies for central nervous system
-ganglia: collection of neuron cell bodies for peripheral nervous system
Name the two regulatory proteins in a sarcomere.
-Troponin: binds to calcium ions during muscle contraction, causes a shift of the tropomyosin
-Tropomyosin: blocks myosin binding sites
Both found together in the actin
What is the main function of a dendrite?
A dendrite is used for the transportation of signals through the neurons. It receives the signals from other neurons and conveys the information with the soma (cell body) to then travel down the axon and onto the next neuron.
What structure is the T Tubule an extension of? (transverse Rubule)
It is an extension of the sarcolemma (cell membrane of muscle cell) and extend into the center of cardiac and skeletal muscle. They are found at the Z disks in cardiac muscle and transmit electrical signals from cell membrane into the cell.
What is the resting membrane potential of a muscle cell?
Around -70mV and is the steady state of the cell
Differentiate between the optic nerve and optic tract in terms of their location
-optic nerve: between the eye and the optic chiasm (carries information from retina to optic chiasm)
-optic tract: between optic chiasm and the brain (end of peripheral vision)
Which protein binds with calcium in a muscle cell?
Calcium binds with troponin (specifically troponin C) when they are released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
What is the role of calcium in muscle contraction?
When calcium binds to troponin C it causes a change in shape, moving the tropomyosin away from the binding sites. The myosin heads then attach to the open binding sites attached to actin. That then leads to the muscle contraction.
Define isometric contraction.
It is a type of skeletal muscle contraction. The muscle produces tension without changing the angle of a skeletal joint. The sarcomere shortens and increases muscle tension but doesn't move. (example: if you try to pick up a hand weight that is too heavy to move and you flex your muscle but don't pick it up)
-isotonic contraction: the skeletal muscle tension stays constant
What is the difference between myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers in terms of signal conduction?
The primary difference is the speed and efficient of the signal
-Myelinated: fibers wrap around (myelin sheath) and the electrical impulse can jump from the gaps between them (nodes of ranvier) for a faster signal transmission
-Unmyelinated: the signal travels down the axon as there is no myelin sheath (continuous depolarization)
Describe the sequence of events in muscle contraction.
Motor neuron send signal/action potential to the neuromuscular junction where it releases acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the sarcolemma (cell membrane) and sodium ions enter the muscle cell. This causes depolarization
The action potential triggers calcium ions to be released into the sarcoplasm
Calcium binds to troponin and pushes away the tropomyosin from the myosin binding sites in the actin
This allows for the myosin head to attach to the actin (cross bridges form as they are connected)
The myosin heads pivot and pull the actin towards the center with the myosin (sliding filament theory). This uses energy in the form of ATP and breaks down into ADP and phosphate
The myosin then detaches from the actin when contraction is over and a new ATP molecule is replaced, resetting the contraction
During a bicep curl, what role does the triceps play?
The triceps act as the antagonist muscle, (the biceps are the agonist). While the biceps contract, the triceps lengthen to allow the movement
What is a local potential and how does it differ from an action potential?
-local potential (graded potential): depends on the strength of the stimulus, and potentials can also be combined together
-action potential: all-or-none, involves reaching the threshold or not to see contraction in the specific muscle fiber (all have the same effect once it reaches threshold)
Where does aerobic respiration occur in a muscle cell?
The mitochondria, for sustained energy in slow-twitch muscle fibers that rely on a steady supply of ATP (endurance work)
Which muscle fiber type is best for endurance?
Slow twitch fibers because of their reliance on ATP and allows for prolonged use with a steady supply of oxygen
- fast-twitch can only be used for 10-15 seconds because it doesn't have oxygen and they must generate ATP (anaerobic respiration)
Describe the structure and function of the sarcolemma.
Sarcolemma is the outer layer (membrane) of a muscle fiber. It has a phospholipid bilayer with ion channels and pumps, receptors, and proteins. It also have T-Tubules which transport action potential deep into the cell for contraction.
What ions move during depolarization of a neuron?
Sodium Ions move into the neuron through sodium channels during depolarization(electrochemical gradient), adding a positive charge to help reach the threshold (-70mV resting rate closer to +). Potassium channels will them open to repolarize the cell.
Explain the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction.
When Calcium is entered into the Z-bands and connected to troponin, the tropomyosin changes shape and is forced to move out of the way, leaving the myosin channels open for connection. One connected, bridges are formed between myosin and actin. The myosin turns around and moves inward taking the actin with it, contracting the muscle.