Finals - Nanoparticles
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Nanoparticle
These refer to a particle of matter with a diameter of 1 to 100 nanometers (nm).
Ultrafine particles
Nanoparticles are also known as __________.
1 - 100 nm
A nanoparticle is a particle of matter with a diameter of ____ to ____ nanometers (nm).
FALSE
Nanoparticles are undetectable by the human eye.
TRUE or FALSE. Nanoparticles are detectable by the human eye.
FALSE
Nanoparticles can exhibit significantly different physical and chemical properties to their larger material counterparts.
TRUE or FALSE. Nanoparticles cannot exhibit significantly different physical and chemical properties to their larger material counterparts.
FALSE
Nanoparticles are particles that have a tiny size and a colossal surface area.
TRUE or FALSE. Nanoparticles are particles that have a tiny size and a small surface area.
FALSE
The periodic boundary conditions of the crystalline particle are destroyed when the size of a particle approaches the nano-scale with the characteristic length scale close to or smaller than the de Broglie wavelength or the wavelength of light.
TRUE or FALSE. The periodic boundary conditions of the crystalline particle are destroyed when the size of a particle deviates the nano-scale with the characteristic length scale close to or smaller than the de Broglie wavelength or the wavelength of light.
de Broglie wavelength
The periodic boundary conditions of the crystalline particle are destroyed when the size of a particle approaches the nano-scale with the characteristic length scale close to or smaller than the ________________ or the wavelength of light.
Wavelength of light
de Broglie wavelength is also known as the ______________.
Silver nanoparticles
Spherical gold nanoparticles
Quantum dots
Titania nanoparticles
Cellulose nanoparticles
Upconverting nanoparticles
Graphene & carbon nanotubes
Gold nanorods
Enumerate some common examples of Nanoparticles (8)
Silver nanoparticles
This is a a form of metallic colloidal nanoparticle with diameters ranging from 1 to 100 nm. They are part of the emerging nanotechnology that have gained increasing interest in the field of nanomedicine because of their particular properties and therapeutic potential in treating a large variety of diseases.
Silver nanoparticles
These nanoparticles combine strong plasmonic optical properties with antimicrobial capabilities.
d. Magnetic properties
Which is not a unique physical and chemical property of a silver nanoparticle?
a. optical
b. high electrical conductivity
c. high thermal conductivity
d. magnetic properties
Spherical gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)
These nanoparticles are monodispersed colloidal particles composed of elemental gold with a spherical morphology.
Spherical gold nanoparticles (AuNPs)
These nanoparticles exhibit unique size- and shape-dependent physicochemical properties, most notably surface plasmon resonance (SPR), which results in strong absorption and scattering of light in the visible to near-infrared spectrum.
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR)
These nanoparticles exhibit unique size- and shape-dependent physicochemical properties, most notably _____________, which results in strong absorption and scattering of light in the visible to near-infrared spectrum.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. Gold nanoparticles have been utilized for centuries by artists due to the vibrant colors produced by their interaction with visible light.
Quantum dots (QDs)
These nano particles are nanoscale semiconductor crystals typically ranging from 2 to 10 nanometers in diameter, exhibiting size-dependent quantum confinement effects that result in discrete electronic energy levels.
Quantum dots (QDs)
The primary advancement in nanotechnology is the creation of innovative fluorescence probes called ___________.
2 - 10 nanometers
Quantum dots (QDs). are nanoscale semiconductor crystals typically ranging from ____ to ____ nanometers in diameter,
High photostability
brightness
sharp emission peaks
Give some unique optical and electronic properties of quantum dots (3)

read lang
read lang

Titania nanoparticles (TiO₂ nanoparticles)
These are ultrafine particles of titanium dioxide typically less than 100 nanometers in size.
photocatalytic
UV-absorbing
Chemical stability
Give the three (3) exceptional properties of titania nanoparticles
anatase
rutile
brookite
What are the three crystalline phases of titania nanoparticles?
anatase
Among the three crystalline phases of titania nanoparticles, what is the most photoactive form?
Cellulose nanoparticles
These are nanoscale structures derived from natural cellulose.
Natural cellulose
What is the most abundant biopolymer on Earth that are typically extracted from plant fibers?
5 - 100 nm
Cellulose nanoparticles range from _____ to _____ nanometers in width and several hundred nanometers in length.
Cellulose nanoparticles
These nanoparticles possess exceptional mechanical strength, high aspect ratio, biodegradability, low density, and large surface area.
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs)
Cellulose nanofibers (CNFs)
What are the two (2) main forms of cellulose nanoparticles?
Cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs)
This form of cellulose nanoparticles is rod-like and highly crystalline.
Cellulose nanofibers (CNFs)
This form of cellulose nanoparticles is longer, entangled, and partially crystalline.
Upconverting nanoparticles (UCNPs)
These nanoparticles are a class of luminescent nanomaterials, typically composed of a crystalline host matrix (commonly NaYF₄) doped with rare earth ions such as ytterbium (Yb³⁺), erbium (Er³⁺), thulium (Tm³⁺), or holmium (Ho³⁺).
Luminescent nanomaterials
Upconverting nanoparticles (UCNPs) are a class of _____________.
Photon upconversion
Upconverting nanoparticles exhibit a unique optical phenomenon known as ___________, in which they absorb two or more low-energy near infrared (NIR) photons and emit a single higher energy photon in the visible or ultraviolet range.
Graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs)
These nanoparticles are carbon-based nanomaterials that share a common structural foundation of sp²-hybridized carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice.
Hexagonal lattice
What is the arrangement of carbon atoms in graphene and carbon nanotubes (CNTs)?
Carbon nanotubes
These are formed when graphene sheets are seamlessly rolled into cylinders.
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs)
Multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs)
Give the two (2) types of Carbon Nanotubes
Gold nanorods
These nanoparticles are anisotropic gold nanoparticles characterized by their rod-like morphology.
10 - 100 nm
Gold nanorods typically have lengths between ____ to ____ nm and aspect ratios (length-to-width) ranging from 2 to 5 or more.
2 to 5
Gold nanorods typically have lengths between 10 to 100 nm and aspect ratios (length-to-width) ranging from ____ to ____or more.
Transverse mode
Longitudinal mode
Due to the unique shape of gold nanorods, they exhibit two (2) distinct surface plasmon resonance (SPR) modes. What are these modes?
Transverse mode
This surface plasmon resonance (SPR) mode of gold nanorods refers to the oscillation of electrons across the short axis.
Longitudinal mode
This surface plasmon resonance (SPR) mode of gold nanorods refers to the oscillation along the long axis.

d. SUBTRACTIVE POWDERS
Which does not belong to the group?
a. AGAROSE PARTICLES
b. SILICA PARTICLES
c. POLYMER PARTICLES
d. SUBTRACTIVE POWDERS
Chemical reduction
This is a widely used wet-chemical technique for producing zero-valent nanoparticles by reducing metal salts dissolved in water.
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. Chemical reduction requires at least one reducing agent to supply electrons that convert metal ions into their neutral, zero-valent form.
a. CTAB
cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) is a stabilizing agent while citrate, ascorbate, and borohydride are reducing agents
Which does not belong to the group?
a. CTAB
b. Citrate
c. Ascorbate
d. Borohydride
TRUE
TRUE or FALSE. In some cases, the stabilizer can also serve as a reducing agent.
Sodium citrate
Which compound acts both as a stabilizer and a reducing agent in the synthesis of silver nanoparticles?
Precipitation
This is a widely used technique in nanoparticle synthesis, where dissolved substances form solid particles under supersaturated conditions.
FALSE
Precipitation is a widely used technique in nanoparticle synthesis, where dissolved substances form solid particles under supersaturated conditions.
TRUE or FALSE. Precipitation is a widely used technique in nanoparticle synthesis, where dissolved substances form solid particles under unsaturated conditions.
Nucleation
When supersaturation is reached, this process initiates the formation of nanoscale particles.
FALSE
Rapid or excessive nucleation can lead to a broad size distribution,
TRUE or FALSE. Rapid or excessive nucleation can lead to a uniform size distribution, reducing the quality and consistency of the final product.

read lang
read lang

Seeding method
This method involves growing nanoparticles by reducing metal salts in an aqueous solution that contains pre-formed seed particles.
Frens
The seeding method was introduced by ________ in the early 1970s.
nucleation sites
In the seeding method, the seed nanoparticles serve as __________ which directs and promotes controlled growth.
read onleh
Stabilizers play a crucial role in the seeding method, as they help regulate both the size and shape of the developing nanoparticles. Over time, the technique has been refined through the use of different seed types, reducing agents, and stabilizers, allowing for greater precision and versatility in nanoparticle synthesis
Microemulsion
This is a widely used technique for synthesizing nanoparticles, based on an isotropic, thermodynamically stable mixture of water, oil, and surfactants, often with co surfactants.
Direct microemulsion
Reverse microemulsion
What are the two (2) primary types of microemulsion?
Direct microemulsion
This is a type of microemulsion where oil is dispersed in water.
Reverse microemulsion
This is a type of microemulsion where water is dispersed in oil.
Inverse microemulsion
This method is particularly effective for producing multifunctional nanoparticles. It allows for the formation of a silica matrix within the aqueous phase, which can encapsulate and stabilize individual particles.
Hydrothermal method
This method involves the growth of nanoparticles from initially insoluble substances through heterogeneous reactions conducted under high temperature and pressure.
Autoclave
The process of the hydrothermal method occurs in a sealed steel vessel called ________.
Water
In the hydrothermal method, which substance acts as both the solvent and the medium for crystal growth within the autoclave?
300°C
In the hydrothermal method, hydrothermal reactions are carried out at temperatures below ____ °C.
Nutrients
What is supplied within the autoclave during synthesis to facilitate controlled nucleation and particle formation?
Carbon-based nanoparticles
Ceramic nanoparticles
Metal nanoparticles
Semiconductor nanoparticles
Polymeric nanoparticles
Lipid nanoparticles
Enumerate the Types of Nanoparticles (6)
Carbon-based nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles is widely used in electronics, energy storage, construction, and biomedical applications.
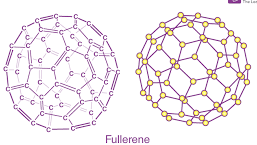
Fullerenes
This carbon-based nanoparticle possesses a hollow-cage-like arrangement.
Ceramic nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles are inorganic materials known for their thermal stability and chemical resistance.
Ceramic nanoparticles
These nanoparticles have been successfully applied in treating diseases and are now being explored for bone repair.
Metal nanoparticles
This is a type of nanoparticles that were made from gold, silver, and copper, are commonly synthesized using chemical, electrochemical, or photochemical methods.
Semiconductor nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles exhibit properties between those of metals and non-metals and are typically derived from groups II–VI, III–V, or IV of the periodic table.
Semiconductor nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles is widely used in modern technologies, including computers, mobile phones, and communication systems.
Polymeric nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles are organic-based systems typically prepared as either nanospheres or nanocapsules.
Nanospheres
This polymeric nanoparticle has a matrix structure in which the active compound is uniformly distributed.
Nanocapsules
This polymeric nanoparticle features a core-shell structure, enclosing the active agent within a polymer shell
Polymeric nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles has high biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Lipid nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles are spherical carriers, typically 10 to 100 nm in size, composed of a solid lipid core and stabilized by surfactants or emulsifiers.
10 - 100 nm
Lipid nanoparticles are typically ____ to ____ nanometers in size.
Lipid nanoparticles
This type of nanoparticles has the ability to encapsulate poorly water-soluble molecules which makes them especially effective in cancer and gene therapy applications.
read lang
read lang

read lang
read lang
