naplex - Nonsterile Compounding
1/140
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Compounding
the process of combining/altering ingredients to create a NON FDA-APPROVED medication for an individual based on a prescription
USP (U.S. Pharmacopeia)
organization that sets minimum acceptable standards for compounding required by the FDA, state boards of pharmacy, and the Joint Commission
USP 795
USP chapter focusing on non-sterile preparations
USP 797
USP chapter focusing on sterile preparations
USP 800
USP chapter focusing on hazardous drugs
Nonsterile Compounding
the preparation of products administered orally, via tube, rectally, vaginally, topically, nasally, or in the ear
what is NOT considered compounding?
**SPLITTING, REPACKAGING, OR RECONSTITUTING ARE NOT CONSIDERED COMPOUNDING**
Reasons for Nonsterile Compounding
typically to...
1. PREPARE A DOSE/FORMULATION THAT IS NOT COMMERCIALLY AVAILABLE
2. AVOID AN EXCIPIENT
3. ADD A FLAVOR
Space Requirements of Nonsterile Compounding
includes...
1. specifically designated OPEN-AIR area SEPARATE from dispensing area of the pharmacy
2. ingredients, equipment, and containers stored off the floor
3. daily/continuous temperature monitoring
4. easily accessible sink with HOT AND COLD WATER
5. PURIFIED WATER/DISTILLED WATER/REVERSE OSMOSIS WATER for rinsing equipment and utentils
Personnel Requirements of Nonsterile Compounding
includes...
1. specifically designated person responsible for overseeing performance and operation of compounding
2. core competency training INITIALLY & EVERY 12 MONTHS
non sterile compounding training must be done:
initially then
q12 mos
hand hygiene, garbing, etc
documentation of proficiency
Hand Hygiene:
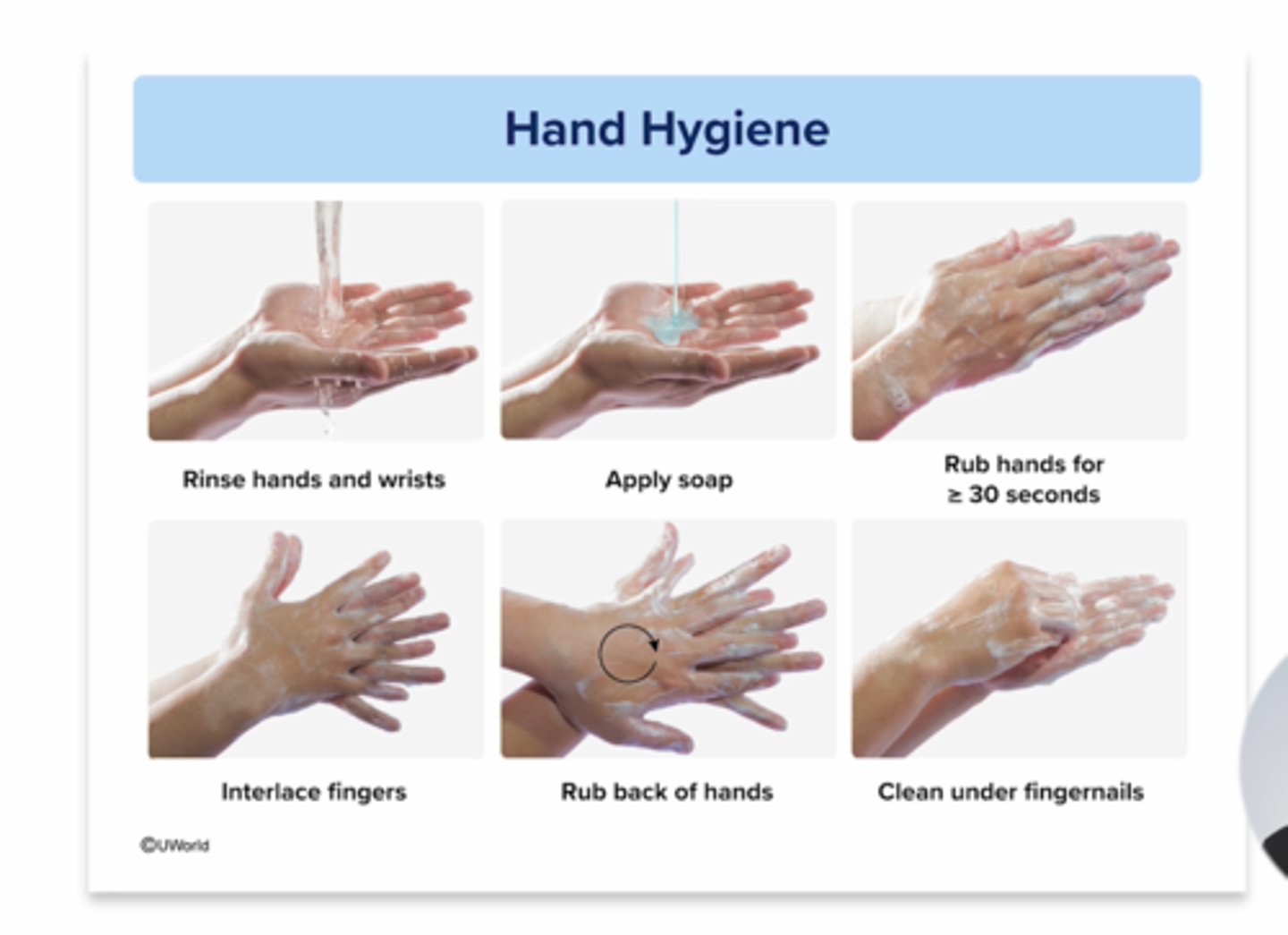
non sterile garbing

Class III Torsion Balance (Class A Torsion Balance)
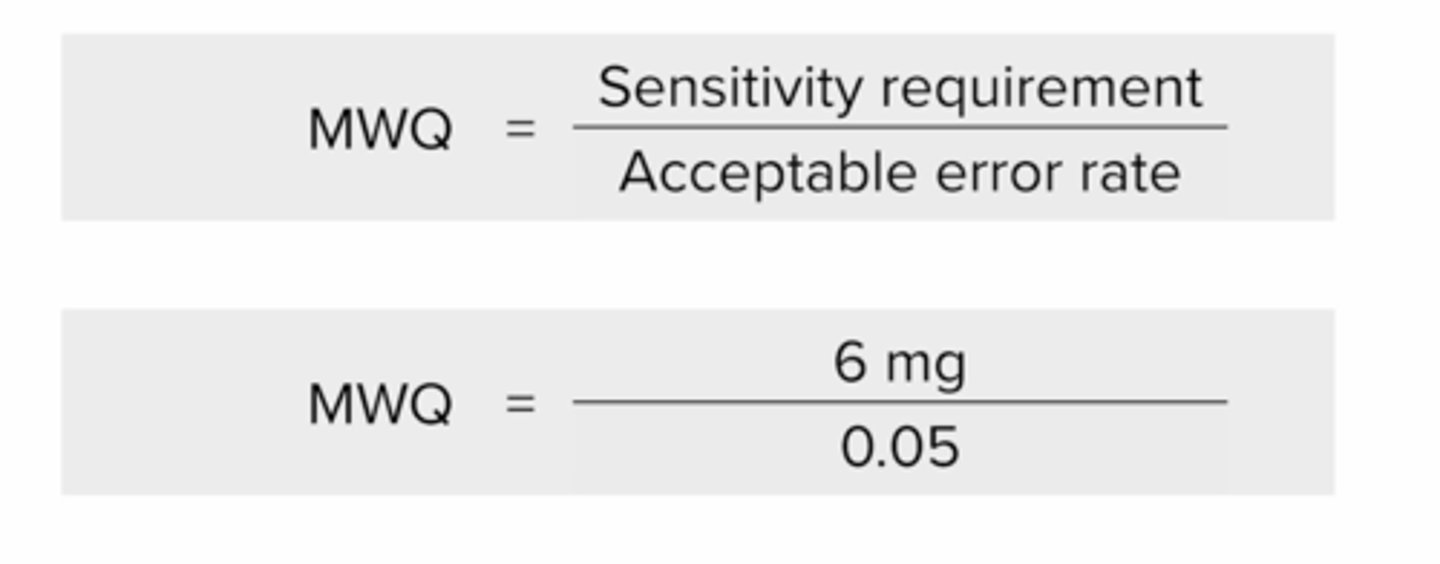
LESS COMMON and LESS PRECISE balance that has a lower sensitivity requirement and requires calculation of the minimum weighable quantity (MWQ) which calculates the smallest amount that can be weight on the balance
MWQ = SENSITIVITY REQUIREMENT / ACCEPTABLE ERROR RATE
MWQ formula
MWQ = SENSITIVITY REQUIREMENT / ACCEPTABLE ERROR RATE
Electronic (Analytical) Balance
MORE COMMON and MORE PRECISE balance that has a higher sensitivity requirement to allow very small amounts to be measured
Conical Graduated Cylinder
LESS PRECISE graduate
**THE WIDER THE MOUTH, THE LOWER THE ACCURACY**
conical graduated cyclinder, wider mouth = ____ accuracy
**THE WIDER THE MOUTH, THE LOWER THE ACCURACY**
Graduated Cylinder
MORE PRECISE graduate
20% rule
never measure volumes smaller than 20% of capacity
eg. measuring 5 ml in a 100 ml has higher risk of error than measuring 87 ml in 100 ml
the smallest amount of the graduate's total volume that can be measured without causing error
Syringes
equipment used to most accurately measure a SMALL VOLUME useful for measuring viscous/thick liquids
**CLEARLY LABEL ORAL SYRINGES WITH "FOR ORAL USE ONLY" STICKER OVER THE SYRINGE CAP**
Volumetric Pipette
equipment that draws up a set volume only and releases in drops
Mohr Pipette
equipment that draws up measured different volumes and releases in drops
Mortar and Pestle
equipment used to grind substances into a finer consistency or to stir and mix small amounts of ingredients
Glass Mortar
a type of mortar that is used for liquids
Wedgwood Mortar
a type of mortar that is used for GRINDING dry crystals and hard powders
Porcelain Mortar
a type of mortar that is used for BLENDING powders and PULVERIZING gummy consistencies
Spatula
equipment used to mix ingredients, flatten/grind ingredients, transfer ingredients, and pack preparations into containers
Metallic Ions should not be used with what spatulas
compounded mixtures that contain THIS should NEVER be handled with a steel/metal spatula
Ointment Slab
equipment used as a work surface for making ointments and other purposes
Sieve
equipment used to ensure uniform particle size
Electric Mixing Equipment
equipment that speeds up the mixing process such as...
1. OINTMENT MILL
2. HOMOGENIZER
3. GRINDER
ointment mill
mixes and reduces the particle size of powders to make ointments or creamsh
homogenizer
Electric mortar and pestle
Hot Plate
equipment that provides direct heat to soften/melt ingredients and hasten chemical reactions
Hot Plate with a Water Bath
technique used with hot plates that protects ingredients from overheating and burning for when temperatures need to be carefully controlled
Hot Plate with a Magnetic Stirrer
technique used with hot plates that continuously stirs ingredients to dissolve and mix them
Molds
equipment that helps to shape and prepare tablets, lozenges, troches, and suppositories
Tube Sealers
equipment that heats and squeezes the ends of tubes shut
compoudning ingredients =
active pharmaceuticals ingredients (drug)
+ excipients
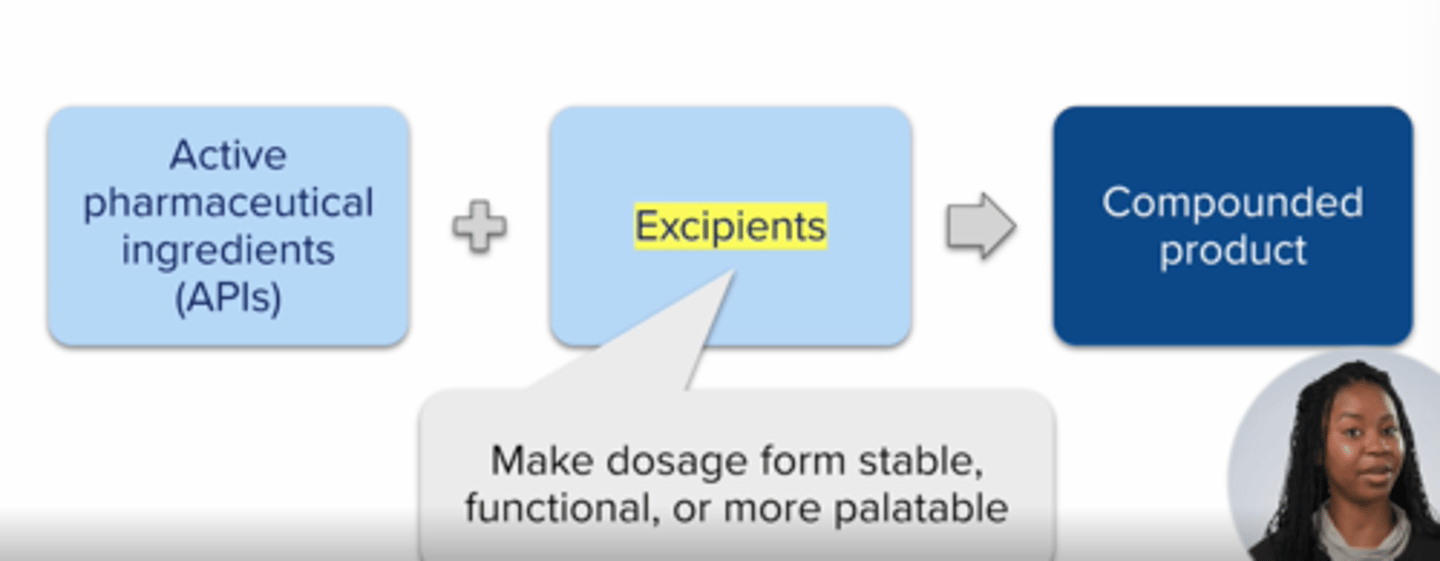
Excipients
inactive ingredients that DO NOT PRODUCE ANY THERAPEUTIC EFFECT but make the dosage form stable, functional, and/or palatable
USP-NF
official list the ensures purity and safety of ingredients used in compounding such that ALL ingredients should be listed and come from an FDA-registered facility
Expiration Date
the last day a product is considered potent and non-toxic
if a product lacks an expiration date what should the expiration date be?
**IF A PRODUCT LACKS AN EXPIRATION DATE, SHOULD BE ≤ 3 YEARS FROM DATE OF RECEIPT**
Surfactants
excipient that LOWERS surface tension between two preparations through amphiphilic interactions to make them easier to mix together
Wetting Agent/Levigating Agent
a surfactant that reduces the surface tension between a LIQUID and a SOLID
Mineral Oil
a common wetting/levigating agent for LIPOPHILIC compounds
Glycerin or PEG
a common wetting/levigating agent for AQUEOUS compounds
Suspending Agent/Dispersing Agent
a surfactant that keeps solid particles from settling when added to a suspension
Ora-Plus, Ora-Sweet, and Ora-Blend
common suspending/dispersing agents commercially available
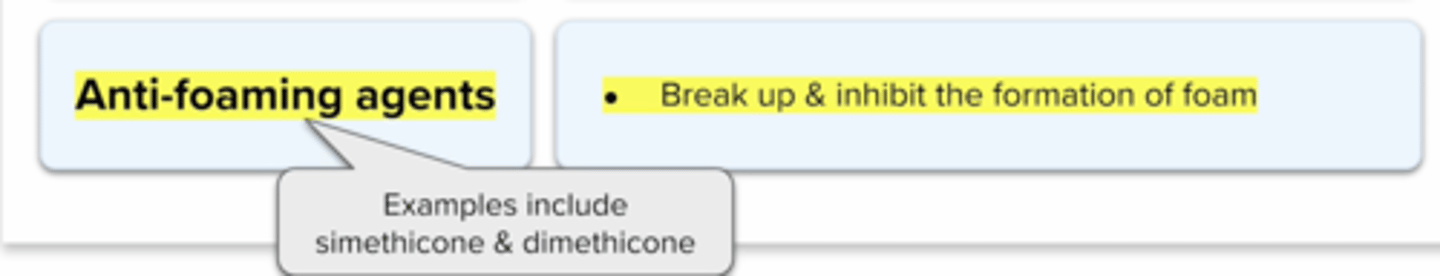
Foaming Agent
a surfactant that helps foam form to reduce the surface tension between dirt and water
eg. simethicone
glycols and gels
- Used as surfactant & delivery vehicles
eg. peg , plo
Emulsifier
a surfactant that helps keep liquid droplets dispersed throughout the liquid vehicle when added to an emulsion
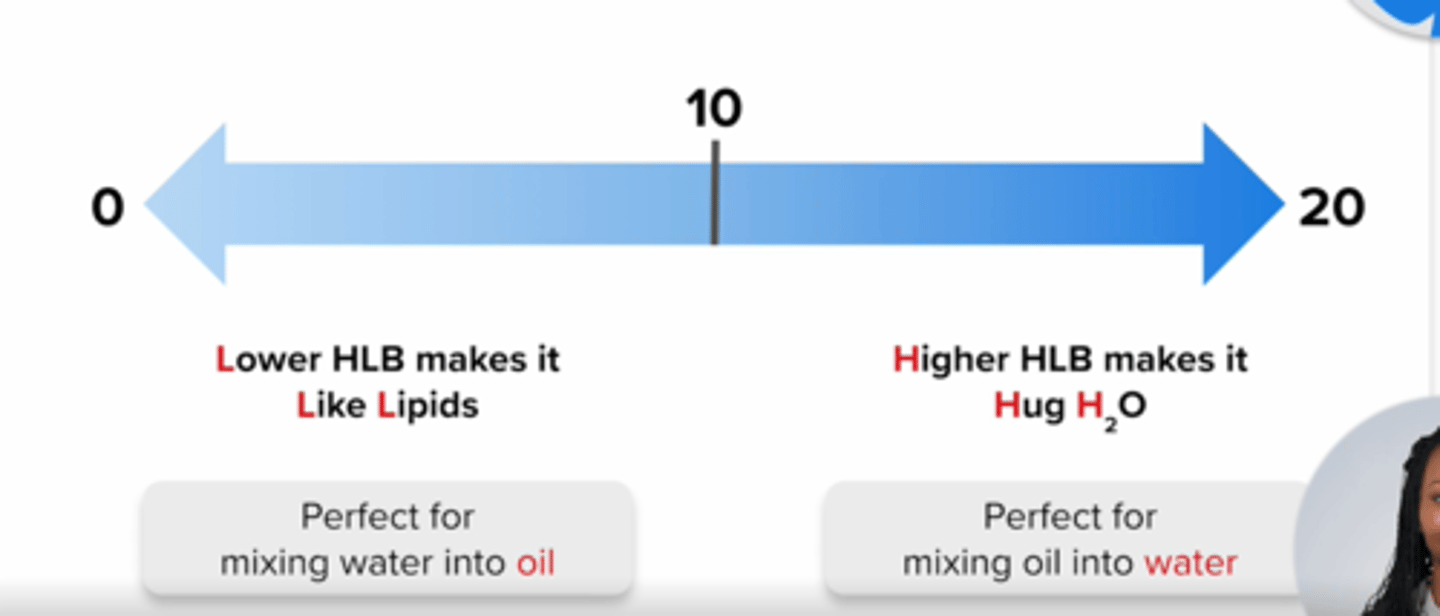
HLB Number (Hydrophillic-Lipophilic Balance Number)
value that determines the type of surfactant required to make an emulsion
HLB < 10
describes surfactants that are LIPID-SOLUBLE for use in water-in-oil (w/o) emulsions
FOR EXAMPLE: glyceryl, Span 65
remember: Lower hlb makes it Like Lipids
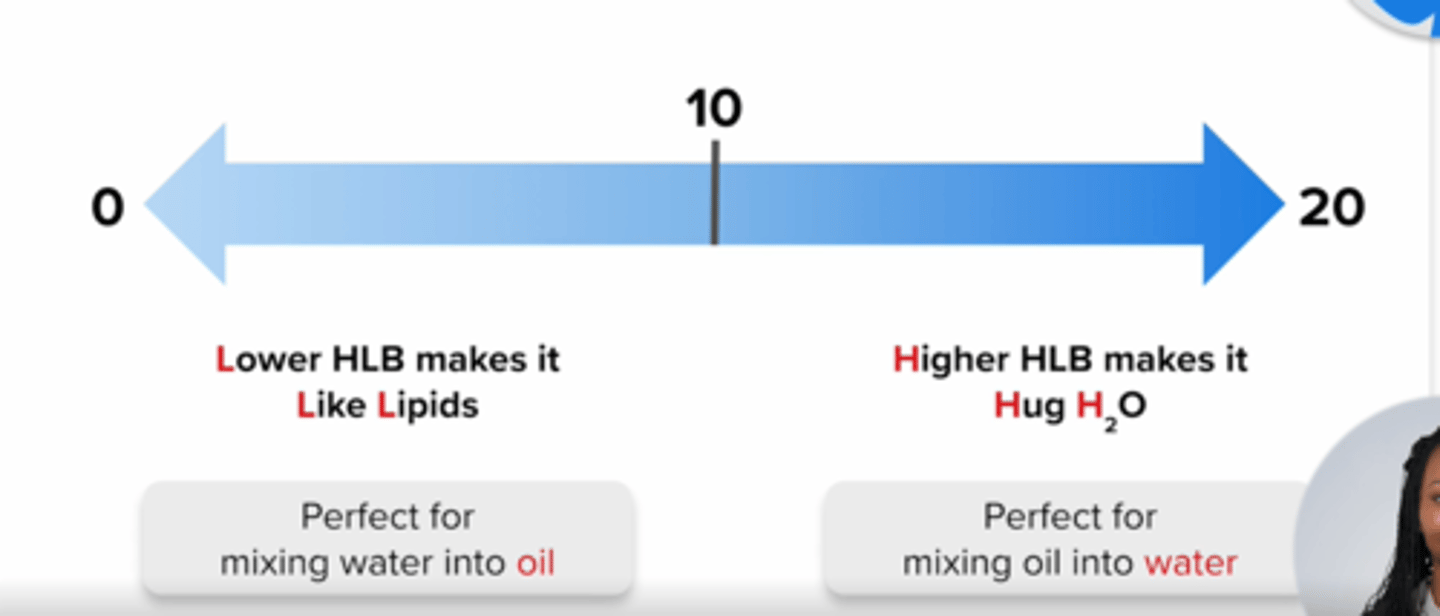
HLB > 10
describes surfactants that are WATER-SOLUBLE for use in oil-in-water (o/w) emulsions
FOR EXAMPLE: PEG 400, Tween 85
remember: Higher hlb makes it Hug water
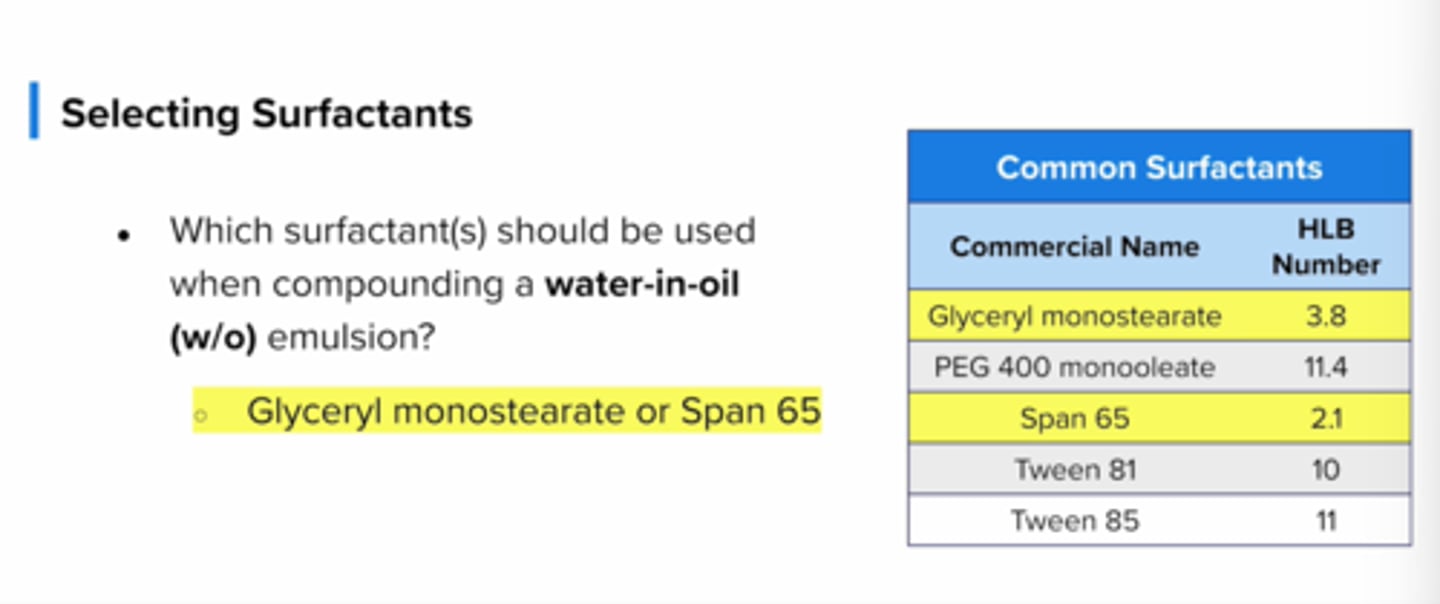
Based on the values below which surfactant(s) Should be used when compounding a water in oil emulsion?
hlb
Glyceryl monostearate 3.8
pegg 400 11.4
span 65 2.1
tween 81 10
tween 85 11
Lower = like lipids
want lower hlb <10
Binders
Allow contents of tablet to stick together to provide stability
EG. starch paste

Diluents/Fillers
To make something more dilute
fillers: To bulk up a small amount
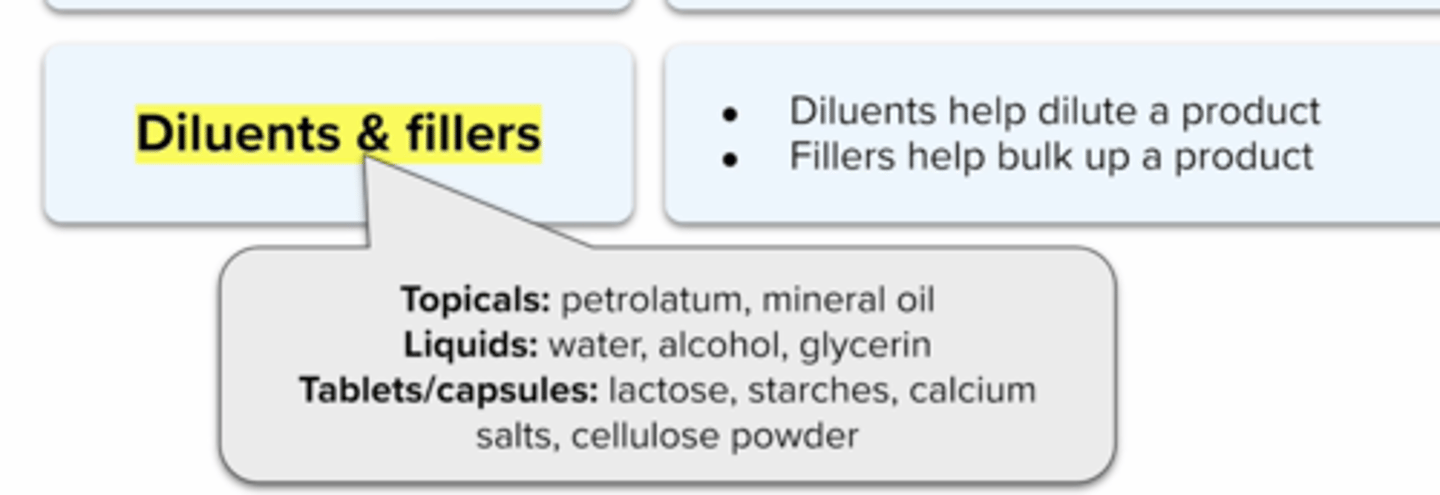
Examples of Diluents/Fillers
lactose
starches
calcium salts
cellulose
topicals:petrolatum
Disintegrants

Flavorings & colorings
Lubricants

Examples of Lubricants
mag stearate
Preservatives

Examples of Preservatives
chlorhexidine
povidine iodine
Sodium benzoate, benzoic acid, benzalkonium chloride
Sorbic acid, potassium sorbate
Methyl/ethyl/propyl parabens
EDTA
THIMEROSAL
CETYLPYRIDINIUM chloride
Buffers

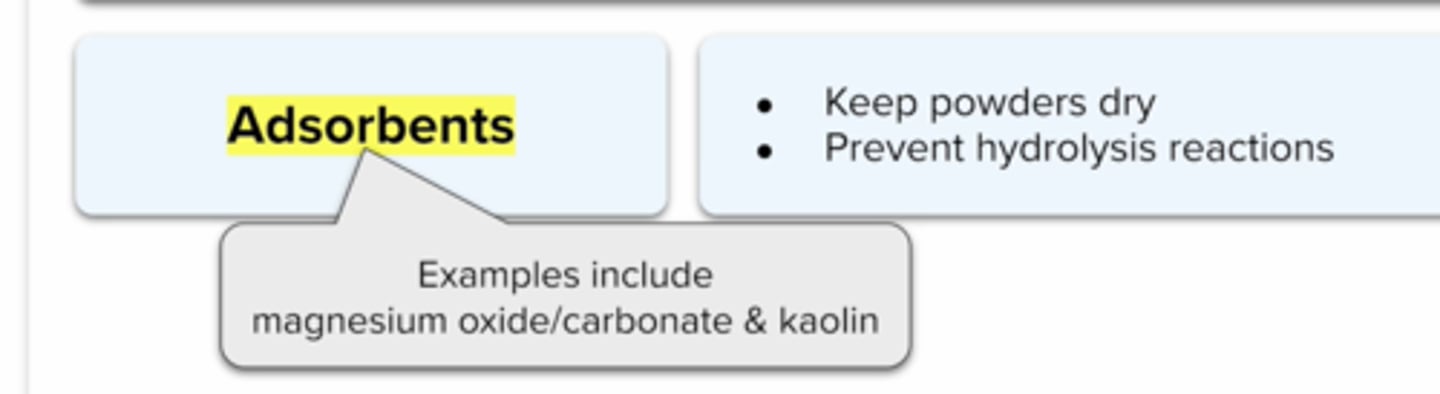
Adsorbents
Anti-Foaming Agents
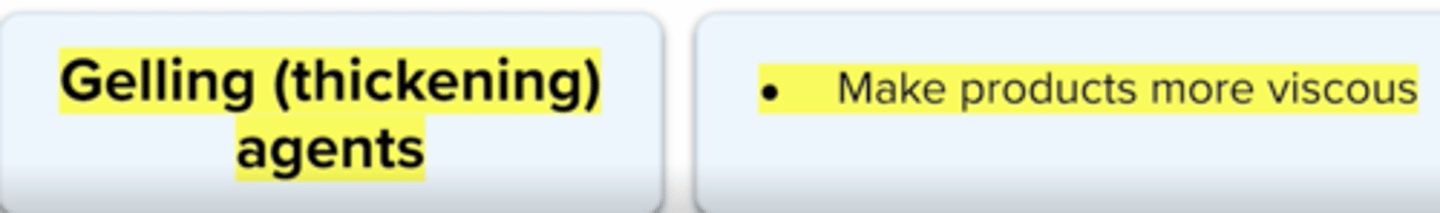
Gelling Agents
Examples of Gelling Agents
agar
Alginates
various gums( GUAR Xanthan Acacia )
gelatins
bentonite
cellulose
starches
poloxamer (pluronic) gels
Examples of Humectants
glycerin or glycerol, propylene glycol, PEG

coatings
shellac, gelatin, gluten
cellulose acetate pthelate (enteric)
mask unpalateable taste or enteric
Hydrophilic solvents
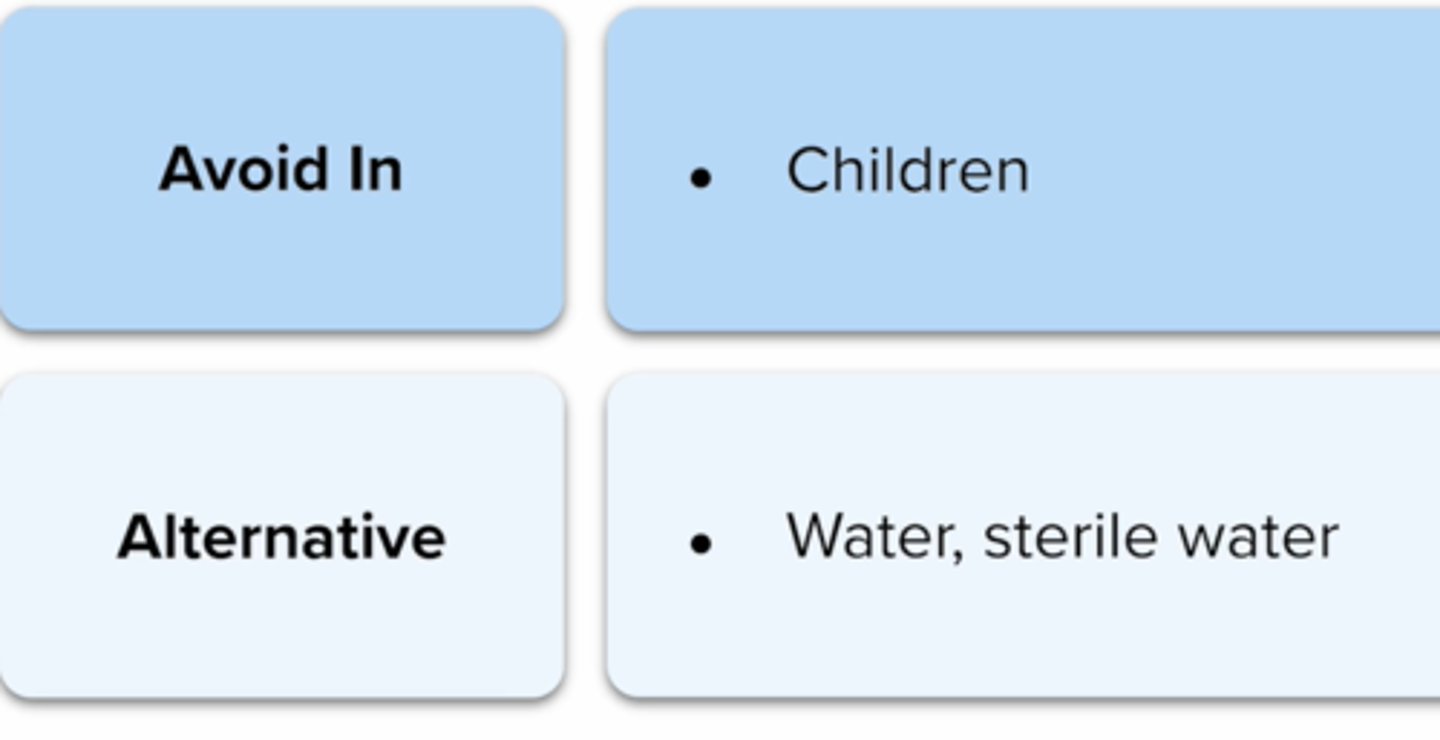
Water
Sterile water
Alcohols (benzyl alcohol, IPA 70%)
Glycols (PEG 400, poly base)
Water
Purified Water
Water treated to remove chemicals in contaminants
types of purification include distillation deionization and reverse osmosis
Distilled Water
Used to reconstitute oral suspensions and in non-stero compounding
Potable Water
Drinking/tap water
has not undergone any sterilization processes
used for hand washing
bacteriostatic water for injection contains what
who should not use it
Sterile water with preservatives
neonates should not use
Alchohols
Dissolve water insoluble solute
Benzyl alcohol contains
Preservatives
fragrance
What is the preferred disinfectant for sterile compounding
ipa 70%
polybase
peg suppository base; good emulsifier
hydrophobic solvents
oils and fats (mineral oil)
Emollients
an excipient that softens and soothes the skin which includes ointments, creams, lotions, gels, and pastes
Ointments
an emollient used for extremely dry and thick skin that contains 0-20% water of which is separated into FOUR groups...
1. HYDROCARBON BASE
2. ABSORPTION BASE
3. WATER-REMOVABLE BASE
4. WATER-SOLUBLE BASE
Hydrocarbon Base in ointments
oleaginous ointments that CONTAIN NO WATER and are hard to wash off from greasy nature
eg petrolatum , vaseline
Absorption Base in ointments
ointments that can be used to form w/o emulsions
Water-Removable Base in ointments
ointments that are o/w emulsions more akin to CREAMS per USP
Water-Soluble Base in ointments
ointments that are o/w emulsions more akin to GELS per USP
Creams
an emollient used for normal and dry skin that contains 20-50% water
Lotions
an emollient used for oily skin that contains 50+% water
Gels
works well for transdermal
Pastes
an emollient that consists of a powder in an ointment base
Alcohol Avoidance
excipient to be avoided in children
Aspartame Avoidance
excipient to be avoided in patients with phenylketonuria from inability to metabolize phenylalanine

Gelatin Avoidance
excipient to be avoided in anyone looking to avoid animal products
Gluten AvoidanceS
excipient to be avoided in anyone looking to avoid gluten

Lactose Avoidance
excipient to be avoided in lactose intolerance/allergy
Preservative Avoidance
excipient to be avoided in neonates
