SHS 300 - Respiratory System
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
functions of the respiratory system
respiration - gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) that is required for life
ventilation - movement of air (inspiration and expiration)
provides air to power the voice for speech (vibrates the vocal cords)
chest wall components
thorax/rib cage (upper cavity)
diaphragm (between upper and lower cavities)
abdomen (lower cavity)
respiratory organs
lungs
components of the upper airways
oral cavity
nasal cavity
pharynx
separation between the upper and lower airways
larynx
components of the lower airways
trachea
bronchial tree
lungs
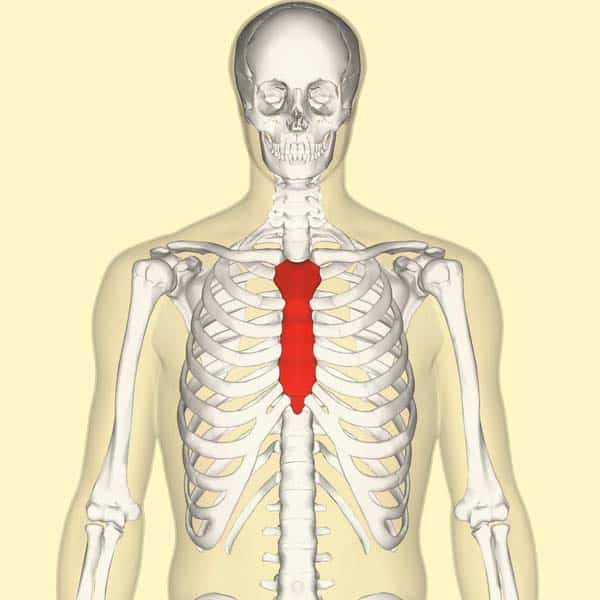
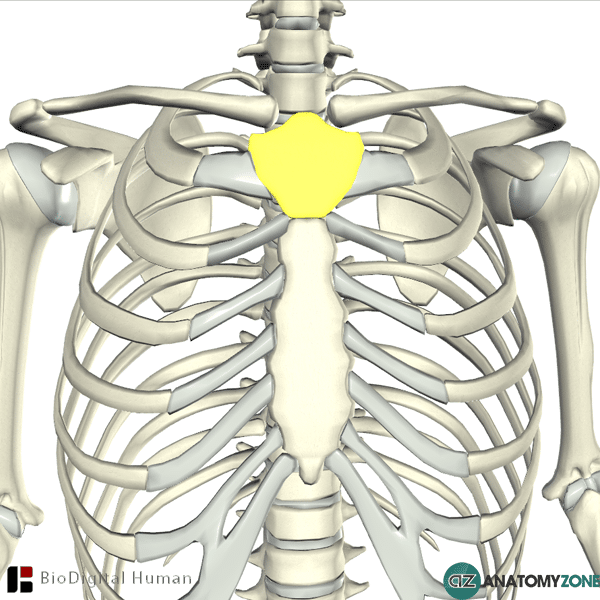
components of the sternum
manubrium
corpus/body
xiphoid process
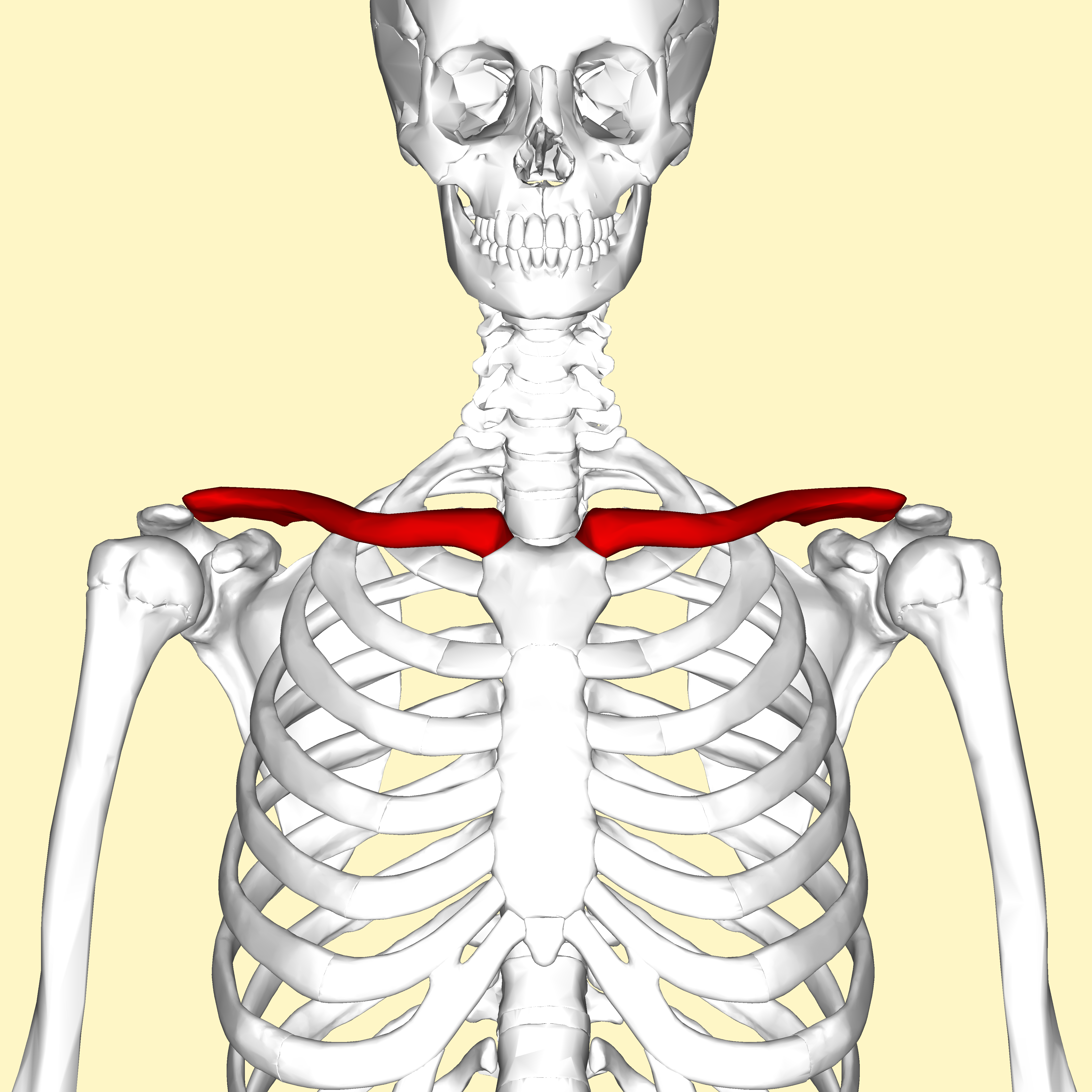
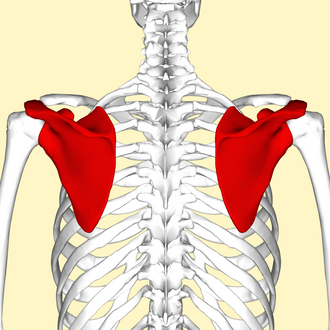
bones of the pectoral girdle
clavicle
scapula
sheets of connective tissue in the abdomen
abdominal aponeurosis (anterior)
lumbodorsal fascia (posterior)
structures that make up the pelvic girdle
coxal bone
sacral and coccygeal segments of the vertebral column
parts of the coxal bone
ilium
ischium
pubis
function of the alveoli
small, bubble-like epithelial cells located in the terminal bronchioles where CO2 and O2 are exchanged
function of the pleurae
translates the movements of the rib cage and abdominal wall to the lungs (so they move as a unit during respiration)
allows inspiration and expiration to be more efficient; prevents structures from collapsing
pleura that covers the inner surface of the rib cage and diaphragm
parietal pleura
pleura that covers the outer surface of the lungs
visceral pleura
main function of the diaphragm
increases thoracic volume and decreases alveolar pressure for inspiration
how the diaphragm moves when it contracts and relaxes
contracts - pulls the central tendon down and forward (increase thoracic volume)
relaxes - displaced upwards by contraction of the abdominal muscles (decrease thoracic volume)
motor innervation of the diaphragm
phrenic nerve - C3, C4, C5
main abdominal muscles - effect on respiratory system
muscles:
rectus abdominis
external obliques
internal obliques
transversus abdominis
effect:
compress abdominal contents and increase abdominal pressure
displace diaphragm up, which decreases thoracic cavity size
how the abdominal wall moves during respiration
inhalation - abdominal wall moves outwards
exhalation - abdominal wall moves inwards
define alveolar pressure
the pressure inside the lungs
passive forces in breathing
elastic recoil of the lung-thoracic unit, torque, and gravity
active forces in breathing
muscle forces
typical chest wall shape for conversational speaking in an upright position
rib cage wall is larger than resting
abdominal wall is smaller than resting
abdominal wall is displaced INWARDS —> slight elevation of the diaphragm
define inspiratory checking (what muscle group is primarily responsible?)
occurs when the major inhalation muscles (diaphragm and external intercostals) are contracted during the first part of the CONTINUOUS utterance
purpose: maintains positive alveolar pressure by counteracting the elastic recoil of the lungs and chest wall (sustains voice production)
muscle groups that are active during running speech activities (which are the most active?)
main inspiratory muscles (diaphragm and external intercostals)
main expiratory muscles (abdominal muscles)
most active: main expiratory muscles
starting at a smaller lung volume = less intense contraction of the inspiratory muscles
continued contraction of the expiratory muscles to force air out and sustain voice production
how breathing changes as we develop (infants to adults)
pediatric larynx (funnel-shaped) develops into a cylindrical shape as the child grows; also located higher in the neck (serves a protective function)
smaller diameter of the bronchial tree in children (results in a higher respiratory rate and less sounds/words per breath cycle)
flatter thorax/diaphragm in children (chest wall only moves up and down)
how breathing changes as we become older (younger adults to older adults)
decreased vital capacity
increased residual volume and resting level due to stiffer costal cartilages and loss of elasticity/recoil in the lungs
speech
initiated at a higher lung volume (>60%)
expend more air per syllable
use more of the vital capacity when talking
presence of a leaky valve (a gap exists between the vocal folds when they should be completely closed)
location of nerves supplying the rib cage wall muscles in relation to the nerves supplying the abdominal wall muscles
generally higher (closer to the head)
example: the diaphragm is innervated by C3-C5 while the abdominals are innervated by T6-T12
location of control of tidal breathing
brainstem (specifically the reticular formation in the medulla)
how ventilation changes when central chemoreceptors sense a change in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the cerebrospinal fluid
increased rate and depth of breathing
receptors that are stimulated when the lungs and airways are stretched
mechanoreceptors
central nervous system control of tidal breathing
higher cortical pathways can modify respiration input and output
***when overriding autonomic functioning becomes harmful, the autonomic regulation will take over
example: holding your breath
clavicle
scapula
sternum
manubrium
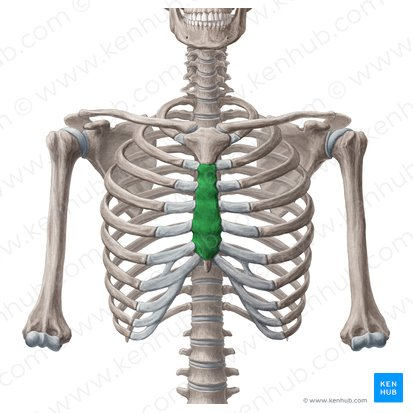
corpus
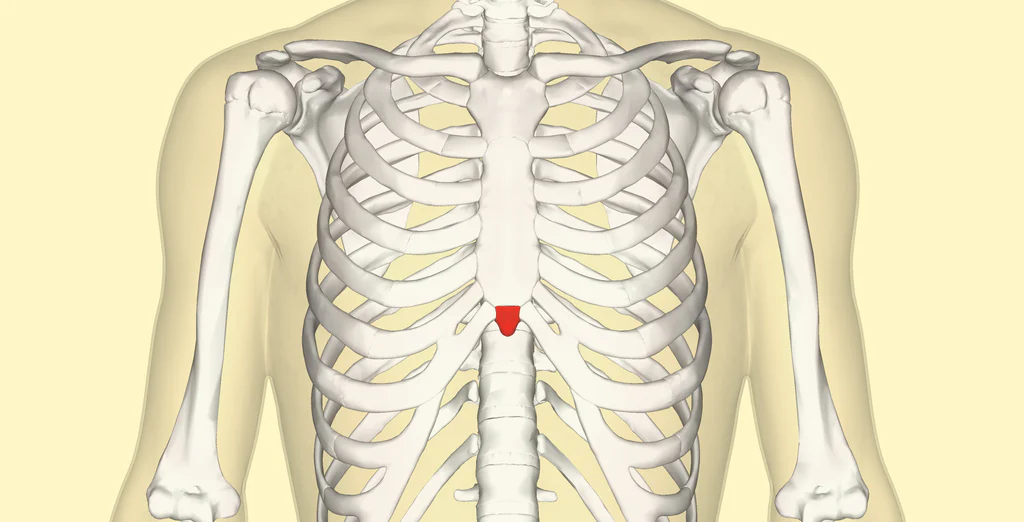
xiphoid process
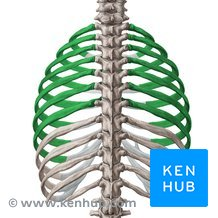
true ribs (1-7)
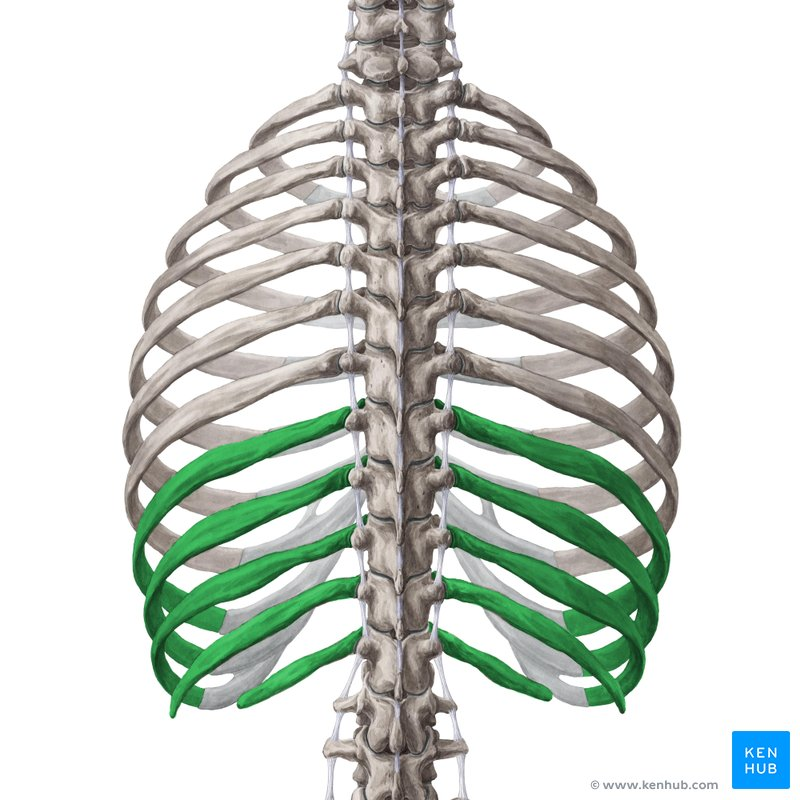
false ribs (8-12)
floating ribs (11-12)
costal cartilage
cervical vertebrae
thoracic vertebrae
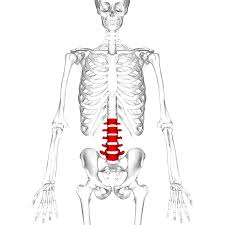
lumbar vertebrae
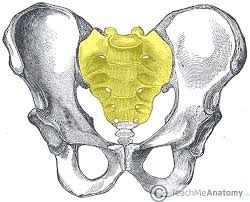
sacrum
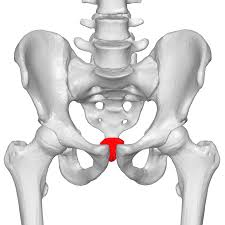
coccyx
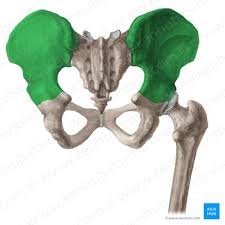
ilium
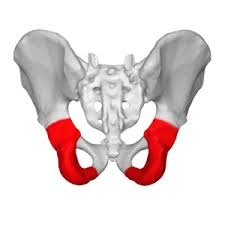
ischium
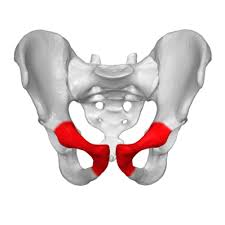
pubis
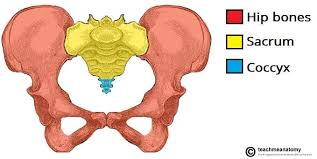
pelvic girdle
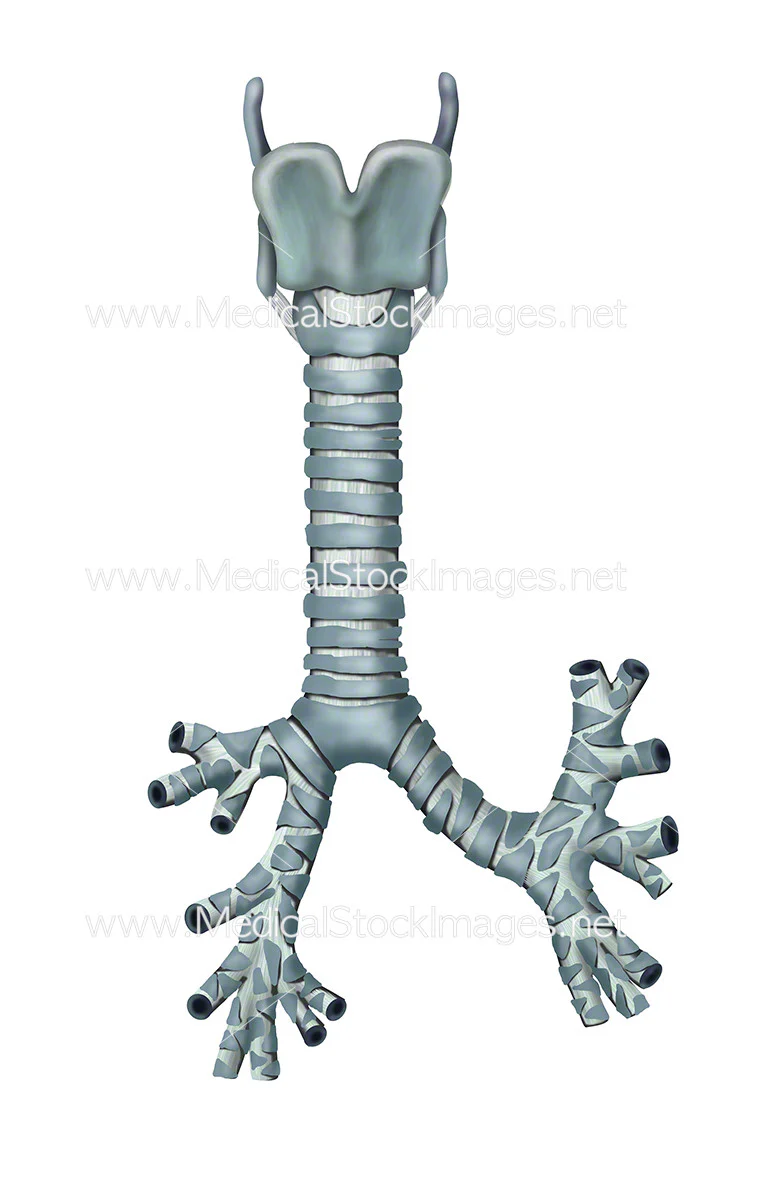
trachea
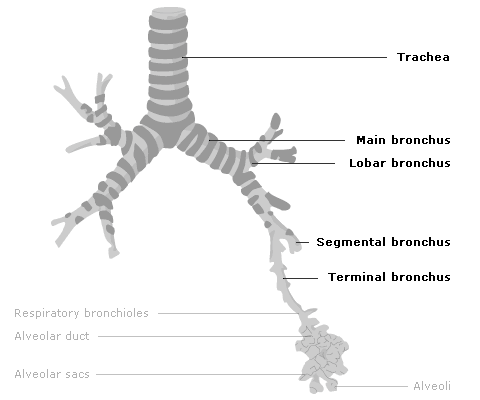
main bronchi and lobar bronchi
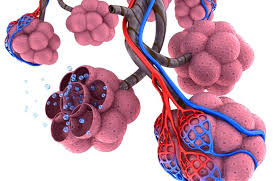
alveoli
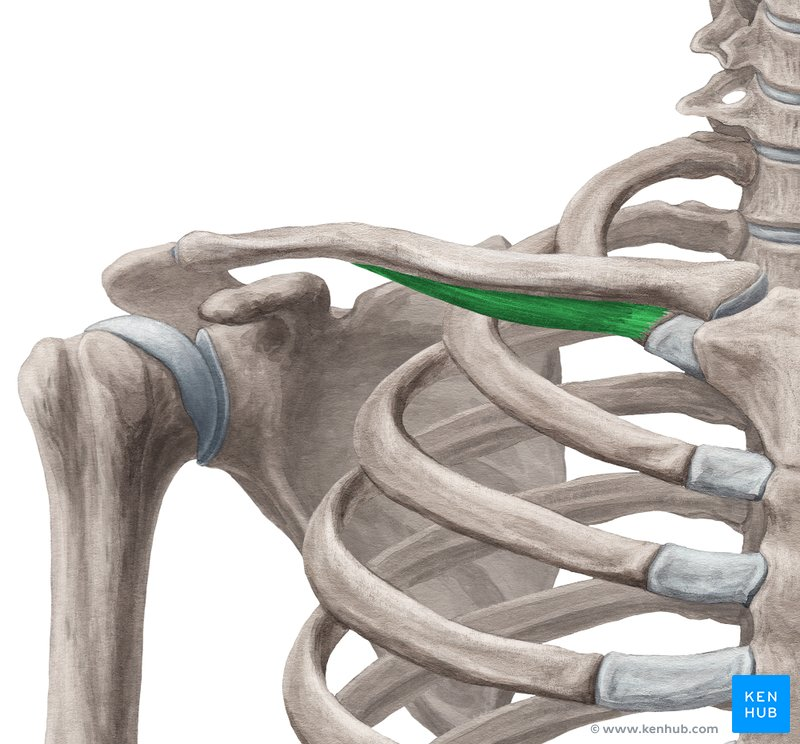
subclavius - elevate first rib
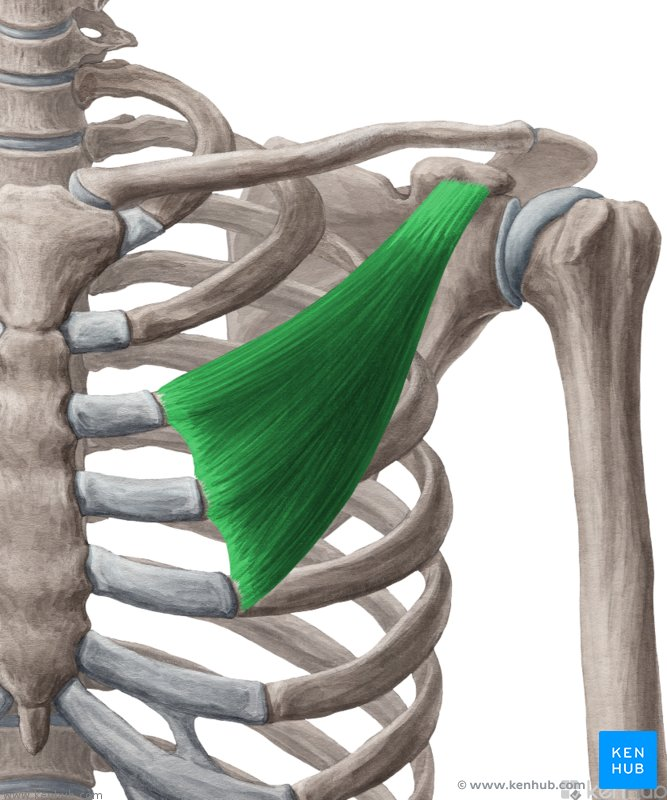
pectoralis minor - lifts ribs 2-5 (scapula fixed)
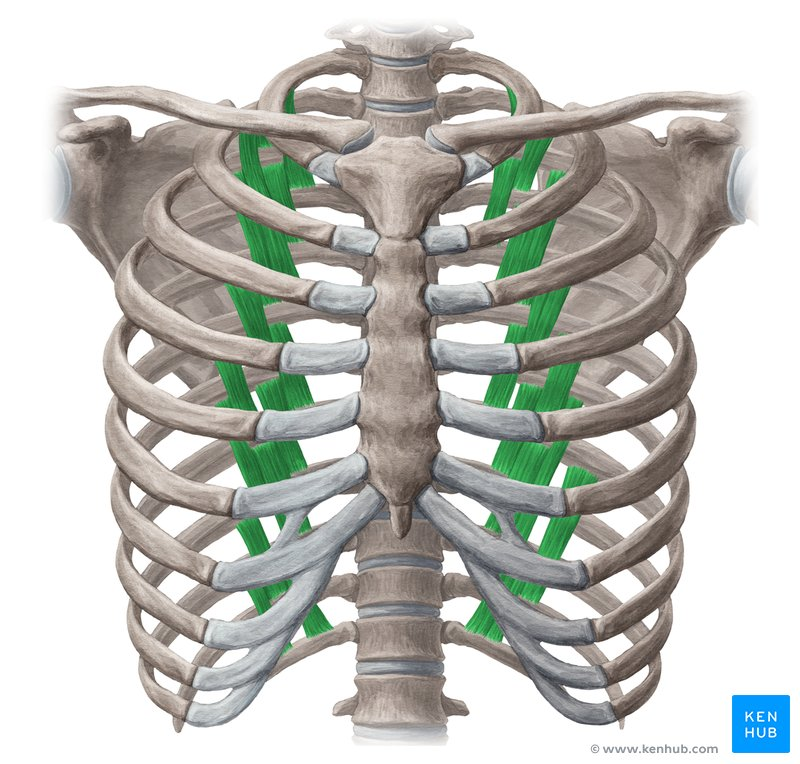
subcostal muscles - lower ribs
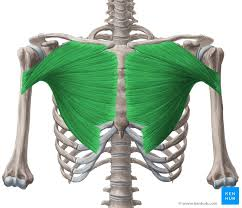
pectoralis major - draw sternum and ribs 6-7 up (shoulders fixed)
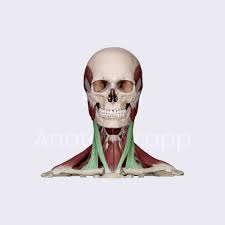
sternocleidomastoid - elevate sternum and clavicle (head fixed)
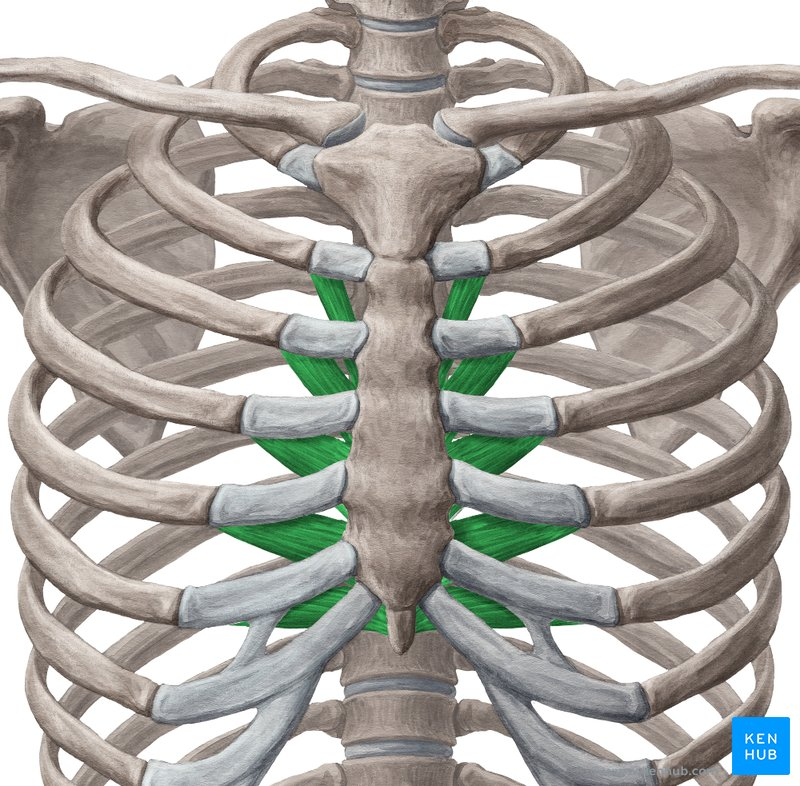
transversus thoracis - lower ribs 2-6
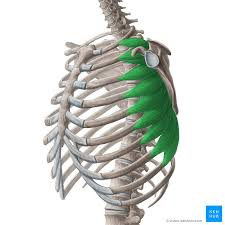
serratus anterior - elevate upper ribs (1-8)
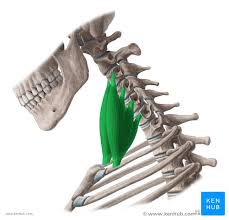
scalene muscles - elevate ribs 1 and 2 (head fixed)
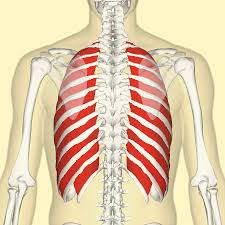
external intercostal muscles - lift rib cage upward and outward by “fixing” upper rib and raising lower one
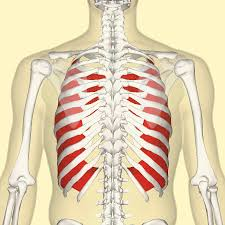
internal intercostal muscles - pulls ribs downward and inward
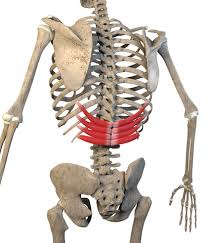
serratus posterior inferior - lower ribs 9-12
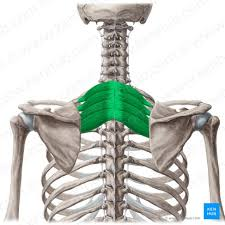
serratus posterior superior - elevate ribs 2-5
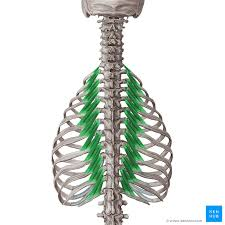
levatores costarum - elevate ribs
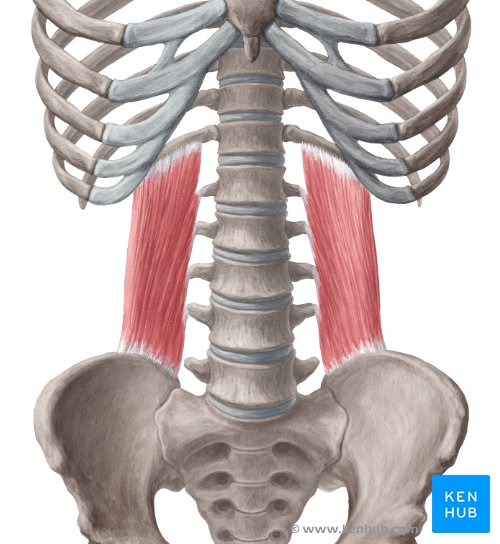
quadratus lumborum - lower lowest rib (12)
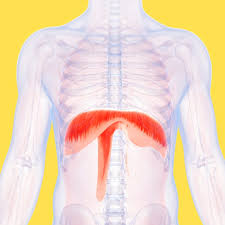
diaphragm - pulls central tendon down and forward
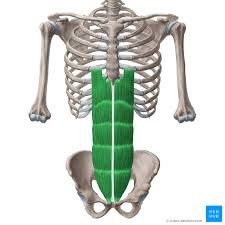
rectus abdominis - compress abdomen and lower ribs and sternum when exhaling
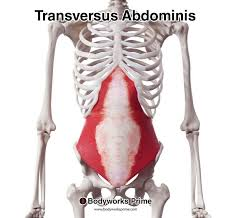
transversus abdominis - compress abdominal wall
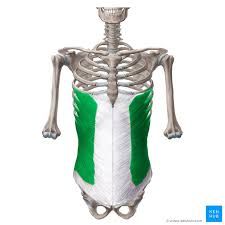
external obliques - compress abdomen and depress lower ribs (5-8)
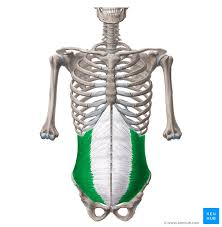
internal obliques - compress abdomen and depress lower ribs (9-12)
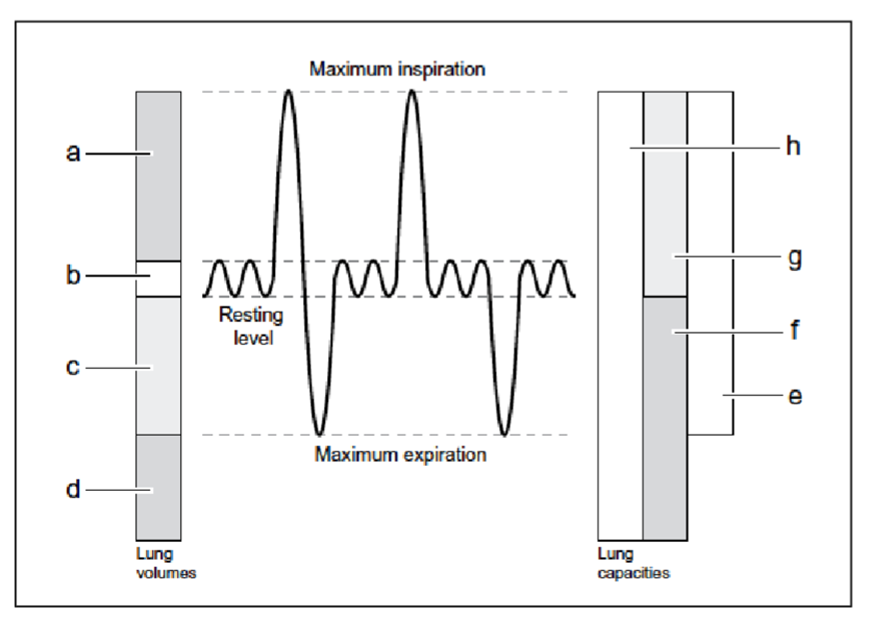
A - inspiratory reserve volume
B - tidal volume
C - expiratory reserve volume
D - residual volume
E - vital capacity (IRV + TV + ERV)
F - functional residual capacity (ERV + RV)
G - inspiratory capacity (TV + IRV)
H - total lung capacity (IRV + TV + ERV + RV)