Cross Sectional Anatomy I Chapter 5 Spatial encoding
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
After reading this chapter, you will be able to: Describe gradients and how they work. Explain slice-selection. Understand how gradients spatially locate signal in a slice. Apply what you have learned to explore how gradients are used in common pulse sequences.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
True/False
The pharynx is approximately 15 cm long.
False
True/False
The thyroid cartilage is the smallest and most inferior of the unpaired cartilages in the larynx
False
True/False
The salivary glands produce saliva and empty it into the oral cavity via ducts.
True
True/False
The thyroid gland is located at the level of the hyoid bone
False
True/False
The trachea bifurcates into the right and left mainstem bronchi at approximately the T5 level
True
True/False
The anterior triangle of the neck contains the scalene muscles
False
True/False
The vertebral arteries pass through the transverse foramina of C6–C1 vertebrae.
True
True/False
The glottis is the part of the larynx most directly involved in voice production
True
True/False
The esophagus lies immediately anterior to the trachea
False
True/False
There are approximately 300 lymph nodes located in the head and neck region
True
Larynx
Bony skeleton that surrounds and protects the vocal cords
Pharynx
Contains the superior, middle, and inferior constrictor muscles
Trachea
Located anteriorly to the esophagus and reinforced by C-shaped cartilage
Thyroid gland
Excretes thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin
Vertebral arteries
Supplies blood to the posterior aspect of the brain
Sublingual glands
Smallest of the three major salivary glands
Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
Divides the neck into anterior and posterior triangles
Oropharynx
Contains palatine and lingual tonsils
Epiglottis
Elastic cartilage shaped like a leaf
Thyroid cartilage
Forms a vertical projection called the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple)
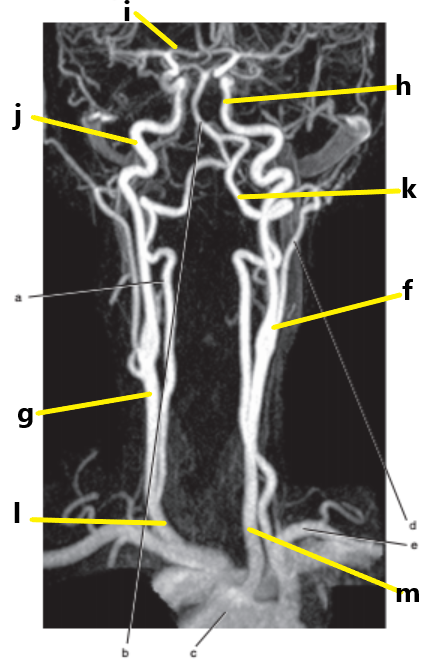
What is letter l ?
Common carotid
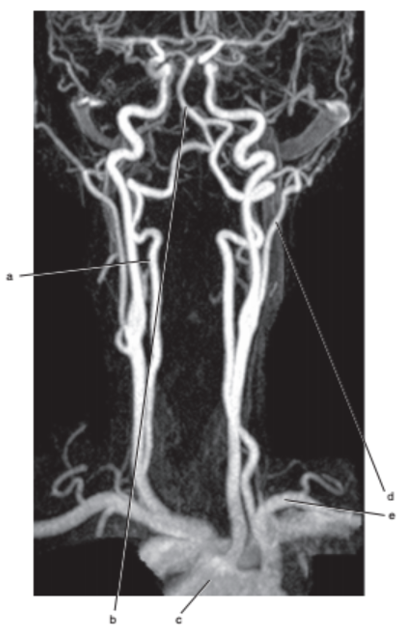
What is letter e ?
Subclavian artery
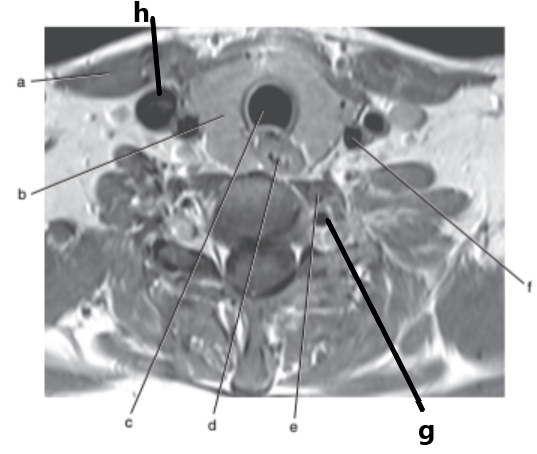
What is letter f ?
Common carotid artery
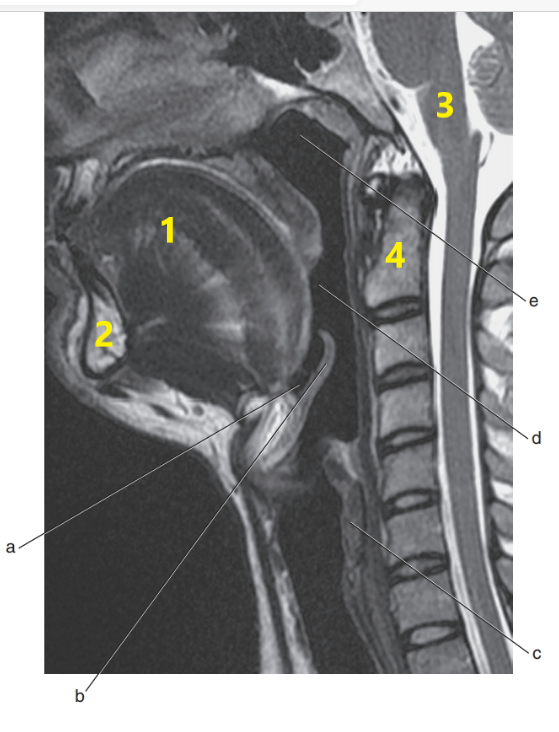
What anatomy is letter e ?
Nasopharynx
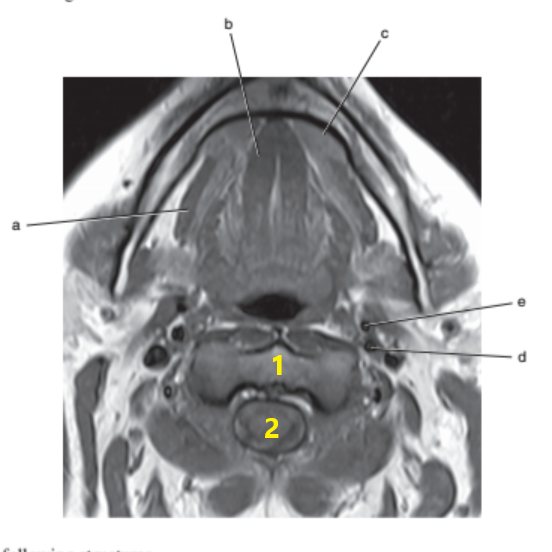
What is letter c ?
Sublingual gland
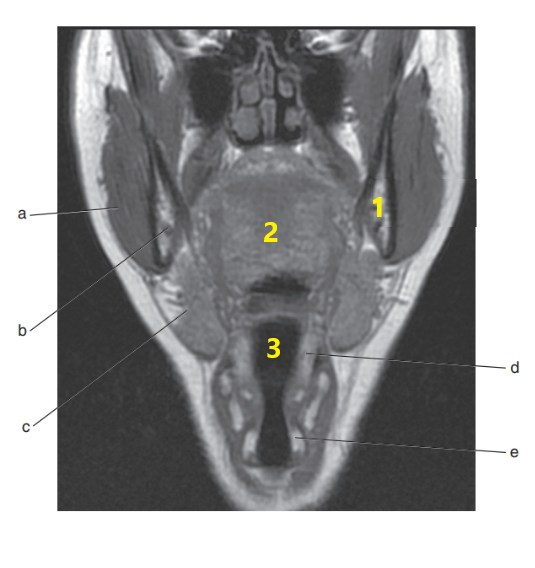
What is # 1 ?
Mandible
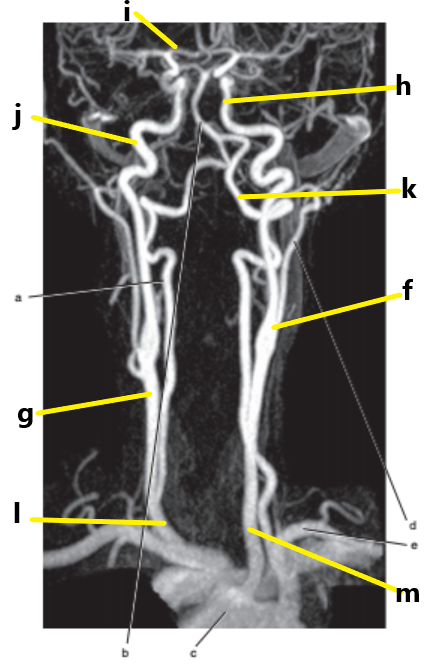
What is letter i ?
Anterior cerebral artery
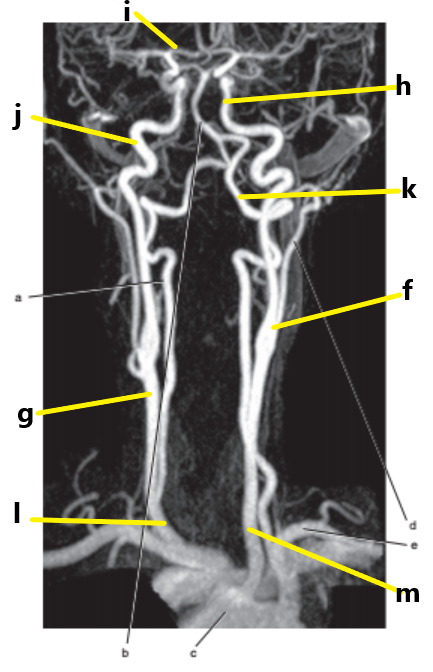
What is letter m ?
Common carotid artery
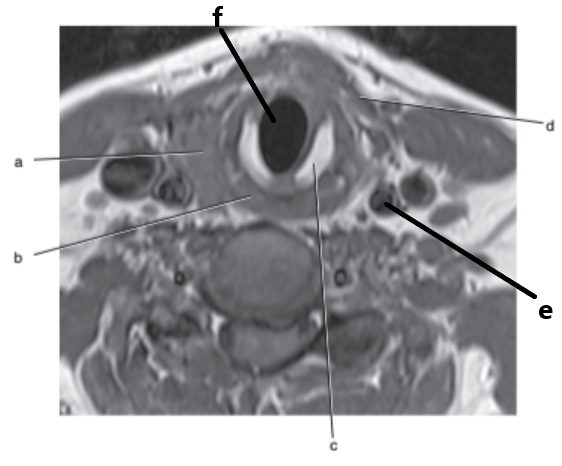
What is letter c ?
Cricoid cartilage
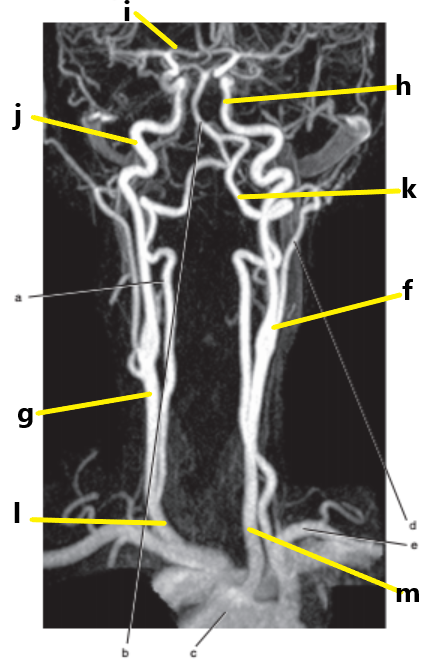
What is letter j ?
Internal carotid artery
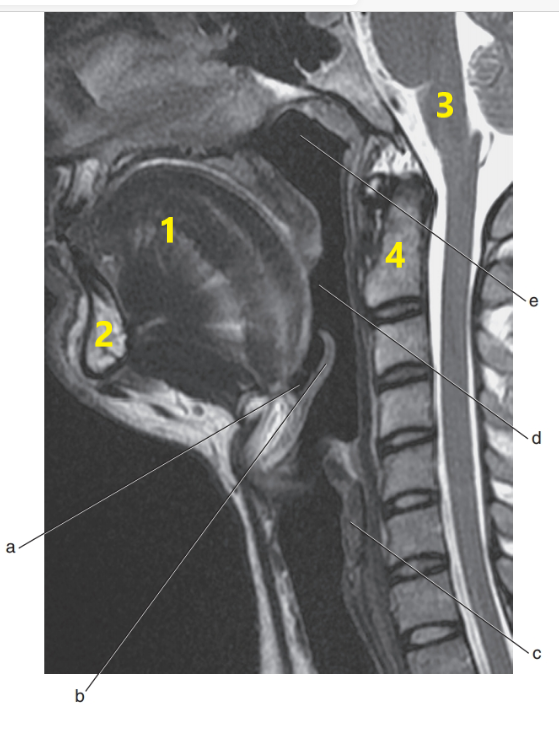
What is # 4 ?
C-1/C-2
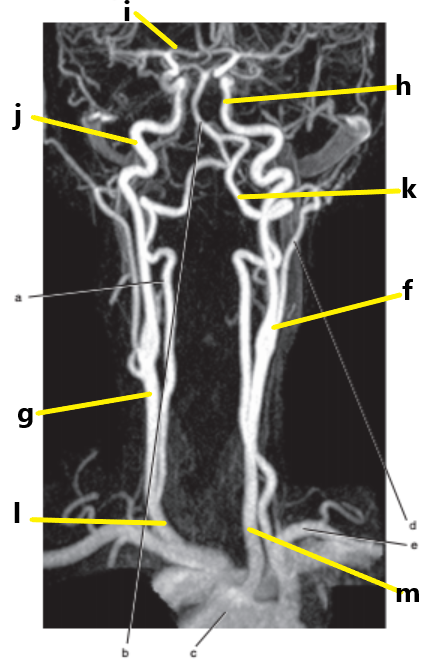
What is letter g ?
Common carotid artery
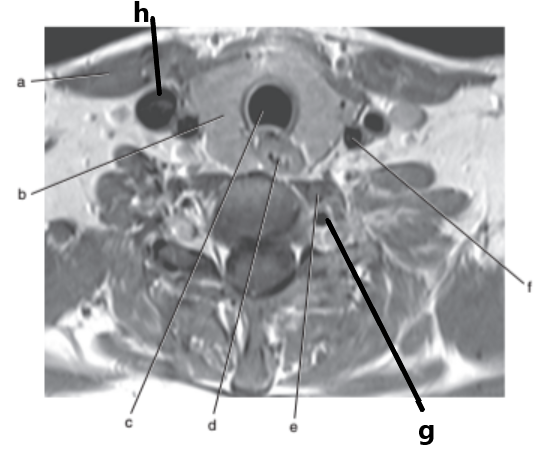
What is letter c ?
Trachea
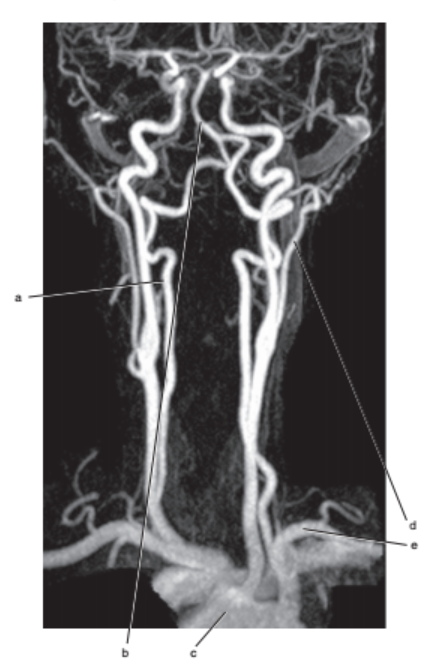
What is letter a ?
Vertebral artery
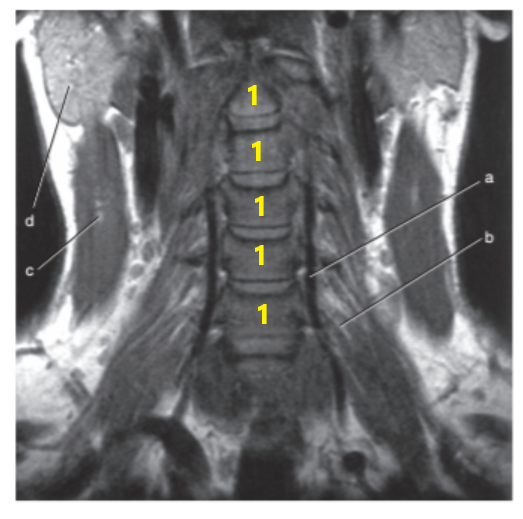
What is letter c ?
Sternocleidomastoid muscle
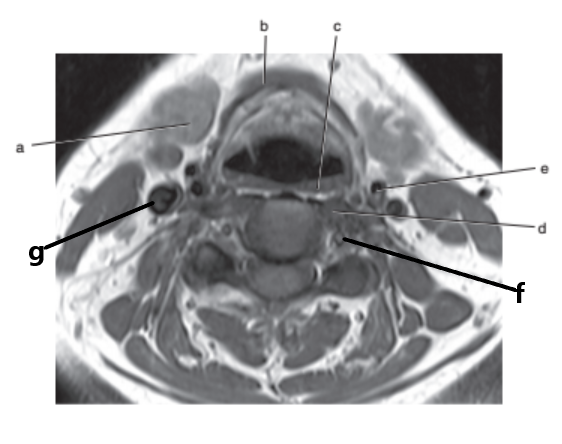
What is letter a ?
Submandibular gland
The esophagus enters the abdominal cavity to join the stomach through an opening in the diaphragm
termed the ______________________________.
Esophageal hiatus

What is letter c ?
Aortic arch
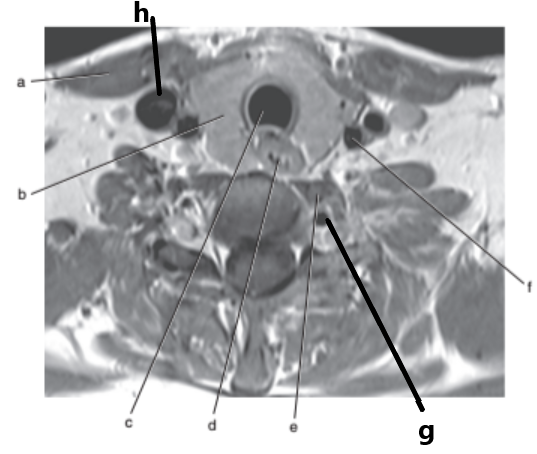
What is letter b ?
Thyroid gland
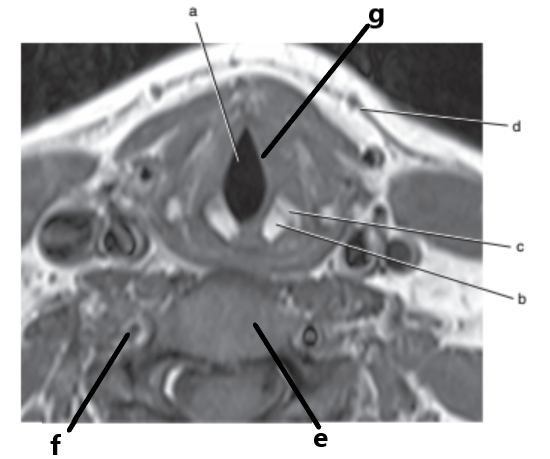
What is letter g ?
Vocal cords
Which muscle divides the neck into anterior and
posterior triangles?
Sternocleidomastoid
The thyroid gland is located at the level of the:
Cricoid cartilage
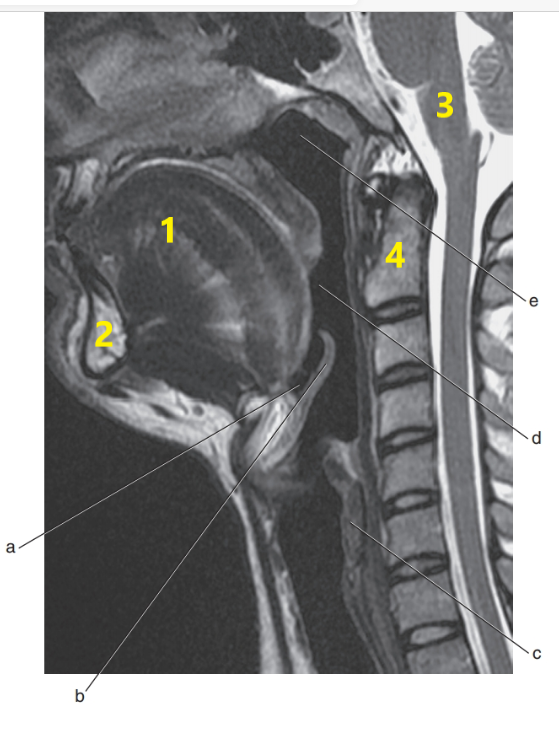
What is # 1 ?
Tongue
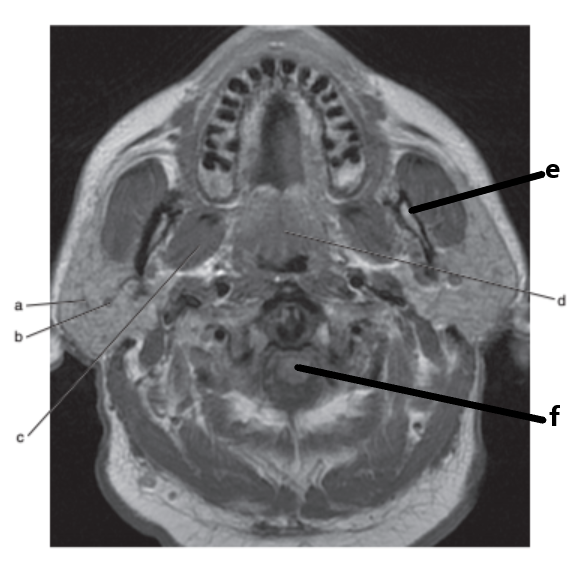
What is letter a ?
Parotid gland
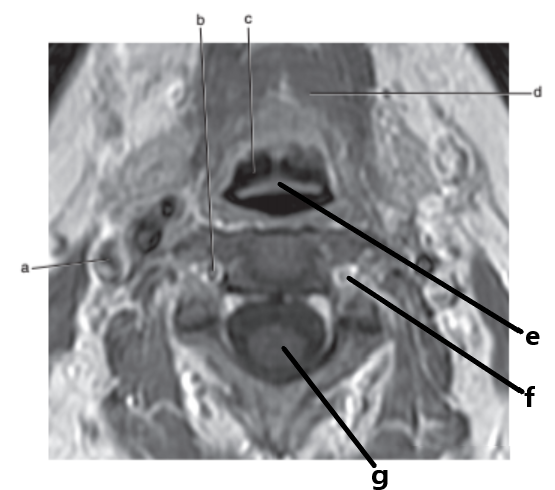
What is letter a ?
Internal jugular vein
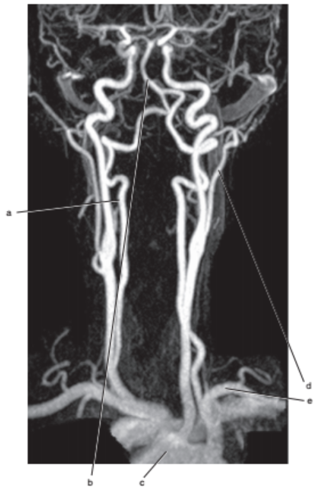
What is letter d ?
External carotid artery
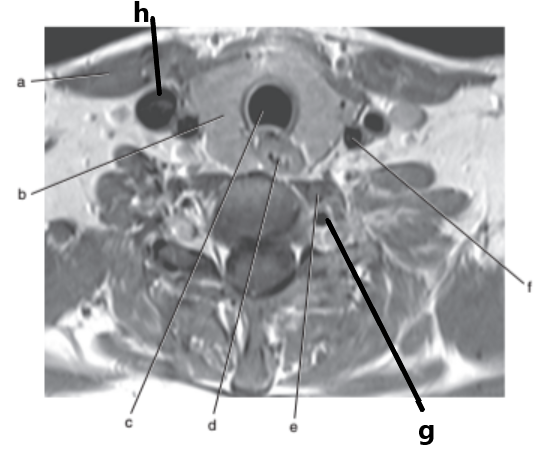
What is letter c ?
Trachea
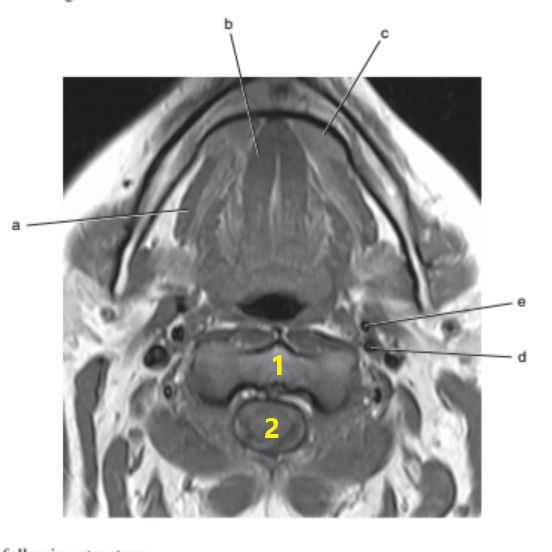
What is letter d ?
Internal carotid artery
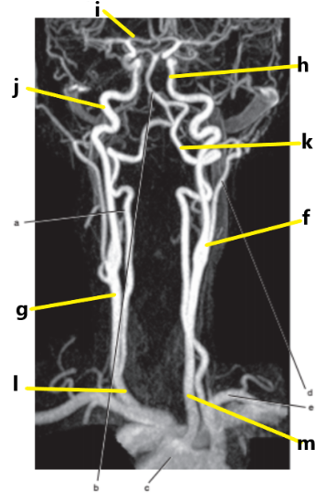
What is letter m ?
Common carotid artery
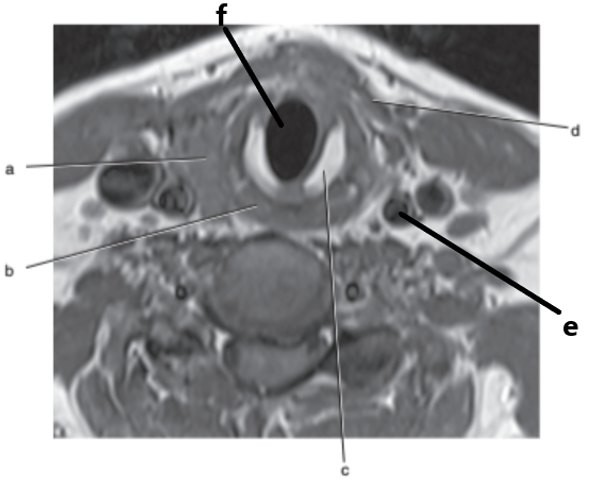
What is letter f ?
Larynx
Tendons bind muscle to:
bone
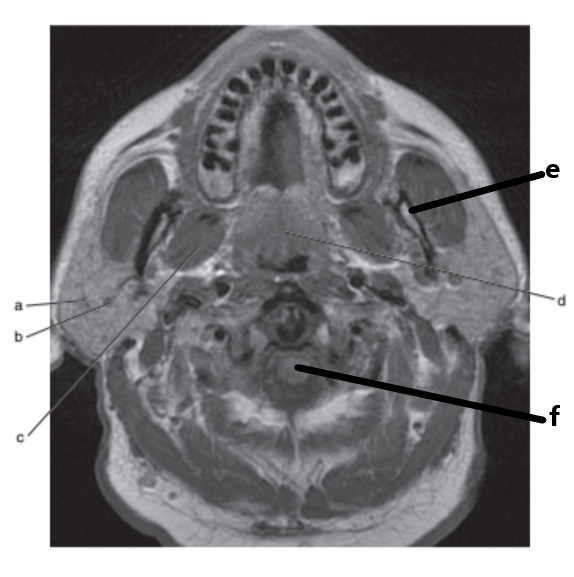
What is letter f ?
Spinal cord
Ligaments bind bone to:
bone
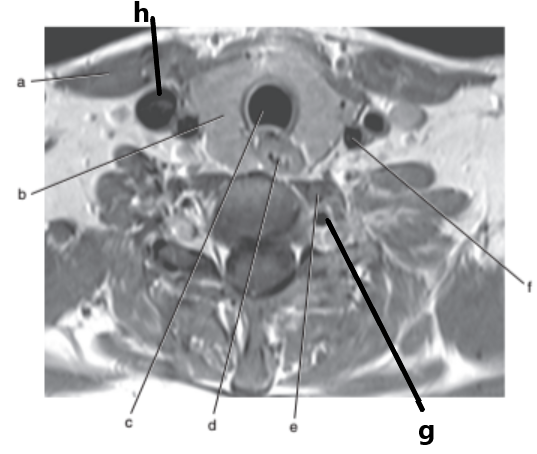
What is letter h ?
Internal jugular vein
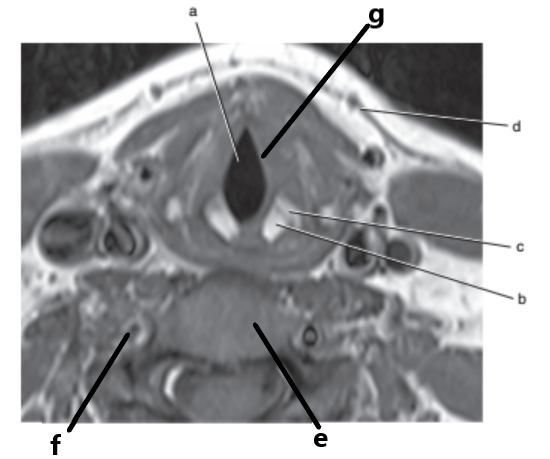
What is letter g ?
Vocal cords
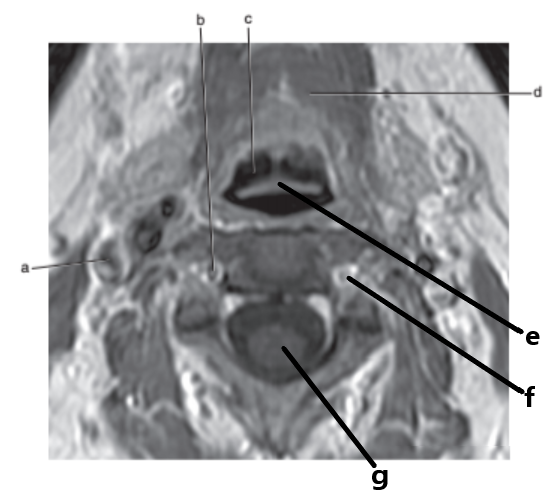
What is letter a ?
Internal jugular vein
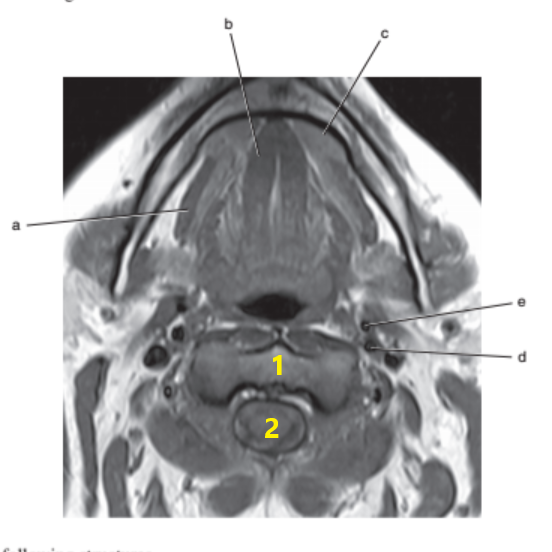
What is letter e ?
External carotid artery
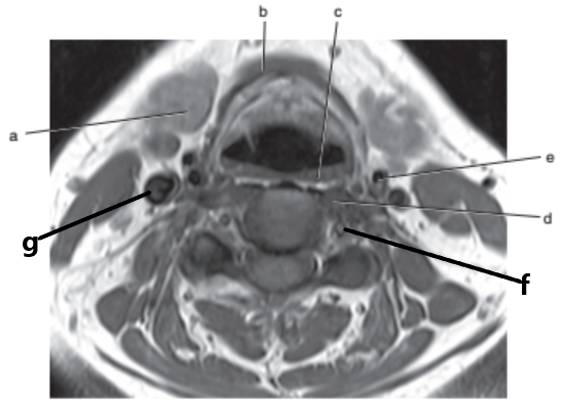
What is letter g ?
Internal jugular vein
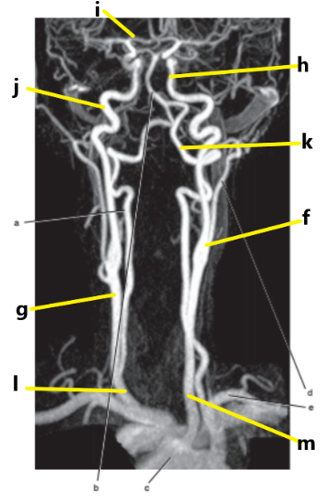
What is letter k ?
Vertebral artery
Hypothyroidism is an underproduction of the thyroid hormone. Hypothyroidism is also known as:
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
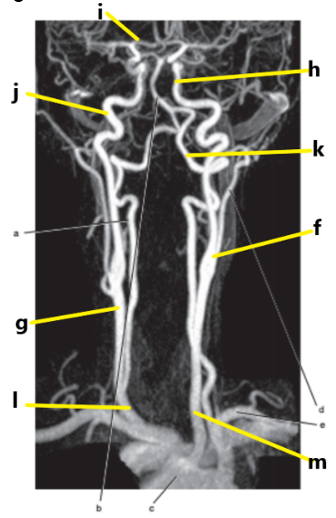
What is letter j ?
Internal carotid artery
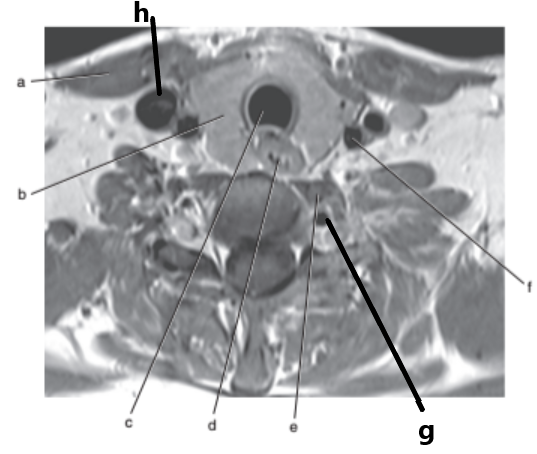
What is letter f ?
Common carotid artery
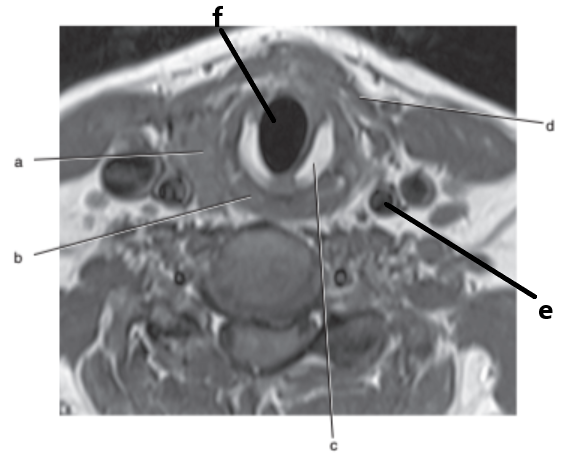
What is letter a ?
Thyroid gland
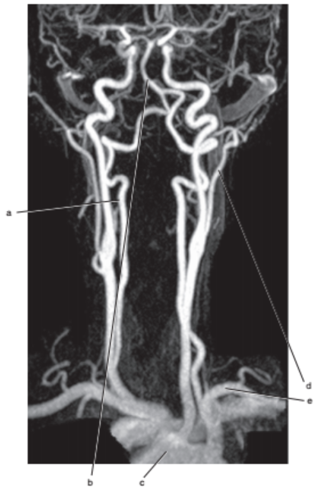
What is letter c ?
Aortic arch
Carotid bifurcation is -
superior border of thyroid cartilage
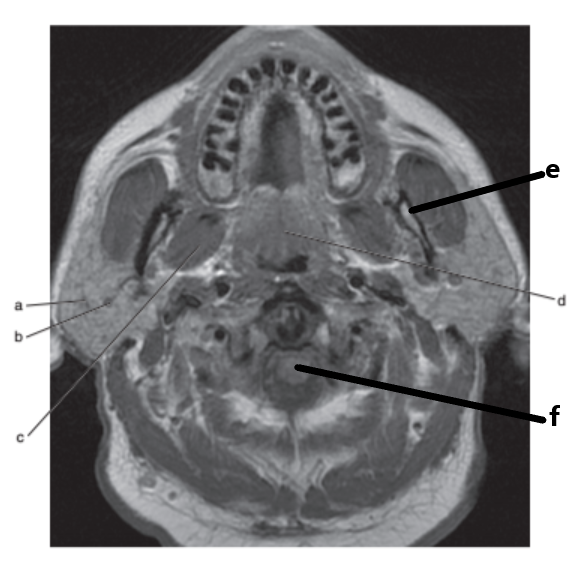
What imaging plane is this ?
transverse
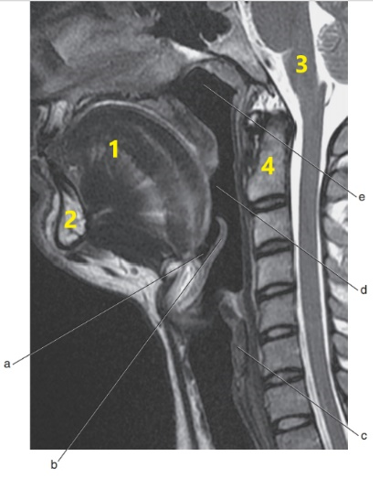
What anatomy is letter b ?
Epiglottis
The common carotid artery bifurcates at the level of -
C3-C4
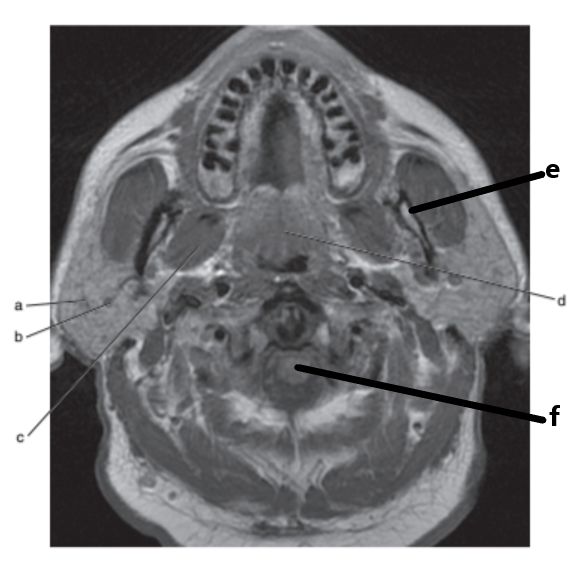
What is letter d ?
Soft palate
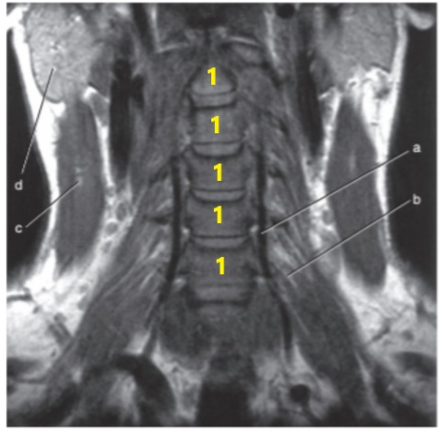
What is # 1's ?
Cervical spine
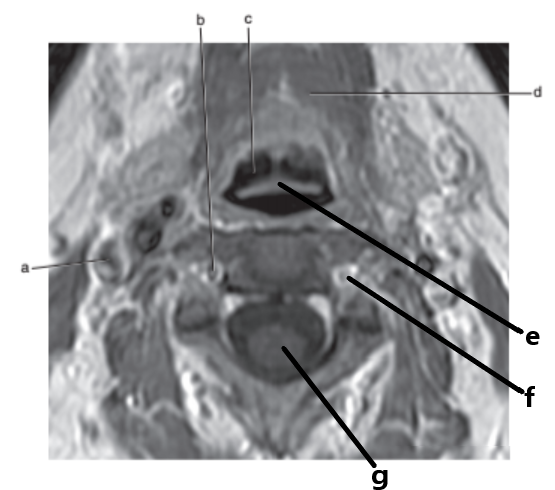
What is letter f ?
Vertebral artery
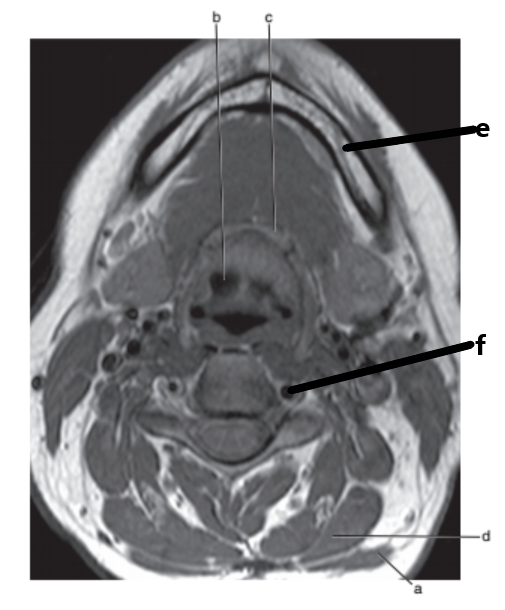
What is letter f ?
Vertebral artery
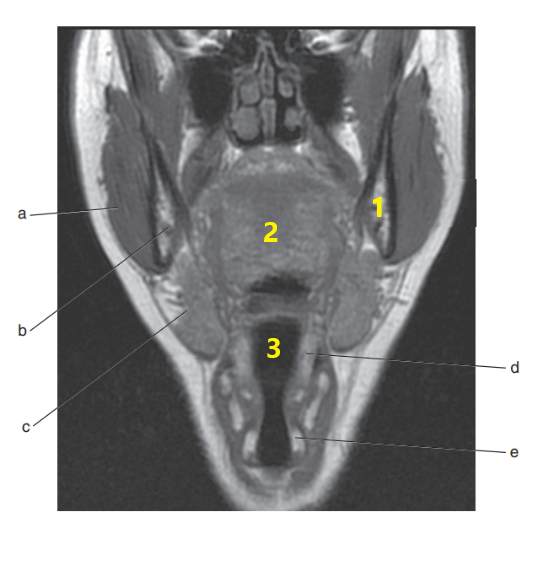
What is letter a ?
Masseter muscle
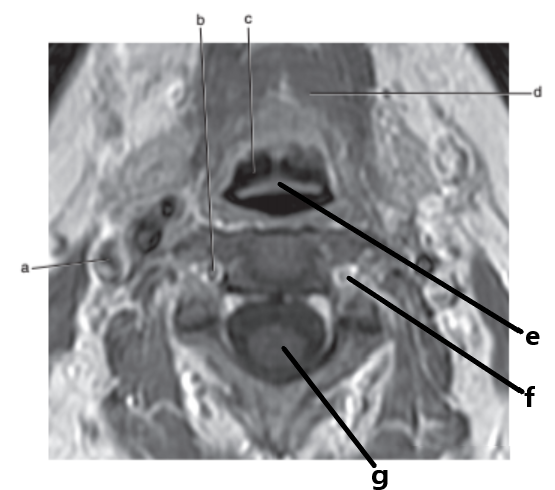
What is letter e ?
Epiglottis
The esophagus enters the abdominal cavity to join the stomach through an opening in the diaphragm
termed the ______________________________.
Esophageal hiatus
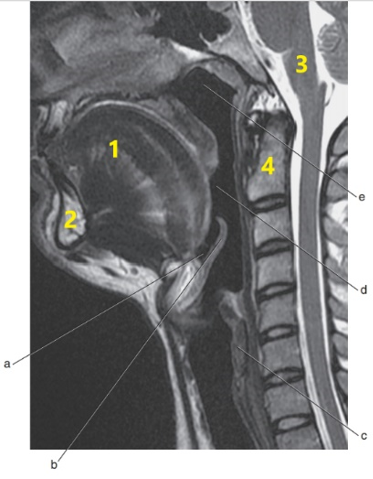
What is # 3 ?
Brain stem
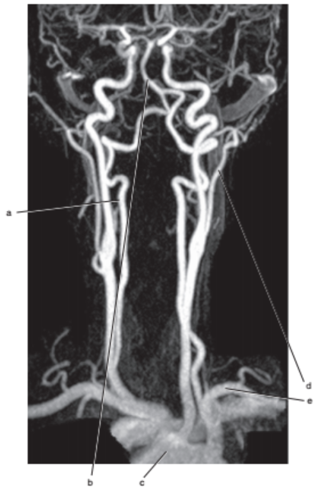
What is letter e ?
Subclavian artery
Which of the following is typically the largest vascular structure located in the neck?
Internal jugular vein
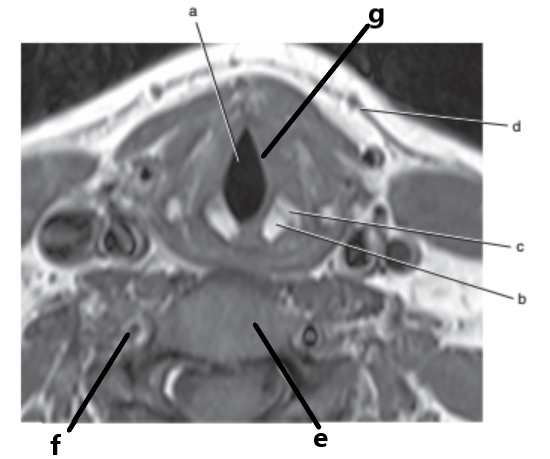
What is letter a ?
Glottis
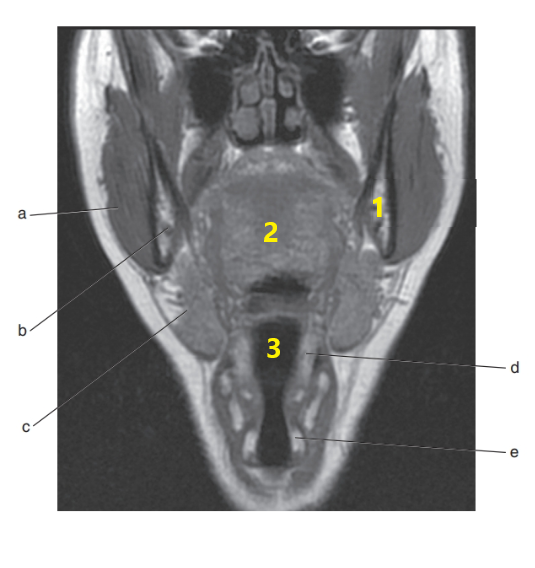
What is letter c ?
Submandibular gland
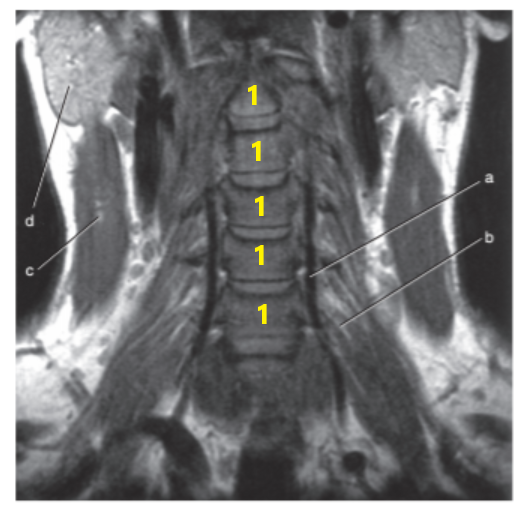
What is letter a ?
Vertebral artery
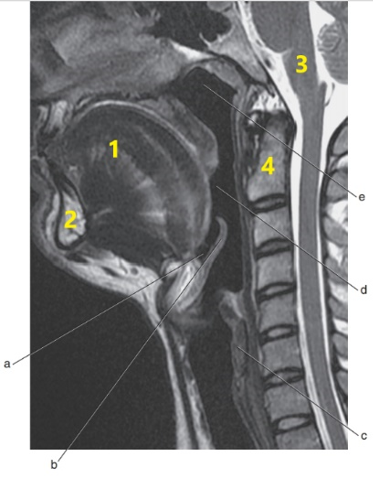
What is # 1 ?
Tongue
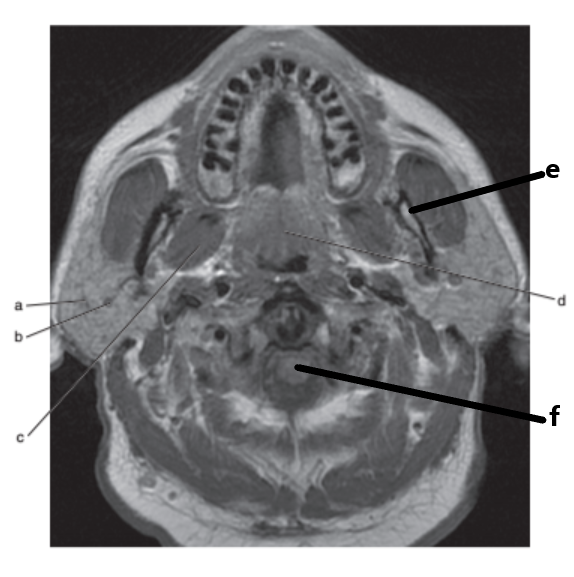
What is letter e ?
Mandible
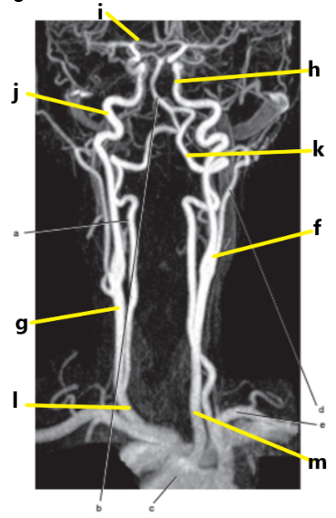
What is letter h ?
Internal carotid artery
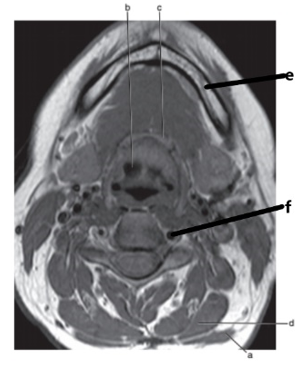
What is letter c ?
Hyoid bone
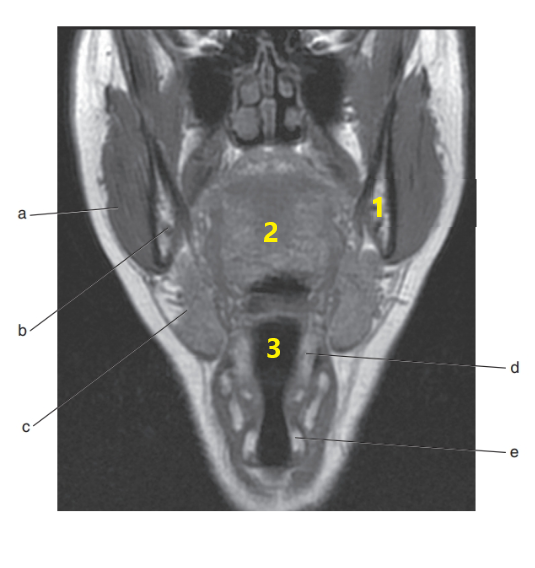
What is # 1 ?
Mandible
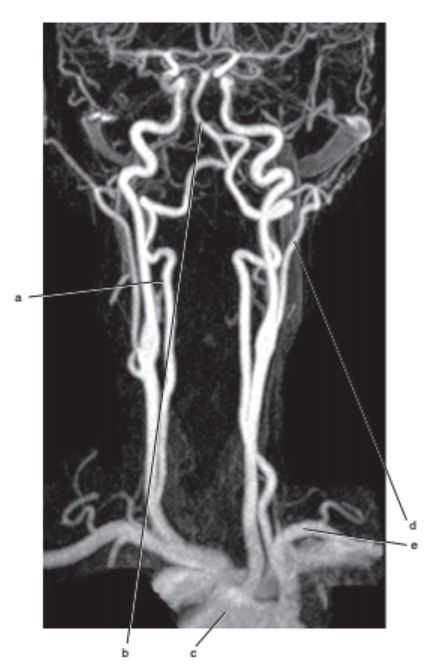
What is letter a ?
Vertebral artery
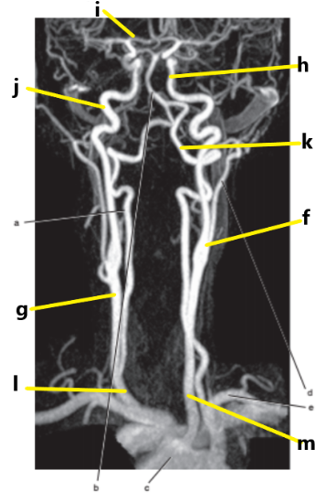
What is letter l ?
Common carotid
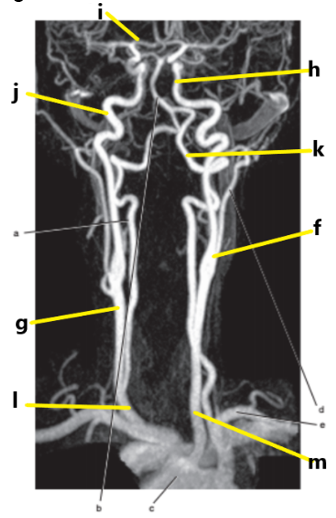
What is letter g ?
Common carotid artery
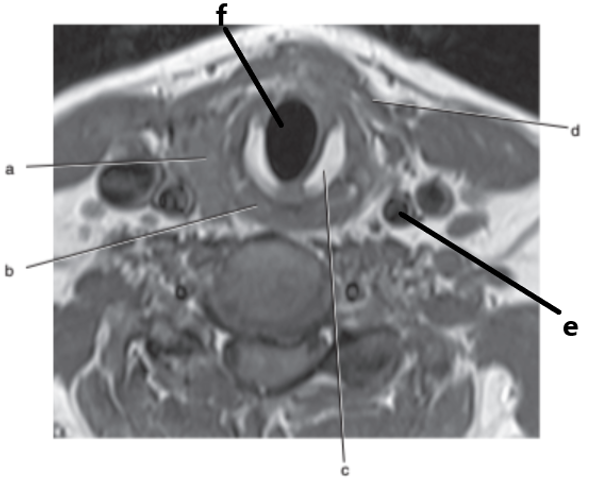
What is letter b ?
Esophagus
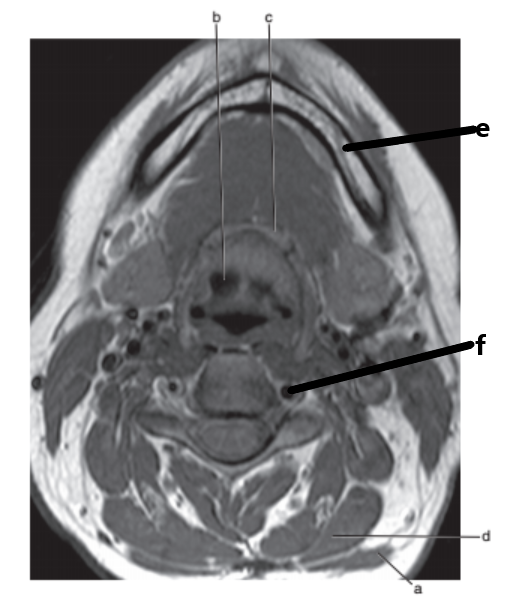
What is letter e ?
Mandible
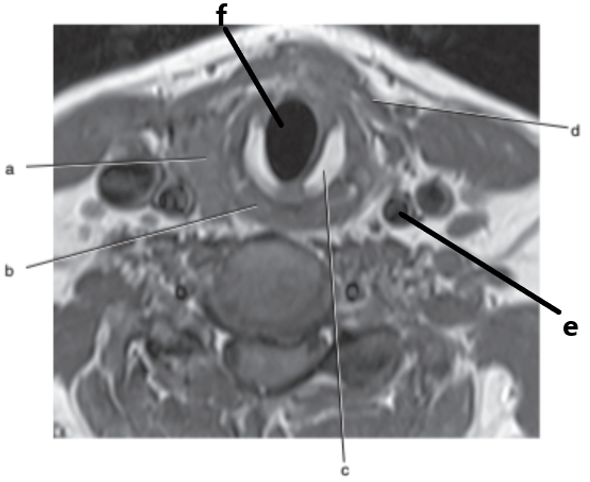
What is letter e ?
Common carotid artery
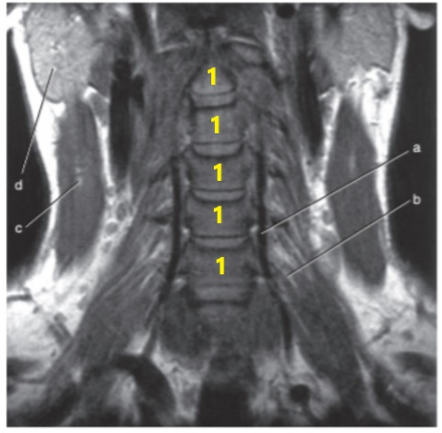
What is letter d ?
Parotid gland
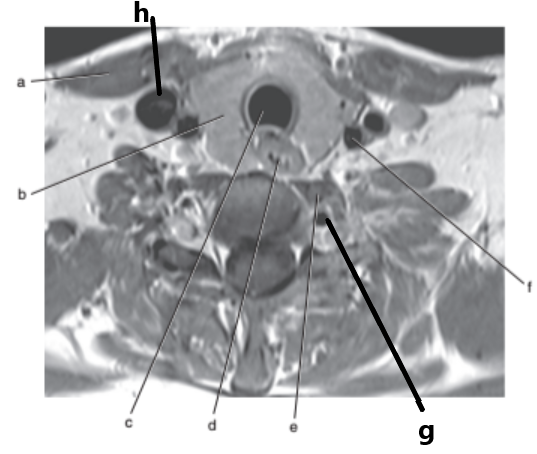
What is letter b ?
Thyroid gland
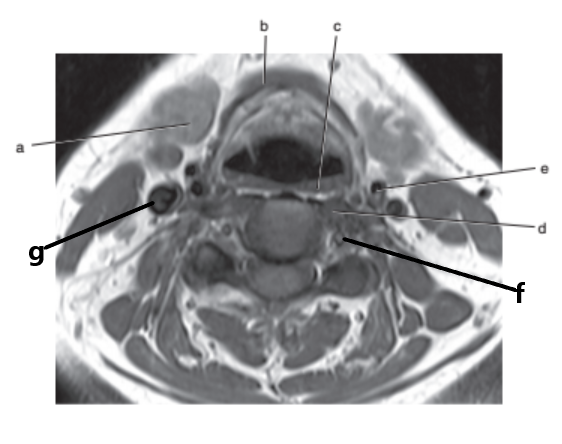
What is letter a ?
Submandibular gland
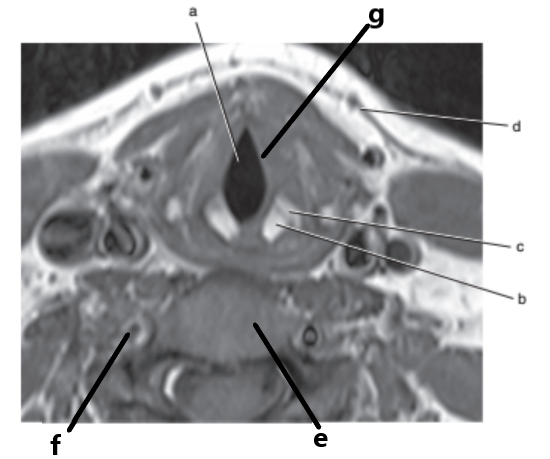
What is letter b ?
Cricoid cartilage
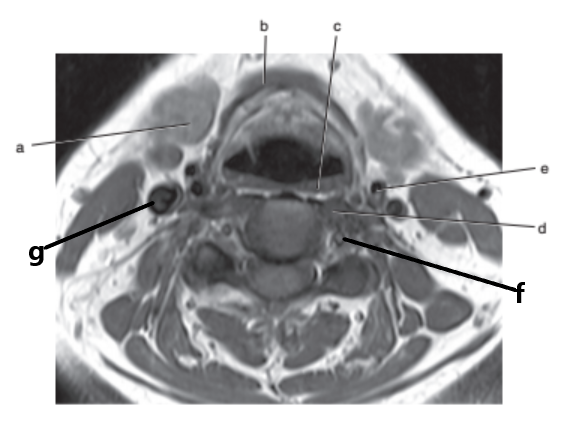
What is letter f ?
Vertebral artery
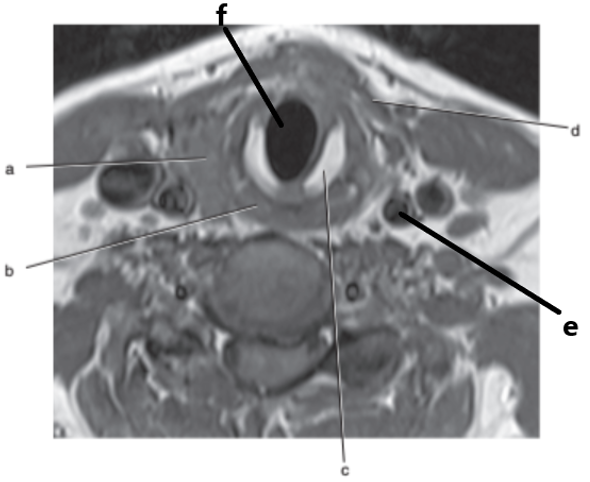
What is letter c ?
Cricoid cartilage
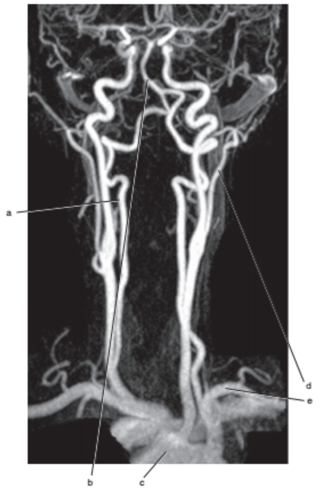
What is letter b ?
Basilar artery
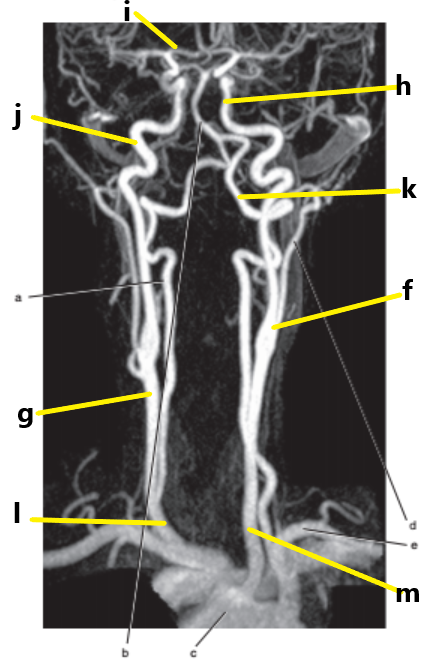
What is letter f ?
Carotid sinus/bifurcation