Biology Chapter 7 - Photosynthesis
5.0(2)Studied by 15 people
Card Sorting
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:52 PM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
1
New cards
Autotrophs
produce their own food by using photosynthesis (or chemosynthesis) to produce organic molecules from inorganic inputs.
2
New cards
heterotrophs
must consume other organisms to get their food. Other organisms are the source of organic molecules.
3
New cards
auto
plants are ____trophs
4
New cards
grana, granum
stacked thylakoids =
5
New cards
chloroplast
photosynthesis occurs in _______ organelles
6
New cards
stroma
fluid surrounding thylakoids/granum =
7
New cards
pigment in thylakoid membrane that captures sunlight
chlorophyll
8
New cards
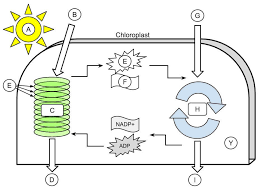
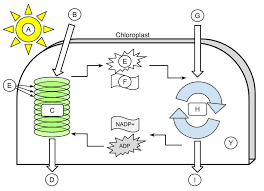
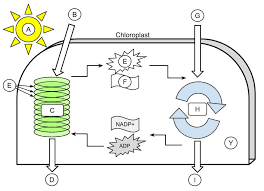
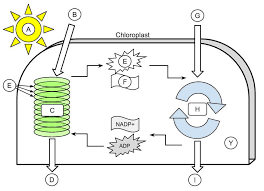
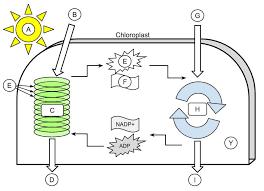
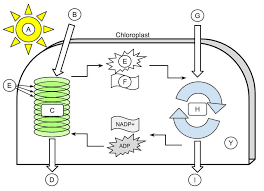
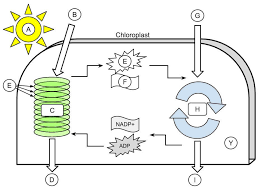
sunlight
A
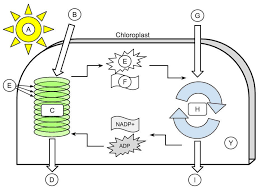
9
New cards
H2O
B
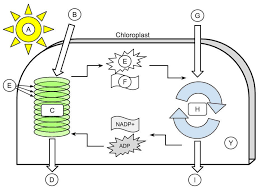
10
New cards
light dependent reactions
C
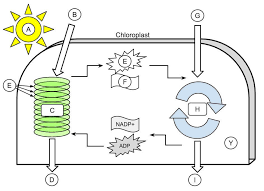
11
New cards
Oxygen
D
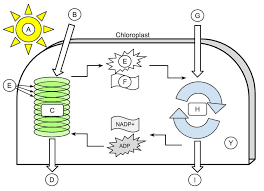
12
New cards
thylakoid
E (the green ovals)
13
New cards
ATP
E (the little starbursty thing in the middle)
14
New cards
NADPH
F
15
New cards
CO2
G
16
New cards
Calvin cycle
H
17
New cards
Glucose
I
18
New cards
Stroma
Y
19
New cards
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
20
New cards
allows for gas exchange (CO2 enters, oxygen exits)
stomata function
21
New cards
absorbs, reflects
Chlorophyll _____ __red, blue, violet wavelengths, and _______ green and yellow wavelengths.__
22
New cards
Chlorophyll reflects green
Why do leaves appear green?
23
New cards
sunlight
What energy powers photosynthesis?
24
New cards
substances (proteins) that absorb light, give color to objects based on which wavelengths they absorb or reflect.
What are pigments?
25
New cards
thylakoid membrane
Where is chlorophyll found?
26
New cards
reduced
CO2 is _______ to a G3P molecule
27
New cards
stroma
Where does the Calvin cycle occur?
28
New cards
thylakoid membrane
Where do the light dependent reactions occur?
29
New cards
light dependent reactions
energy-capturing reaction
30
New cards
calvin cycle
carbon dioxide becomes glucose in which reaction
31
New cards
do include other atoms
the carbon molecules in the calvin cycle do or do not include other atoms besides carbon?
32
New cards
light dependent reaction
NADP+ takes up energized electrons in which reaction
33
New cards
light dependent reaction
NADPH and ATP are made in which reaction
34
New cards
calvin cycle
NADPH and ATP are used in which reaction
35
New cards
oxygen and glucose
2 things released by photosynthesis
36
New cards
H2O, CO2, sunlight
3 things reacting in photosynthesis
37
New cards
ATP, NADPH, O2
3 products of LDR
38
New cards
ADP+P, NADP+, glucose
3 products of Calvin cycle
39
New cards
H2O, ADP+P, NADP+, sunlight
4 reactants of LDR
40
New cards
CO2, ATP, NADPH
3 reactants of Calvin cycle
41
New cards
blue
Photosynthesis happens most efficiently at ____ wavelengths
42
New cards
green
Photosynthesis happens least efficiently at ____ wavelengths
43
New cards
Calvin cycle and light dependent reactions
2 major sets of reactions involved in photosynthesis
44
New cards
chemiosmosis
Process by which hydrogen ions are concentrated in the thylakoid space
45
New cards
RuBP, Rubisco, G3P
CO2 is fixed to ______ __by__ _______, and is reduced to__ _____
46
New cards
one out of 6
How many G3P molecules leave the Calvin cycle each turn?
47
New cards
regenerating RuBP
the other five G3P cells are used for what?
48
New cards
5-carbon molecule in Calvin cycle
RuBP
49
New cards
enzyme that joins RuBP and CO2
Rubisco
50
New cards
they immediately split apart into two 3 carbon molecules
What happens when RuBP and CO2 join?
51
New cards
carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration of RuBP
3 stages of the Calvin cycle
52
New cards
CO2 joins to RuBP using rubisco
What happens in carbon fixation?
53
New cards
the 3-carbon molecule is reduced to G3P using atp and NADPH
What happens in reduction?
54
New cards
reduction and regeneration
In what stages of the calvin cycle is ATP used?
55
New cards
Electrons fuse to 3-carbon molecule using energy of ATP
What is the role of atp and nadph in reduction?
56
New cards
6
How many G3P are made in reduction?
57
New cards
G3P reforms RuBP to continue the cycle
What happens in regeneration?
58
New cards
glucose
G3P is used to create *_____*
59
New cards
C3
Most plants are ____ plants
60
New cards
C3
What type of plants photorespirate?
61
New cards
oxygen enters the plant, creating a useless product that must be broken down
photorespiration
62
New cards
stomata only open at night
CAM plant adaptation
63
New cards
fixation stage happens in a different cell from the rest of the Calvin cycle
C4 plant adaptation
64
New cards
CAM
succulents and cactus are ____ plants
65
New cards
capture sunlight energy and guide excited electrons to the electron transport chain
What is the function of photosystem II?
66
New cards
re-energize electrons to be sent to reduce NADP+
What is the function of photosystem I?
67
New cards
harvest energy from excited electrons to actively transport H+ ions across the thylakoid membrane to increase the concentration gradient
What is the function of the electron transport chain?
68
New cards
lower, higher
The concentration of H+ ions is ______ __in the stroma and__ _____ in the thylakoid space
69
New cards
H+ ions will then passively transport by facilitated diffusion through ATP synthase
What is the function of the concentration gradient of H+ ions in the thylakoid membrane/stroma?
70
New cards
ATP synthase spins like a water wheel, providing the energy to create ATP from ADP and P
What happens when the H+ ions flow through ATP synthase?
71
New cards
protons
H+ ions are also known as
72
New cards
water splits and provides electrons
How does photosystem II replace lost electrons?
73
New cards
H+ ions (protons), electrons, and oxygen
3 things released when water splits
74
New cards
lumen
thylakoid space is also known as
75
New cards
C3
carbon dioxide is fixed into a 3-carbon molecule in the fixation stage in _____ plants
Explore top notes
Chapter 11: Human Genetic Variation (and Chapter 15.2 Chromosomal Abnormalities)
Updated 1074d ago0.0(0)
Chapter 11: Human Genetic Variation (and Chapter 15.2 Chromosomal Abnormalities)
Updated 1074d ago0.0(0)