IT fundamentals reading - half of Week 3 and then week 4
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes fox chapter 5 and 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
2 levels of Abstraction of a file system
Physical - Taking the Name + Identifying the physical location within the hard disks (and other storage media)
Logical - How the physical system is partitioned into independently named entities
3 entities in a file system
Partitions, Directories, Files
Partition
A logical division within the file system.
What does a partition refer to in Linux?
In Linux, a partition refers to a separate logical disk drive
How does a file differ from a directory?
Directories are folders that allow the user to coordinate where files are stored.
What makes the file space hierarchical?
It’s organized in a way where the top is the root, underneath are top-level directories, and then are subdirectories branching out and files.
Why are disk files broken up into blocks and scattered across the disk surfaces?
Because of the speed by which a disk is spun, if the read/write head had to access multiple consecutive disk blocks it would take more time transfer the block’s content to memory.
What is a pointer and what is a linked list?
A file’s logical location in the file system is denoted by a pointer - the descriptor of the file will also contain its location within the file system space. A linked list is when the OS maintains listing of the first disk block of each file, also each block contains the locations of the next disk block in the file.
What is a FAT? Where is the FAT stored
File Allocation table accumulates all of the pointers of every disk block into a single file stored at the beginning of the disk and loaded into memory so OS only searches memory. Includes successor block too.
Why is the FAT loaded into memory?
So the OS needs to only search memory to find the location of a given block, rather than searching the disk itself.
How much slower is disk access than the CPU?
A factor of millions of times slower than CPU and memory response rates.
What is an indirect block inode?
Inode pointers can be created so that the inode pointer points to a block of pointers, each of which point to additional disk blocks.
What would happen if your Linux file system were to run out of inodes?
You will unable to create any new files or directories on that file system
In the Linux file system, where do you find most of the system configuration files?
/etc: configuration files specific to the machine
In the Linux file system, where do you find the system administration commands (programs)?
/sbin: Programs stored here are intended for the system administrator. (not part of user’s path)
In the Linux file system, where do you find the general Linux commands?
/bin : common operating system programs such as ls, grep, cp, mv.
In the Linux file system, where do you find the user (application) programs
/usr: various system and user application software with subdirectories.
Which of the Linux items listed under /dev are not physical devices?
/dev/null- destination for program output, /dev/zero- get many 0s, /dev/random- random number generators
If a disk partition is not mounted, what are the consequences to the user?
The user cannot access the files stored on that partition.
What do each of the Linux commands do? Cd, cp, ln, ls, mkdir, pwd, rm, rmdir
ls –lists the files and subdirectories of the given directory
cp- copy a file or directory to a new location
mkdir–create new (sub)directory
rmdir–remove a directory; the directory must be empty for this to work
rm–remove (delete) a file
Cd-change directory
Pwd-writes the full path name of the current working directory
Ln-create links for files in Linux, basically a hard link or symbolic link
What is the difference between ls and ls-l in Linux?
ls lists the contents of the subdirectory or directory but ls-l includes size, last modification time and date, owner.
What is the difference between rm-i, rm-f, rm-r in Linux?
rm-i (interactive mode) - prompts the user for confirmation before removing each file.
rm -f (force mode) - forces the removal of files without prompting for confirmation
rm -r (recursive mode) -recursively removes directories and their contents
What does ~ mean in linux?
Home Directory
What does .. mean in Linux?
Parent directory
What is the difference between an absolute path and a relative path?
An absolute path provides the complete details of a file or directory starting from the root directory /. A relative path specifies the location of a file or directory in relation tot he current working directory.
If you set up a symbolic link to a file in another user’s directory, what happens if the user deletes that file without you knowing about it? What happens if you delete your symbolic link?
The symbolic link will be a broken link where it points to a non-existent target and therefore we get an error about how the file or directory doesn’t exist. If we delete a symbolic link we just won’t have a shortcut to the file, but file is unaffected.
What are files?
Meaningful units of storage in a file system, they comprise data and programs
(T/F) Today file names can include spaces and other forms of punctuation
True
Why are longer file names useful?
Because the name should be very descriptive
What do extensions do in file names?
Extensions tell the user what type of file it is and are also used by the OS to determine how it should be opened.
Files are broken into fixed-sized units known as ___ and they could be distributed across multiple disk surfaces.
blocks
What does cat,more,less do?
Display the contents of a file to the screen
How can a user reduce the impact that large files have on available space in a file system?
File compression
Lossless file compression
A file is reduced in size without losing its data so it can be uncompressed to its original size.
Lossy file compression
Discards some data to reduce the file’s size
What type of compression: image, sound, and movie files
Lossy compression
What type of compression: text and source files
Lossless compression
Mounting
Growing or shrinking fie space by adding and deleting media
Fragmentation
We may not be able to fill in the space of the item we no longer want or it is unused for a long time
If scattered, how does the OS find a given block
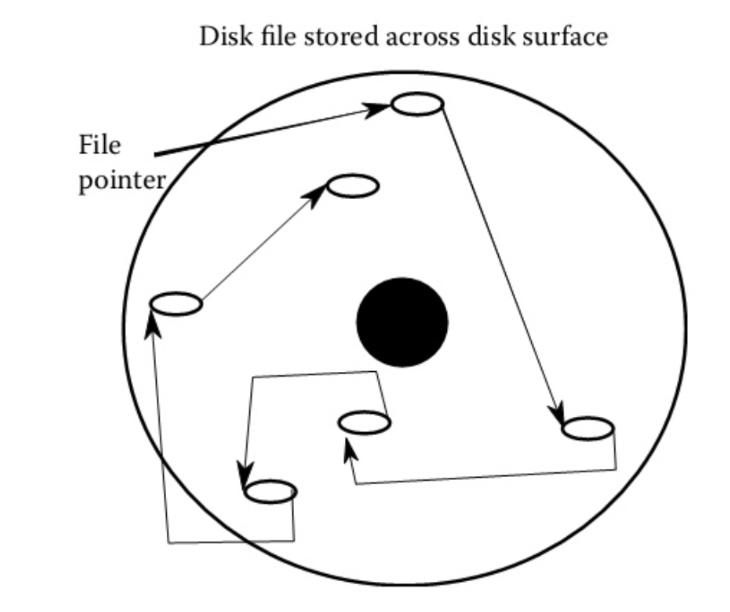
OS maintains listing of the first disk block of each file, also each block contains the locations of the next disk block in the file, storage is a pointer - creates linked list.
Why can linked lists be inefficient?
Because each block requires a separate disk access
What do disk utilities do?
Help a user or system administrator manage and maintain the file system by performing tasks that are otherwise not available.
Disk defragmentation
Moves disk blocks across the disk surfaces to move them together and remove free blocks from between used blocks→ for efficiency and prevent fragments
What do file recovery programs do?
Piece together a file and restore it – as long as the disk blocks that made up the file have not been written over with a new file.
Hard link vs soft link
Pointers that link the file name to the physical location in the disk drive are referred to as hard links. The soft link points to another entry in the directory
Alias
Means that a particular entity (file) can be referenced through multiple names, is risky because someone can change an item without realizing it.
/root:
The home directory for the user root
/dev:
device files, help the user interface with various devices on the system
/tmp:
Temporary file storage for running programs that need to create and use temporary files.
/boot:
files used by a bootstrap loader
/home:
the user’s file space
/var:
Run time data stored by various programs including log files, and email files.
/etc / passwd (user account files)
The user account database, with fields storing the username, real name, home directory, log-in shell, and other information.
/etc / shadow (user account files)
Stores user passwords in an encrypted form
/etc/sudoers (user account files)
list of users and access rights who are granted some privileges beyond normal user access rights
/etc/hosts (network configuration files)
Stores list of commonly used machine’s host names and their IP
/etc/hosts.allow, /etc/hosts/deny (network configuration files)
Stores lists of IP addresses of machines that are either allowed or disallowed login access.
/etc/fstab (file system files)
Defines the file systems mounted at system initialization time
/etc/mtab (file system files)
List of currently mounted file systems
Allows specific areas of the file space to be dedicated for different uses such as kernel, swap space, user directory space
Damage to one may not impact others sometimes
Can establish different access controls.
Linux Partitions
Which partition stores the /boot directory that contains the boot programs
Root partition
Largest partition
/home directory that has all of the user’s directories and subdirectories.
Inode
Not a file but is a data structure that stores information about a file
What does the inode point to?
Points to the file on disk, and also points to the blocks of a file
Symbolic Link
Alternate path to reach a file
Computer virus
A program that can replicate itself, it’s also a malicious program that wants to damage the computer on which it is stored or spy on users on the computer.
How to avoid viruses?
Have up-to-date antivirus software, disable cookies, avoid opening attachments
What is a user
An agent who uses a computer.
User account
A set of data, directories, and privileges granted to a user, as set up by a system administrator.
How is authentication accomplished?
By using a login whereby the user enters both the user name and password, which gets compared to the database of stored usernames and passwords.
Characteristic of a strong password?
Strong passwords are typically those that do not appear in the dictionary. Contain one nonalphabetic character or combination of upper and lower case letters.
Multiuser system
Require user accounts so that the operating system knows who the current user is and can match up the user with proper permissions.
(T/F) User can set up user accounts along with the system administrator
False
2 ways to set up user accounts in Linux and Command Line
GUI and command line
(T/F) IN GUI: When creating a new user, you must enter and confirm the initial user password.
True
Why do we prefer the initial password?
The user account can easily be broken into and therefore some initial password should be created.
As you add a user, the user’s account information is added to the file ______. The information in this file includes for each account, the account name, ID number, group ID number, name, home directory, and login shell.
/etc/passwd
(T/F) /etc/passwd is where the passwords are stored
False
All passwords are stored in the file _____, and this is only accessible by the root.
/etc/shadow
In this example, what is the number of minimum days required between password changes : foxr:$1$KJ1lWAtJ$aElYjCp9i5j924vlUxx.V.:15342:0:38:31:::
0
In this example, what is the number of maximum days until the password will expire from the last change, requiring the user to update it: foxr:$1$KJ1lWAtJ$aElYjCp9i5j924vlUxx.V.:15342:0:38:31:::
38
In this example, what is the number that the user will start receive warning s to change their password?
31
The _____ instruction is used to change a passwd, for a typical user they can us this command and then enter current password to ensure that the user is allowed to change the password then enter a new password twice for confirmation.
passwd
This is an example of which way of breaking into a user’s account: trying a variety of passwords such as no password maybe just an enter key, dictionary words, the user’s name, or the name of the user’s spouse, children pets, parents, etc.
Password cracking
This is an example of which way of breaking into a user’s account: Trying to get the user to give you their password, for instance, by calling on the phone and saying “This is Bob from IT, our server crashed and in order to restore your account we need ur password” ← phishing
Social Engineering
This is an example of which way of breaking into a user’s account: Many people write passwords on sticky notes so looking around their workplace or trashcan
Dumpster Diving
This is an example of which way of breaking into a user’s account: by changing your IP address, you may be able to intercept Internet messages intended for someone else, passwords might be found this way.
IP spoofing
In Linux, permissions can be established for 3 different classes of users:
the file’s owner, those users who share the same group as the file’s owner, and the rest of the world.
Group creation command
groupadd
What does this do in terminal: useradd -G cit130 zappaf
Adds user to a group
Why are user accounts needed in computer systems? Are user accounts needed if only one person is going to be using the computer?
User accounts provide security in that only authorized users are allowed to use the computer and its available resources. A single-user system does not require any user accounts because it is assumed that the same user will always use that system.
How does a normal user account differ from a software account?
User accounts are for humans and Software accounts will not have a login shell and a home directory.
What is the difference between a user account and an administrator account?
The user account has access to its own file space and permission to use shared resources, including application software. System administrator/root: Access to every program, file, and resource, no matter who the owner of that resource is.
Why do we need groups?
If some files have access limited to specific users we can use groups, group members can have different permissions compared to the owner.
How do you create a new user account in Linux from the command line?
useradd
How do you change ownership of a file in Linux from the command line?
chown
How do you change group ownership of a file in Linux from the command line?
chgrp
What does the usermod allow you to do in Linux?
The usermod command is used to modify a user’s account.
What is the difference between read access and execute access in a directory?
If a directory is not readable, not only can you not view its contents but you wouldn’t be able to view the contents of individual files in that directory. If a directory is executable then you can cd into it.
What does the sudoers file store? What does the sudo command do?
/etc/sudoers file stores a list of users and access rights who are granted some privileges beyond normal user access rights. Sudo temporarily grants higher-level permissions to perform administrative tasks.