8.4 - Orthopedics
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Pectus Deformities Defn
Abnormal growth of the sternum and ribs at the cartilaginous connection
Pectus Carinatum
Creates a protrusion outwards
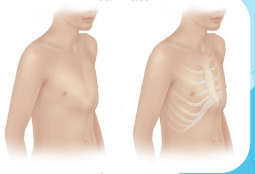
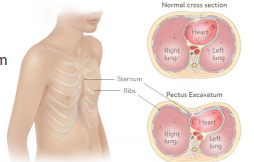
Pectus Excavatum
Creates a protrusion inwards
List the types of Pectus Carinatum
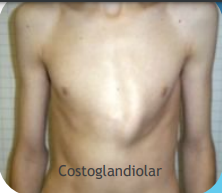
Costoglandiolar
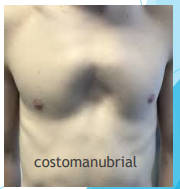
Costomanubrial
What is the most common Pectus Carinatum?
Costoglandiolar
Costoglandiolar
Affects the body of the sternum
Costomanubrial
Affects the upper part, manubrium
What is the least common pectus carinatum?
Costomanubrial
What is Costomanubrial also known as?
Horseshoe pectus
Incidence rate of pectus carinatum
1:1000 teens
Who does pectus carinatum mostly impact?
males
Etiology behind pectus carinatum
No defined etiology - suspecting a genetic link
What is pectus carinatum associated with?
Scoliosis and inherited connective tissue disorders (Marfan’s, Ehlers-Danlos, etc)
Symptoms of Pectus Carinatum
Often asymptomatic - except visible deformity
Pain
Decreased stamina, rapid fatigue
Psychological issues (body image and self-confidence)
Pectus Carinatum treatment
Compression orthosis that is worn for 8-20 hours a day until skeletal maturity
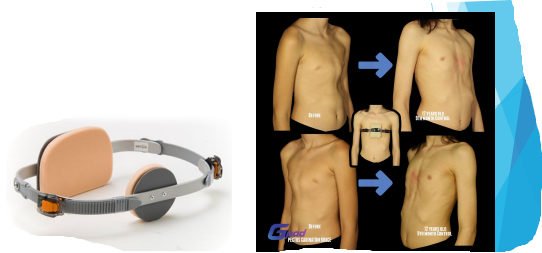
Why is a compression orthosis used for pectus carinatum treatment?
Wolff’s law! when healthy bone and cartilage are loaded with constant and increasing force, they will adapt, strengthen, and gradually remodel under pressure
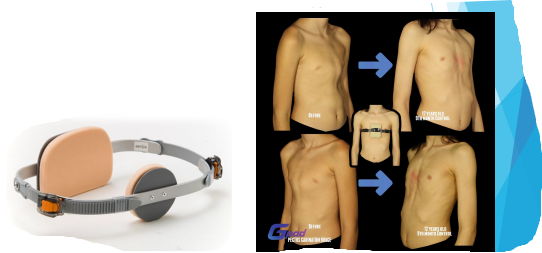
Pectus Excavatum symptoms
Varies depending on the depth of the indentation but includes
Decreased exercise tolerance, rapid heartbeat/heart palpitations, wheezing or coughing, chest pain, fatigue, dizziness
What can Pectus Excavatum do?
Can reduce the room the lungs have to expand and squeeze the heart
Who does Pectus Excavatum mostly impact?
Males
What is Pectus Excavatum associated with?
Scoliosis, osteogenesis imperfecta, and inherited connective tissue disorders (Marfan’s, Ehler’s-Danlos, etc)
Pectus Excavatum treatment options
Vacuum bell and surgery
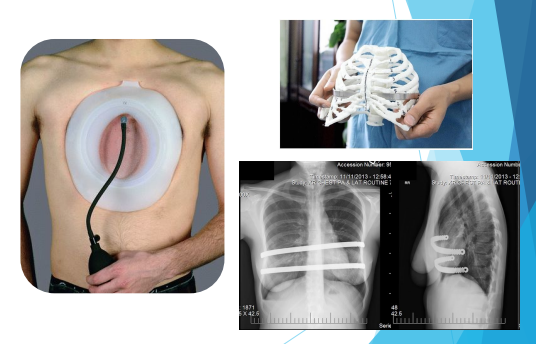
Osteogenesis Imperfecta is also known as
Brittle bone disease
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta caused by?
Dominant autosomal mutations in the type I collagen coding genes (~85% of the cases). In the past decade, recessive, dominant and X-linked defects in a wide variety of genes have been shown to cause OI
What does OI affect?
Collagen quantity or quality - the abnormal collagen increases the fragility of the bones making them more prone to fractures
OI symptoms
Short stature
triangular face
breathing problems
hearing loss
brittle teeth
sclera color changes
bone deformities, such as bowed legs or scoliosis
What is the most common and mildest type of OI?
Type I
Type I OI
Collagen structure is normal but there is less of it, minimal bone deformity, but bones are fragile and easily broken, teeth may be prone to cavities and crackling, the whites of the eyes may have a blue, purple, or gray tint
What is the most severe form of OI?
Type II
Type II OI
Collagen does not form properly, bones may break even while the fetus is in the womb, many infants do not survive.
Type III OI
Improperly formed collagen, often severe bone deformities
The infant is often born with fractures
Whites of eyes may be white, blue, purple, or gray
Usually shorter than average height
May have spinal deformities, respiratory complications, and brittle teeth
Type IV OI
Moderately severe with improperly formed collagen
Bones fracture easily
Whites of eyes are NORMAL
May be shorter than average height and may have brittle teeth
Bone deformities are mild to moderate
Compare and contrast Osteoporosis to OI
Osteoporosis - normal bone, but there is LESS bone, prone to fractures
OI - Abnormal bone due to collage type I mutation where it is poor quality or low quantity of collagen, Collagen is the primary protein that forms the framework for the bone providing its strength, abnormal or low collagen creates weak bone structure, prone to fractures
Do fractures in OI patients increase or decrease in most patients post puberty? Why?
DECREASE - due to hormonal and metabolic changes
People with OI can develop what? Why?
Osteoporosis because they do not develop appropriate bone mass at any age
In OI patients, what are methods of preventing age-related bone loss and maintaining good bone density?
Diet - calcium and vitamin D
Exercise - moderate exercise! such as walking and swimming
NO SMOKING
medications - bisphosphonates
Non-surgical OI treatments
Bisphosphonates - slow down bone resorption
Immobilization - cast or orthosis
Exercise - low impact, swimming and walking
Surgical OI treatment options
Rodding - repeated fractures, angulation
Spinal fusion (scoliosis)
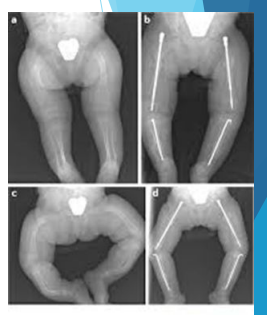
Describe Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
Presents at birth with multiple contractures, muscles only being fibrous bands, and joint deformities
What causes Arthrogryposis - surface level?
Decreased fetal movement in an intact skeleton - joint deformities are secondary due to the lack of active motion during intrauterine development
What can cause Arthrogryposis?
Can be caused by ANY underlying condition resulting in decreased fetal movement. SUch as CNS disorders, LMN disorders, Fetal environment not having enough amniotic fluid (oligohydramnios), and congenital muscular dystrophy
Signs of Arthrogryposis
Joint contracture
webbing of joints
rigidity
muscle weakness
normal cognition
delayed motor development (independent sitting at 15 months and ambulation at 2-3 years)
What are two different postures that indicate Arthrogryposis?
Jackknife and Frog postures
Describe jackknife posture
Flexed hips, extended knees, clubfeet
Describe the frog posture
Abducted, externally rotated hips, flexed knees, and clubfeet

Arthrogryposis treatment
PT (exercise, improve ROM, and increase strength),
OT (develop fine motor skills and increase independence),
serial casting (improve alignment or ROM),
orthosis (provide functional support for ambulation),
surgery (increase ROM through joint capsule release, tendon release, clubfoot treatment)
What is the most common cause of limb deficiency? What is the most commonly impacted limb? What sex is impacted the most?
Congenital - arm - male
What are the causes of congenital limb deficiency?
Unknown
What do the majority of congenital limb deficiency cases impact?
The arm
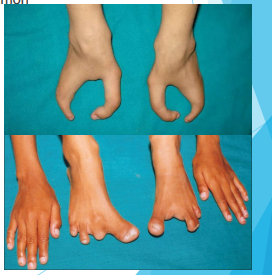
In the upper limb, congenital deficiencies most frequently involve the ______
Hand
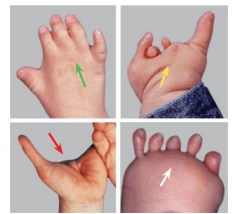
In the lower limb, ______ deficiency is the most common
Toe
Limb development begins in the ____ week of gestation and is almost complete by the _____ week
4th - 8th
In 1959-1962, _____________ was prescribed for treatment of nausea during pregnancy. This resulted in many cases of ________, which is limb deficiency.
Thalidomide, Phocomelia
Amniotic band syndrome is also known as?
Streeter’s dysplasia
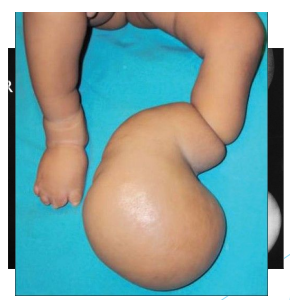
Congenital limb deficiencies often have additional problems such as
Inadequate proximal musculature
Unstable joints
Mal-rotation
Limb-length differences
Is congenital limb deficiency treatment consistent?
NO - every treatment plan is different and needs to be discussed with the parents
List the treatment options for congenital limb deficiency
Sometimes no intervention
Surgical intervention (reconstruction or amputation)
Orthosis
Prosthesis
Prosthosis?