PNS Afferent Division
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
afferent is also known as
sensory
some sensory neurons travel to the cerebrum for _____ perception
other sensory neurons travel to the spinal cord for ____ perception
conscious
unconscious
conscious processing has ______ and _____ senses
special and somatic
special senses are only located where?
the head
what are the special senses?
gustation
olfaction
vision
equilibrium
hearing
is proprioception (related to the body’s position and movement) somatic sensory and somatic stimuli?
yes
subconscious is divided into what two stimuli
somatic and visceral
sensory receptor types
simple receptors: neurons with free nerve endings
complex receptors: nerve endings enclosed in connective tissue capsules (examples: pacininan corpuscles, meissner’s corpuscles)
special receptors: release neurotransmitters onto sensory neurons
mechanoreceptors
thermoreceptors
chemoreceptors
photoreceptors
nociceptors
baroreceptors
mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical pressure
thermoreceptors respond to temperature changes
chemoreceptors respond to chemical changes
photoreceptors convert light into electrical signals
nociceptors respond to damaging stimuli, pain
baroreceptors are stretch receptors that sense blood pressure
vomiting is an example of what type of receptor
visceral receptor
do olfactory pathways travel to the thalamus
no, they go straight to the olfactory cortex
do equilibrium pathways travel to the thalamus?
no, they travel straight to the cerebellum
which two pathways do not travel to the thalamus
olfactory and equilibrium
sensation is the ______ of stimuli
awareness
perception is the _____ of stimuli
conscious interpretation
Principles of Sensory Coding
when a stimulus reaches a receptor, the following events take place:
1. reception: specialized cells (receptors) absorb physical energy
2. transduction: physical energy is converted into electrochemical energy
each receptor is specialized to absorb and transduce only one kind of energy
the strength of the receptor potential determines how strongly the receptors are activated. These are graded potentials, not action potentials
sensory receptors encode 4 types of information
modality- the specific form of energy of a stimulus
location- the receptive fields (smaller receptive fields = higher acuity aka precision)
intensity- intensity of the stimulus
duration- how long a stimulus lasts
what does a stronger stimulus do to the action potential
increases the frequency of action potentials
how do tonic receptors react to a prolonged stimulus?
show little adaptation
how do phasic receptors react to changes in the intensity of a stimulus?
adapts quickly to changes in stimulus
a strong stimulus that is applied to one neuron and results in the inhibition of transmission to neighboring neurons is called?
lateral inhibition
lateral inhibition increases/ decreases acuity?
increases
two point discrimination
the ability to distinguish two fine points against the skin rather than perceiving them as one
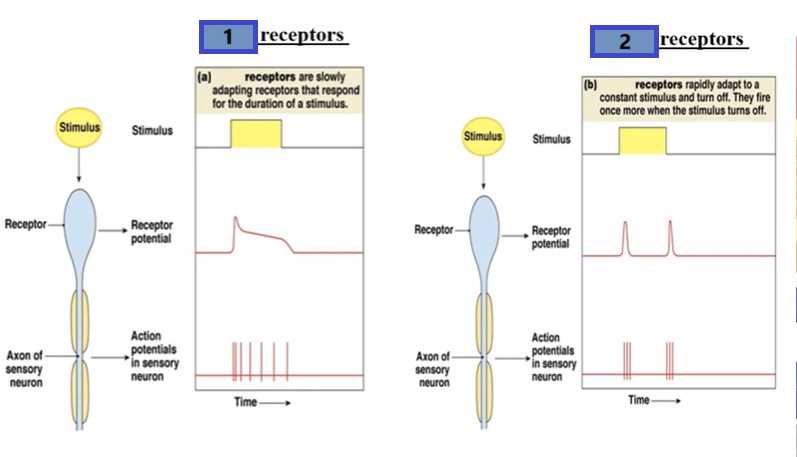
1
tonic
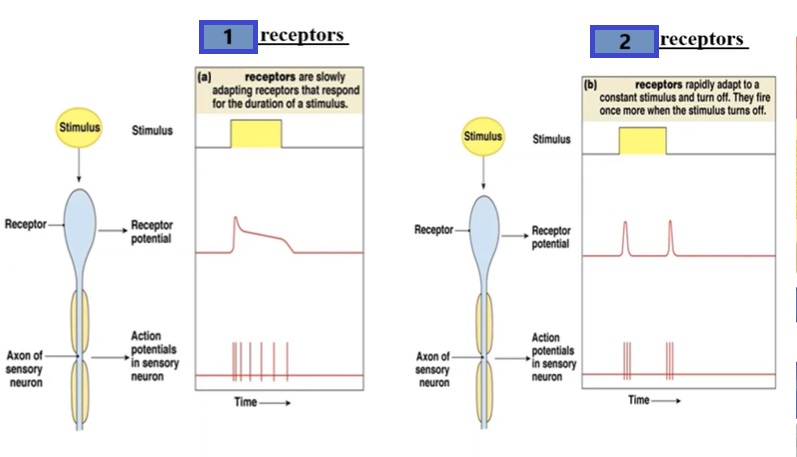
2
phasic