economics theme 3
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Aggregate demand
Total demand for goods and services produced in the economy over a period of time
Equation for aggregate demand
AD = C + I + G + [X-M]
AD curves
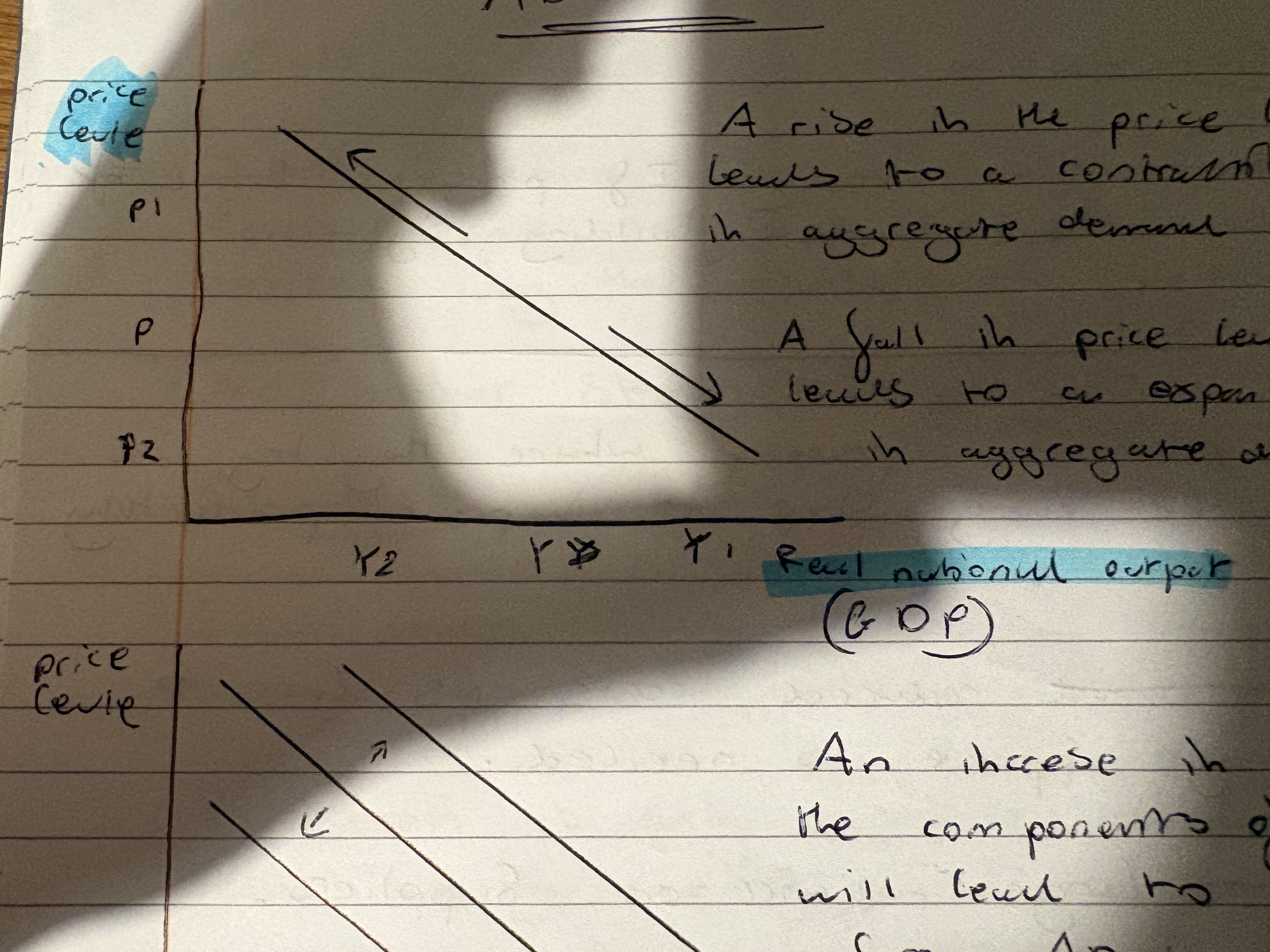
what can cause the aggregate demand curve to shift
A rise or decrease in any of the components.
When demand is perfectly elastic or supply is perfectly elastic who does the incidence fall on ?
On the consumer
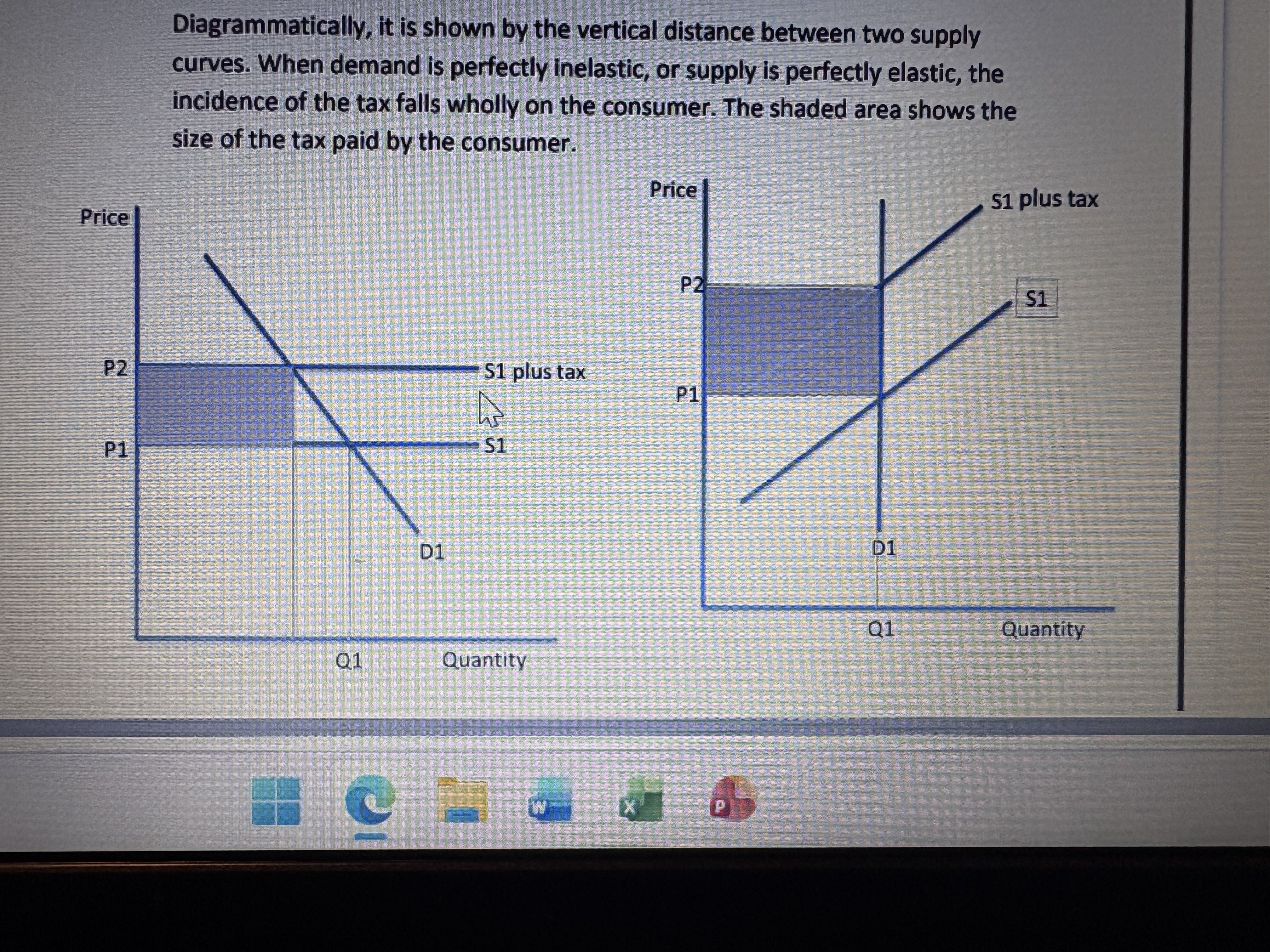
If the demand curve is more elastic the incidence falls on ?
Mainly on the supplier. But some on the consumer
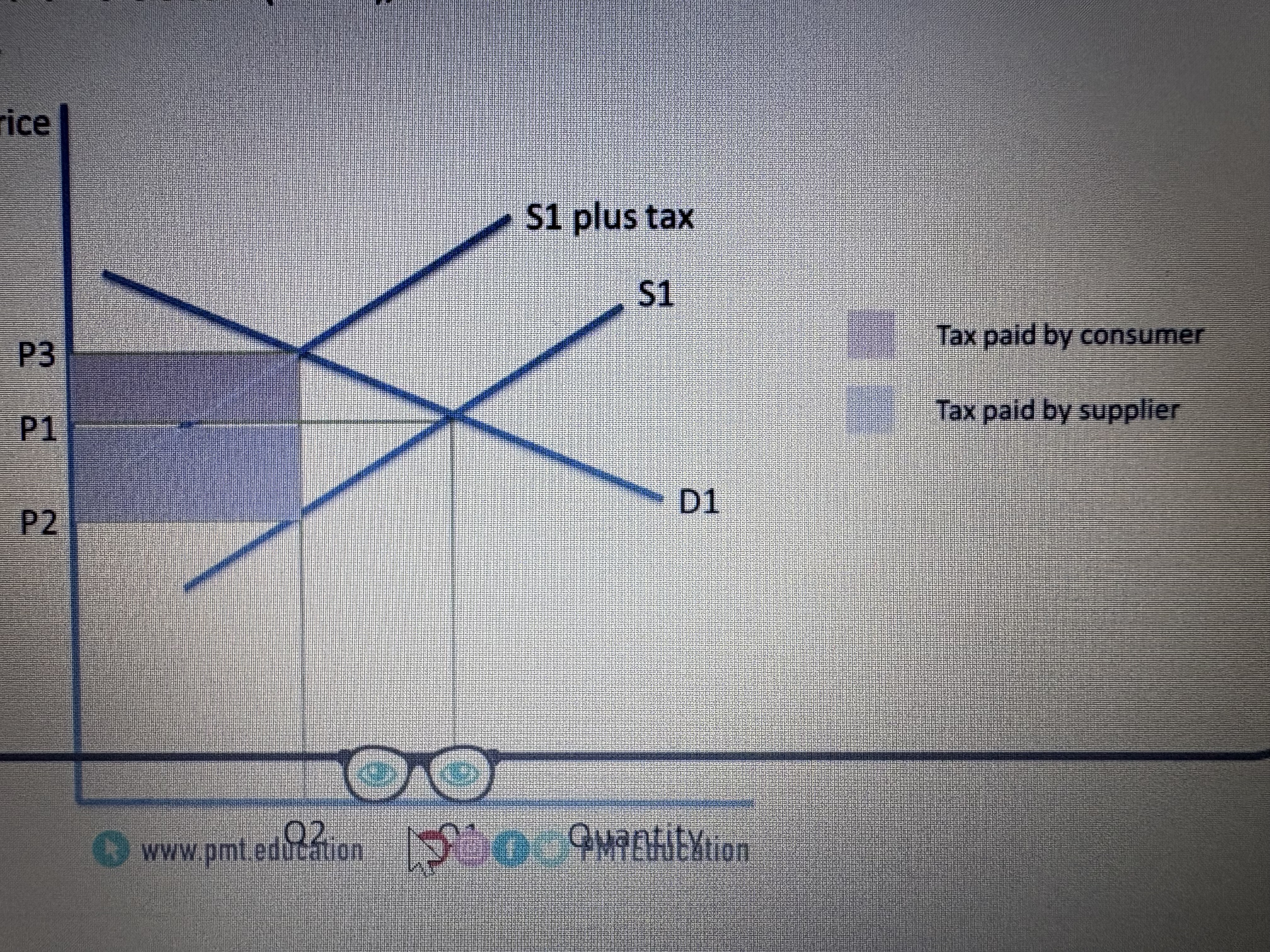
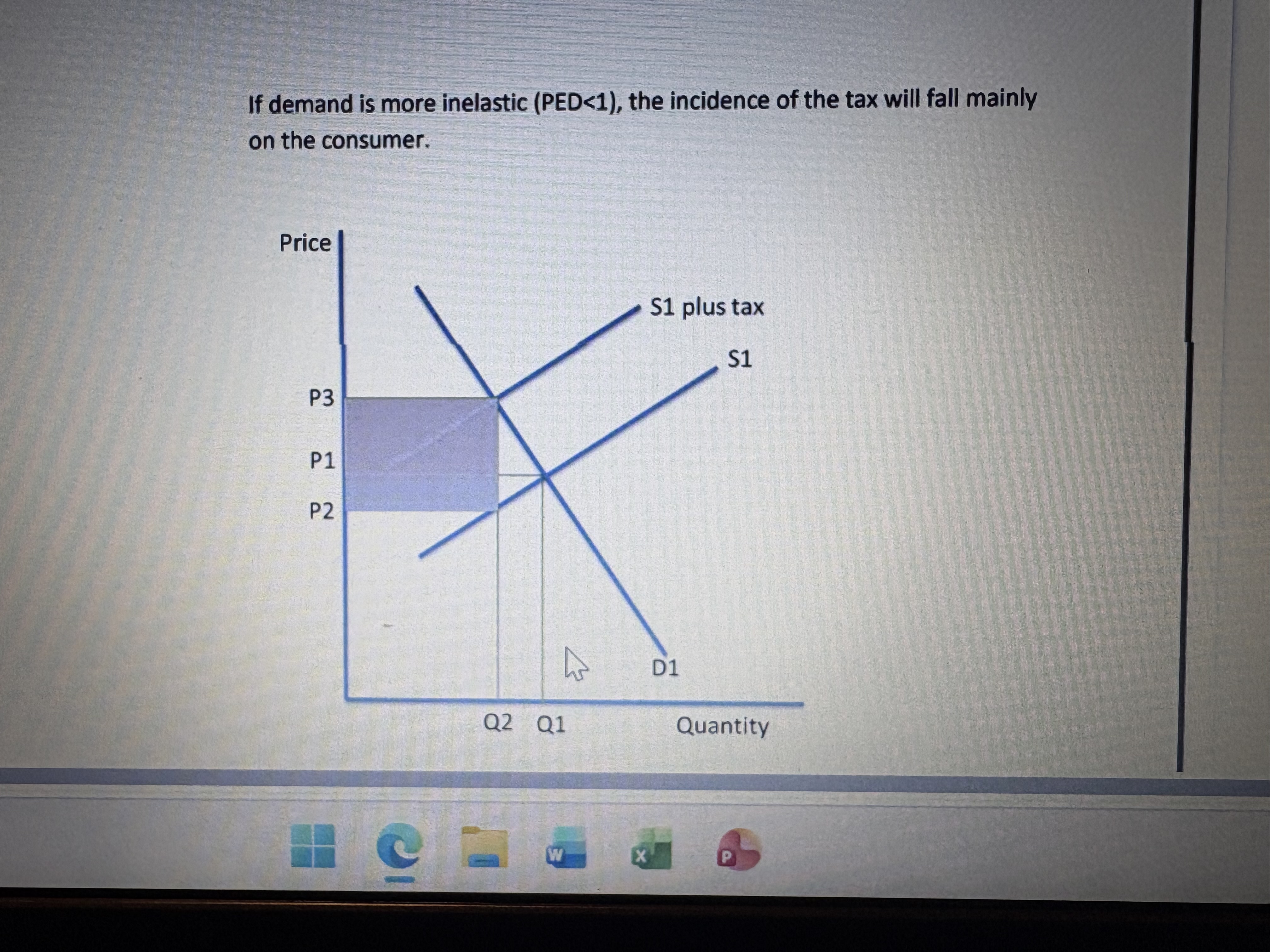
If demand is more inelastic the incidence will fall mainly on the ?
Consumer. But also some on the supplier
Effects of increasing interest rates on firms
More expensive to take out a loan = less spending and investment. Encourages saving as reward is higher = more retained profits.
Effects of a depreciation of the pound for firms
Exports become more price competitive. Unless goods are inelastic. Imports become more expensive= less profit.
Affects of raising unemployment for firms
Larger supply of labour to employ from. Less disposable income for consumers= less sales
Impacts of variable inflation on firms
Saving more attractive than borrowing. Less investment. Increased costs. Less confidence.
Market mapping
A map identifies which existing products meet customer needs. Gaps can then be identified to allow the firm to enter the meat
Competitive advantage of a product
A firm has a competitive advantage over another when its product is deemed better by the consumers. Can be done by price, quality or through USP.
Competitive advantage of a service
Strong brand reputation or exceptional customer service
Product differentiation
Firms differentiate their products to make it seem more favourable than a competitor. They do this by adding unique features (design). Or being convenient to the consumer. This all adds value
Methods of adding value
brand
Quality
Good service
USP
Convenience
What is added value
Additional value a firm creates during the production process. The more added value the more profitable the firm is
How firms decide on price and level of output
Using supply and demand. Profit maximising company’s total cost and total revinue are at its widest.
Stable market
Where trade can be conducted in large volumes without causing the price to change significantly.
a dynamic market
A dynamic market is one which changes constantly and rapidly. E.g technology markets like mobile phones.
Purpose of government intervention
They intervene to correct failure. For example they might provide healthcare and education
Methods of government intervention
government introduce laws to ban consumers from consuming a good. Or make it illegal to not do something
Could introduce stricter punishment for breaking rules
Indirect taxation
Indirect taxes are on expenditures. Increase costs for producers. Leads to increase market price. Could use to discourage the consumption of a good.
Ad valorem
Taxes are percentages such as VAT. Inelastic goods means incidence falls on consumers. Used to discourage the consumption of a god like cigarettes or alcohol.
Specific taxes
Are a set tax per unit. The more inelastic the demand the higher the tax burden is on the consumers. Indirect could reduce the quantity of demerit goods consumed.
what is a subsidy
A subsidy is a payment from the government to a producer to lower their costs of production.
What do subsidy’s do
Encourage the consumption of merit goods as they encourage the producer to produce more of the good. E.G recycling schemes
What does a shift in the supply curve mean
If it shifts to the left the more of the merit good is produced the price falls. Difference between the two supply lines shows the subsidy given per unit
Who benefits from subsidies depending on price elasticity
Consumers gain more from the subsidy on inelastic goods. Producers supply more when demand is price elastic
Distortion of price signals due to government intervention
If price is distorted could lead to government failure as inefficient allocation of reasorses. For example if they subsidise which is failing
Government intervention leading to unintended consequences
A policy could be undermined which could make government policies expensive to implement since it’s harder to achieve their original goals
Government failure in various markets advantages
farmer incomes remain stable because fluctuations in the market are reduced as the government buy when they have a surplus of products
Government failure in various markets disadvantage (farmers)
governments might not have the financial resources to buy up the stock. Could lead to farmers overproducing which is expensive and damaging to the environment
Government failure in various markets disadvantage ( housing)
due to the wealth affect there is a ride in consumer spending leading to a shift right in the demand curve. House prices increase
What is contribution + equation
It is the profit made on each product.
Selling price - variable costs. Per unit
What is total contribution equation
contribution per unit X number of units sold
Margin of safety
Is the difference between the actual level of output and the break even level of output.
The assumptions made of break even analysis are ?
the selling price per unit is constant and does not change with quantity produced
The variable costs of the unit is the same
Fixed costs do not change with output
Everything produced is sold
Why is disposable income
Amount of income consumers have left over after taxes and social security charges have been removed
Influences on consumer spending in changing interest rates
A decreasing interest rates it makes borrowing cheaper. Increase disposable income
Capital investment
This accounts for around 20-30% of GDP in the UK per annum
The rate of economic growth
If growth is high firms will be making more revenue due to higher rates of customer spending. More profits available to invest
Influence on investments. Demand for exports
The higher the demand for exports the more it is that a firm will invest. This is as they expect higher sales
Government spending to cause economic growth
During recessions the government might increase spending to try and stimulate the economy. E.g increase welfare payments or cutting taxes
Fiscal policy
Changing of government spending and taxation. It’s a demand side policy works by influencing the level of AD.
Expansionary fiscal policy
Used during periods of economic decline. Involves increasing spending to boost AD
Contractionary fiscal policy
Decreasing expenditure on purchases. Tax rates may increase. Reduces the size of the government budget deficit
Consumers during economic growth
When consumers have higher incomes they can afford to consume more.
effects of exchange rates
A depreciation of the pound means imports are more expensive and exports are cheaper. It depends what currency the pound deprecated to more significant inpact if it is a trade partners currency