Tissues-Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
What are the four tissues types?
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, and Nervous Tissue
Role of Epithelial tissues
Absorption, Secretion, Protection, Filtration, Excretion, and Sensory reception
Role of Connective Tissues
Connect, support, attach, and separate
Role of Muscle Tissues
Movement
Role of Nervous tissues
Send and receive impulses
3 Shapes of regular Epithelial Tissues
Squamous, Cuboidal, and Columnar
2 Kinds of Special Epithelial Tissues
Psuedostratified and Transtional
Role of simple squamous tissue
Rapid diffusion and filtration
Where is simple squamous tissue found?
In the lungs
Role of Simple cuboidal Epithelium
Secretion and absorption
Where is Simple Cuboidal epithelium found
Kidneys
Role of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Absorption and Secretion of mucus
Where is simple columnar epithelium found
In the digestive tract
Role of Stratified squamous tissue
Protection of underlying tissue
Where is stratified squamous tissue found
In the esophagus and mouth
Where is Stratified cuboidal and columnar epithelium found
In the ducts of sweat glands and throat, at transition areas
Role of Pseudostratified Epithelium
Secretion and propulsion of Mucus
Where is pseudostratified epithelium found
In the trachea (windpipeR
Role of transitional epithelium
Stretches and contracts in order for organ to fill or empty
Where is transitional epithelium found
In the bladder
Types of connective tissues
Bone, Blood, Connective Tissue Proper, and Cartilage
Types of Cartilage
Hyaline, Elastic, and Fibrocartilage
Role of Hyaline Cartilage
Protection and cushioning
Where is hyaline cartilage found
Ends of bones and attaches the ribs to the collarbone (sternum)
Role of Elastic Cartilage
Stretchyness
Where is elastic cartilage found
External Ear
Role of Fibrocartilage
Cushioning and protection
Where is Fibrocartilage found
In between discs of vertebrae (Spinal discs) and discs of knee
Types of Connective Tissue Proper
Loose and Dense
Types of Loose Connective Tissue
Areolar, Reticular, and Adipose
Role of Areolar loose CT proper
Protects organs and keeps them held in place
Where is Areolar Loose CT found
Outside of organs
Role of Adipose Loose CT
Protection, Insulation, and stored energy
Where is Adipose loose CT found
Under skin, around the kidneys, heart, and eyes
Role of reticular loose CT
Holds white blood cells (helps fight off infection)
Where is reticular loose CT found
Inside of organs important to the immune system- spleen and liver
Types of dense connective tissue
Regular, Irregular, and Elastic
Role of regular dense CT
Movement and structure
Where is regular dense CT found
In tendons and ligaments
Role of Dense irregular CT
Gives stretch
Where is Dense Irregular CT found
Deep in the skin
Role of Dense elastic CT
Gives stretch and recoil
Where is Dense elastic CT found
Walls of large arteries and lungs
Types of Bone
Spongy and Compact
Parts of blood
Red and white blood cells
Role of Bones
Structure and protection
Role of Blood
Transports oxygen and nutrients
Ground Substance
Material that fills the space between calls and fibers in Connective Tissue
3 Types of FIbers found in Connective Tissue
Collages, Elastin, and Reticular
Role of Collagen fibers
Thickly bundled together for tensile strength
Role of elastin fibers
Thin and branching to allow stretching and recoiling
Role of Reticular fibers
Delicate networks to support soft organs
Types of Muscle Tissue
Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac
Role of Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary Movement, Striated with Multiple Nuclei
Where is Skeletal Muscle found
Next to bones
Role of Smooth Muscle
Helps move food and substances, involuntary movement. No striated, one nucleus
Where is smooth muscle found
In digestive tract
Role of Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary Movement. Cells are striated and have 1 nucleus, with intercalated discs so they can beat in unison
Where is cardiac muscle found
in the heart
Role of neurons
Receive stimuli, transmit info to and from the brain, coordinates bodily functions
Role of Neuroglia
Support Neurons

Simple Squamous Epithelium

Simple Cuboidal epithelium
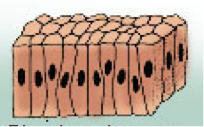
Simple columnar epithelium
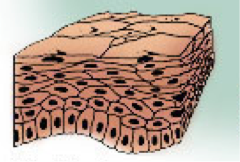
Stratified squamous epithelium
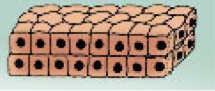
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium

Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
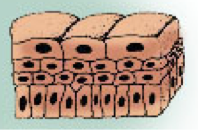
Transitional Epithelium
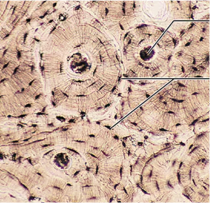
Bone (Connective Tissue)

Adipose Loose CT
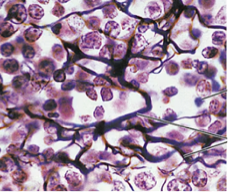
Reticular Loose CT
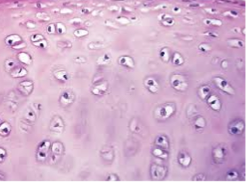
Hyaline Cartilage CT
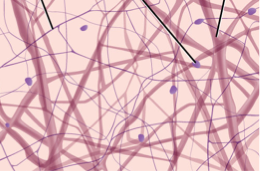
Areolar Loose CT
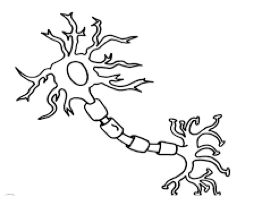
Neuron
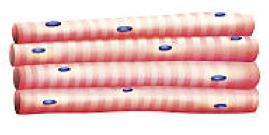
Skeletal Muscle
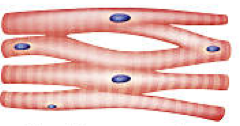
Cardiac Muscle
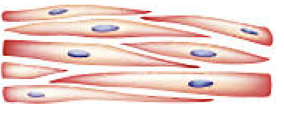
Smooth Muscle