(copy) Chapter 38 - Physiology, Homeostasis, and Temperature Regulation
1/156
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Extract ___ and ___ from the environment
Energy and nutrients
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Build ____
All internal structures
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Eliminate ____ and ______
Toxins and wastes
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Sense and respond to the ____
Environment
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Homeostasis, which is ____
The maintenance of constant internal conditions
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
Reproduce
Reproduce
6 Essential Things for Animal Survival
(Try to say all of them with no help or hints)
Extract energy and nutrients from the environment
Build all internal structures
Eliminate toxins and metabolic wastes
Sense the environment and respond to it in various ways, including movement
Homeostasis – Maintenance of constant internal conditions
Reproduce
Multicellularity and Large Size
Organisms have developed complex body systems in order to deal with the challenges of the 6 essential things for survival. They became multicellular and bigger in size.
What are the (2) advantages of multicellularity?
Can become large in size
Specialization of cells
Multicellularity and Large Size
Organisms have developed complex body systems in order to deal with the challenges of the 6 essential things for survival. They became multicellular and bigger in size.
What are the (2) advantages of large size?
Ability to prey on other organisms
Resistance to forces in nature such as ocean waves
Size of single-celled organisms is constrained by cell membrane _____ that limits exchange of materials with the environment.
Surface area
If a multicellular animal consists of only a few layers of cells, those cells can ______ with the environment
Exchange materials directly
Cells of larger animals must be served by an ________
Internal environment of extracellular fluid
Different cells are specialized to contribute to the ________
Maintenance of the internal environment (homeostasis)
What is the relationship between cells and homeostasis (maintaining internal environment)
Each cell contributes to the internal environment, and each cell is supported by that internal environment.
What are the pros and cons of cell specialization?
(1 pro and 1 con)
It has great adaptive value, but those cells will lose other functions
Tissue
Groups of similar cells
What are the four types of tissue?
Epithelial
Muscle
Connective
Nervous
Epithelial/Epidermal Tissue
What is it?
Sheets of cells that create barrier and often have secretory functions. There are 4 types (stratified, cuboidal, columnar, and secretory/simple squamous)
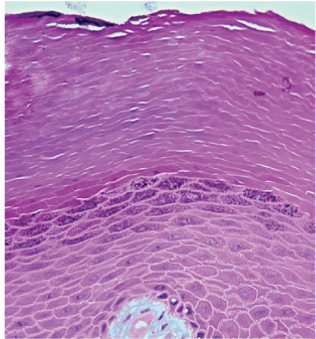
Stratified Squamous Epithelium is 1 of 4 epithelial tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this type.
Stratified
Found in skin
Protects body and separates internal environment from external environment
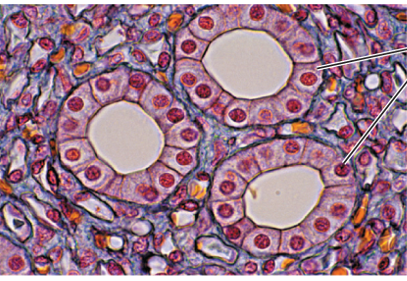
Cuboidal Epithelium is 1 of 4 epithelial tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this type.
Cuboidal
Tubules and ducts
Secretion and absorption
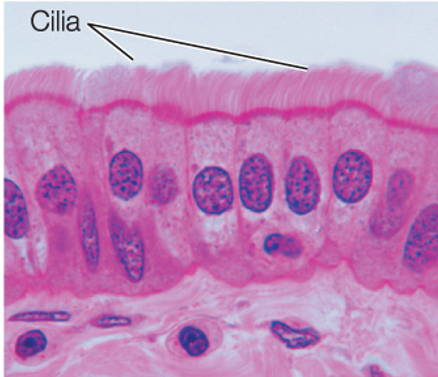
Columnar Epithelium is 1 of 4 epithelial tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this type.
Columnar
Lining of internal organs (like airway and intestine)
Has cilia or villi. Enables movement of substances between body compartments
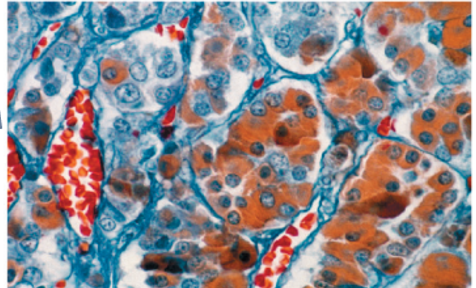
Secretory/Simple Squamous Epithelium is 1 of 4 epithelial tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this type.
Which type of epithelial tissue?
Where is it found?
Function and unique features?
Secretory/Simple Squamous
Lines blood vessels and body cavities, and found in glands
Secretion and absorption
Muscle Tissue
What is it?
Tissue that contracts to generate force and movement. There are three types: cardiac, smooth, and skeletal
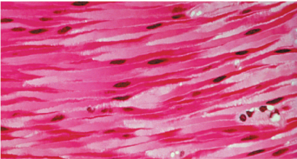
Cardiac muscle is 1 of 3 muscle types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Found in the heart only
Allows for heart contractions
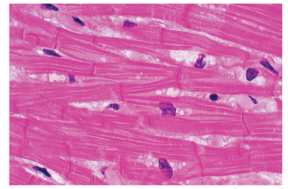
Smooth Muscle is 1 of 3 muscle types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Involuntary muscle (we cannot control it)
Found in internal organs
Controls diameter of blood vessels & provides movement for internal organs
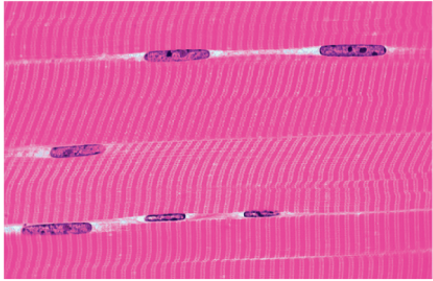
Skeletal Muscle is 1 of 3 muscle types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Voluntary (we control the movement)
Found attached to bones via tendons
Connective Tissue
What is it?
Tissue that provides structure and support. There are four types: bone, adipose, blood, and tendons & ligaments
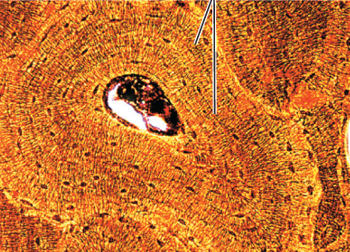
Bone is 1 of 4 connective tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Provides support structures for the body that allow for muscle generation
Adipose (Fat) is 1 of 4 connective tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Two types (brown and white fat)
White fat cushions and supports organs
Brown fat produces heat
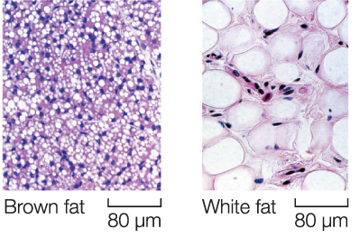
Function of white fat tissue
Cushions and supports organs
Function of brown fat tissue
Produces heat
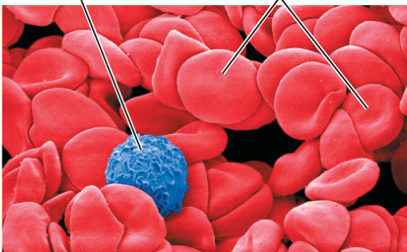
Blood is 1 of 4 connective tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Red blood cells carry oxygen
White blood cells protect against foreign
Ligaments & Tendons are 1 of 4 connective tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Connect bones to bones and muscles to bones (respectively)
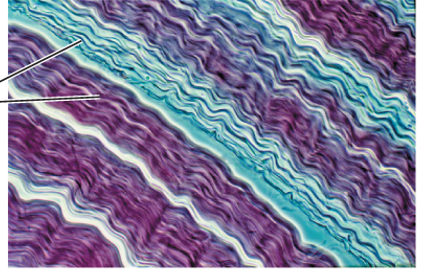
Function of ligaments
Attach bones to bones
Function of tendons
Attach bones to muscles
Nervous Tissue
What is it?
Type of tissue that conveys and processes information. There are three types: sensors, neurons, and glia
Sensors are 1 of 3 nervous tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Encode information about the external environment
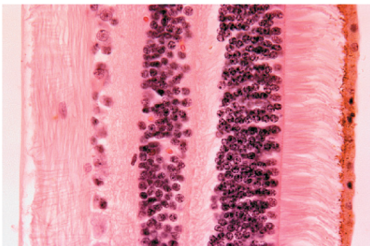
Neurons are 1 of 3 nervous tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Send info from sensors to central nervous system (CNS)
Store and integrate info
Send commands to muscles and glands
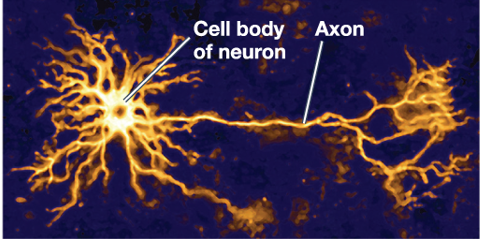
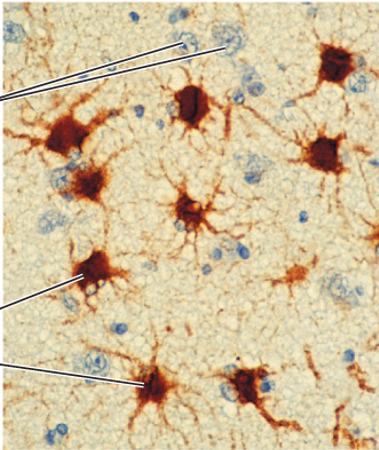
Glia are 1 of 3 nervous tissue types. Indicate which is the correct description and appearance of this tissue type.
Support neurons and moderate their signaling
Insulate neuronal processes
Provide immune functions for the central nervous system (CNS)
Organs
Internal structures that carry out specific functions (most have all four tissue types)
Individual organs are part of an _____, a group of organs that work together
Organ System
What is the organizational hierarchy from cells to multicellular organisms?
Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Multicellular Organism
A sponge is an aquatic organism that brings its food in through pores using flagella on specialized cells to create an incurrent of water. This specialization in which cells have different functions within an organism is an advantage that is not possible in a(n)
a. multi-celled organism.
b. single-celled organism.
c. organ.
d. tissue.
single-celled organism
Macrophages engulf cellular debris, microbes, cancer cells, and foreign substances, so it is advantageous for them to be large. Why don’t they keep growing ever larger?
a. They run out of ATP.
b. Their mitochondria stop dividing when they get too large.
c. Their size is limited by the amount of cell membrane surface area they have.
d. Their size is limited by the number of chromosomes they have.
Their size is limited by the amount of cell membrane surface area they have
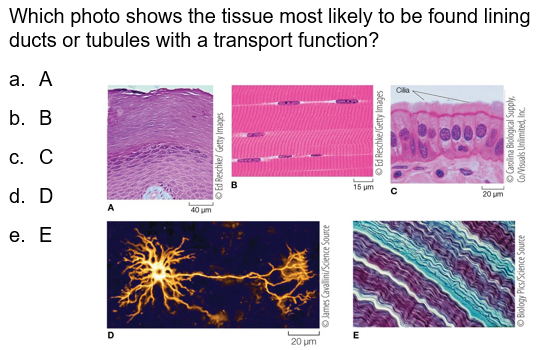
Which photo shows the tissue most likely to be found lining ducts or tubules with a transport function?
C
Loss of some functions in specialized cells is compensated for by the ______
constancy of the internal environment
Evolution of physiological systems to maintain the internal environment made it possible for multicellular animals to become _____
larger, more complex, and occupy many different environments
Individual cells get nutrients from the ______ and dump wastes into it.
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
ECF includes ______ (20%) and the _____ (80%) that bathes every cell.
Blood plasma, interstitial fluid
Organisms must maintain their internal environment in a state of ______
Homeostasis (a narrow range of stable and optimal physical and biochemical conditions)
What controls (speeds & slows down) the activities of the physiological systems?
Nervous and endocrine system
Set Point
A reference point (ex: desired temperature)
Comparator
Senses current condition and compare it to the set point (desired condition)
Feedback
Information that is compared to the set point
Error Signal
Any difference between the set point and feedback information
Regulatory Systems
Obtain, integrate and process information and issue commands to effectors
Effectors/Controlled Systems
System that is controlled by neural or hormonal signals from regulatory systems.
Receives commands from regulatory systems. Then causes change to the internal environment.
Sensors
Provide the feedback information
Negative Feedback
Information used to counteract the influence that created an error signal
Whatever force is pushing the system away from its set point must be ____ or ______
“Negated” or reversed
Ex: When air temperature falls below the set point, the thermostat causes the furnace to be turned on thereby reversing the direction of the change in air temperature
Positive Feedback
Information that amplifies a response and increases deviation from a set point.
But responses tend to reach a limit and terminate rapidly. Ex: Sexual behavior, in which little stimulation causes more behavior which causes more stimulation and so on. Another Ex: Contraction of the uterus pushes the baby into the birth canal and stretching of the birth canal causes more and stronger contractions until the baby is delivered at which time the contraction ceases.
Feedforward Information
Another feature of regulatory systems; Information that anticipates internal changes and changes the set point
Ex: A timer on a thermostat may lower the set point at night. Another Ex: Hearing the words “on your mark” before a race is feedforward information that increases heart rate in anticipation of running.
Studies on racehorses have shown that when the starting gate closes just prior to a race, the breathing rate of a racehorse increases, even though the horse is standing still. This response is an example of
a. an error signal.
b. negative feedback.
c. positive feedback.
d. feedforward control.
e. homeostasis.
Feedforward control
The testes release testosterone, and the rising levels of testosterone inhibit its further release. This is an example of
a. feedbackward information.
b. negative feedback.
c. feedforward information.
d. positive feedback.
e. changing the set point.
Negative feedback
Most cells function over a ____ range of temperatures
Narrow
Below 0°C, ice crystals form and damage cell structures. Some animals have ______ in their blood that help them resist freezing; others can simple survive freezing.
Antifreeze molecules
Antifreeze Molecules
Molecules in blood that help some animals resist freezing
Urea and glucose accumulation act as ______ in frogs. Urea and glucose are both ____
Antifreeze, cryoprotectants (a substance used to protect biological tissue from freezing damage)
Cryoprotectant
A substance used to protect biological tissue from freezing damage
_____ is redistributed to the extracellular fluid (ECF), which can freeze without damaging cells
Intracellular water
Above 45°C, proteins begin to ______ and ______
Denature and lose function
*Denature means change shape
Denature
Change shape
Some specialized algae can grow in hot springs at __°C
70°C
Some archaea live at near ___°C
100°C
Heat Shock Proteins (HSPs) are ___ proteins that function to _____ other proteins and prevent ____
Chaperone proteins
Stabilize other proteins
Prevent denaturation
We can survive hot temperatures via _____. They bind to other proteins and protect them from denaturing.
Heat shock proteins (HSPs)
Survival limits for most cells fall between ___° and ___°C, but most organisms have a much narrower tolerance range.
0° and 40°C
To stay within the survival limits (between 0° & 40°C), animals have evolved many _______
Thermoregulatory adaptations
Biochemical reactions are ________. In other words, the rate increases as temperature increases.
Temperature-sensitive
The rate of biochemical reactions is ____ proportional to temperature
Directly
Q10 describes temperature-sensitivity. Q10 is ____
The rate of a reaction at once temperature divided by the rate of the same reaction at a temperature 10° lower
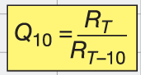
The rate of reaction doubles as temperature increases by
10°C
When Q10 is equal to 1, this means it is temperature ______
Independent/insensitive
Change in body temperature can disrupt physiology because not all biochemical reactions have the same Q10.
These reactions are linked in complex networks: products of one reaction are reactants for other reactions. Shifting _____ can disrupt the overall network.
Reaction rates
The body temperature of some animals is is coupled to the temperature of the ________.
Environment
*One example is fish. The body temp. of fish is the same as the temp. of water
The body temperature of fish is the same as the temperature of the water they are in. During the winter, the fish will _____ to colder water, and will have a higher ________ in order to remain active
(separate answers with comma)
Acclimatize, metabolic rate
*Acclimatization is the process or result of becoming accustomed to a new climate or to new conditions
One mechanism for acclimatization is to express ______ (different forms of an enzyme) that have different temperature optima.
*Acclimatization is the process or result of becoming accustomed to a new climate or to new conditions
Isozymes
Isozymes are ___
Different forms of an enzyme
Acclimatization is _____
The process or result of becoming accustomed to a new climate or to new conditions
Hyperthermia
The reduction of heat-generating muscular work and increase of heat loss
Which statement is true?
a. At temperatures below 32°C, ice crystals form and damage all cells.
b. No organism can survive in the boiling hot springs of Yellowstone National Park.
c. Some animals have antifreeze molecules in their blood, which help them resist freezing.
d. Low temperatures are problematic for animals because proteins denature.
e. Most cells can function over a range of temperatures from 0°C to 100°C.
Some animals have antifreeze molecules in their blood, which help them resist freezing.
You measure metabolic rates of several four-toed salamanders at 20°C and at 30°C and calculate a Q10 equal to 2 for the species. Based on this information, which statement is true?
a. Metabolic rate is not temperature sensitive in this species.
b. 30°C must be above the thermoneutral zone for this species.
c. Metabolic rate at 20°C is twice that at 30°C for this species.
d. Metabolic rate at 20°C is half that at 30°C for this species.
Metabolic rate at 20°C is half that at 30°C for this species.
An ectotherm’s metabolism adjusts to compensate for seasonal thermal changes. This is most likely made possible by the production of different
a. thermogenins.
b. thermoneutral zones.
c. isozymes with temperature optima matching the season.
d. countercurrent exchangers.
e. kinds of adipose tissue.
Isozymes with temperature optima matching the season.
Animals continuously exchange heat with their environment; balance between heat gain and heat loss determines the animal’s _______
body temperature
What are the two types of animals with regard to constancy of body temperature?
Homeotherms and poikilotherms
Homeotherms
animals that maintain constant body temperature
Poikilotherms
animals with fluctuating body temperatures
What are the three types of animals with regard to the source of heat that determines their body temperature?
Ectotherms, endotherms, and heterotherms
Ectotherms
Body temperature depends on external sources of heat.
Ex: non avian reptiles, fishes, amphibians, invertebrates
Endotherms
Can vary metabolic heat production
Ex: mammals and birds