WEEK 2 clinicals ROTATION
1/212
Earn XP
Description and Tags
a
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
Amalgam restorations
silver colored dental restorative material made of a mixture of mainly silver, metals, primarily mercury, silver, tin, and copper, used to fill cavities in teeth.
Amalgam carver
dental instruments used as part of restorative procedures to carve anatomical features and remove excess materials.
Amalgam procedure instruments
Tofflemire matrix retainer- Holds Matrix band ans allows for tightening of matrix bands and creating proper contours for amalgam restorations.
Tofflemire matrix band- a thin strip of metal used to create a temporary wall around a tooth for filling with amalgam.
Wooden Wedge - A small piece of wood used to hold the matrix band in place and ensure a tight seal during the amalgam filling process.
Condenser- Instrument used to pack amalgam against the floor and walls of a prepared tooth
Amalgam carrier - used to carry amalgam to a prepared tooth
Tofflemire matrix retainer
- Holds Matrix band ans allows for tightening of matrix bands and creating proper contours for amalgam restorations.
Tofflemire matrix band
- a thin strip of metal used to create a temporary wall around a tooth for filling with amalgam.
Wooden Wedge
- A small piece of wood used to hold the matrix band in place and ensure a tight seal during the amalgam filling process.
Condenser
- Instrument used to pack amalgam against the floor and walls of a prepared tooth
Amalgam carrier
- used to carry amalgam to a prepared tooth
amalgam carver
Instrument used to shape and carve the surface of an amalgam restoration after it has been placed in the tooth.
amalgamator
machine to mix alloy and merucry
burnisher
instrument used to smooth the harden surface and margins of an amalgam restoration
dapen dish/ amalgam well
Made of metal or glass picked up with amalgam carrier and hand to dentist
wooden wedge
amalgamator

amalgam carrier
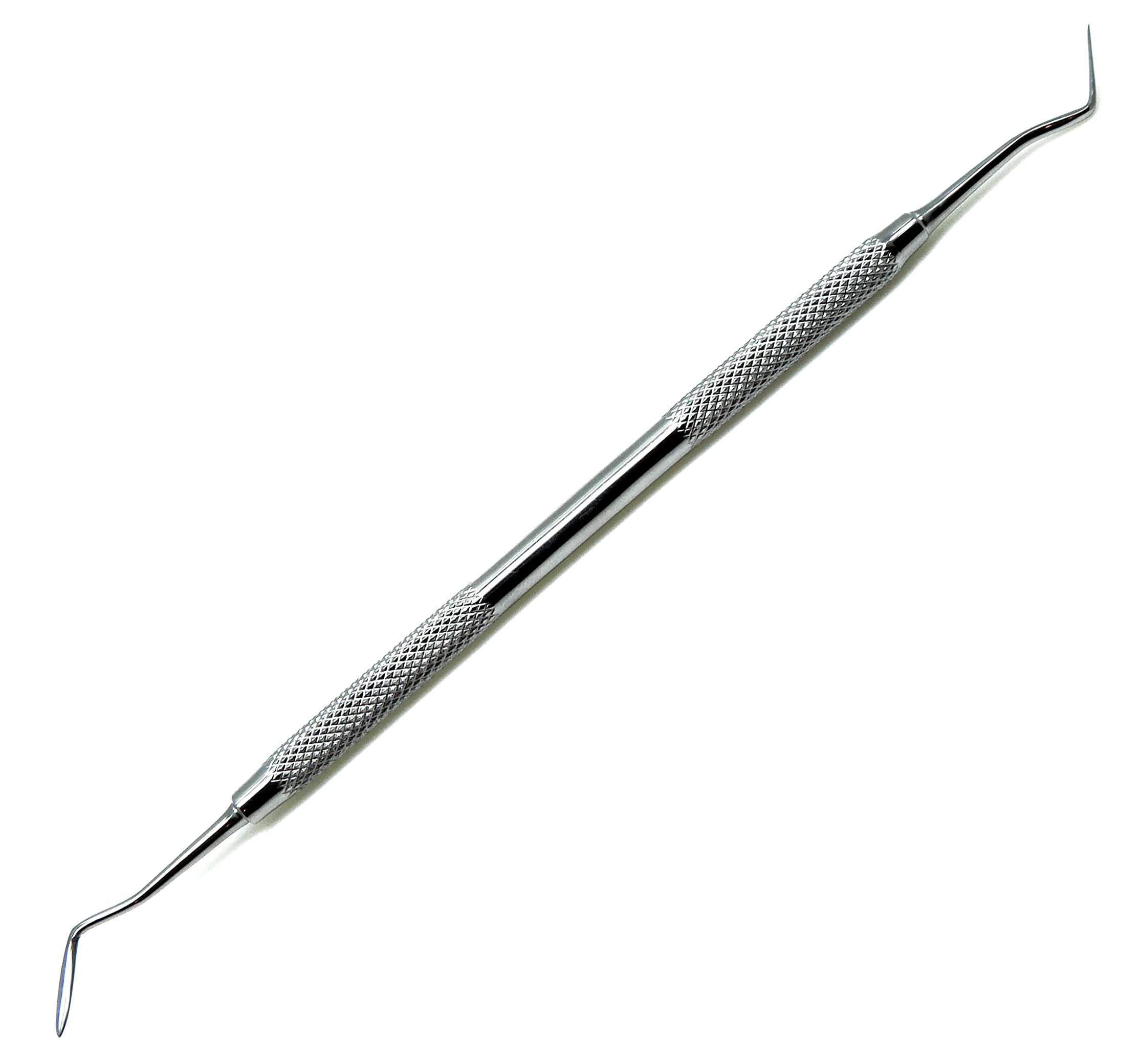

amalgam carver
ball burnisher
1.Tarnishes
, typically used only for posteriors due to lack of esethic appeal
contains toxic mercuryThese are disadvantages of amalgam restorations
These are disadvantages of amalgam restorations
whats the purpose of matrix retainers?
when interproximal wall been removed To hold the matrix band in place and create a proper contour for amalgam restorations.
composite filling-
a tooth-colored resin restoration
Composite restoration procedure
Anesthetic/ anesthesia
prep tooth/ Remove Decay
Acid Etch (If applicable 15 seconds)
Rinse/ Dry
Prime ’Dry
Bond
Cure
Apply composite
cure
adjust if needed
Check occlusion with articulating paper
coronal polish
composite procedure cont’d instruments
high speed hand piece
low speed hand piece
plastic instruments
micro brush
polishing cup/point ‘
curing light
coronal polishing
a technique used to remove plaque and stains and smooths restorations from coronal surfaces of the teeth
Wax bite impression
Most useful in fabrication of diagnostic casts relationship between complete maxillary and mandibular aches
Aseptic technique
refers to creating a procedure free of disease producing organism
Osha may review procedures and practices in a dental office for compliance when
1.An employee or patient complaint is made
2.periodically in a office of eleven or more employees
3.When requested by an office
some standards of the 1992 osha bloodborne pathogen standard
Provide written procedure for thr event of an exposure
explain biohazards and labeling to employees
plan for disposal of hazardous waste materials
Overall guidelines for infection control
1.Sterilize everything that can be sterilized
2.use disposable whenever possible (easier to dispose of than disinfect)
3.use barriers whenever possible
Biohazardous material is disposed in specially marked containers and sent to an outside biohazard agencyBiohazard waste disposal
Biohazard waste disposal
Biohazard waste
Blood- or blood-soaked items that may release blood or infectious material
tissue and extracted teeth
contaminated needles surgical blade or other disposable sharps
Biohazard sharps container-
Sharp instruments and needles should be placed in a puncture resistant sharps container and sent to an outside biohazard agency for safe disposal do not reuse sharps.
MAKE SURE TO USE THE ONE-HANDED TECHNIQUE WHEN RECAPPING A SYRINGE PRIOR TO DISPOSAL
One handed recapping technique
Place a cap on hard flat surface slide syringe needle into cap
scoop up with syringe needle so that cap sitting on needle
using a hard flat surface press cap onto needle until cap snaps into place
If an employee is exposed what should the employer do ?
The employer should immediately make available a confidential medical evaluation at no cost to the employee. There should be a complete written report following osha guidelines prepared for an osha incident .
operator barriers list some examples
Disposable gloves disposable face mask/ shields eye wear lab jacket gown
when it is not possible to provide surface barriers what do you do for disinfection?
use spray wipe method
Etiology
relationship of cause origin or reason for and the effect of a disease
Microbiology
The study of microorganism
bacteria
viruses
protozoa
rickettsiae
mold
sanitization
A form of instrument or surface preparation that physically removes dirt and debris from the object of sanitization
sanitizatiom using the ultrasonic
Disinfection
The process of using chemicals UV light or ionizing radiation as a method to kill bacteria with the expectation of spores and persistent microorganism
Sterilization AKA COMPLETE DESTRUCTION OF MICROORGANISMS
The process of destroying microorganism and the pathogenic products via moist heat under pressure liquids or dry heat
Liquid sterilization
May be accomplished with certain chemicals where exposure to heat is not indicated for a particular instrument
Dry heat sterilization
Works very similar to an oven temperature much reach 140 degrees for 171-degree instruments which may rust, or hinged instruments can be effectively sterilized in dry heat in about one hour
Chemical vapor sterilization
uses special solution for vapor with exposure time about 20 minutes at 270 degrees
steam sterilization autoclave
operates as pressure cooker three minutes at 270 degrees
Handwashing
wet your hands
soap
lather and scrub 20 sec
rinse 10 sec
turn off tap
dry your hands
Advantages of digital radiography
Immediate viewing of images
Less Radiation
No chemicals
No processing errors
Ability to enhance images
Communication with other dentist
90% less radiation
Disadvantages of digital radiography
COST
CONVERTING PREVIOUS RECORDS TO DIGITAL
LEARNING COMPUTER SOFTWARES
THICKNESS AND RIGIDTY OF SENSORS
Surgical aspirating tips
Plastic or metal long thin tapered suction tips used to remove blood and debris from surgical area
Retractors
used to retract soft tissue wide and flat with handle
bite block
black plastic block used to hold a pt mouth open during a procedure
Rongeur forceps
concave ended forceps used to trim and smooth jagged bone
irrigating syringe
used with sterile soluton to clean extraction site
Surgical Bur
Similar to fraction grip bur has longer shaft for longer reach
Cavity varnish
Varnish applied after cavity preparation that seals the exposed dentin tubules preventing chemical irritants from restorative materials and cements from reaching the dental pulp .
Dental Liners
used in the deepest portion of a cavity preparation or as a pulp cap
also type of sealant containing hydroxide or zinc oxide used during resin restoration
the liner is applied to a cavity preparation in the same manner as a cavity varnish
Dental materials - Base
Protective - To protect the pulp for sensitivity and damage before restoration is placed
Insulating-placed in deep preparations to protect the tooth form thermal shock
sedative- help to soothe pulp damage by decay or irritaited fr
Amalgam
composed of silver alloy mercury
zinc phosphate
type of cement consisting of a liquid and powder that are mixed together on a cool glass slab due to the exothermic reaction that takes place
smear layer
after a tooth is prepared a microscopic layer of mineralized tooth and bacterial debris known as the smear layer remains on the tooth the smear layer must be removed before bonding of composite can take place.
acid tech is applied to the tooth to completely clean and roughen the surface of the tooth
The tooth is rinsed dried and ready for prime and bond and composite n
luting
Cementation if metallic restoration such as crowns bridges orthodontic appliances inlays and on lays
why do we use fabricate study models?
diagnostic casts
demonstration of dental
carver/celoid-discoid
Bladed instruments used to carve the dental anatomy into a restoration
plastic instruments
used to mix carry condense trim soft materials
straight handpieces
uses longer burs stones or disk and are frictioj grip design
panoramic radiography
Example of extraoral radiography
panoramic radiographs show the entire maxilla and mandible on single film
Anatomical landmarks -Maxillary anatomical landmarks
Maxillary sinus
Large central incisors
incisive foramen
3rd rooted 1st molars
coronoid process of the manible
radiopaque
area is light due to object being very dense
radiolucent
area is very dark due to object being less dense
dense well defined bone
why would a image Appear more radiopaque in comparison to the less dense bone to the maxillae?
Who on November 8 1895 discovered x rays
wilhem poentgen
the penetrating power of x ray radiation is measured by
KV
what controls the amount of exposure time an x ray film receives
KV/MA
PRIMARY RADIATION
Produced by an x ray machine
secondary radiation
produced when primary radiation borrows off or passes thru objects
name some effects of overexposure of x ray radiation
damage to sex cells
defects in future generations
List two ways an operator may avoid overexposure of x ray radiation
stand back 6-8 feet
stand behind thick wall
List two ways to protect the patient from unnecessary radiation
avoid retakes
lead protectors
name three types of intraoral films
Bite wings
PA
OCCLUSAL
IDENTIFY THE PROPER USE OF THE FOLLOWING TYPES OF X RAY FILms
no.2 adult
no.0 pedo
A blurred image on a radiograph is caused by
moving tube head/ patient moving
overlapping of teeth on a x ray is caused by
improper horizontal angle
elongation or shortening of teeth on an x ray is caused by
improper vertical angle
Periapical radiograph
contains entire tooth and surrounding bone structure
Bitewing radiograph
what radiograph Contains crown portions of opposing mand/max.
panoramic radiograph
contains both full arches and surrounding structures
List six radiogrph landmarks and explain the locatio
An ultrasonic cleaner involves the use of sound waves vibrations and special solutions to remove debris from instruments
True
It is not necessary for dental workers to wear face protection
False
Disinfection is used in the dental operatory for the following that cannot conveniently be sterilized
Counter tops
sterilization
is the total destruction of all forms of microorganisms
The advantages of the autoclave in the dental office is that it will give you fast sterilization and its convenient to use
true
osha may come into your office to review procedures and practices whren
AN employee or pt complaint is made
periodically in an office of 11 or more employees
All of the above
Instruments should be soaked in a closed ultrasonic cleaner using one of the recommended disinfecting solution before putting them into a sterilization pouch of the following reason:
To prevent debris from remaining on the instruments
to prevent the spread of airborne microorganism
to begin the process of killing microrgranisms
all of the above
A radiolucent area of a radiograph appears
Dark
A radiopaque area of a radiograph appears
Light
The cone cut is the result of
Light exposure of the film
identify three maxillary landmarks use in mounting radiographs
pa oclusal bitewing