Ch. 1 - Intro to Statistics
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Population
the entire group of objects in our study
Sample
part of a population
Measurements on populations are called…
parameters
Measurements on samples are called…
statistics
Unit / experimental unit
what we are collecting data on (a singular person, event, thing, etc.)
Variable
a property of a unit we wish to measure
(can be classified as qualitative or quantitative)
Qualitative variable
classifies units into categories; can be observed, not measured numerically
ex. eye color
Quantitative variable
numerical values or counts; can be put into math operations
ex. height and weight
A quantitative variable is discrete when…
it involves limited or exclusively whole numbers
A quantitative variable is continuous when…
it can take on any value in an interval, including decimals
According to the Campus Housing Fact Sheet at a Big-Ten University, 60% of the students living in campus housing are in-state residents. In a sample of 200 students living in campus housing, 56.5% were found to be in-state residents.
In this situation, the value of 60% is a…
A. parameter
B. statistic
parameter
According to the Campus Housing Fact Sheet at a Big-Ten University, 60% of the students living in campus housing are in-state residents. In a sample of 200 students living in campus housing, 56.5% were found to be in-state residents.
In this situation, the value of 56.5% is a…
A. parameter
B. statistic
statistic
A census asks every household in a city how many children under the age of 18 reside there.
Parameter or statistic?
Qualitative, discrete (quantitative), or continuous (quantitative)?
Parameter
Quantitative (continuous)
A runner records the distance he runs each day.
Qualitative, discrete (quantitative), or continuous (quantitative)?
Quantitative (continuous)
A census asks residents for the highest level of education they have obtained: less than high school, high school, 2-year degree, 4-year degree, master’s degree, doctoral/professional degree.
Qualitative, discrete (quantitative), or continuous (quantitative)?
Quantitative (discrete)
Which method of data collection would you use to collect data for this study: the effect of changing flight patterns on the number of airplane accidents.
A. observational study
B. perform an experiment
C. use a simulation
D. administer a survey
use a simulation
Which method of data collection would you use to collect data for this study: the effect of eating oatmeal on lowering blood pressure.
A. observational study
B. perform an experiment
C. use a simulation
D. administer a survey
perform an experiment
Which method of data collection would you use to collect data for this study: how fourth graders solve a puzzle.
A. observational study
B. perform an experiment
C. use a simulation
D. administer a survey
observational study
Which method of data collection would you use to collect data for this study: U.S. residents’ approval rating of the U.S. president.
A. observational study
B. perform an experiment
C. use a simulation
D. administer a survey
administer a survey
Census
a count or measure of an entire population
often expensive and difficult to perform
Sampling
a count or measure of part of a population
most commonly used in statistics
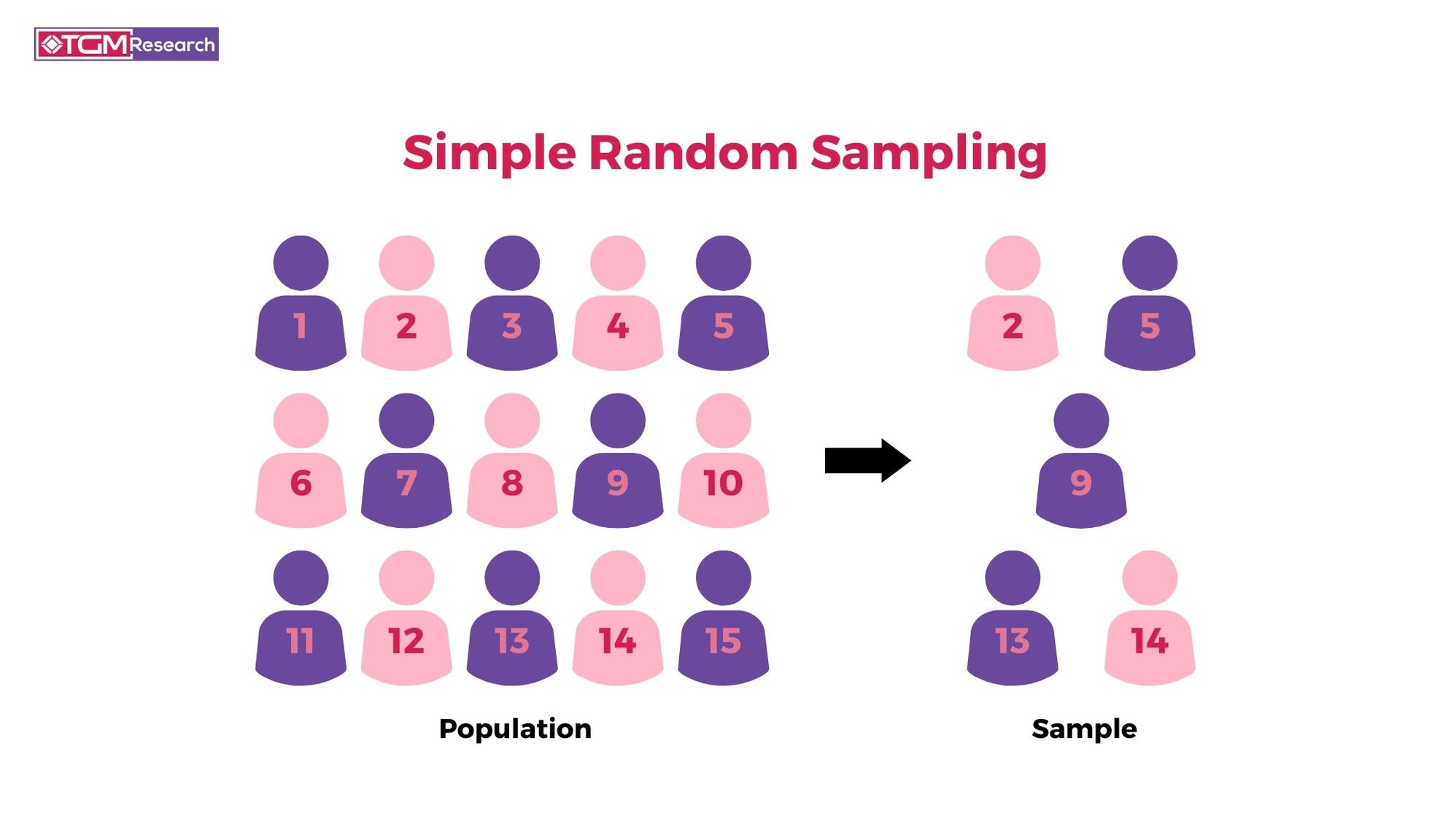
Simple random sample
every sample (of the same size) is equally likely to be picked
most common
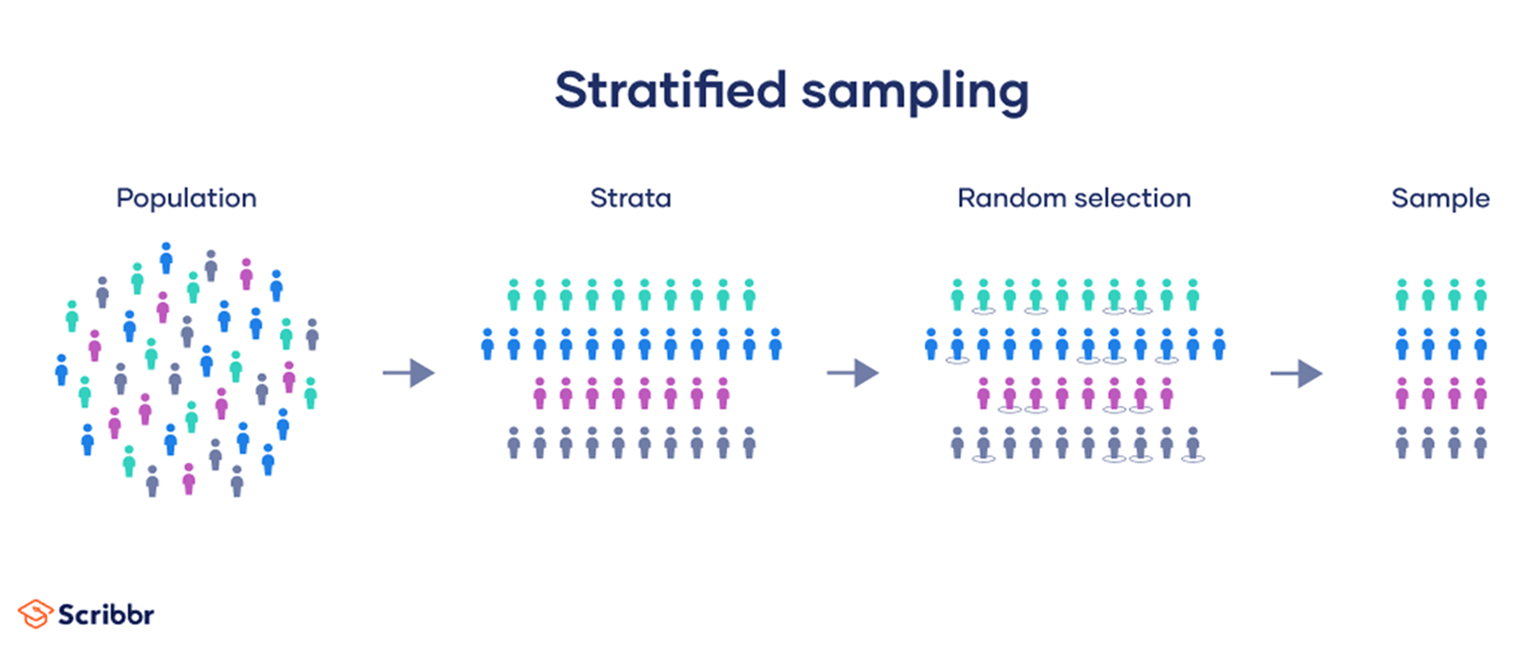
Stratified sample
members of the population are divided into 2+ groups (strata) that share a common characteristic, and then an equal number of samples is randomly selected from each group
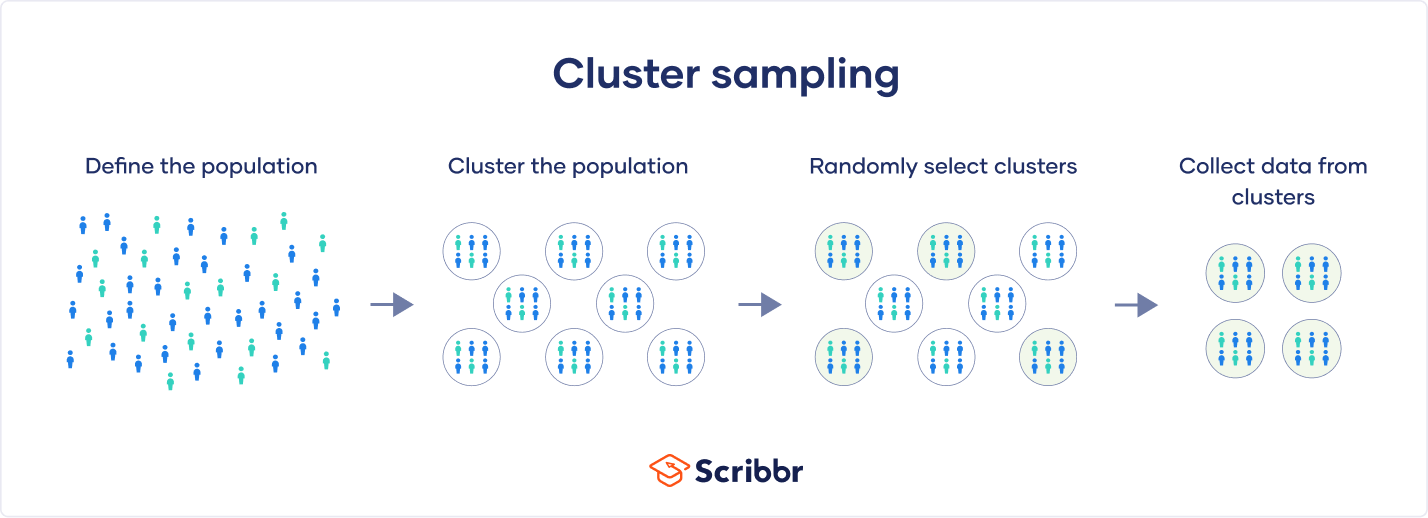
Cluster sample
divide the population into 2+ groups (clusters), select one or more, and sample everyone in the chosen group
occurs when the population is already divided into naturally occurring subgroups
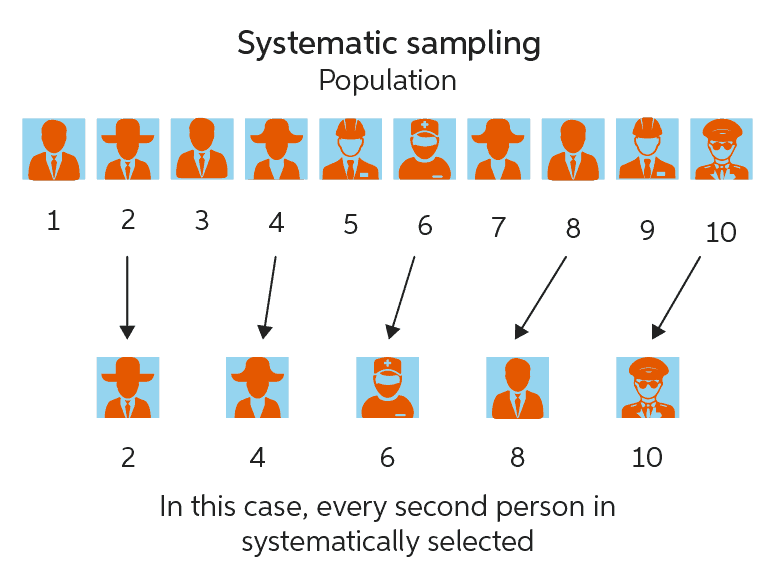
Systematic sample
every member of the population is assigned a number, and samples are pulled at intervals from the starting number
Identify the sampling technique.
Every tenth person entering a mall is asked to name his or her favorite basketball player.
A. simple random
B. stratified
C. cluster
D. systematic
systematic
Identify the sampling technique.
Using random digit dialing, researchers call 1400 people and ask what obstacles (such as childcare) keep them from exercising.
A. simple random
B. stratified
C. cluster
D. systematic
simple random
Identify the sampling technique.
After a hurricane, a disaster area is divided into 200 equal grids. Thirty of the grids are randomly selected, and every occupied household in the grid is interviewed to help focus relief efforts on what residents require the most.
A. simple random
B. stratified
C. cluster
D. systematic
cluster
Identify the sampling technique.
Chosen at random, 500 rural and 500 urban persons age 65 or older are asked about their health and their experience with prescription drugs.
A. simple random
B. stratified
C. cluster
D. systematic
stratified
Bias
the systematic favoring of certain outcomes
Sampling / systematic bias
systematic favoring of certain outcomes due to the methods employed to obtain the sample
Non-response bias
a type of systematic (sampling) bias where certain outcomes are favored when the individuals who choose to participate in a study differ from the individuals who choose to not participate
Response bias
a type of systematic (sampling) bias where certain outcomes are favored when participants do not respond truthfully (possibly to align with social norms or to appease the researcher)
Classify as response bias or non-response bias.
Retail Store Hours: A retail store was considering expanding their operating hours. To determine if this was a need perceived by their customers, they conducted a survey over the telephone to obtain data. Research assistants called the phone numbers of customers who were randomly selected to participate between the hours of 9AM and 4PM. Individuals who were at work were less likely to answer their phone call or agree to participate in the study than individuals who were at home at that time.
Non-response bias
Classify as response bias or non-response bias.
Using an anonymous online survey, a professor asks his students: have you cheated on an exam in my class? Many of the students who have cheated still answered no.
Response bias