Lab 2 - Microscopic Analysis of Blood
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Plasma and formed elements
Blood is divided into...
Water
What is the plasma primarily composed of?
Connective
Blood is ____________ tissue
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
What are formed elements?
Nutrients, waste, gases, enzymes, protein, hormones, and electrolytes
What is dissolved within plasma?
true cells
Not all formed elements are ______ _______
red bone marrow
Erythrocytes (RBCs) are produced in the ____ _______ ________
The cell has a pinch in the middle
What does biconcave mean?
Rouleau
A cylinder of flowing RBCs
blood vessels
Biconcavity aids in allowing RBCs to travel single file through narrow ________ _________
more flexible
Does biconcavity make RBC more or less flexible
anucleate
Erythrocytes have no nuclei, aka
Hemoglobin
Because RBCs are anucleate they can contain a large amount of the protein __________
Bind and release oxygen
Function of hemoglobin?
Oxygen transport within the body
Function of erythrocyte?
They are biconcave in shape, have no nucleus, and contain large hemoglobin
3 factors help RBCs carry out their function
Platelet
The second most abundant formed element
Small
What is the size of a platelet?
Platelets
Membrane-bound sacks of chemicals that are vital to the blood clotting process
red bone marrow
Platelets are formed in the _____ ________ __________
Purple
Color of platelet?
platelet plug
When the wall of a blood vessle is damaged, platelets respond by sticking to the wall and forming a _____________ _______
temporary
The platelet plug is a ___________ clot
Erthrocytes
Almost half of our blood is _____________
Erythrocytes (red blood cells)
What are the red circles?
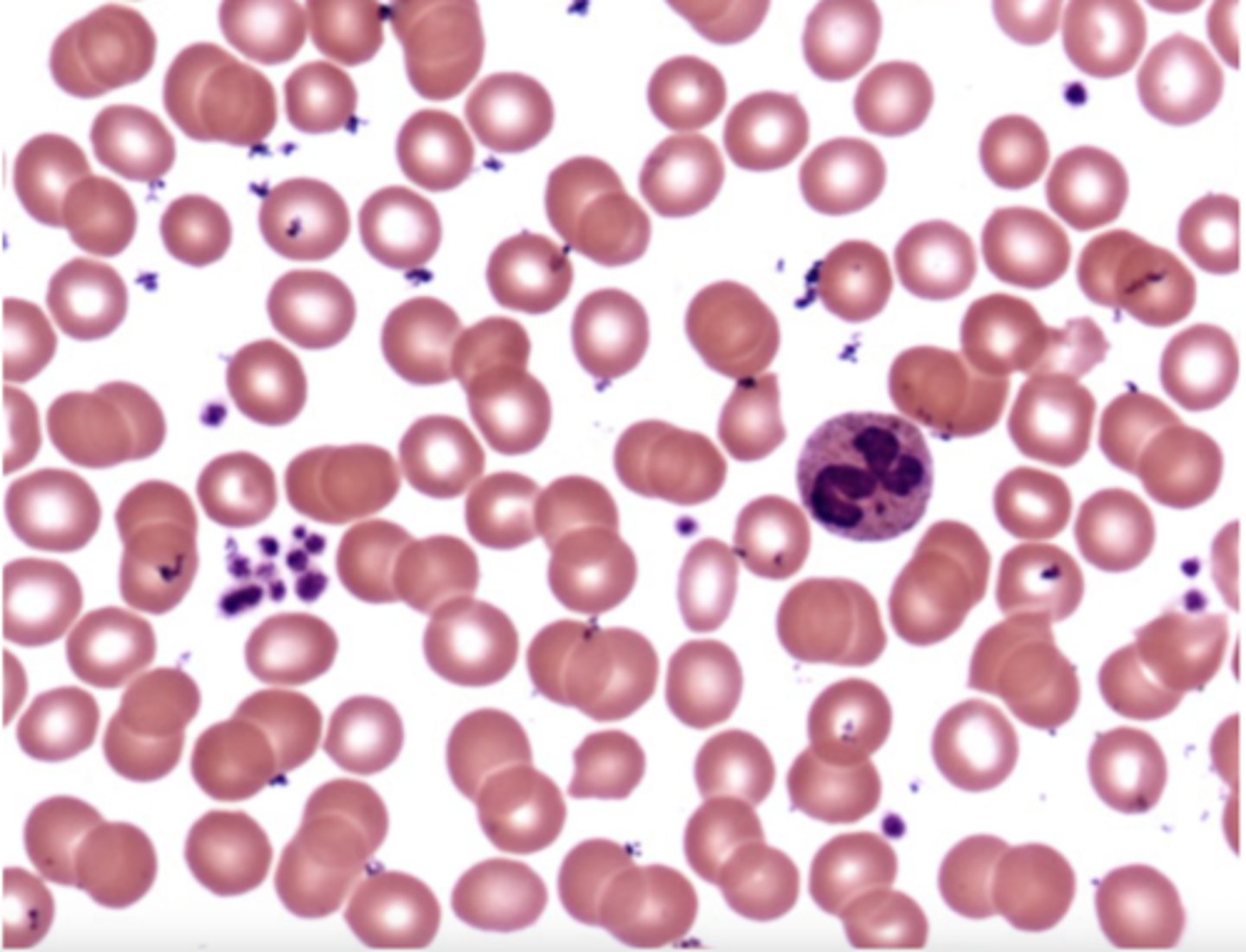
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
What are the purple dots?
Leukocytes
least abundant formed element
Bone marrow
WBCs are produced in the...
Granulocytes and agranulocytes
WBCs are divided into 2 classes called:
Granulocytes
Leukocytes with stained cytoplasmic granules are known as
Agranulocytes
Leukocytes without stained cytoplasmic granules are known as
Neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
What are the 3 types of granulocytes?
Monocytes and lymphocytes
What are the 2 types of agranulocytes?
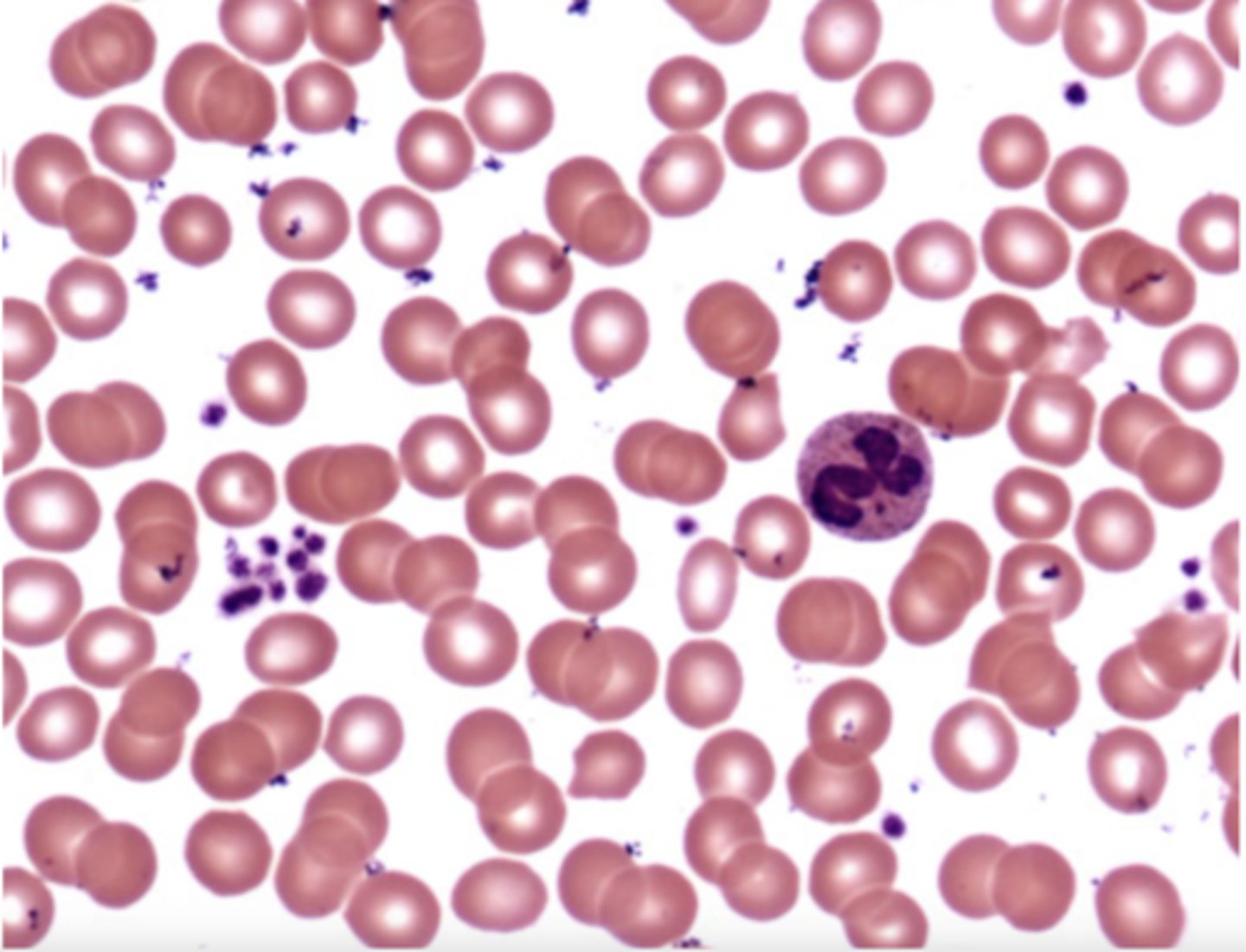
Neutrophil
What is the center cell?
They look like they have 4 lobed nuclei
Why are neutrophils sometimes said to be polymorphonuclear leukocytes?
Neutrophil
The most abundant WBC
lilac (light purple)
What is the color of neutrophil granules?
Acute bacteria slayer (bacteria destroyer)
Function of neutrophil?
60%
Neutrophils form about ____ of circulating leukocytes
First
Neutrophils are the _______ to arrive at an injury site
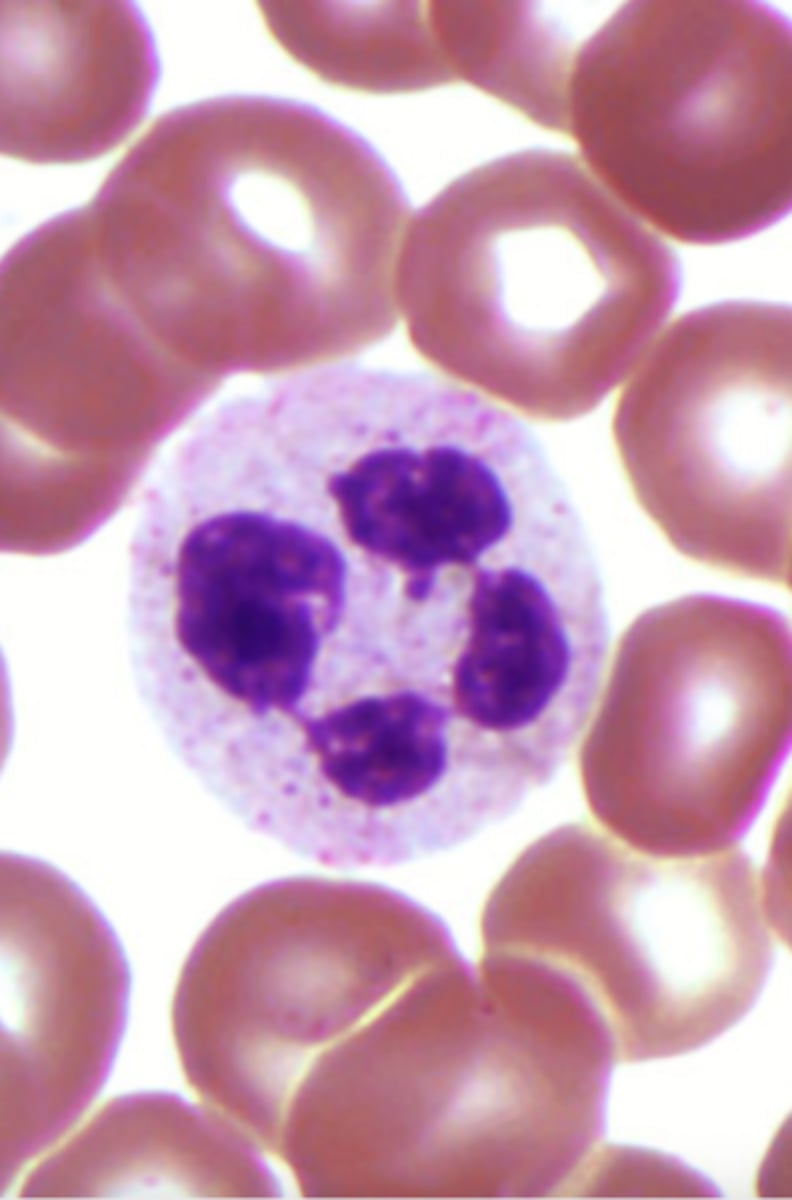
Eosinophil
What is the center cell?
Red
What is the color of eosinophils' granules
U-shaped/bent
What is the shape of eosinophils' nucleus
3%
Eosinophils form about ____ of circulating leukocytes
Kill parasitic worms and release granules during an allergic response
Function of eosinophil?
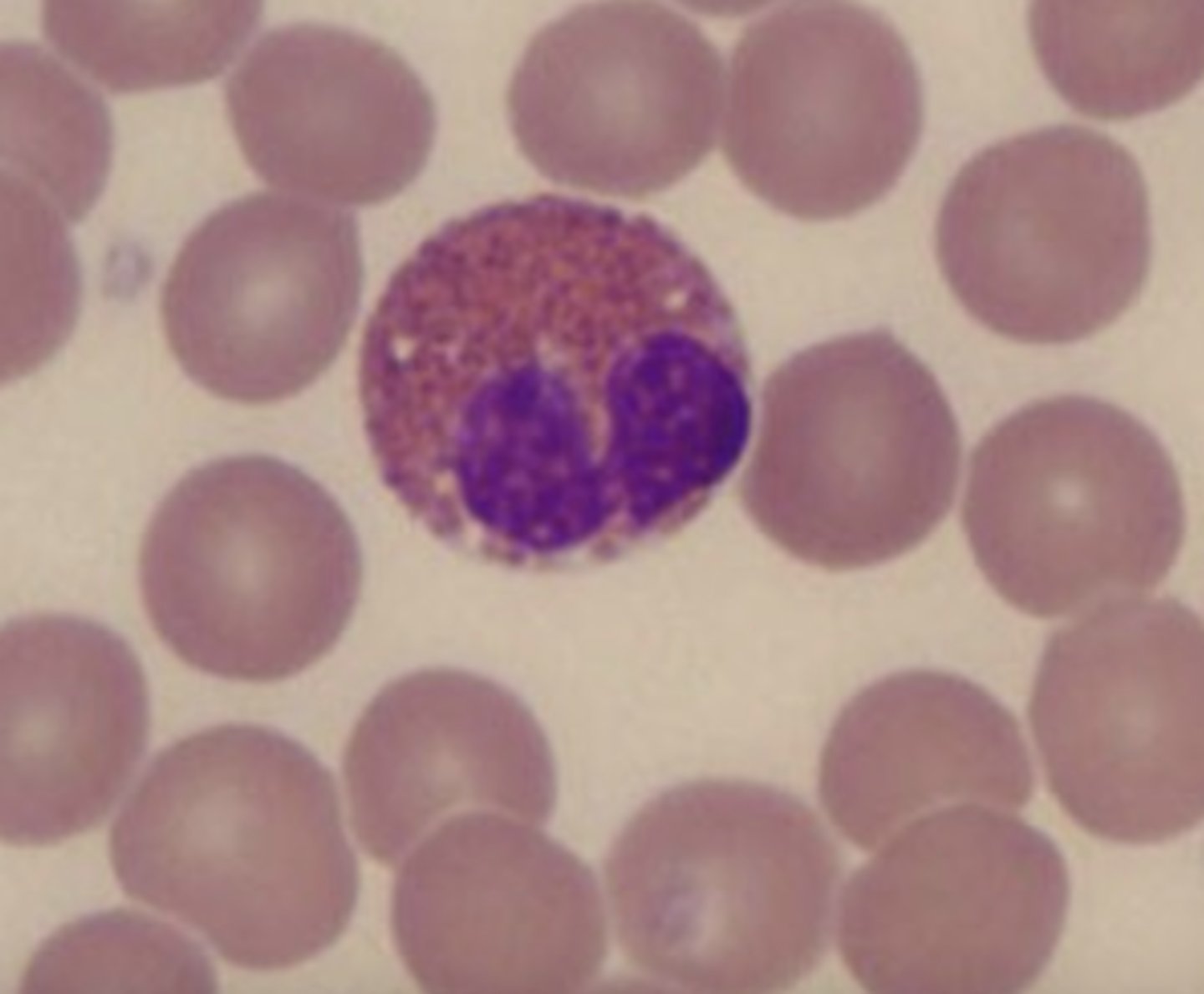
Basophil
What is the center cell?
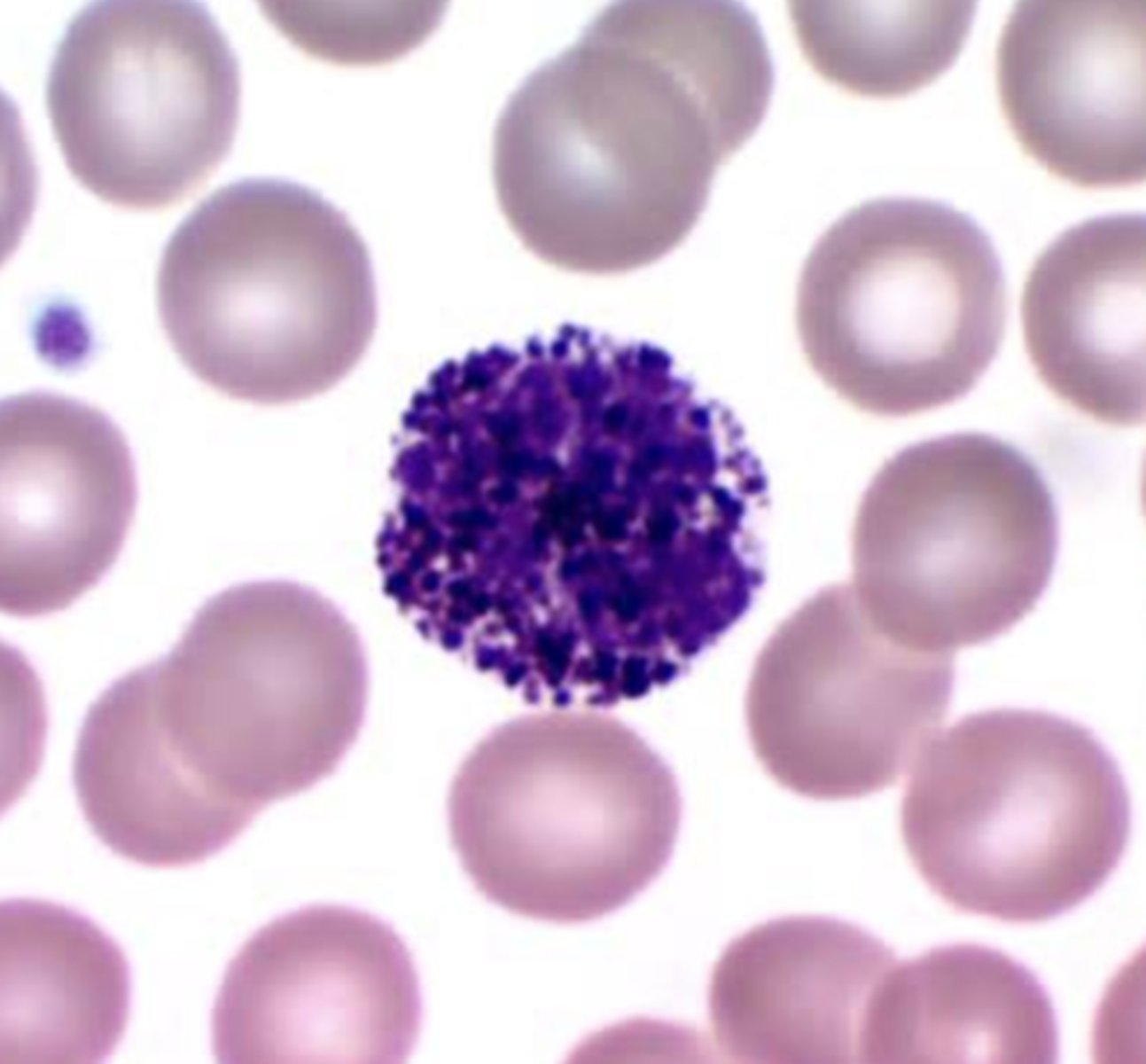
Lobed
What is the shape of a basophil's nucleus?
Dark purple/black
What is the color of basophils' granules
1%
Basophils form less than ____ of circulating leukocytes
Releases its granules (histamine and heparin) at the injury site, which enhances inflammation
Function of basophils
Histamine and heparin
What are the 2 chemicals in the granules of a basophil?
A vasodilator
Function of histamine?
A anticoagulant
Function of heparin?
Lymphocyte
What is the center cell?
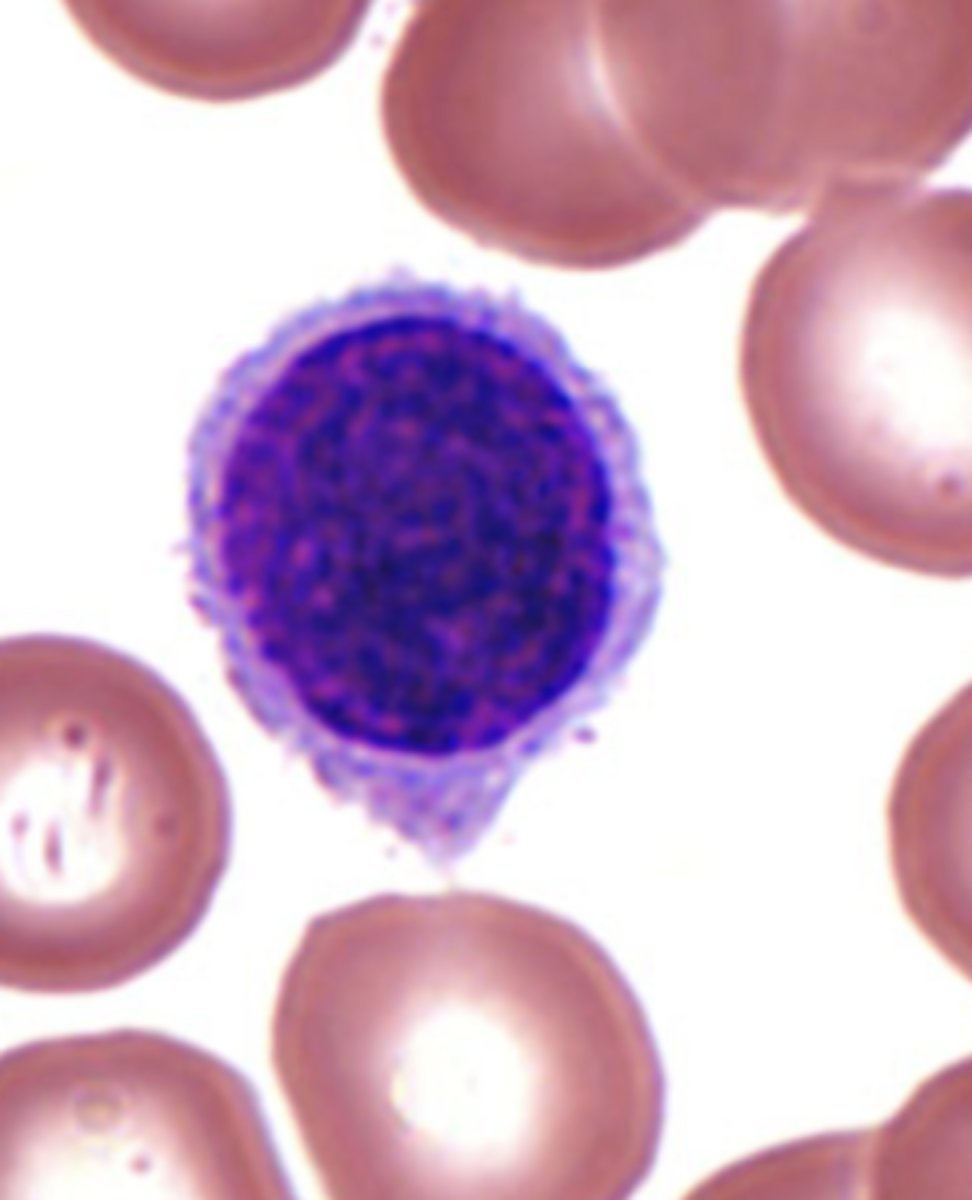
Round
What is the shape of a lymphocyte's nucleus?
Only a little
How much cytoplasm is visible in a lymphocyte?
None
How many stained granules does the lymphocyte contain?
30%
Lymphocyte form about ____ of circulating leukocytes
T cells and B cells
What are the 2 main types of lymphocytes
Secrecion of antibodies
Function of B cells
Controls the immune system and kills cancerous cells
Function of T cells
Monocyte
What is the center cell?
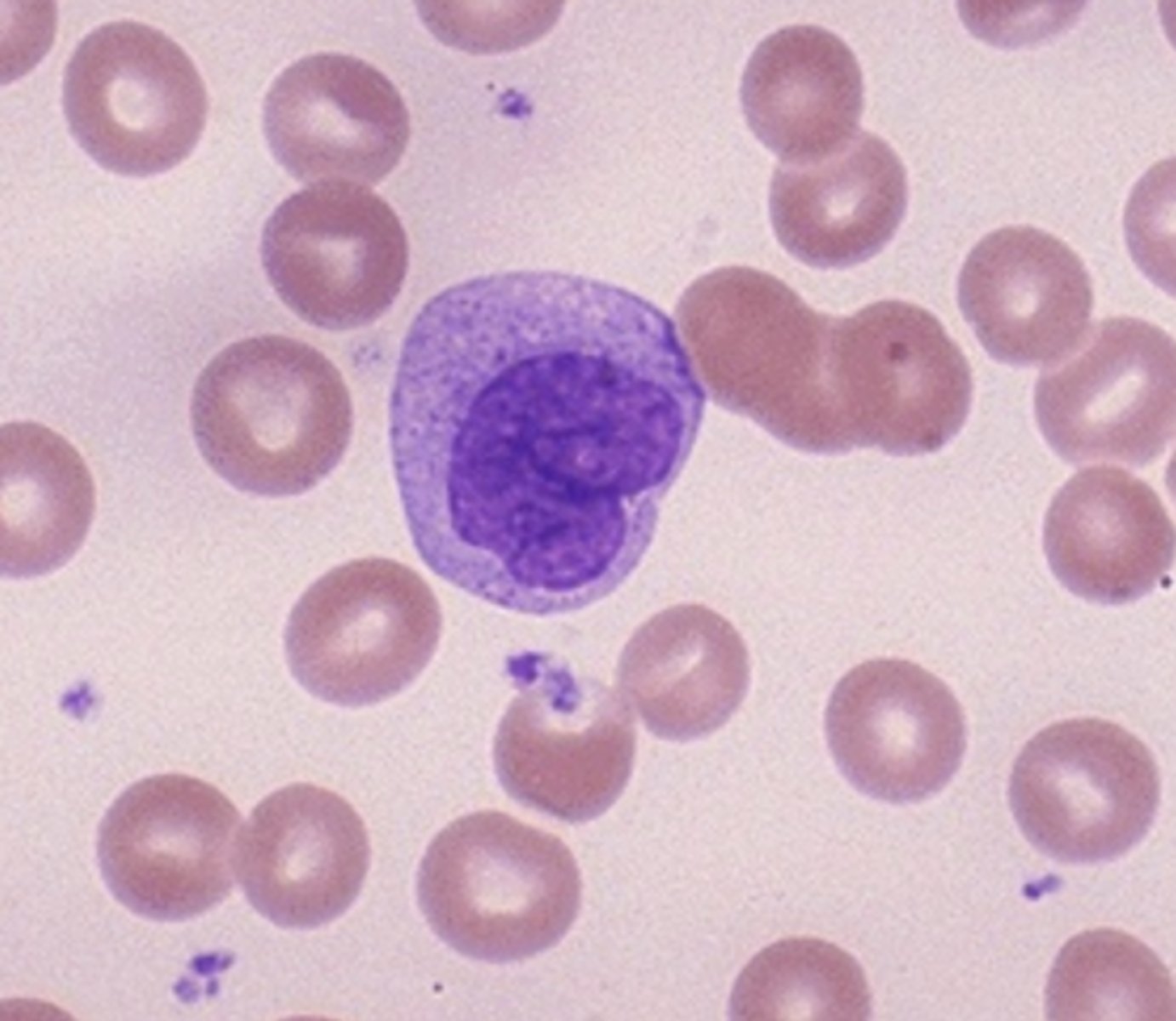
C-shaped/bent
What is the shape of a monocyte's nucleus?
Very little
How many stained granules does this monocyte contain?
Bigger
Is a monocyte bigger or smaller than an RBC?
6%
Monocytes form about ____ of circulating leukocytes
Macrophages
Monocytes turn into ____________ when they exit the blood and enter peripheral tissue
Chronic bacteria slayer
Function of monocyte?
Rid the body of foreign invaders and cellular debris
Function of macrophage?
Float
Monocytes ______ through tissue constantly
Lymphoid organs; loose connective tissue
The majority of WBCs are not found in the blood. Most reside in the _________ ____________ (eg., spleen/lymph nodes) or in the bodies __________ _____________ ________
travel
The blood is mainly used by leukocytes as a means of...
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
Phrase to remember the abundance of circulating WBCs
Differential white cell count
When you calculate the percentage of WBCs that are each type.
(# of specific WBC/total # WBCs) x 100
What is the differential white cell count formula
pathological conditions
Abnormality in the differential count indicates a
Pregnacy
High count of neutrophils could indicate
Hepatitis
High count of lymphocytes could indicate
leukemia
High count of monocytes could indicate
allergic reaction
High count of eosinophils could indicate
cancers
High count of basophils could indicate
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Low count of neutrophils could indicate
HIV infection
Low count of lymphocytes could indicate
Bone marrow suppression
Low count of monocytes could indicate
Stress
Low count of eosinophils could indicate
ovulations
Low count of basophils could indicate
Decreased clotting ability
What would be the most important consequence of platelet deficiency?
Leukocytes, because they are nucleated and have organelles
Which formed elements are the only "true cells"? Why?
Parasitic worm infections
Rachel's differential white cell count showed that 19% of her circulating leukocytes were eosinophils. What is the reason why?
Platelet
Formed element associated with blood clotting?
Monocyte
Formed element associated with chronic bacterial infection?
Eosinophil
Formed element associated with cestode infection (intestinal worm)?
Erythrocyte
Formed element associated with gas transport?
Basophil
Formed element associated with a normal inflammatory response?
Lymphocyte
Formed element associated with the destruction of cancerous cells?
Erythrocytes
Formed element associated with anucleate?
Monocyte
Formed element associated with macrophage?
Neutrophil
Formed element associated with weakly staining granules?
Neutrophil
Formed element associated with a multi-lobed nucleus?
Neutrophil
Formed element associated with acute bacterial infections?